Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cosmology: History of Cosmology & Astronomy
Uploaded by
Jamina Jamaloding0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Cosmology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCosmology: History of Cosmology & Astronomy
Uploaded by
Jamina JamalodingCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Cosmology
Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that involves the origin and evolution of the universe,
from the Big Bang to today and on into the future. According to NASA, the definition of
cosmology is "the scientific study of the large scale properties of the universe as a
whole."
Cosmologists puzzle over exotic concepts like string theory, dark matter and dark
energy and whether there is one universe or many (sometimes called the multiverse).
While other aspects astronomy deal with individual objects and phenomena or
collections of objects, cosmology spans the entire universe from birth to death, with a
wealth of mysteries at every stage.
History of cosmology & astronomy
Humanity's understanding of the universe has evolved significantly over time. In the
early history of astronomy, Earth was regarded as the center of all things, with planets
and stars orbiting it. In the 16th century, Polish scientist Nicolaus Copernicus suggested
that Earth and the other planets in the solar system in fact orbited the sun, creating a
profound shift in the understanding of the cosmos. In the late 17th century, Isaac
Newton calculated how the forces between planets — specifically the gravitational
forces — interacted.
The dawn of the 20th century brought further insights into comprehending the vast
universe. Albert Einstein proposed the unification of space and time in his General
Theory of Relativity. In the early 1900s, scientists were debating whether the Milky Way
contained the whole universe within its span, or whether it was simply one of many
collections of stars. Edwin Hubble calculated the distance to a fuzzy nebulous object in the
sky and determined that it lay outside of the Milky Way, proving our galaxy to be a small
drop in the enormous universe. Using General Relativity to lay the framework, Hubble
measured other galaxies and determined that they were rushing away from the us,
leading him to conclude that the universe was not static but expanding.
In recent decades, cosmologist Stephen Hawking determined that the universe itself is
not infinite but has a definite size. However, it lacks a definite boundary. This is similar
to Earth; although the planet is finite, a person traveling around it would never find the
"end" but would instead constantly circle the globe. Hawking also proposed that the
universe would not continue on forever but would eventually end.
You might also like
- Cosmos, Earth and Mankind Astronomy for Kids Vol I | Astronomy & Space ScienceFrom EverandCosmos, Earth and Mankind Astronomy for Kids Vol I | Astronomy & Space ScienceNo ratings yet
- Meteoric Astronomy - A Treatise on Shooting-Stars, Fire-Balls, and AerolitesFrom EverandMeteoric Astronomy - A Treatise on Shooting-Stars, Fire-Balls, and AerolitesNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton - A Biography of Newton Including Descriptions of his Greatest Discoveries - Including a Poem by Alfred Noyes and a Brief History AstronomyFrom EverandIsaac Newton - A Biography of Newton Including Descriptions of his Greatest Discoveries - Including a Poem by Alfred Noyes and a Brief History AstronomyNo ratings yet
- Astronomical EssayDocument2 pagesAstronomical EssayVibsNo ratings yet
- Strange New Worlds: The Search for Alien Planets and Life beyond Our Solar SystemFrom EverandStrange New Worlds: The Search for Alien Planets and Life beyond Our Solar SystemRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)
- Tycho Brahe - The Nobel Astronomer - Including a History of Astronomy, a Biography of Brahe and his DiscoveriesFrom EverandTycho Brahe - The Nobel Astronomer - Including a History of Astronomy, a Biography of Brahe and his DiscoveriesNo ratings yet
- Heliocentric Astrology or Essentials of Astronomy and Solar Mentality with Tables of Ephemeris to 1913From EverandHeliocentric Astrology or Essentials of Astronomy and Solar Mentality with Tables of Ephemeris to 1913No ratings yet
- The Astronomy of the Bible - An Elementary Commentary on the Astronomical References of Holy ScriptureFrom EverandThe Astronomy of the Bible - An Elementary Commentary on the Astronomical References of Holy ScriptureRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Astrology to Astronomy - The Study of the Night Sky from Ptolemy to Copernicus - With Biographies and IllustrationsFrom EverandAstrology to Astronomy - The Study of the Night Sky from Ptolemy to Copernicus - With Biographies and IllustrationsNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Cosmological TheoriesDocument9 pagesBrief History of Cosmological TheoriesmrsgoodNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument22 pagesAstronomyallysa riveraNo ratings yet
- Kings Dethroned - A History of the Evolution of Astronomy from the Time of the Roman Empire up to the Present Day: Showing it to be an Amazing Series of Blunders Founded Upon an Error Made in the Second CenturyFrom EverandKings Dethroned - A History of the Evolution of Astronomy from the Time of the Roman Empire up to the Present Day: Showing it to be an Amazing Series of Blunders Founded Upon an Error Made in the Second CenturyNo ratings yet
- Johannes Kepler - Including a Brief History of Astronomy and the Life and Works of Johannes Kepler with Pictures and a Poem by Alfred NoyesFrom EverandJohannes Kepler - Including a Brief History of Astronomy and the Life and Works of Johannes Kepler with Pictures and a Poem by Alfred NoyesNo ratings yet
- The Expanding UniverseDocument4 pagesThe Expanding UniverseLunaAlchemist27No ratings yet
- Terra Firma: the Earth Not a Planet, Proved from Scripture, Reason, and FactFrom EverandTerra Firma: the Earth Not a Planet, Proved from Scripture, Reason, and FactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- HO1 UniverseDocument6 pagesHO1 UniverseClaire ArribeNo ratings yet
- Ancient To Modern AstronomyDocument2 pagesAncient To Modern AstronomyMahesh Tanpure100% (1)
- We're the Center of the Universe!: Science's Biggest Mistakes about Astronomy and PhysicsFrom EverandWe're the Center of the Universe!: Science's Biggest Mistakes about Astronomy and PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Astronomers and How They Shaped AstronomyDocument36 pagesAstronomers and How They Shaped AstronomySay KhoNo ratings yet
- Gravity's Century: From Einstein's Eclipse to Images of Black HolesFrom EverandGravity's Century: From Einstein's Eclipse to Images of Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Theories About The Origin of The Universe: Brahmanda (Cosmic Egg) UniverseDocument12 pagesTheories About The Origin of The Universe: Brahmanda (Cosmic Egg) UniverseDexter DalusongNo ratings yet
- Medieval and Modern-Age AstronomyDocument7 pagesMedieval and Modern-Age AstronomyKevin CalNo ratings yet
- Dreams of Other Worlds: The Amazing Story of Unmanned Space Exploration - Revised and Updated EditionFrom EverandDreams of Other Worlds: The Amazing Story of Unmanned Space Exploration - Revised and Updated EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Discovery and ExplorationDocument1 pageDiscovery and ExplorationShadman SadikNo ratings yet
- AstronomyDocument34 pagesAstronomyMICHELLE DE GUZMAN SOTTONo ratings yet
- Quest For Other WorldsDocument15 pagesQuest For Other WorldsumityilmazNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "The Roots And The Fruits: Topics Of Philosophy Of Science" By Eduardo Flichman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "The Roots And The Fruits: Topics Of Philosophy Of Science" By Eduardo Flichman: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- History of Black HolesDocument1 pageHistory of Black HolesHanny GustonNo ratings yet
- Life Is ItDocument5 pagesLife Is ItSojibNo ratings yet
- Dispatches from Planet 3: 32 (Brief) Tales on the Solar System, the Milky Way, and BeyondFrom EverandDispatches from Planet 3: 32 (Brief) Tales on the Solar System, the Milky Way, and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- A Journey Through Space and TimeDocument22 pagesA Journey Through Space and TimeSeptian Hadi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Theories On The Origin of UniverseDocument15 pagesTheories On The Origin of Universesyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument5 pagesHistory of EarthJudy GuevarraNo ratings yet
- BASICSOFTHEUNIVERSEDocument12 pagesBASICSOFTHEUNIVERSEAryaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Importance of AstronomyDocument4 pagesImportance of AstronomyJaja CarlinaNo ratings yet
- Space Science PresentatioDocument21 pagesSpace Science PresentatioPrathamesh KharabeNo ratings yet
- History: Ancient TimesDocument4 pagesHistory: Ancient TimesJohn Kenneth BentirNo ratings yet
- OSMOLOGICAL THEORIES THROUGH HISTORYDocument9 pagesOSMOLOGICAL THEORIES THROUGH HISTORYTeacher Jefferson EgallaNo ratings yet
- RM Tut 1Document2 pagesRM Tut 1Natangwe YaNatangweNo ratings yet
- 04 - Background On GravityDocument14 pages04 - Background On GravityAdrianNo ratings yet
- Fly Me to the Moon: An Insider's Guide to the New Science of Space TravelFrom EverandFly Me to the Moon: An Insider's Guide to the New Science of Space TravelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Από Την Αρχαιότητα Στον ΑϊνστάινDocument14 pagesΑπό Την Αρχαιότητα Στον ΑϊνστάινChristos NasiopoulosNo ratings yet
- Astrology Is Not A Science CosmologyDocument7 pagesAstrology Is Not A Science Cosmologyapi-461589129No ratings yet
- Space Science: Exploration, Astronomy & Celestial BodiesDocument21 pagesSpace Science: Exploration, Astronomy & Celestial BodiesCrossface GamerNo ratings yet
- Cosmigraphics. Picturing Space Through Time in 4,000 Years of Mapping The UniverseDocument25 pagesCosmigraphics. Picturing Space Through Time in 4,000 Years of Mapping The UniverseHằng ChengNo ratings yet
- Scientific Revolution PPT Accompanying Lecture 2019 UpdatedDocument21 pagesScientific Revolution PPT Accompanying Lecture 2019 UpdatedjhbomNo ratings yet
- Important Points on the History and Study of CosmologyDocument3 pagesImportant Points on the History and Study of CosmologyOrlando Umali100% (3)
- 50 Ideas You Really Need To Know Universe Joanne BakerDocument286 pages50 Ideas You Really Need To Know Universe Joanne Bakerzergs galgao100% (2)
- Assessment Guide GlossaryDocument4 pagesAssessment Guide GlossaryJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- A Critical Comprehension Paper On BBDocument2 pagesA Critical Comprehension Paper On BBJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
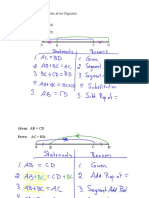
- 2-6 Proving Statements About SegmentsDocument7 pages2-6 Proving Statements About SegmentsJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Australian Professional Standards For TeachersDocument32 pagesAustralian Professional Standards For Teachersapi-525093925No ratings yet
- 1.6-1.7 Quiz Review Math Geometry MidpointsDocument5 pages1.6-1.7 Quiz Review Math Geometry MidpointsJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Integrated Algebra: - RZ, - V - Y - (-) - 'Document22 pagesIntegrated Algebra: - RZ, - V - Y - (-) - 'Jamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Field Act. 1-JamalodingDocument5 pagesField Act. 1-JamalodingJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Activity #4 Terminology ListDocument15 pagesActivity #4 Terminology ListJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Practice: Triangle Congruence by ASA and AASDocument2 pagesPractice: Triangle Congruence by ASA and AASJamina Jamaloding100% (1)
- 1Document1 page1Jamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Activity #4 Terminology ListDocument15 pagesActivity #4 Terminology ListJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Observations and HypothesesDocument2 pagesObservations and HypothesesJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Activity #4 Terminology ListDocument15 pagesActivity #4 Terminology ListJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Animal Behavior Case Study 1 - Red Winged BlackbirdsDocument3 pagesAnimal Behavior Case Study 1 - Red Winged BlackbirdsJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Population Ecology GraphsDocument5 pagesInterpreting Population Ecology GraphsJamina Jamaloding100% (2)
- BeesDocument1 pageBeesJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Group 4 EcologyDocument2 pagesGroup 4 EcologyJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- QUIZ ON PPT JamalodingDocument32 pagesQUIZ ON PPT JamalodingJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Inductive vs Deductive Reasoning and Graphing Calculator InsightsDocument3 pagesInductive vs Deductive Reasoning and Graphing Calculator InsightsJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Rhyme Time by Jamina P. JamalodingDocument13 pagesRhyme Time by Jamina P. JamalodingJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Act 1 JamalodingDocument1 pageCase Analysis Act 1 JamalodingJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Breakfast Menu ArpiyaDocument1 pageBreakfast Menu ArpiyaJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes LessonDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes LessonJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- HeleDocument12 pagesHeleJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet
- City BansDocument1 pageCity BansJamina JamalodingNo ratings yet