Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tesla Motor Case Review
Uploaded by
Shafat AhmedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tesla Motor Case Review
Uploaded by
Shafat AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
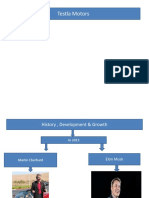
Company Background:
Incorporated in 2003 by Eberhard and Tarpenning
First vehicle introduced in 2008
Elon Musk contributed major fund and became chairperson of the company
Strategic Partnership with Daimler AG in 2009, after Tesla was struggling with cash crunch
Received $465 billion from US Dept. of Energy (P of PESTEL)
In 2008, Musk became chief executive as he was making all the major decisions
Elon Musk Background:
In 2002, founded SpaceX
Other notable companies are PayPal, Zip2, SolarCity Inc.
Involved with Tesla Motors because he was “concerned with the environment”
Split his time between Tesla and SpaceX
Both praised and criticized for his management style
Strategic Vision of Musk:
Bring full range of affordable electric powered vehicles to market
Transition from carbon producing gasoline powered motor vehicles to zero emission electric
vehicles
At its core, Tesla’s strategy was aimed squarely at utilizing the company’s battery and electric
drivetrain technology to disrupt the world automotive industry
The challenges in 2016 were:
o Gasoline prices had dropped
o Formidable competition
o Loss rather than profit achieving
Products of Tesla:
Tesla Roadstar, the Model S, Model X, Model 3
Innovating and offering better values than previous models
Distribution:
Relied on company owned retail stores (Forward Integration)
Other rival motor companies sold to franchised dealers
There was a US legislation which blocked motor vehicle manufacturers from becoming retailers
These laws halted Tesla to sell vehicles at company owned showrooms
Product Development Strategy:
In 2016, Tesla’s strategy was focused on broadening the company’s model lineup, expanding the
company’s production capacity
Upto 2016, spent over $2 billion on R&D
Core intellectual property: battery pack, power electronics, induction motor, gearbox and
control software
Tesla had more than 500 patents, but they pledged not to initiate a lawsuit against anyone
infringing it
Cars were made light
Engineers gad core competency in design and crash test simulations
Manufacturing Strategy
In 2010, purchased a plant in California for $42M.
Location favored them as talented engineers were nearby in Silicon Valley
Previously done in London
In 2012, new facility opened in Netherlands for final assembly
Tesla’s strategy was to source a number of parts and components from outside suppliers but to
design, develop and manufacture in-house those key components where it had considerable
intellectual property and core competencies
Initially production costs for the Model S were adversely impacted by assortment of startup
costs
Engineers redesigned various elements for greater ease of manufacturing
Production volume greatly rose
Marketing Strategy:
Manage the existing customer base to create brand loyalty
Traditional marketing costs were low
Build long term brand awareness
Tesla’s innovative resale guarantee program, where the buyers were given the option of selling
their vehicle back to Tesla within a window of 36 to 39 months after delivery for a guaranteed
percentage of the purchase price
Thus enabling them to enjoy the benefits of ownership without concerning for the resale value
Tesla partnered with various financial institutions to lease vehicles to customers
Credits from Regulatory Bodies
Earned credits for zero emission vehicles (ZEV), green house gas (GHG), corporate average fuel
economy (CAFE).
These credits produced revenues of $2.7 M in 2011.
Competition:
All other major companies working on Electric Vehicles
In 2013, BMW began selling i3 series electric car models
Audi, Mercedes, Porsche, Lexus are developing high end electric vehicles
Hydrogen Fuel Cells, more eco-friendly than electric cars
Tesla Motor’s financial numbers:
In May 2013, Tesla raised over $1 B by issuing shares of common stock
Ended 2015 with $1.2B in cash and cash equivalents
Loss of $888,663 in 2015
You might also like
- Tesla's Competitive StrategiesDocument17 pagesTesla's Competitive StrategiesMorenti RegoNo ratings yet
- Tesla Marketing Strategy Case Study: Muhammad EddiebDocument12 pagesTesla Marketing Strategy Case Study: Muhammad EddiebRetheesh Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Tesla Case StudyDocument3 pagesTesla Case StudyYash PawarNo ratings yet
- TESLA India Marketing PlanDocument3 pagesTESLA India Marketing PlanAvinash SinhaNo ratings yet
- Final Project Marketing ManagementDocument15 pagesFinal Project Marketing ManagementHesham Mansour50% (2)
- Aqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedDocument31 pagesAqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedExal Eduardo Cabrera VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Company BackgroundDocument2 pagesCompany BackgroundThanh TungNo ratings yet
- Tesla CaseDocument9 pagesTesla CaseSHUN (경영전문대학원 경영(Global MBA)) KAJITANo ratings yet
- MoT Case Presentation - SecA - Group4 - TeslaDocument12 pagesMoT Case Presentation - SecA - Group4 - TeslaRishabh Singh100% (2)
- Tesla CaseDocument4 pagesTesla CaseMary JhoyNo ratings yet
- Tesla's Major Strengths:: 1. A Best Employer CompanyDocument4 pagesTesla's Major Strengths:: 1. A Best Employer CompanyHumna KhalidNo ratings yet
- Case - 3 - Tesla With Cover Page v2Document25 pagesCase - 3 - Tesla With Cover Page v2Chi BongNo ratings yet
- Tesla Marketing Case Study: By: Muhammad Eddieb Supervised By: Dr. Reham Moawad 12/21/2018Document15 pagesTesla Marketing Case Study: By: Muhammad Eddieb Supervised By: Dr. Reham Moawad 12/21/2018prateek0% (1)
- FWD - MHS2022042117.editedDocument15 pagesFWD - MHS2022042117.editedSonal PandeyNo ratings yet
- PSM - Tesla Draft 1Document33 pagesPSM - Tesla Draft 1vijay2293No ratings yet
- Tesla Company: StrategyDocument3 pagesTesla Company: Strategysonali mishraNo ratings yet
- Group 3 TestlaDocument34 pagesGroup 3 TestlaRahul Samant100% (1)
- Tesla Inc. Company AnalysisDocument12 pagesTesla Inc. Company Analysisr.saran152006No ratings yet
- SM Final Case of Texla IncDocument10 pagesSM Final Case of Texla IncShershah JalalzaiNo ratings yet
- A1 Case Analysis Assignment - Tesla (Team 9) PDFDocument6 pagesA1 Case Analysis Assignment - Tesla (Team 9) PDFSagar TanejaNo ratings yet
- Tesla Motors: Name: Robin Gupta IAP Roll No. 71Document6 pagesTesla Motors: Name: Robin Gupta IAP Roll No. 71Robin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management (STRA701) : Amity Business SchoolDocument19 pagesStrategic Management (STRA701) : Amity Business Schoolkumar.abhi.modiNo ratings yet
- Case Study On CRMDocument6 pagesCase Study On CRMamarjogdande09No ratings yet
- Tesla Motors, Inc. Issue/Problem IdentificationDocument4 pagesTesla Motors, Inc. Issue/Problem IdentificationJennyNo ratings yet
- Tesla ResearchDocument11 pagesTesla ResearchPavan BarhateNo ratings yet
- Company Name: Tesla Business Sector: Automobile and Energy Operating Geography: North America, USA, GlobalDocument3 pagesCompany Name: Tesla Business Sector: Automobile and Energy Operating Geography: North America, USA, GlobalArslanKamranNo ratings yet
- TeslaDocument7 pagesTeslaUsama HakeemNo ratings yet
- TeslaDocument10 pagesTeslaSwetaSarojNo ratings yet
- Tesla Motors Shelby LeeDocument13 pagesTesla Motors Shelby Leeflh21gmail100% (1)
- Tesla - Strategic ManagementDocument12 pagesTesla - Strategic ManagementsreutschiirNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Strategy and Business Policy: Strategic Management ProjectDocument11 pagesFundamental Principles of Strategy and Business Policy: Strategic Management ProjectAmit GroverNo ratings yet
- TESLA Motors Strategic AuditDocument26 pagesTESLA Motors Strategic AuditMutisya JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Session 13Document17 pagesSession 13Megha GautamNo ratings yet
- Student's Name and Signature: Ravi Sai Teja G: DeclarationDocument8 pagesStudent's Name and Signature: Ravi Sai Teja G: DeclarationRavi saiNo ratings yet
- A Project Work On: TeslaDocument14 pagesA Project Work On: TeslaDeepan SamalNo ratings yet
- Business - TeslaDocument13 pagesBusiness - TeslaGina Al TabbaaNo ratings yet
- NikeDocument21 pagesNikeabanoub khalaf 22No ratings yet
- Contemp Project Model-Gov8Document19 pagesContemp Project Model-Gov8Ahmed Mohamed Walid100% (1)
- Tesla FinalDocument23 pagesTesla FinalJonas Schindler100% (1)
- SMPPTDocument37 pagesSMPPTvrayNo ratings yet
- Research GateDocument28 pagesResearch GateaskmeeNo ratings yet
- Assiement of Busness StrategyDocument3 pagesAssiement of Busness StrategyAlain-b Nguma MwakaNo ratings yet
- Tesla OverviewDocument5 pagesTesla OverviewJoshuaNo ratings yet
- The Tesla Business Model Operates As A DirectDocument11 pagesThe Tesla Business Model Operates As A Direct6py9smqckqNo ratings yet
- Tesla Motors: Bas$en Mar$nez - Thomaz Talarico - Maria Garcia-MorenoDocument29 pagesTesla Motors: Bas$en Mar$nez - Thomaz Talarico - Maria Garcia-MorenoAndrew Neuber100% (1)
- Tesla: Business Model and Strategic AnalysisDocument11 pagesTesla: Business Model and Strategic AnalysisVadim Timofeev100% (1)
- Tesla MotorsDocument8 pagesTesla Motorsmayor titusNo ratings yet
- TESLA Group.18 SMDocument35 pagesTESLA Group.18 SMPratik GawaiNo ratings yet
- TeslaDocument12 pagesTeslaabeera100% (1)
- Problems Faced by Automobile Industries Case StudyDocument12 pagesProblems Faced by Automobile Industries Case StudySai Jelene LaysonNo ratings yet
- Tesla Motors - A Look at Strategic ModelDocument27 pagesTesla Motors - A Look at Strategic ModelAyush Vashishtha91% (11)
- Pearson - Strategic.management - Tesla Car 765 780Document16 pagesPearson - Strategic.management - Tesla Car 765 780Đan ThanhNo ratings yet
- By-Megha Bandhav Kilaru Dhanush Goud Chetan Akula Santhosh Dheeraj Hari HaranDocument11 pagesBy-Megha Bandhav Kilaru Dhanush Goud Chetan Akula Santhosh Dheeraj Hari HaranMegha Bandhav KilaruNo ratings yet
- Corporate Communication Hepes MaximilianDocument6 pagesCorporate Communication Hepes MaximilianTabitha BălanNo ratings yet
- Be AssignmentDocument2 pagesBe Assignmentdhruvprajapati34340No ratings yet
- About: OperationsDocument10 pagesAbout: OperationsAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Tesla Production ProjectDocument2 pagesTesla Production ProjectTabish haneefNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument10 pagesTerm PaperZarish SohailNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TeslaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Teslaverbie kalita100% (1)
- TeslaaaaaDocument2 pagesTeslaaaaaMaryam ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- Business Development Plan: Model Answer SeriesFrom EverandBusiness Development Plan: Model Answer SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Composite Insulators Ed1Document8 pagesComposite Insulators Ed1Eduardo_Godoy_6160No ratings yet
- Report PDFDocument12 pagesReport PDFShailendra RajputNo ratings yet
- Ghorahi Cement Industry Ltd.Document71 pagesGhorahi Cement Industry Ltd.सुबास अधिकारीNo ratings yet
- Silvertop Oxygen SensorDocument1 pageSilvertop Oxygen SensorJustin LeoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectronics Interview QuestionsshyamNo ratings yet
- 6000 Chiller ManualDocument43 pages6000 Chiller Manualhytham.midani.63No ratings yet
- ME MotronicDocument3 pagesME Motronicdory7dawNo ratings yet
- Eks Energy PresentationDocument17 pagesEks Energy PresentationFrancisco Javier Marín SuárezNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument14 pagesPDFMixa SazonovNo ratings yet
- PRIMER - Cost Estimation - Chemical Engineering ProjectsDocument9 pagesPRIMER - Cost Estimation - Chemical Engineering ProjectsMarkoNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress UU, CU, CDDocument101 pagesShear Stress UU, CU, CDMohamad Khaled NordinNo ratings yet
- Hydro ExecutionDocument2 pagesHydro ExecutionMohit .kNo ratings yet
- Fahrzeugverdichter / Vehicle Compressor / Compresseur Pour AutomobilesDocument1 pageFahrzeugverdichter / Vehicle Compressor / Compresseur Pour AutomobilesZoraida100% (1)
- Toyota 7M Manual Charging SDocument14 pagesToyota 7M Manual Charging SBerny GarciaNo ratings yet
- PID Temperature Control: Proportional GainDocument5 pagesPID Temperature Control: Proportional Gainvamsikumar reddyNo ratings yet
- Metravi: Digital Ac/Dc Clamp MeterDocument1 pageMetravi: Digital Ac/Dc Clamp MeterSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- Phy094 Tutorial 9 QDocument2 pagesPhy094 Tutorial 9 Qhafiz_yusoff1620No ratings yet
- WPS, PQR & WQT According To ASME Section IX - 2019Document50 pagesWPS, PQR & WQT According To ASME Section IX - 2019Anon YmousNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Modules Assemblies For Medical Laser ApplicationsDocument8 pagesThermoelectric Modules Assemblies For Medical Laser Applicationsricardo.barredo7464No ratings yet
- Wells Thermostat IDDocument18 pagesWells Thermostat IDJuan A Aguilera ANo ratings yet
- SunPower Guideline For PVSyst Modeling - Oasis 3 - P-SeriesDocument17 pagesSunPower Guideline For PVSyst Modeling - Oasis 3 - P-Seriesvineets058100% (1)
- Technical System Catalogue RilineDocument21 pagesTechnical System Catalogue RilineTomislav ŠeplNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Hammermill Performance PDFDocument62 pagesFactors Affecting Hammermill Performance PDFdileepreddy220No ratings yet
- P445PTDocument141 pagesP445PTRafael ArandaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Directory of China's Coal-to-Gas Projects PDFDocument2 pages2017 Directory of China's Coal-to-Gas Projects PDFarapublicationNo ratings yet
- SSR 2015-2016Document42 pagesSSR 2015-2016RamkumarNo ratings yet
- SBSBattery VRLA Tubular Gel VRZ Series PDFDocument1 pageSBSBattery VRLA Tubular Gel VRZ Series PDFAleiska Victoria Gómez BetancourthNo ratings yet
- Retrofit Guidelines For Suva 95 (R-508B) : RefrigerantsDocument4 pagesRetrofit Guidelines For Suva 95 (R-508B) : RefrigerantsPhilNo ratings yet
- Merlin Gerin Masterpact (00689992a) PDFDocument161 pagesMerlin Gerin Masterpact (00689992a) PDFyerut0130100% (4)