Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organization Structure and Theory
Uploaded by
ljjbOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organization Structure and Theory
Uploaded by
ljjbCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 2
Organization Structure and Theory
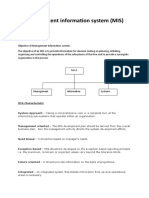
An Organizational Need for MIS in a Company
The main reason for finding MIS in a company is to facilitate the management decision making at all
levels of company, the MIS must be integrated. MIS units are company wide. MIS is available for the
Top management. The top management of company should play an active role in designing, modifying
and maintenance of the total organization wide management information system. Information system
and Information technology have become a vital component of any successful business and are
regarded as major functional areas just like any other functional area of a business organization like
marketing, finance, production and HR. Thus it is important to understand the area of information
system just like any other functional area in the business. MIS is important because all businesses have
a need for information about the tasks which are to be performed. Information and technology is used
as a tool for solving problems and providing opportunities for increasing productivity and quality.
Information has always been important but it has never been so available, so current and so
overwhelming. Efforts have been made for collection and retrieval of information, However,
challenges still remain in the selection analysis and interpretation of the information that will further
improve decision making and productivity.
MIS for a Business Organization :
1. Support the Business Process : Treats inputs as a request from the customer and outputs as
services to customer. Supports current operations and use the system to influence further way
of working.
2. Support Operation of a Business Organization : MIS supports operations of a business
organization by giving timely information, maintenance and enhancement which provides
flexibility in the operation of an organizations.
3. To Support Decision Making : MIS supports the decision making by employee in their daily
operations. MIS also supports managers in decision making to meet the goals and objectives
of the organization. Different mathematical models and IT tools are used for the purpose
evolving strategies to meet competitive needs.
4. Strategies for an Organization : Today each business is running in a competitive market.
MIS supports the organization to evolve appropriate strategies for the business to assented in
a competitive environment.
Requirement of an Effective MIS :
(i) Qualified System and Management Staff : The prerequisite of an effective MIS is that it should
be managed by qualified officers. These officers should have a mutual understanding about the roles
and responsibilities of each other. be understand clearly the view of their fellow officers. For this,
each organization should have two categories of officers :
(a) System and Computer Experts who in addition to their expertise in their subject area , they
should also be capable of understanding management concepts to facilitate the understanding of
problems asked by concern. They should also be clear about the process of decision making and
information requirements for planning.
(b) Management experts who should also understand quite-clearly the concepts and operations of a
computer. This basic knowledge of computer will be useful will place them in a comfortable position,
while working with systems, technicians in designing or other wise, of the information system.
(ii) Futuristic Perspective : An effective MIS should be capable of meeting the future requirements
of its executives as well. This capability can be achieved by regular monitoring and updating the MIS.
(iii) Support of Top Management : For a management information system to be effective, it must
receive the full support of top management. The Reasons for this are :
(a) Subordinate managers are usually lethargic about activities which do not receive the support of
their superiors.
(b) The resources involved in computer based information system are larger and are growing larger
and larger in view of importance gained by management information system.
(iv) Common Database : It is an integrated collection of data and information which is utilized by
several information subsystems of an organization. A common database may be defined as a super
file which consolidates and integrates data records formerly stored in a separate data file. Such a
database can be organized as an integrated collection of data records into a single super file or it can
be organized as an integrated collection of several data file.
(v) Control and maintenance of MIS : Control of the MIS means the operation of the system as it
was designed to operate. Some times, users develop their own procedures or short cut methods to use
the system which reduces its effectiveness.
various types of Information.
A business has several information systems :
(A) Formal Information System
(B) Informal Information System
(C) Computer Based Information System
(a) Formal Information System: It is based on organizational chart represented by the organization.
(b) Informal Information System : It is an employee based system designed to meet personal and
vocational needs and to help in the solution of work-related problems. It also funnels information
upward through indirect channels. It works within the framework of the business and its stated
policies.
(c) Computer Based Information System (CBIS) : This category of information system depends
mainly on the computer for handling business application. System analysis develops different types
of information system to meet variety of business needs. There is class of system known as
collectively as computer based information system. They are categorized in the following 6 classes:
i) Transaction Processing System (TPS)
ii) Management Information System (MIS)
iii)Decision Support System (DSS)
iv)Executive Support System (ESS)
v)Office Automation Systems (OASs), and
vi)Business Expert Systems (BESs)
The organization has executive support systems (ESS) at the strategic level; management information systems (MIS)
and decision-support systems (DSS) at the management level; knowledge work systems (KWS) and office systems
at the knowledge level; and transaction processing systems (TPS) at the operational level. Systems at each level in
turn are specialized to serve each of the major functional areas. Thus, the typical systems found in organizations are
designed to assist workers or managers at each level and in the functionsof sales and marketing, manufacturing,
finance, accounting, and human resources.
1. Transaction Processing System:
TPS processes transaction and produces reports. It represents the automation of the fundamental,
routine processing used to support business operations.It does not provide any information to the
user to his/her decision-making. TPS uses data and produces data as shown in the following
diagram.
Previously, TPS was known as Management Information System. Prior to computers, data
processing was performed manually or with simple machines. The domain of TPS is at the lowest
level of the management hierarchy of an organization.
2. Management Information System (MIS)
MIS is an information system, which processes data and converts it into information.A management
information system uses TPS for its data inputs. The information generated by the information
system may be used for control of operations, strategic and long-range planning. Short-range
planning, management control, and other managerial problem solving. It encompasses processing in
support of a wide range of organizational functions & management processes. MIS is capable of
providing analysis, planning & decision making support. The functional areas of a business may be
marketing, production, human resource, finance and accounting.
3. Decision Support System (DSS)
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system application that assists decision-making.
DSS tends to be used in planning, analyzing alternatives, and trial and error search for solution. The
elements of the decision support system include a database, model base & software. The main
application areas of DSS are Production, finance and marketing.
DSS can be differentiated from MIS on the basis of processing the information. MIS processes data
to convert it into information. DSS processes information to support the decision making process of
a manager.
4. Executive Support System (ESS)
Executive Support System (ESS) is an extension of the management information system, which is a
special kind of DSS; An ESS is specially tailored for the use of chief executive of an organization to
support his decision-making. It includes various types of decision-making but it is more specific
and person oriented.
5. Office Automation Systems (OAS)
Office automation refers to the application of computes and communication technology to office
functions. Office automation systems are meant to improve the productivity of managers at
various levels of management of providing secretarial assistance and better communication
facilities.
Office activities may be grouped under two classes, namely
i)Activities performed by clerical personnel (clerks, secretaries, typist, etc.,) and
ii)Activities performed by the executives (managers, engineers or other professionals like
economist, researches etc.)
In the first category, the following is a list of activities.
a) Typing
b) Mailing
c)Scheduling of meetings and conferences,
d) Calendar keeping, and
e)Retrieving documents
The following is a list of activities in the second category (managerial category)
a)Conferencing.
b)Production of information (messages, memos, reports, etc.) and controlling performance.
Business Expert Systems :These systems are one of the main types of knowledge-based
information systems. These systems are based on artificial intelligence, and are advanced
information systems. A business expert system is a knowledge based information system that uses
its knowledge about a specific, complex application area to act as an expert. The main components
of an expert system are:
a. Knowledge Base
b. Interface Engine
c. User Interface.
You might also like
- Chapt 3 Introduction of MisDocument10 pagesChapt 3 Introduction of MisBhuvanvignesh VengurlekarNo ratings yet
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- MIS Meaning, Ojective and CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesMIS Meaning, Ojective and CharacteristicsMpangiOmarNo ratings yet
- Management Information System 7267 kGm1usTDocument12 pagesManagement Information System 7267 kGm1usTAliyu Umar IsaNo ratings yet
- ISM Unit - 1Document5 pagesISM Unit - 1Fake MailNo ratings yet
- Unit 03Document20 pagesUnit 03harsh hariharnoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Management Information Systems (MISDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Management Information Systems (MISRachit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System For Effective and EfficientDecisionDocument13 pagesManagement Information System For Effective and EfficientDecisionMary Grace Baston OribelloNo ratings yet
- Mboo31 - Management Information Systems Set - 1Document14 pagesMboo31 - Management Information Systems Set - 1Yash koradiaNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Business Management: Chennai - 020 Second Semester Emba/Mba Subject: Management Information SystemDocument14 pagesNational Institute of Business Management: Chennai - 020 Second Semester Emba/Mba Subject: Management Information SystemAtul Raut100% (1)
- What Is Management Information SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is Management Information SystemRuffa Mae MaldoNo ratings yet
- NCRD'S Sterling Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-Management Information System Assignment No.: - 1, 2, 3Document13 pagesNCRD'S Sterling Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-Management Information System Assignment No.: - 1, 2, 3Nishita ShivkarNo ratings yet
- Module in MisDocument15 pagesModule in Miskristina_eleventhNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Introduction To MIS FinalDocument11 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To MIS FinalMilka ThuoNo ratings yet
- Role of MIS in Management Decision Making for Processing EnterprisesDocument8 pagesRole of MIS in Management Decision Making for Processing EnterprisesSounds You WantNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument9 pagesManagement Information SystemSandeep SahadeokarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-PGDM-Management Information SystemsDocument18 pagesUnit 1-PGDM-Management Information SystemsRohan KhuranaNo ratings yet
- MIS FinalDocument9 pagesMIS FinalSounds You WantNo ratings yet
- MIS-Increasing HR Efficiency in IT SectorDocument16 pagesMIS-Increasing HR Efficiency in IT SectorAlisha OberoiNo ratings yet
- Mis 2Document3 pagesMis 2durgesh7998No ratings yet
- BCM 2208 Management Information Systems Lecture IIDocument14 pagesBCM 2208 Management Information Systems Lecture IIHillary OdungaNo ratings yet
- MisDocument32 pagesMisGeethika K MararNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument10 pagesManagement Information SystemPankaj Kr LakraNo ratings yet
- MIS & Other SubsystemsDocument89 pagesMIS & Other SubsystemsDebi Mohapatra33% (3)
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1shalini selvarajNo ratings yet
- MIS - Question and AnswerDocument13 pagesMIS - Question and AnswerMohdfahmihusin mohd100% (9)
- Master of Business Administration - MBA Semester 2 (Book ID: B1136) Assignment Set-1 60 MarksDocument23 pagesMaster of Business Administration - MBA Semester 2 (Book ID: B1136) Assignment Set-1 60 MarksAnand PrasadNo ratings yet
- MIS Management Unit 1 OverviewDocument12 pagesMIS Management Unit 1 Overview71002750No ratings yet
- Management Information System: Unit - I: IntroductionDocument14 pagesManagement Information System: Unit - I: IntroductionSOCIAL STUDIESNo ratings yet
- CMP 361Document39 pagesCMP 361ibraheembello31No ratings yet
- MIS-management information system definitionDocument15 pagesMIS-management information system definitionVinayak MangotraNo ratings yet
- Management Information System FullDocument28 pagesManagement Information System FullHalar KhanNo ratings yet
- MIS IntroductionDocument41 pagesMIS IntroductionP. Akthar Sulthana0% (1)
- MIS - Management Information System Prof. Purvish ShahDocument34 pagesMIS - Management Information System Prof. Purvish ShahPrasad ShankarwarNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Management Information System: 1. Office Automation System (OAS)Document13 pagesTopic 2: Management Information System: 1. Office Automation System (OAS)Hildah JJNo ratings yet
- MIS SolutionDocument8 pagesMIS SolutionMarkib Singh AdawitahkNo ratings yet
- MIS (Final)Document24 pagesMIS (Final)sharath pNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Management Information SystemDocument2 pagesThe Concept of Management Information SystemMeenal VarmaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: MeaningDocument5 pagesManagement Information System: Meaningbinoy parekhNo ratings yet
- Ans. MIS Is The Use of Information Technology, People, and Business Processes To Record, Store and Process Data To Produce Information That Decision Makers Can Use To Make Day To Day DecisionsDocument3 pagesAns. MIS Is The Use of Information Technology, People, and Business Processes To Record, Store and Process Data To Produce Information That Decision Makers Can Use To Make Day To Day DecisionsTaiyabaNo ratings yet
- Mis Final Assignment: Old Campus - Se AfternoonDocument45 pagesMis Final Assignment: Old Campus - Se AfternoonArslan UmarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 ISMDocument25 pagesUnit-1 ISMupkeeratspamNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument176 pagesManagement Information SystemJithin SajanNo ratings yet
- What Is MIS? Characteristics, Objectives, Role, ComponentDocument18 pagesWhat Is MIS? Characteristics, Objectives, Role, ComponentGrophel MesaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System and Decision Making Process inDocument5 pagesManagement Information System and Decision Making Process inpurvi mittalNo ratings yet
- characteristics-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagescharacteristics-WPS OfficeVoldemortNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems (MIS) - Increasing Efficiency of HR FunctionDocument17 pagesManagement Information Systems (MIS) - Increasing Efficiency of HR FunctionAlisha OberoiNo ratings yet
- Notes CH 1 2 Revision For Mid 1Document13 pagesNotes CH 1 2 Revision For Mid 1juhanaNo ratings yet
- Project Management InfoDocument13 pagesProject Management InfoB.ShyamalaNo ratings yet
- Mis ProjectDocument44 pagesMis ProjectVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Role of MIS in Business: Opportunities and ChallengesDocument10 pagesRole of MIS in Business: Opportunities and ChallengesadarNo ratings yet
- MIS Concept, Role and ImportanceDocument5 pagesMIS Concept, Role and ImportancejohnNo ratings yet
- Mis Unit 1Document23 pagesMis Unit 1mugundhanmgnNo ratings yet
- Mis File 1Document17 pagesMis File 12304 Abhishek vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 ppt1 Part1 NewDocument78 pagesUnit1 ppt1 Part1 NewLaksha AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Overview of MISDocument33 pagesChapter One Overview of MISabdirizak husseinNo ratings yet
- 1 MIS Unit 1Document2 pages1 MIS Unit 1Eric Rajat100% (1)
- Management Information Systems Paper OverviewDocument27 pagesManagement Information Systems Paper OverviewRitika Diwakar100% (1)
- MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM(MISDocument45 pagesMANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM(MISYt NoobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Evolutionary Computation: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Evolutionary Computation: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahljjbNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Inference Systems: Linguistic HedgesDocument21 pagesFuzzy Inference Systems: Linguistic HedgesljjbNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Inference Systems: Linguistic HedgesDocument21 pagesFuzzy Inference Systems: Linguistic HedgesljjbNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Relation Composition and ExtensionDocument66 pagesFuzzy Relation Composition and ExtensionljjbNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms Tutorials: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahDocument20 pagesGenetic Algorithms Tutorials: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahljjbNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Genetic Algorithms: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahDocument43 pagesFundamentals of Genetic Algorithms: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahljjbNo ratings yet
- Hand Geometry: Presented By: Dr. Saif Alabachi Computer Engineering University of TechnologyDocument8 pagesHand Geometry: Presented By: Dr. Saif Alabachi Computer Engineering University of TechnologyljjbNo ratings yet
- To Biometrics: Presented By: Saif Alabachi Computer Engineering University of TechnologyDocument28 pagesTo Biometrics: Presented By: Saif Alabachi Computer Engineering University of TechnologyljjbNo ratings yet
- Swarm Intelligence Concepts: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahDocument20 pagesSwarm Intelligence Concepts: Assist. Prof. Dr. Mohammed Najm AbdullahljjbNo ratings yet
- Biometrics Course Image Enhancement TechniquesDocument23 pagesBiometrics Course Image Enhancement TechniquesljjbNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Recognition Techniques and TechnologiesDocument28 pagesFingerprint Recognition Techniques and TechnologiesljjbNo ratings yet
- Biometrics Course Image Enhancement TechniquesDocument23 pagesBiometrics Course Image Enhancement TechniquesljjbNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform: Advanced Mathematics IDocument7 pagesLaplace Transform: Advanced Mathematics IljjbNo ratings yet
- Code Biometric 2 Hours/Week 2 Units: Contents of Syllabus HoursDocument1 pageCode Biometric 2 Hours/Week 2 Units: Contents of Syllabus HoursljjbNo ratings yet
- Font Info Socialmedia PDFDocument1 pageFont Info Socialmedia PDFljjbNo ratings yet
- Prototyping: Information SystemsDocument7 pagesPrototyping: Information SystemsljjbNo ratings yet
- 8251 - UsartDocument26 pages8251 - UsartSreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTUREDocument7 pages8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTUREljjbNo ratings yet
- Qos and Network Performance: Computer NetworksDocument6 pagesQos and Network Performance: Computer NetworksljjbNo ratings yet
- 8086 Addressing Mode: MicroprocessorsDocument9 pages8086 Addressing Mode: MicroprocessorsljjbNo ratings yet
- Rapid-Application Development (RAD) : Software EngineeringDocument11 pagesRapid-Application Development (RAD) : Software EngineeringljjbNo ratings yet
- Games: Direct3DDocument2 pagesGames: Direct3DljjbNo ratings yet
- 3D Transformations and ProjectionsDocument27 pages3D Transformations and ProjectionsljjbNo ratings yet
- 8251 - UsartDocument26 pages8251 - UsartSreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- MATH 106 Permutations & Combinations: Player NumbersDocument11 pagesMATH 106 Permutations & Combinations: Player NumbersMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- AM Demodulator AnalysisDocument9 pagesAM Demodulator AnalysisljjbNo ratings yet
- 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTUREDocument7 pages8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTUREljjbNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Geom3dDocument13 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Geom3dvijaykumarzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Classification of Signal and System: Houshou ChenDocument95 pagesChapter 1: Classification of Signal and System: Houshou ChenApurbo BiswasNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 37.236.134.12 On Wed, 24 Jun 2020 16:53:46 UTCDocument11 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 37.236.134.12 On Wed, 24 Jun 2020 16:53:46 UTCljjbNo ratings yet
- Art defined through Filipino lensDocument2 pagesArt defined through Filipino lensSzarena Santos100% (2)
- English Grammar-Sentence StructureDocument10 pagesEnglish Grammar-Sentence StructureShipra HarshitNo ratings yet
- General Administrative TheoryDocument8 pagesGeneral Administrative TheoryElmer PerezNo ratings yet
- How College Differs from High SchoolDocument4 pagesHow College Differs from High SchoolPaul BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Grammar - BasicDocument2 pagesUnit 5 - Grammar - BasicvamsrorgeNo ratings yet
- Inside The Montessori ClassroomDocument18 pagesInside The Montessori ClassroomZandria Camille Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Conducting Effective Meetings WorkBookDocument36 pagesConducting Effective Meetings WorkBookCheri HoNo ratings yet
- Composite Writing MatrixDocument11 pagesComposite Writing MatrixmrkballNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade ReadingDocument26 pages1st Grade Readingmary maryNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Pet and Fce Exams Con VideoDocument7 pagesStrategies For Pet and Fce Exams Con VideoCONSTANSA BARCONo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal ToolsDocument17 pagesPerformance Appraisal Toolsamit_bohraNo ratings yet
- American Accent Reduction CousreDocument3 pagesAmerican Accent Reduction CousreProf. AlexNo ratings yet
- Kernberg, Handbook of Dynamic Psychotherapy For Higher Level Personality PathologyDocument275 pagesKernberg, Handbook of Dynamic Psychotherapy For Higher Level Personality PathologyAlejandro Enriquez Lóyzaga100% (5)
- Aim:-To Study Differential Encoding Techniques For DataDocument5 pagesAim:-To Study Differential Encoding Techniques For DataTushar PatilNo ratings yet
- Christina BartonDocument1 pageChristina Bartonapi-406107839No ratings yet
- Rational Number Open Task RubricDocument2 pagesRational Number Open Task Rubricapi-319586327No ratings yet
- Behavioral Management TechniquesDocument25 pagesBehavioral Management TechniquesgabrielguilasNo ratings yet
- Bsbcmm401 CADocument12 pagesBsbcmm401 CADarcie Jo-aNo ratings yet
- QS 27 - Building Services Assignment 2Document8 pagesQS 27 - Building Services Assignment 2Ahamed Manazir HazzaanNo ratings yet
- Special Occasion Speeches GuideDocument3 pagesSpecial Occasion Speeches GuideMaia Dela Cruz MindoNo ratings yet
- Analogies Homework HelpDocument7 pagesAnalogies Homework Helpafmtibboa100% (1)
- Oralcom11 q2 Mod5 FINALDocument22 pagesOralcom11 q2 Mod5 FINALBay-as OlagetNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Motivation and EmotionDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Motivation and Emotionjonaxx enthusiastNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Descriptive TextDocument9 pagesModul 3 Descriptive TextRien SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Neural NetworksDocument27 pagesNeural NetworksDania DallahNo ratings yet
- Story Point PDFDocument20 pagesStory Point PDFnirvana notNo ratings yet
- FS2 Ep4Document7 pagesFS2 Ep4Kent Bernabe100% (1)
- VerbsDocument1 pageVerbsapi-364107972100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 9th Grade - FoodDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 9th Grade - FoodalexandraNo ratings yet
- NLN Competencies FinalDocument5 pagesNLN Competencies Finalapi-357388170No ratings yet