Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conduction: A C A C
Conduction: A C A C
Uploaded by
Mohd Azhari Mohd RodziOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conduction: A C A C
Conduction: A C A C
Uploaded by
Mohd Azhari Mohd RodziCopyright:
Available Formats
CONDUCTION
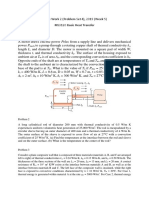
The composite wall of an oven consists of three materials, two of which are of known thermal
conductivity, kA = 20W/m·K and kC = 50W/m·K, and known thickness, LA = 0.30m and LC =
0.15m. The third material, B, which is sandwiched between materials A and C, is of known
thickness, LB = 0.15m, but unknown thermal conductivity kB. Under steady-state operating
conditions, measurements of temperature are shown in figure above. The inside convection
coefficient h is known to be 25 W/m2·K.
(a) Provide equivalent thermal circuit network from T∞ inside the oven, to outer oven surface
temperature Ts,o. Also provide thermal resistance equation for each element.
(b) Express the heat flux, q” due to conduction for the three materials A, B and C, in term of
available values of k, L and T.
(c) Find the heat flux, q” due to convection inside the oven.
(d) Find the value of kB.
CONVECTION
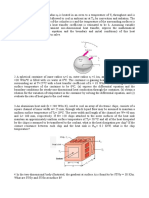
Computer chips generate heat during operation, and their failure rate increases with
temperature. In the figure above, a chip is cooled by a flow of air at 20°C and atmospheric
pressure. The maximum allowable chip surface temperature is 65°C and the air velocity is 3.4
m/s. Determine:
(a) Reynolds number, Re and the flow regime for the air.
(b) Prandtl number, Pr.
(c) Nusselt number, Nu.
(d) Convection coefficient, h.
(e) Heat that can be removed, q through convection.
You might also like
- ASSIGNMENT - scsj2000201 - Attempt - 2021-04-08-09-48-18 - Siah Rhu Hoong SCSJ2000201 Assessment Eat 223 Thermofluid & EngineDocument6 pagesASSIGNMENT - scsj2000201 - Attempt - 2021-04-08-09-48-18 - Siah Rhu Hoong SCSJ2000201 Assessment Eat 223 Thermofluid & EngineMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Document44 pagesFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315AndrestorpNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer Quiz2Document2 pagesThermodynamics & Heat Transfer Quiz2kerroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document6 pagesLecture 9ashfaque ahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Example 2-Heat ConductionDocument4 pagesExample 2-Heat Conductionqusai almshaqbehNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer 2011-Midterm Solutions FinalDocument11 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer 2011-Midterm Solutions FinalJaspreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- Assignment and Solution For Heat TransferDocument5 pagesAssignment and Solution For Heat TransferSoumen PandaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TransferenciaDocument5 pagesEjercicios TransferenciaPablo RuizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 HMTDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 HMTAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- sm3 084Document2 pagessm3 084Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1AdarshpatankarNo ratings yet
- Conduction QuestionDocument2 pagesConduction Questionsandyengineer13No ratings yet
- hmt22 hw3Document1 pagehmt22 hw3KaanNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document43 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- HT AssignmentDocument2 pagesHT AssignmentShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- HW2Document2 pagesHW2lucasNo ratings yet
- Sheet (4) SolDocument6 pagesSheet (4) Solsamadony100% (1)
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer WorksheetDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer WorksheetBISRAT YIHUNNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3 CalorDocument3 pagesTarea 3 CalorLuis AngelNo ratings yet
- Ass 7Document4 pagesAss 7Puneet MeenaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Thermal Contact ResistanceDocument3 pagesCalculation of Thermal Contact ResistanceAhmed QasimNo ratings yet
- Work 4 - Perpandas-2019Document3 pagesWork 4 - Perpandas-2019hungNo ratings yet
- Work 4 - Perpandas-2019 PDFDocument3 pagesWork 4 - Perpandas-2019 PDFrafiqi khairalNo ratings yet
- MAE 101C (Spring 2020) - Midterm Exam #1: (80 Minutes)Document1 pageMAE 101C (Spring 2020) - Midterm Exam #1: (80 Minutes)Dinger RectileNo ratings yet
- CHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Document3 pagesCHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Clinton OkereNo ratings yet
- SKKK 2313a1Document2 pagesSKKK 2313a1Gomathy GunasekharanNo ratings yet
- Lab de Termodinamica No 3Document9 pagesLab de Termodinamica No 3edja5No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Solved ProblemsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - Solved ProblemsHashem MansiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-1Document4 pagesTutorial 2-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document3 pagesAssignment No 1Sumit NagpalNo ratings yet
- Assignment3-FVM For ConductionDocument1 pageAssignment3-FVM For ConductionPatrice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer AssinmentDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer AssinmentbaruaoleNo ratings yet
- Northern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesNorthern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferAj ZNo ratings yet
- Study Questions (Chapter - 3) PDFDocument6 pagesStudy Questions (Chapter - 3) PDFefeln1No ratings yet
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Document44 pagesFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315TortelliniTimNo ratings yet
- TranscalDocument60 pagesTranscalIvan TumaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Homework #2 Professor: Albio Gutiérrez - Office E33-2005 InstructionsDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Homework #2 Professor: Albio Gutiérrez - Office E33-2005 InstructionsalejandroNo ratings yet
- sm3 3Document1 pagesm3 3jrhowell2323No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 HEATDocument1 pageAssignment 1 HEATDevesh RehanNo ratings yet
- MEEG 306 Tutorial Revised May 2019Document30 pagesMEEG 306 Tutorial Revised May 2019sagar100% (1)
- Examen+1+calor+th 16Document4 pagesExamen+1+calor+th 16Denisse M. ZamoraNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument4 pagesConductionjaibalayyaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Transient 2D Heat Conduction Problem Using Freefem++Document4 pagesSolution of Transient 2D Heat Conduction Problem Using Freefem++Chicca PantanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Thermal Conductivity and The Mechanism of Heat TransportDocument33 pagesChapter 8: Thermal Conductivity and The Mechanism of Heat TransportConrad MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Mechanism of Heat ConvectionDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Mechanism of Heat Convectionarul mozhiNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER - Chapter 2Document2 pagesHEAT TRANSFER - Chapter 2ghostlenyNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerDocument2 pagesFigure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerIcy45No ratings yet
- Work Sheet 1 2022Document6 pagesWork Sheet 1 2022Fikadu GonfaNo ratings yet
- Assignment QB 2015Document3 pagesAssignment QB 2015RutvikLathiaNo ratings yet
- CHENG314 Ass1 S1 20 21Document1 pageCHENG314 Ass1 S1 20 21Imi_dash9No ratings yet
- sm3 087Document1 pagesm3 087Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Mms Assignment No. 1 Session 16171Document7 pagesMms Assignment No. 1 Session 16171Gurjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document10 pagesTutorial Sheet 3kushalNo ratings yet
- Problemas Mecanismos de Transferencia de CalorDocument2 pagesProblemas Mecanismos de Transferencia de CalorMaria Fernanda Bermudez ValeroNo ratings yet
- HMT AssignmentDocument2 pagesHMT AssignmentAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- We M2Document18 pagesWe M2FuriNo ratings yet
- Dry FrictionDocument18 pagesDry FrictionMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Note06. HGL & EGLDocument8 pagesNote06. HGL & EGLMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid BodiesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of ParticlesDocument13 pagesEquilibrium of ParticlesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- MomentDocument34 pagesMomentMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument30 pagesForcesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- SCSJ 002 EAT103 Final Exam EQP - SupplementDocument4 pagesSCSJ 002 EAT103 Final Exam EQP - SupplementMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear KinematicsDocument8 pagesRectilinear KinematicsMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- SCSJ Eat103 Exam 2019Document11 pagesSCSJ Eat103 Exam 2019Mohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- SCSJ 001 EAT103 Online CW3Document7 pagesSCSJ 001 EAT103 Online CW3Mohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- SCSJ Eat103 Exam 2019 MSDocument9 pagesSCSJ Eat103 Exam 2019 MSMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- The Ideal-Gas Equation of State: Pressure, Specific Volume and Temperature) of A SubDocument8 pagesThe Ideal-Gas Equation of State: Pressure, Specific Volume and Temperature) of A SubMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - scsj2000777 - Attempt - 2021-05-06-10-31-36 - EAT 223 FINAL EXAMDocument12 pagesFinal Exam - scsj2000777 - Attempt - 2021-05-06-10-31-36 - EAT 223 FINAL EXAMMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument11 pagesKineticsMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument11 pagesThermal Properties of MatterMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear KinematicsDocument10 pagesCurvilinear KinematicsMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument11 pagesEquilibriumMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument18 pagesElasticityMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Physical QuantitiesDocument24 pagesPhysical QuantitiesMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT - scsj2000631 - Attempt - 2021-04-09-11-33-32 - EAT223 Assignment 1Document8 pagesASSIGNMENT - scsj2000631 - Attempt - 2021-04-09-11-33-32 - EAT223 Assignment 1Mohd Azhari Mohd Rodzi100% (1)
- Segi College Subang Jaya: Bachelor of Automotive EngineeringDocument3 pagesSegi College Subang Jaya: Bachelor of Automotive EngineeringMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Thermal Comfort: 1 © I-Station Solutions SDN BHDDocument7 pagesThermal Comfort: 1 © I-Station Solutions SDN BHDMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - scsj2000631 - Attempt - 2021-05-06-10-52-00 - EAT223 FINAL EXAMDocument4 pagesFinal Exam - scsj2000631 - Attempt - 2021-05-06-10-52-00 - EAT223 FINAL EXAMMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- HVAC OutlineDocument1 pageHVAC OutlineMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Fis0224 Test 2 PDFDocument1 pageFis0224 Test 2 PDFMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Thermal Comfort in Classrooms of SEGI College Subang Jaya: Arul Saktivel A/L M.Nagarajan SCSJ 1500794Document5 pagesThermal Comfort in Classrooms of SEGI College Subang Jaya: Arul Saktivel A/L M.Nagarajan SCSJ 1500794Mohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet
- Extra Name TemplateDocument1 pageExtra Name TemplateMohd Azhari Mohd RodziNo ratings yet