Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Redox Reaction: Examples of Oxidizing Agent
Uploaded by
Akilesh Moosaye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageOriginal Title
REDOX REACTION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageRedox Reaction: Examples of Oxidizing Agent
Uploaded by
Akilesh MoosayeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
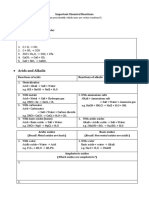
REDOX REACTION
Most reactions are redox except:
i. Neutralization/Neutralization with effervescence
Acid + Alkali/Base Salt + H2O
Acid + Carbonate Salt + H2O + CO2
ii. Precipitation- preparation of insoluble salts
Ex: BaSo4, CaCO3, PbI2
iii. Thermal decomposition of metal carbonate
Metal carbonate metal oxide + carbon dioxide
(Potassium and sodium carbonate do not decompose on heating)
Definition of Oxidation
Gain in oxygen
Increase in oxidation number
Loss of hydrogen
Loss in electron
Examples of oxidizing agent
I. Acidified potassium manganate(7),KMnO4, color changes form purple to pale pink
II. Acidified potassium dichromate(6),K2Cr2O7, color changes from orange to green
III. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2
IV. Chlorine, Cl2
Examples of reducing agent
I. Metals, potassium is most powerful reducing agent
II. Hydrogen
III. Iron(2) sulphate,FeSO4 (Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+)
IV. Hydrogen peroxide
V. Sulfur dioxide, SO
You might also like
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1Document4 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1ysheng98No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 EquationsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- REDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)Document34 pagesREDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)jiaNo ratings yet
- Prep3 Final Revision..Document26 pagesPrep3 Final Revision..Amira Hekal0% (1)
- Physical and Chemical Properties of s-Block ElementsDocument29 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of s-Block ElementsRobiul AlomNo ratings yet
- Types of Decomposition ReactionDocument19 pagesTypes of Decomposition ReactionSrynnENo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONSDocument4 pagesREDOX REACTIONSajakazNo ratings yet
- 19 Jan S Block 2Document17 pages19 Jan S Block 2sachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Sree?Document44 pagesSree?Mohammed RamzanNo ratings yet
- Cha 11Document11 pagesCha 11Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument17 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- Std.8 Module.7 Semester.2Document56 pagesStd.8 Module.7 Semester.2Md ZayedNo ratings yet
- FORM4CHEMNOTESDocument12 pagesFORM4CHEMNOTESAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Salt 2020 PDFDocument42 pagesSalt 2020 PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- All Reactions - PadhleDocument18 pagesAll Reactions - Padhlerakshitham603No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbon - Chem - f3 - v1 1Document25 pagesChemistry of Carbon - Chem - f3 - v1 1Lubanga N JamesNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationJasmeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of SaltsDocument7 pagesChapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of SaltsPrincess Ting TingNo ratings yet
- P-Block Board Youtube Part-2Document53 pagesP-Block Board Youtube Part-2vaibhav sainiNo ratings yet
- Oxides Classification and PropertiesDocument4 pagesOxides Classification and Propertiesgauri guptaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 - (Notes) (23-24) Very ShortDocument3 pagesCh-1 - (Notes) (23-24) Very Shortamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- Chemistry Info SheetDocument3 pagesChemistry Info SheetClara GreenNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613Document7 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985613abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document14 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Heng HoweNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDocument32 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyNo ratings yet
- Viva 1Document4 pagesViva 1Nao tomoriNo ratings yet
- Decomposition Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pagesDecomposition Reactions WorksheetNarci ssusNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEN1Document3 pagesHYDROGEN1chukwuemekacollins058No ratings yet
- Answers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEDocument5 pagesAnswers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEAbgyyg LuRf UNo ratings yet
- CARBON: AN IMPORTANT ELEMENTDocument33 pagesCARBON: AN IMPORTANT ELEMENTDavyieNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGESDocument11 pagesPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGESBarkha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsDocument11 pagesElements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsKasman Kasonde MumbaNo ratings yet
- SALTDocument22 pagesSALTparitoshNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsDocument56 pagesFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Document29 pagesChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations - Copy (3)_watermark (1)_pagenumberDocument24 pagesChemical Equations - Copy (3)_watermark (1)_pagenumberAjay Sharma Online ClassesNo ratings yet
- Important Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesImportant Chemical Reactionsdarkstar3125b1No ratings yet
- General Chemistry Part II 5 6Document109 pagesGeneral Chemistry Part II 5 6LUH EKA YANTHINo ratings yet
- IOC all reactionsDocument56 pagesIOC all reactionsKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- Maha FaridDocument49 pagesMaha FaridRamY El NahasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDocument8 pagesChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualCindyCurrydwqzr100% (74)
- All Chemical ReactionsDocument29 pagesAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Revision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Document20 pagesRevision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Bharadwaj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesRedox Reactionschong56No ratings yet
- Cramming NotesDocument7 pagesCramming NotesMuhammad ali WasimNo ratings yet
- WWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Document15 pagesWWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Nur AmaleenaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Group IIIDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Group IIIRozenNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its CompoundsDocument19 pagesChlorine and Its Compoundskakembo hakimNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgeDocument2 pagesNomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgemohammedNo ratings yet
- Quiz ChemDocument4 pagesQuiz ChemCherryNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAmf Talino AhNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesFrom EverandOrganometallic Mechanisms and Catalysis: The Role of Reactive Intermediates in Organic ProcessesNo ratings yet