Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizational Culture, Manager Dilemmas, and Planning
Uploaded by
Lorrianne RosanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizational Culture, Manager Dilemmas, and Planning
Uploaded by
Lorrianne RosanaCopyright:
Available Formats
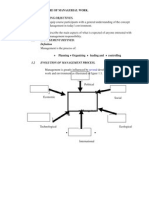
ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE AND ENVIRONMENT o Supervise
o Sustain
1. Manager’s Dilemma
o Uphold
Manager - is a person who is responsible for o Assume responsibility for the work
a part of a company, i.e., they ‘manage‘ the of others in his group, team,
company. department or organization.
Top-Level
Dilemma - situation in which different choic
has to be made between two alternatives o general and strategic
especially equally undesirable ones. o long-term organizational concerns
o emphasize organization's stability,
Manager's Dilemma
development, progress and overall
A dilemma is a complicated issue created when a
efficiency and effectiveness
manager has to accomplish more than one goal at a
time, and at first glance there is no right answer. As an Authority
OMNIPOTENT VIEW SYMBOLIC VIEW o designing strategies
o controlling various resources
1.Managers are directly 1. Managers are not
responsible for an directly responsible for an o must act as organizational guides to
organization’s success or organization’s success or elaborate organizational purpose
failure. failure. Therefore, a quality manager must have:
2.Quality 2. whole control is not on o Conceptual Skills
Organization=Quality managers o Communication Skills
Manager/s quality of o Technical Skills
organization≠quality of
Dilemma Management: is the process of
3.Manager’s managers
addressing complicated problems and
Permormance influences
resolving them in a systematic manner.
the organization’s goals. 3. Manager’s
Permormance does not Symbolic View
4. Manager’s ability is to influence the Symbolic view of management is the view
gain success and failure by organization’s goals managers have a limited effect substantive
good or bad performance organizational outcomes because of large
4.Manager’s ability to number of factors outside their controls.
(e.g. Coaches, Faculties, affect the outcomes are
Group Leaders, influenced by limited o Factors:
supervisors etc,) external factors.
the economy
governmental policies
(e.g. economy,customers,
competitors
competitors,
industry conditions
governmental policies,
technology
industry conditions,
action of previous
technology)
managers
Omnipotent View: management view that 2. Organizational Culture
managers are directly responsible for organization's
success or failure.
Functions and Roles of Managers
refers to the shared beliefs, values, o Controlling
attitudes, principles and different actions
that affects a member or members of an 3. Managing Workforce Diversity: means
organization (Robbins, S.2010). similarities and differences among employees in
terms of age, cultural background, physical
Dimensions of Organizational Culture abilities, and disabilities, race, religion, gender,
1. Attention to Detail - employees are expected to and sexual orientation.
exhibit precision, analysis, and attention to detail.
2. Outcome Orientation - managers are focus on 1. Start with hiring.
results or outcomes rather than on how these 2. Create with inclusive policies and practices.
outcomes are achieved. 3. Provide Diversity Training
3. People Orientation - management decisions take 4. Facilitate Effective Communication
into account the effects on people in the 5. Encourage Interaction.
organization.
4. Team Orientation - work is organized around 4. The Environment
teams rather than individuals. Internal Environment - direct and
5. Aggressiveness - employees are aggressive and immediate impact to organization.
competitive rather than cooperative. External Environment - affects
6. Stability - which organizational decisions and organization’s impact indirectly.
actions emphasize maintaining the status quo.
Environmental Scanning: A process of gathering,
7. Innovation and Risk Taking - employees are
analyzing, and dispensing information for tactical or
encouraged to be innovative and take risk.
strategic purposes.
Basic Elements of Culture:
o Artifacts
o Values
o Assumptions
5. Managing in a Global Environment
Different Types of Global Organizations:
o Multinational Corporation
How Employees Learn Culture:
o Transnational Corporation
o Stories o Borderless Organization
o Rituals
Global Perspectives:
o Material Symbols
o Language o Ethnocentric
o Polycentric
Managerial Decisions Affected by Culture:
o Geocentric
o Planning
Four Stages of Globalization:
o Organizing
o Leading o Domestic Stage
o International the top level of an organization and
o Multinational then broken-down into sub goals
o Global for each level of the organization.
o Management By Objectives (MBO): A
PLANNING process of setting mutually agreed upon
goals and using these goals to evaluate
1. Foundations of Planning employee performance.
What is Planning? Steps in Goal Setting:
o A primary managerial activity that 1. Review the organization’s mission
involves: statement
2. Evaluate available resources
Defining the organization’s goals 3. Determination of goals
Establishing an overall strategy for 4. Write down and communicate the
achieving those goals goals
Developing plans for organizational 5. Review of results.
work activities.
2. Organizational Goals and Objectives
Types of Planning
Goals and objectives provide the foundation
o Informal: not written down, short-term for measurement.
focus; specific to an organizational unit
o Formal: written, specific, and long-term o Goals vs. Objectives
focus, involves shared goals for the Goals are outcome statements
organization. that define what an
Elements of Planning organization is trying to
accomplish, both
o Goals: desired outcomes for individuals, programmatically and
groups, or entire organizations organizationally.
o Plans: documents that outline how Objectives are very precise,
goals are going to be met; describe how time-based, measurable actions
resources are to be allocated and that support the completion of
establish activity schedules a goal.
TYPES OF GOALS: Measures: actual metrics used to gauge
Financial Goals and Strategic performance on objectives.
Goals
o Without measurement, you cannot
TYPES OF PLANS: tell where you have been, where you
Strategic Plans, Operational Plans, are now, or if you are heading in the
Long-Term Plans, Short-Term Plans, direction you are intending to go.
Specific Plans, Directional Plans,
Single-Use Plan, Standing Plans As a general rule, organizational goals focus
on four major areas:
Establishing Goals and Developing Plans (i) Financial and other monetary measures;
(ii) Environmental relationships;
o Approaches of Goal Setting
(iii) Participants in the organization; and
Traditional goal setting: an (iv) Survival.
approach in which goals are set at
Goals, Objectives, and Planning Quantitative Forecasting
Techniques: uses statistical
o Planning: Vision and a Mission; Vision tools and analyses to
Statement; and Mission Statement predict the future.
Goals, Objectives, and Organizing, Leading, Qualitative Forecasting
and Controlling Techniques: use of opinions
or perceptions from experts
o The role of goals and objectives does for prediction purposes.
not stop in the planning stage. o Benchmarking: a technique to find
o Goal setting is thus a primary out what other organizations are
function of leadership, along with doing well and then incorporating
holding others accountable for their those best practices into the
respective goals and objectives. operations of one’s organization to
improve its cost and effectiveness.
3. Strategic Management
External Benchmarking:
A strategy is a set of related actions that comparing the methods
managers take to increase their company’s and approaches used by
performance (C. Hill & G. Jones, 2013) high-performing companies
with those of one’s
Strategic Leadership is on how managers company.
effectively manage the strategy-making to Internal Benchmarking:
have a competitive advantage. learning the best practices
Strategic Managers: from other units within the
organization.
o Functional-level managers: Contingency Planning
responsible for the specific business o the process of identifying
functions or operation. alternative courses of action in the
o Business-level managers: head of event that unforeseen or
the business unit. uncontrollable events take place.
o Corporate-level managers: consist Scenario Planning
of the highest managers in a o Involves predicting potential
company like the chief executive alternative events that might
officer and other senior executives. happen.
Participation and Involvement
4. Planning Tools and Techniques
o Participatory planning requires that
Pertains to the different methods of the planning include people who
determining, analyzing, and predicting will be affected by the plans or will
situations that will likely to occur. help implement them.
Assessing the Environment References:
Robbins, S. & Coulter, M. (2010). Management (Tenth
o Environmental Scanning: careful Edition). London, UK: Pearson Education, Inc.
monitoring of an organization’s Hill, Charles W.L., et al. 2015. Strategic Management: an
Integrated Approach..Cengage Learning Asia Pte Ltd.
internal and external environments. Kavitha, N. 2012. Management Principles. LAP Lambert
o Forecasting: Pertains to the use of Academic Publication.
scientific techniques to predict the Janice R.W. Joplin and Catherine S. Daus (Aug 1997. "
Dimension of Workforce Diversity” The Academy of
likelihood of certain events or Management Executive (1993-2005) Vol.11 No.3
factors to happen in the future.
Robbins, S. & Coulter, M. (2010). Management (Tenth
Edition). London, UK: Pearson Education, Inc.
Daft, R. & Marcic, D. (2004). Understanding Management
(Fourth Edition). Burgin, USA: South-Western College
Publishing, Inc.
Robbins, S. (2010). Organizational Culture and Environment.
Management (10th Ed). Pearson Education,Inc.
You might also like
- 101 Relationship QuestionsDocument2 pages101 Relationship QuestionsCarol100% (5)
- Applying Social PsychologyDocument185 pagesApplying Social PsychologyMariana93% (14)
- Self-Compassion and MindfulnessDocument42 pagesSelf-Compassion and MindfulnessPrateekGandhi100% (6)
- Handbook of Social Indicators and Qol ResearchDocument604 pagesHandbook of Social Indicators and Qol ResearchSamNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Challenges of Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument33 pagesPersonal Development Challenges of Middle and Late Adolescencedave lorenzeNo ratings yet
- Psychology Powerpoint - Self MotivationDocument53 pagesPsychology Powerpoint - Self MotivationAlpha Beta100% (1)
- A Visit From The Goon Squad by Jennifer EganDocument2 pagesA Visit From The Goon Squad by Jennifer EganAnonymous 4qvaR8ZeNo ratings yet
- Reflective Teaching PracticeDocument24 pagesReflective Teaching Practicejoycepeter100% (3)
- Managing People and Organizations EffectivelyDocument38 pagesManaging People and Organizations EffectivelyMyries Alido BungagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ManagementDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To ManagementNur Hidayah Bustam100% (3)
- Uncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'From EverandUncommonly Observant Leadership; Overcoming 'Management by Ignorance'No ratings yet
- Module 3 Managerial Roles and SkillsDocument6 pagesModule 3 Managerial Roles and SkillsNor Shailanie NalamNo ratings yet
- Snyder Et Al. 1977 Social Perception and Interpersonal BehaviorDocument11 pagesSnyder Et Al. 1977 Social Perception and Interpersonal BehaviorBelmaDžinićNo ratings yet
- Management Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesManagement Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions Manualeddiehickmanfwgdmnxbyz100% (15)
- Difference Between Management and AdministrationDocument17 pagesDifference Between Management and AdministrationMd Alamin100% (2)
- Organizational Behaviour - SDDocument22 pagesOrganizational Behaviour - SDDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Full Download Management Canadian 11th Edition Robbins Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Management Canadian 11th Edition Robbins Solutions Manualjacob7tmoore100% (38)
- Management Canadian 11th Edition Robbins Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesManagement Canadian 11th Edition Robbins Solutions ManualJoshuaMartinezmqjp100% (50)
- Managers Guide to Understanding Changing Business EnvironmentsDocument3 pagesManagers Guide to Understanding Changing Business EnvironmentsShalini PereraNo ratings yet
- Q.NO.1) What Is The Difference Between Management and Administration?Document6 pagesQ.NO.1) What Is The Difference Between Management and Administration?तोइच मोइचNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Management Today-DoneDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Management Today-Donebbypia johnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument84 pagesChapter 1 PDFDanny TamrakarNo ratings yet
- ManagemenDocument25 pagesManagemengmnakivNo ratings yet
- Organization & Management (1)Document3 pagesOrganization & Management (1)Lara MarceloNo ratings yet
- Indorman ReviewerDocument6 pagesIndorman ReviewerAquino, Maricar A.No ratings yet
- Imem Unit IVDocument60 pagesImem Unit IVjanagyrama1No ratings yet
- Introduction To ManagementDocument23 pagesIntroduction To ManagementGaneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1 PDFEYENNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1 PDFEYENNo ratings yet
- Management 14th Edition Robins Test BankDocument15 pagesManagement 14th Edition Robins Test BankKeithMitchelltofsm100% (13)
- Constantino Mary Grace D. Report Mba522Document9 pagesConstantino Mary Grace D. Report Mba522Gear Arellano IINo ratings yet
- Full Download Management Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesFull Download Management Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions Manualmarlingmarguerites100% (22)
- Dwnload Full Management Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Management Global 13th Edition Robins Solutions Manual PDFredfinch.exedent.ti8uaz100% (6)
- POM NotesDocument10 pagesPOM NotesAmit JNo ratings yet
- Management 14th Edition Robins Test BanDwnload Full Management 14th Edition Robins Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesManagement 14th Edition Robins Test BanDwnload Full Management 14th Edition Robins Test Bank PDFosbornelechleruk100% (13)
- The Millennium University: Class Lecture of MBA ProgrammeDocument3 pagesThe Millennium University: Class Lecture of MBA ProgrammeMd WhaheduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2 Organization and ManagementDocument31 pagesChapter 1&2 Organization and ManagementDexter BacaniNo ratings yet
- Changing Nature of Managerial WorkDocument10 pagesChanging Nature of Managerial WorkakramNo ratings yet
- Lesson1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDocument21 pagesLesson1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDonnalyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- 1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsDocument20 pages1-Foundations of Management and OrganizationsKezia Rose SorongonNo ratings yet
- Department of Commerce, Mar Thoma College of Science & Technology, AyurDocument7 pagesDepartment of Commerce, Mar Thoma College of Science & Technology, AyurNaveen Jacob JohnNo ratings yet
- OM - Q1 - Lesson 4 (Environmental Forces and Environmental Scanning)Document60 pagesOM - Q1 - Lesson 4 (Environmental Forces and Environmental Scanning)jofel yarcia100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Introduction To ManagementDocument52 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To ManagementAngelineNo ratings yet
- Management 14th Edition Robins Test BankDocument35 pagesManagement 14th Edition Robins Test Bankpauldiamondwe8100% (23)
- ACCA SBL Slides - Stage 1 PDFDocument104 pagesACCA SBL Slides - Stage 1 PDFPhạm Thành CôngNo ratings yet
- Influence of The External Environment & The Organization's-1-1Document42 pagesInfluence of The External Environment & The Organization's-1-1Ter DeeNo ratings yet
- Notes MEDocument39 pagesNotes MEShreya shashidharNo ratings yet
- Module1Document102 pagesModule1Jahnavi VurityNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - MGT400Document28 pagesTopic 1 - MGT400ifatie hahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Management in 21st CenturyDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Management in 21st CenturyCarl AmboyNo ratings yet
- OrgMan ReviewerDocument5 pagesOrgMan ReviewerChirsten ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument23 pagesOrganizational BehaviorKanwar ZainNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 ManagementDocument128 pagesUNIT-1 ManagementDeepa Shree100% (1)
- MANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESSDocument6 pagesMANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESSCielo PetilNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - PomDocument62 pagesUnit 1 - PomJyotirmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- W2: Foundation of Management: 1. What Is An Organisation?Document6 pagesW2: Foundation of Management: 1. What Is An Organisation?Mai Hương QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- FOM Notes V-2Document15 pagesFOM Notes V-2AbaidUllahNo ratings yet
- MNJC01 - Pengantar Bisnis dan ManajemenDocument41 pagesMNJC01 - Pengantar Bisnis dan ManajemenAnabel LuluNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions of ManagementDocument61 pages3 Functions of ManagementalonemojadifeNo ratings yet
- Introduction .ManagementDocument12 pagesIntroduction .Managementsaranya amuNo ratings yet
- 1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pages1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)emmy.anitagilbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document7 pagesChapter 9Ryan FajriNo ratings yet
- ManagementsDocument11 pagesManagementsSULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Module 1 IntroductionDocument39 pagesPrinciples of Management Module 1 IntroductionMeghana MeghaNo ratings yet
- Organizations DefinedDocument13 pagesOrganizations DefinedMara JavierNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 Introduction To ManagementDocument36 pagesCHP 1 Introduction To Managementreduan hasanNo ratings yet
- Strategy & HR Linkage Basics of HRM - Dec 2006Document67 pagesStrategy & HR Linkage Basics of HRM - Dec 2006api-3719687No ratings yet
- Principles of Management (HMM121)Document125 pagesPrinciples of Management (HMM121)ricardo njiniNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest: I PV X I X NDocument4 pagesSimple Interest: I PV X I X NLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Role of S&T On Nation BuildingDocument6 pagesRole of S&T On Nation BuildingLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Valedictory SpeechDocument2 pagesValedictory SpeechLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- 3 BFIncome StatementsDocument3 pages3 BFIncome StatementsLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- 1 BFTypesof BusinessDocument1 page1 BFTypesof BusinessLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- UTS Book ReviewDocument2 pagesUTS Book ReviewLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Vivre sa Vie Film AnalysisDocument2 pagesVivre sa Vie Film AnalysisLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Economics Reviewer 1Document3 pagesEconomics Reviewer 1Lorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organization and MAnagementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Organization and MAnagementLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Rosana FLDocument1 pageRosana FLLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- 1 BFTypesof BusinessDocument1 page1 BFTypesof BusinessLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- André Ampère, Father of ElectrodynamicsDocument5 pagesAndré Ampère, Father of ElectrodynamicsLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- UTS Book ReviewDocument2 pagesUTS Book ReviewLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- 3 BFIncome StatementsDocument3 pages3 BFIncome StatementsLorrianne RosanaNo ratings yet
- Cumbria's guide to promoting young children's emotional well-beingDocument32 pagesCumbria's guide to promoting young children's emotional well-beingAlbina ScutaruNo ratings yet
- Level 5 5013v1 Exemplar Assignment 2 For WebsiteDocument5 pagesLevel 5 5013v1 Exemplar Assignment 2 For WebsiteKareemAdams902950% (2)
- Ielts Academic Reading Practice Test 53 67f338b4a6Document4 pagesIelts Academic Reading Practice Test 53 67f338b4a6Sithija WickramaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Prof.P.Kameswar A RaoDocument35 pagesProf.P.Kameswar A Raokameswara rao PorankiNo ratings yet
- Gender Dysphoria QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesGender Dysphoria QuestionnairePsyuni IndiaNo ratings yet
- Political CultureDocument31 pagesPolitical CulturePamelaNo ratings yet
- HUMANITAS Vol. 11-2.131-142 ISSN : 1693-7236 Kualitas Kehidupan Kerja, Kecerdasan Emosi dan Efetivitas Tim Kerja dengan Mediator Komitmen OrganisasiDocument12 pagesHUMANITAS Vol. 11-2.131-142 ISSN : 1693-7236 Kualitas Kehidupan Kerja, Kecerdasan Emosi dan Efetivitas Tim Kerja dengan Mediator Komitmen OrganisasialbertNo ratings yet
- Ausubels Meaningful Verbal TheoryDocument4 pagesAusubels Meaningful Verbal TheoryRay Lorenz OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Lesson 2 3Document19 pagesPractical Research 2 Lesson 2 3Sherwin100% (1)
- Edad 694 SHDocument9 pagesEdad 694 SHapi-508707703No ratings yet
- Functional Assessment: Analyzing Child Behavior: Behavioral AnalysisDocument3 pagesFunctional Assessment: Analyzing Child Behavior: Behavioral AnalysisRue TapaoNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To HRMDocument9 pages1.introduction To HRMVishalNo ratings yet
- Human Services Intervention StrategiesDocument6 pagesHuman Services Intervention StrategiesRebecca TedNo ratings yet
- Why Pictures Easier to Recall Than WordsDocument2 pagesWhy Pictures Easier to Recall Than WordsUmmu MukhlisNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Personality Traits of Students Belonging To ICSE and CBSE BOARDDocument5 pagesA Comparative Study of Personality Traits of Students Belonging To ICSE and CBSE BOARDDr. Manoranjan TripathyNo ratings yet
- Nursing AdministrationDocument38 pagesNursing AdministrationNinez Manzanillo-BalmadridNo ratings yet
- Explaining Consumer Buying Behaviours - Picking, Impulse, Sub-Contracted, Legalist, Problem-Solving & HeuristicDocument2 pagesExplaining Consumer Buying Behaviours - Picking, Impulse, Sub-Contracted, Legalist, Problem-Solving & HeuristicRam Ratan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Brief Report Effects of Tact Training On EmergentDocument10 pagesBrief Report Effects of Tact Training On EmergentMichel Armando Chaparro NiviaNo ratings yet
- Sociology Sample Paper BDocument2 pagesSociology Sample Paper BKanupriya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease and Dementia: Understanding the LinkDocument45 pagesParkinson Disease and Dementia: Understanding the LinkraniNo ratings yet
- Teen Suicide Causes - Environmental CausesDocument3 pagesTeen Suicide Causes - Environmental Causessiti maisarah binti amranNo ratings yet