Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ Discontinuation
Uploaded by
Jhet CoritanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ Discontinuation
Uploaded by
Jhet CoritanaCopyright:
Available Formats
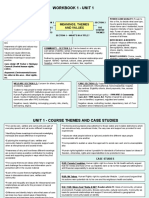
tttof treatment by means of Roles
therapeutic exercise…
1. Team Approach – working with other
professionals
According to APTA – PT is a health 2. Prevention & Health Promotion
profession whose purpose is the promotion
of optimal health and function
Patient/Client Model
Hierarcy
1. Lifetime Commitment
2. Representative Organization
Discharge/
3. Specialized Education Discontinuation
Coordination,
4. Service to clients Communication, Patient/ Client
Documenting Interaction
5. Autonomy of judgement
Sickness in WW1 – Poliomyelitis PT Assistant – health provider whose
function is to assist the PT in the provision
of PT Services
Core Values Types of Supervisions
Accountability General supervision – Not required on site
Altruism Direct Supervision – physically available
Compassion / Caring Direct Personal Supervision – Immediately
Excellence Available
Integrity APTA - American Physical Therapy
Association
Professional Duty
Distrct – Local
Social Responsibility
Chapters – State level
Sections – members with similar interests
(Special Interest Groups)
Assemblies – Applies to students
House of Delegates – highest policy making Types of Regulations
body
Federal Regulations, State Regulations ,
Board of directors – President, VP, Professional Misconduct
Treasurer, Speaker of House of delegates.
Federal
Vice speaker
Centers for Medicaid and medicare
services
Purpose of Law Revisions to medic aid
Failure to comply – no
Protect the public
reimbursements
Creates scope of practice
Rights & protection but must be State
responsible
State physical therapy board
Statues & Regulations Assist in licensing procedures
Law – Body of rules Professional Misconduct
Statutes – legislative department Inability to meet professional
standards
Regulations – regulate industry or program
The Court System
Criminal Law vs Civil Law
2 Types of Statutes
Criminal law
Federal & State
Crime need not to be related to
Federal
profession
American w/ Disabilities Act Lying under oath
Individuals w/ disabilities education Difficulty obtaining license
act
Civil law
Social Security Amendments of 1965
Not directed to license
State
Defamation
Practice Act Malpractice or Negligence
Licensure Act
Health Insurance
Certification
Registration Vary out patient to in patient
Model Practice Act Insured > Subscribers > insurer
Benefits
Premium – individuals pay for insurance
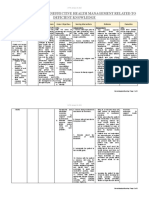
Employer Sponsored – payroll deduction Cultural Destructiveness Dehumanizing Manner
Cultural Incapacity bias
Cultural Blindness No biases, all same
2 types of healthcare Cultural Precompetence Expansion of cultural
knowledge
Medicare – Cultural Proficiency Differences are highly
regarded
Part A, Part B, Medicare advantage, Part D
Medicaid Culture of Medicine
Affected by high & low context
Retrospective Methodology assumptions
Primarily on low context
Paid after health care services are rendered
I forgot kun ano ini haha surata nala
Different spiritual / religious beliefs
Prospective Methodology Different generations
Payments are established in advance Family members
Who speak little to no English
Impairments
Professional Behaviors (IGDRAWING NALA) Health care team
Patient Care
Cognitive – knowledge, application
Interprofessional collaboration
Psychomotor – Hands on Professional
Affective – attitude, values, Orientation
communication skills Awareness of cultural diversity
Culture Shared values,norms,traditions,
Rapport – Trust, relationship history
Cultural Competence Increase understanding, cultural
Cultural Rapport difference
Cultural Diversity Difference in
Verbal Rapport race,language,nationality
Behavioral Rapport Cultural Sensitivity Awareness of one’s own culture
Cultural Appropriate
Ethnic Common group
Race Socially defined population
Level of Continuum Definition Health Insurance Portability Act
- Enhances the information - Based on a list of patient problems
protection/ confidentiality - Enhances communication among
health professionals
(CHECK NOTES FOR THE PROCESS )
Advance Health Care Directives
Entry Corrections :
1. Living Will
- Draw a single line through
- Person is not capable of making
inaccurate info but should still be
decisions because of illness
legible
- Physician must certify
- Date & initial correct, add note why
- Provide instruction for the patient
- Enter corrected statement in
2. Power of Attorney chronologic sequence
- Use black ink
- A person who has been appointed
when the patient is no longer Do’s and don’ts in documentation
capable
- Becomes valid as soon as signed by
witnesses - Never use a correction pen / tape
- Do not perform pt notes for
3. Informed Consent
colleague
- Explanation comes before the - Do not draw multiple lines across
treatment entry
- Minors & mentally ill patients
require a parent/guardian
- Give patient the right to accept or Principles of Patient Management
refuse treatment
Principles of Documentation
Patient management :
1. Considerations
Differential Diagnosis and Evidence Based
- Diagnosis Practice
- Physician’s orders
Differential Diagnosis
- Consent to treatment
- Plan of care - Compare and contrast
- Short & long term goals - Observation & interviews
- Risk / benefit treatment - Open ended questions
- Illness present w/ symptoms
Evidence Based Practice
2. POMR(Patient Oriented Medical Record)
- Application of research
- Helps determine effectiveness of
treatment
- Internation classification of
functioning and disability and
health
ICF
- Framework
- Standard language & conceptual
basis
- Integrates major models of
disabilities
Aims
- Multipurpose classification
- Provide scientific basis
- Common language
- Permit comparison
- Systemic coding scheme
Underlying Principle of ICF
Parity & etiological
universality
neutrality
Neutrality Environmental
Influence
You might also like
- Patient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationDocument5 pagesPatient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationLeann CanonoNo ratings yet
- Patient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationDocument5 pagesPatient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationJhet Ardian CoritanaNo ratings yet
- University Urdaneta City: Legal and Ethical IssuesDocument5 pagesUniversity Urdaneta City: Legal and Ethical Issuesmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- HJP Template PresentationDocument15 pagesHJP Template PresentationshyamityNo ratings yet
- Module 7 (PPT) : Ethical Issues of Elder CareDocument3 pagesModule 7 (PPT) : Ethical Issues of Elder CareRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- PCEP-PC Module 3 Slides and Key PointsDocument7 pagesPCEP-PC Module 3 Slides and Key PointsMan MedNo ratings yet
- Mental Health - Dr. Amargo - RevisedDocument9 pagesMental Health - Dr. Amargo - RevisedAngelique Mae Mortejo SalarzaNo ratings yet
- SRHR Responses in Fragile Settings AHMED TANJIMUL ISLAMDocument18 pagesSRHR Responses in Fragile Settings AHMED TANJIMUL ISLAMAHMED TANJIMUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Module - I: JurisprudenceDocument10 pagesModule - I: JurisprudenceReygil CapunoNo ratings yet
- Medical Data: It's Only Sensitive If It Hurts When You Touch ItDocument58 pagesMedical Data: It's Only Sensitive If It Hurts When You Touch Itabikar10No ratings yet
- LEC. PPT 7 Older Adult 1Document24 pagesLEC. PPT 7 Older Adult 1Lester Danan50% (2)
- Ethical Issues in GeriatricsDocument31 pagesEthical Issues in GeriatricslakshmiNo ratings yet
- Current Event Article Healthcare and Immigration 5Document2 pagesCurrent Event Article Healthcare and Immigration 5api-528422127No ratings yet
- Medical and Social Expertise Public Health (Group-2)Document20 pagesMedical and Social Expertise Public Health (Group-2)HashmithaNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Standards of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Practice and Related Laws in Mental HealthDocument12 pagesModule 3: Standards of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Practice and Related Laws in Mental HealthBen ZyNo ratings yet
- 114 Week 6 PPT Narrative GabuleDocument2 pages114 Week 6 PPT Narrative GabuleDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- PE and Health ReviewerDocument3 pagesPE and Health ReviewerCynthia Lasco100% (1)
- FUNDADocument2 pagesFUNDAAlyza HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemmas in The ICU: Kathleen J. Haley, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, HMS Associate Physician, BWHDocument40 pagesEthical Dilemmas in The ICU: Kathleen J. Haley, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, HMS Associate Physician, BWHAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 BioethicsDocument59 pagesWeek 9 BioethicsArchangel LiquitNo ratings yet
- Health Grade 10 First QuarterDocument4 pagesHealth Grade 10 First Quarterjjggfjgh100% (3)
- Advance Directives Malbar Hill Club 21-4-2018Document51 pagesAdvance Directives Malbar Hill Club 21-4-2018pradeepNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of NursingDocument11 pagesLegal Aspects of Nursingapi-3853350100% (11)
- Values Ethics and AdvocacyDocument11 pagesValues Ethics and AdvocacyTunmise EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice and The LawDocument19 pagesNursing Practice and The Lawapi-534059022100% (2)
- 2017 PolicyDocument7 pages2017 Policyshubhii1997No ratings yet
- DR - Professionalism & EthicsDocument167 pagesDR - Professionalism & EthicsOmarNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Yr1 Essentialskills 2a PDFDocument3 pagesMental Health Yr1 Essentialskills 2a PDFdaddy kinkNo ratings yet
- CHCLEG001Document24 pagesCHCLEG001Vaishali Arora0% (1)
- Gerontologic NCPDocument8 pagesGerontologic NCPLouren Grace Quinto AnceroNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review - Student.Fall2022Document52 pagesFinal Exam Review - Student.Fall2022riley liuNo ratings yet
- Midterms For Gerontological NursingDocument5 pagesMidterms For Gerontological NursingNicole SorongonNo ratings yet
- MasysDocument35 pagesMasysTraining DeskNo ratings yet
- Ethical Legal Issues Related To Gerontological Care HCDocument41 pagesEthical Legal Issues Related To Gerontological Care HCtamika sealyNo ratings yet
- Utech Pharmd 2023 November End of LifeDocument20 pagesUtech Pharmd 2023 November End of LifeFred HibbertNo ratings yet
- Blank DSM 5 DAFDocument14 pagesBlank DSM 5 DAFKieran100% (1)
- Laws Affecting Senior CitizenDocument12 pagesLaws Affecting Senior CitizenGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Nur 152 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument6 pagesNur 152 Exam 1 Study GuidemartoNo ratings yet
- Alzheimers NotesDocument3 pagesAlzheimers NotesAleandro DizonNo ratings yet
- CHN QuizzDocument8 pagesCHN QuizzMica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Funda Lec Midterm End ReviewerDocument39 pagesFunda Lec Midterm End ReviewerphoebeNo ratings yet
- Mental Health - An Individual FailureDocument5 pagesMental Health - An Individual FailureVARNIKA TYAGINo ratings yet
- Introduction To BioethicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BioethicsAndrea AputenNo ratings yet
- Advance DirectiveDocument5 pagesAdvance DirectiveVidushi SinghalNo ratings yet
- AsosiasiDocument28 pagesAsosiasiYuliarni HasanNo ratings yet
- PHAR616 - 2nd Shifting ExamsDocument8 pagesPHAR616 - 2nd Shifting Examsmarieeloise.bugayong.iiiNo ratings yet
- R.A. 11036Document69 pagesR.A. 11036Shane Nicole TapitNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Unit 1 and 2Document6 pagesBioethics Unit 1 and 2marykNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 3Document2 pagesNCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 3Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Bioethics - On NursingDocument4 pagesBioethics - On NursingDon Nikko Lemuel OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Ethico Moral and Legal Foundations of Client Education 2019 2020Document18 pagesEthico Moral and Legal Foundations of Client Education 2019 2020A Dummy's AngleNo ratings yet
- Workbook 1 - Unit 1: Meanings, Themes and ValuesDocument46 pagesWorkbook 1 - Unit 1: Meanings, Themes and Valuesasehngeh363No ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Holistic-DiagnosisDocument21 pagesVdocuments - MX Holistic-DiagnosisanitaNo ratings yet
- Ethical PrinciplesDocument7 pagesEthical PrinciplesMichael ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ncma218 FinalDocument12 pagesNcma218 FinalMakspeyn del Valle - MoonNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER GeriaDocument5 pagesREVIEWER GeriaAmir PermitivoNo ratings yet
- Health10 - q1 - Mod1 - Components of Consumer Health - FINAL08092020Document14 pagesHealth10 - q1 - Mod1 - Components of Consumer Health - FINAL08092020Melody Derapite LandichoNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 The Call of Human BeingDocument4 pagesLesson2 The Call of Human BeingJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- 22.6.1. Data and Results: (Weighing of Samples)Document3 pages22.6.1. Data and Results: (Weighing of Samples)Jhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Mobility and Disability Can Result From A Host of Diseases and ProblemsDocument1 pageImpaired Mobility and Disability Can Result From A Host of Diseases and ProblemsJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Darwins Voyage TimelineDocument29 pagesDarwins Voyage TimelineJhet Ardian CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Exam Cle PassDocument3 pagesExam Cle PassJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Rob Band Mansfield ArticleDocument30 pagesRob Band Mansfield ArticleJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet MosesDocument1 pageActivity Sheet MosesJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Call of Joseph The DreamerDocument11 pagesLesson 4 The Call of Joseph The DreamerJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument4 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismMuhammad Naveed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Patient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationDocument5 pagesPatient/ Client Interaction: Discharge/ DiscontinuationJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Wehhhhh HDocument1 pageWehhhhh HJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument3 pagesUCSPJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Test For LipidDocument25 pagesTest For LipidJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Ngee EDocument2 pagesNgee EJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Ngee EDocument2 pagesNgee EJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Ngeii IDocument1 pageNgeii IJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Vii. Documentationssssssssssssstj HyytrtyjyjssssDocument4 pagesVii. Documentationssssssssssssstj HyytrtyjyjssssJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Wehhhhh HDocument1 pageWehhhhh HJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet: ElectrotherapyyyyyyyyyyDocument2 pagesAnswer Sheet: ElectrotherapyyyyyyyyyyJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- II.4 Climate ChangeDocument1 pageII.4 Climate ChangeJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Populatsyon XDDDocument2 pagesPopulatsyon XDDJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Ii.2 Energy ConsumptionssxccccccDocument3 pagesIi.2 Energy ConsumptionssxccccccJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Ngeii IDocument1 pageNgeii IJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Activity Carbohyrdates IDocument10 pages3 Activity Carbohyrdates INur SetsuNo ratings yet
- PopulatsyonDocument2 pagesPopulatsyonJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- NgeDocument1 pageNgeJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- WehhhhhDocument1 pageWehhhhhJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Vii. Documentationssssssssssssss SSSDocument4 pagesVii. Documentationssssssssssssss SSSJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- NgeiDocument1 pageNgeiJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Week2-Mini-Pt1-Freedom - AganaDocument8 pagesWeek2-Mini-Pt1-Freedom - AganaPatrick Jacob AganaNo ratings yet
- Use of Icf To Build A Common Language Among Professionals in Disability Management and RehabilitationDocument3 pagesUse of Icf To Build A Common Language Among Professionals in Disability Management and RehabilitationIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Individualized Education ProgramDocument13 pagesIndividualized Education ProgramkpodomNo ratings yet
- Madras High Court WP 25124 of 2005Document6 pagesMadras High Court WP 25124 of 2005Disability Rights AllianceNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies Applying 21 CenturyDocument7 pagesTeaching Strategies Applying 21 CenturyebellaamayrahaisyahNo ratings yet
- On The Face of It NotesDocument3 pagesOn The Face of It NotesIshita DeepNo ratings yet
- Drug Free Workplace 10.2017 GenericDocument3 pagesDrug Free Workplace 10.2017 GenericMaimoon AliNo ratings yet
- STIC Theory FoundDocument203 pagesSTIC Theory FoundNor HidayahNo ratings yet
- Government Elementary School Profile, Sy 2020-2021: Status Div. In-ChargeDocument49 pagesGovernment Elementary School Profile, Sy 2020-2021: Status Div. In-ChargeKaren Delos Santos ToledoNo ratings yet
- Co-Development of The CMAP Book - A Tool To ParticipationDocument12 pagesCo-Development of The CMAP Book - A Tool To ParticipationCatarina GrandeNo ratings yet
- (Sped Activity) AboguinDocument8 pages(Sped Activity) AboguinVinnie GognittiNo ratings yet
- Admit Card - Candidate LoginDocument3 pagesAdmit Card - Candidate LoginKunal RohillaNo ratings yet
- Cips Student ManualDocument45 pagesCips Student Manualbahadoor22i5583No ratings yet
- Disability and Pauline TheologyDocument19 pagesDisability and Pauline TheologyStanley JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Boala Obsesiv CompulsivaDocument134 pagesBoala Obsesiv CompulsivalumyciunguNo ratings yet
- 11 Phe Unit NotesDocument53 pages11 Phe Unit NotesriojngjdjdndfdjNo ratings yet
- AdvtNo 51 2024 SPCL PrsnAsst Engl 070324Document28 pagesAdvtNo 51 2024 SPCL PrsnAsst Engl 070324Gaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument15 pagesCase Studyapi-354186879No ratings yet
- GAO Report On "Triple-Dipping" VeteransDocument38 pagesGAO Report On "Triple-Dipping" VeteransFedSmith Inc.No ratings yet
- OT Programme Handbook 2016-17Document182 pagesOT Programme Handbook 2016-17Alexander León PuelloNo ratings yet
- Confidential: Directorate General, C.R.P.F., Block No. 1, Cgo Complex, Lodhi Road, New Delhi - 110 003Document47 pagesConfidential: Directorate General, C.R.P.F., Block No. 1, Cgo Complex, Lodhi Road, New Delhi - 110 003Ranjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Adult Mental Health First Aid Manual Update 09.04.20 1Document49 pagesAdult Mental Health First Aid Manual Update 09.04.20 1munsifzmiNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-681711011No ratings yet
- WKF para Karate Kata Competition Rules 2023Document28 pagesWKF para Karate Kata Competition Rules 2023Karim HammmouNo ratings yet
- CASA State Standards 2009Document38 pagesCASA State Standards 2009Beverly TranNo ratings yet
- Counseling Resources 19-20Document2 pagesCounseling Resources 19-20api-422022741No ratings yet
- Communication Skills For Children With Severe Learning DifficultiesDocument10 pagesCommunication Skills For Children With Severe Learning DifficultiesMay Grace E. BalbinNo ratings yet
- AltamimiR Understanding DyslexiaDocument384 pagesAltamimiR Understanding DyslexiaCharitini PetridouNo ratings yet
- Social SkillsDocument261 pagesSocial Skillsbibonzi bobonziNo ratings yet
- Eating DisorderDocument57 pagesEating DisorderJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)