Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Alkyl Halide - Aryl Halide PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed HammadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Alkyl Halide - Aryl Halide PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed HammadCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem.
1 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Section 1: Alkyl halides and aryl halides
Remember: in hydrocarbons, carbon atoms are bonded to hydrogen atoms, And the carbon atom
can form strong covalent bonds with the atoms of other elements such as: S, O, N, P, F, Cl, Br, I
These elements are present as part of the functional group.
Functional group: An atom or group of atoms that enter the composition of the organic compound
molecule, and they always react in the same way.
Note: 1 - When adding a functional group to the hydrocarbon compound it always produces a new
substance that has different chemical and physical properties than the original hydrocarbon compound .
2 - By knowing the properties of the functional group, it is possible to predict the properties of the
organic compounds in which it is present even if you have not previously studied it.
Compound type general formula functional group
Alkyl halides R X
Halocarb
, (X = F - Cl - Br - I)
X
ons
Halogen X
aryl halides
, (X = F - Cl - Br - I)
alcohol
R OH Hrdroxyl OH
Ether
R O R , R O R ether O
NH2
Amine ) Amino(
R NH2 R NH2
Amine Primary amine
R N R R N H
R R
Tertiary amine Secretary amine
O
Aldehyde * C
H Or *-CHO O
O O C
Ketone Carbonyl
R C R , R C R
O O
Carboxylic acid * C C O H COOH
or Carboxyl
OH
O O
Ester * C C O
O R Ester
O H O H
Amide
* C N R Amide C N
Important note: The bonds (-), (=), and (≡) that formed
between carbon atoms are functional groups although
they are present in a compound consisting of only carbon
and hydrogen atoms. Why?
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 2 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Halogens are the simplest of the compensatory functional groups that can replace hydrogen atoms in
hydrocarbons (compensatory = they are a branch of the main carbon chain of the organic compound)
Alkyl halides: is an organic compound containing a halogen atom covalently bonded to an
aliphatic carbon atom.(It has the simplest functional group)
General formula: R - X (X = F – Cl - Br – I )
How to get it: From alkane by replacing a hydrogen atom.
Example:
H H
+ Cl 2
H C H H C Cl + HCl
H H
Alkane Alkyl Halide
methane Chloro methane
Note: The first four halogens (fluorine-chlorine-bromine-iodine) are included in the synthesis of
many organic compounds.
IUPAC Nomenclature :
1 - Halo + Alkan (the main parent alkan name) (Halo: Chloro-Floro-Promo-Iodo).
2 - If there are more than two halogens, the atoms are arranged in English alphabetical order.
3 - The series is numbered so that the lowest position number for the atom related to the halogen
atom is given in alphabetical order.
4 - Note that when halogen is repeated, we use (Di - Tri - ...... preceded by the numbers as before
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 3 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Q: Type the name of the following compounds using IUPAC system:
Br F Cl H H F H H H
H C C C C H H C C C F H C C F
H H H H H H H H H
H F F H Cl H H H Br
Br
H C C C C H H C C C C C H
H H H H
CH3 CH CH3 H H H H H
F Cl Cl Cl
F F F F CH3 CH2 C H CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH
CH3 CH CH CH CH2 F Br
Cl F I Br
Cl C CH2 C CH3 CH C C CH3
3
Cl F I Br
Q: Draw structural formulas for each of the following:
2- Iodo Propane 1, 1, 1, 2- tetra Bromo Propane 1 – fluorohexane
1- Promo - 1,1,3,3,3-penta Iodo Propane 1- Pormo-3,4- Dichlorohexane
2,3,4 - Trichloropentane 1,1-diIodopropane
2,2- dichloro -1,1-difluoro propane
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 4 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Properties of alkyl halides:
) تزداد درجة الغليان والكثافة عند االنتقال عبر الهالوجينات من الفلور ← اليود (أي بزيادة حجم ذرة الهالوجين: علل
فيزداد، وتميل هذه اإللكترونات إلى تغيير مكانها بسهولة، ألنه عند االنتقال من الفلور إلى اليود يزداد بٌعد اإللكترونات الخارجية عن النواة
فتزداد الطاقة الالزمة لفصل الجزيئات عن، ً وبالتالي تتجاذب األقطاب معا، ميل هاليدات األلكيل لتكوين مركبات ثنائية القطب مؤقتة
. وبذلك تزداد درجة غليان هاليدات األلكيل بزيادة حجم ذرة الهالوجين، بعضها
Explain : Boiling point and density increase when moving across halogens from fluorine → iodine
(i.e. by increasing the size of the halogen atom)
Because when moving from fluorine to iodine, the distance of the outer electrons from the nucleus
increases, and these electrons tend to change their position easily, so the tendency of alkyl halides
to form temporary dipole compounds increases, and thus the polars attract together, so the
energy needed to separate the molecules from each other increases, thus increasing the boiling
point of the halides Alkyl increased the size of the halogen atom.
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 5 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Explain: the boiling point and density of alkyl chloride are higher than the boiling point and density
of alkanes containing the same number of carbon atoms
Compound: CH4 CH3Cl
Boiling point: -162oC -24oC
Density: 0.423 g/mL 0.911 g/mL
In chloromethane: the presence of a chlorine atom works as a dipolar compound, so the dipoles
of molecules attract together, the bonding between particles increases, and the boiling
point and density increase.
In methane: a non-polar molecule whose molecules are bonded by the weak forces of London's
dispersion force, so the boiling point and the density decrease.
Note: Human thyroid hormones contain organic iodide (it is rare to obtain organic halide in
nature) (explain) because halogen atoms that bond to carbon atoms are more active than the
hydrogen atoms that have replaced them.
Uses of alkyl halides:
1 - A raw material in many chemical industries(as a starting
materials in the chemical industry)
2 - Solvents and Cleaning agents explain: because they dissolve
non-polar molecules easily, such as oils and fats.
3 - polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), a plastic made from gaseous
tetrafluoroethylene. A plastic is a polymer that can be heated
and molded while relatively soft
يُصنع من غاز رباعي فلورو إيثين ويمكن تسخين هذا البالستيك وتشكيله عندما يكون: PTFE بالستيك رباعي فلورو بولي إيثين- 3
. ً مرنا ً نسبيا
4 - Another plastic commonly called vinyl is polyvinyl chloride
(PVC). It can be manufactured soft or hard, as thin sheets, or
molded into objects.
ويمكن تشكيله على شكل صفائح رقيقة، يمكن صناعته في صورة لينة أو صلبة: " PVC"" بالستيك الفينيل " كلوريد البولي فينيل- 4
)مرنة أو مجسمات أشياء(نماذج لأللعاب
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 6 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Substitution reaction: is the substitution of atom or atomic group by another atom or
atomic group in the compound
Halogenation: It is the substitution of a halogen atom with a hydrogen atom.
►In the case of alkanes: A halogen atom such as Cl or Br can replace a
hydrogen atom in the halogenation process.
►With substitution reactions, alkanes can be converted into different
compounds such as:
Remember: 1- Oil is the primary source of all industrial organic compounds.
2 - Oil is considered a form of fossil fuel, which consists of almost all hydrocarbons,
especially alkanes.
3 - Alkanes may be converted to other compounds such as alkyl halides, alcohols
and amines.
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 7 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
1 - General substitution reactions for the formation of alkyl halides:
(Where X represents a fluorine, chlorine, or bromine atom)
R - CH3 + X2 → R - CH2X + HX
Clarification:
H H
R C H + X X R C X + H X
H H
Alkane Alkyl halide
Complete:
C2H6 + Cl2 → +
☺ When alkanes are halogenated, the alkyl halide becomes permeable to another substitution
reaction. Where one atom or group of atoms replaces a hydrogen atom.
Example: Complete the halogenation in four stages with chlorine, bromine, fluorine, and chlorine
CH4 + Cl2 → +
2 - General substitution reactions for alcohol formation:
Alkyl halide reacts with basic solutions, where the OH-group replaces the halogen atom
to produce alcohol.
- -
R X + OH R OH + X
alkyl halide basic solution alcohol
Ex : CH3CH2Cl + OH - → CH3CH2 OH + Cl -
chloro ethane ethanol
3 - General substitution reactions for amines formation:
Alkyl halide reacts with the NH3 ammonia, where the amine – NH2 group replaces the
halogen atom to produce the alkyl amine
R X + H NH2 R NH2 + HX
CH3(CH2)6 CH2Br + NH3 → CH3(CH2)6 CH2 NH2 + HBr
1-bromooctane Octyl amine
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 8 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Example: Halothane: (2-bromo--2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane):
It was first used in anesthesia in the 1950s for the first time.
Note: In the halogenation process, we use the halogens X = F, Cl, Br, but I (I) is not? because:
Iodine does not interact well with alkanes.
Aryl halides: An organic compound containing a halogen atom bonded with a benzene ring or
other aromatic group.
Writing the structural formula for aryl halides:
1 - Draw the structural formula of the aromatic compound
2- Replace the hydrogen atoms with the halogen atoms
I
F
I Br
Cl
Br Br
Cl
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 Br
Br
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 9 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 10 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 11 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 12 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 13 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 14 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
القسم :2الكحوالت واإليثرات واألمينات
- 1الكحوالت
مالحظة :األكسجين والنيتروجين هما اثنين من أكثر الذرات
شيوعا ً في المجموعات الوظيفية العضوية .
" مركبات عضوية ناتجة من استبدال ذرة هيدروجين من الهيدروكربون بمجموعة هيدروكسيل "
H H
-H
H C H H C OH
+ OH
H H
OH
المجموعة الوظيفية ( - OH :هيدروكسيل) :مجموعة وظيفية مكونة من أكسجين – هيدروجين ،والتي ترتبط تساهميا ً مع ذرة الكربون
الصيغة العامة :R ( R – OH :سلسلة أو حلقة الكربون المرتبطة مع المجموعة الوظيفية)
مثال إلنتاج الكحول في الطبيعة :ينتج اإليثانول وغاز CO2بواسطة الخميرة عند تخمر السكريات كالموجودة في العنب وينتج
CO2أيضا ً من تخمرعجين الخبز.
اإليثانول – 1 : C2H5OHيُدخل في المنتجات الطبية
– 2تطهير الجلد قبل إعطاء الحقن
– 3يُضاف للجازولين لزيادة فعاليته
– 4مادة أولية لتحضير مركبات عضوية أكثر تعقيداً
تسمية الكحوالت ( :تُسمى الكحوالت باالعتماد على األكانات المقابلة كما في هاليدات األلكيل )
– 1حدد السلسلة الكربونية األم األطول المحتوية على مجموعة ) ( (- OHالهيدروكسيل ) وأضف المقطع ( -ول ) لنهاية األلكان .
،ترايـ ول لوجود 3OH دايـ ول لوجود 2OH – 2عند تكرار عدد مجموعات - OHيُضاف المقطع القبلي
– 3رقـّم ذرات الكربون األقرب لمجموعة –OH
– 4أدخل أرقام المواضع لـ -OHقبل اسم الكحول ( األم ) مباشرة
– 5ضع الشرطات والفواصل وراعي ما يلزم سابقا ً
– 6عندما تتكون الكحوالت من 3ذرات كربون أو أكثر ،يجب اإلشارة إلى موقع مجموعة الهيدروكسيل برقم.
س ✿ :بصفة عامة ✿ :لماذا يتم ترقيم سلسلة ذرات الكربون عند تسمية المركبات العضوية ؟
CH3 - CH2 - OH CH3-OH
– 1بروبانول
OH CH3 CH2 CH2 OH
CH3 CH2 CH CH3
- 2بيوتانول
Chemistry grade 12 adv. Third sem. 15 Mr: Ibrahim elnagar
You might also like
- H2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 13 - Organic Chemistry Halogen DerivativesDocument27 pagesH2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 13 - Organic Chemistry Halogen DerivativesArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- How Does An Artificial Neural Network Model The BrainDocument2 pagesHow Does An Artificial Neural Network Model The BrainSyukriah Mat Yatya0% (2)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Revision NotesDocument99 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Revision NotesTECH STOVENo ratings yet
- HaloalkeneDocument20 pagesHaloalkeneRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol (Theory) Module-4Document18 pagesAlcohol (Theory) Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Che 176 AlkanolsDocument42 pagesChe 176 Alkanolsodunowo usmanNo ratings yet
- Structural IsomerismDocument9 pagesStructural IsomerismJue MayaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Alkenes and AlkynesDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 3 Alkenes and AlkynesJoseph Zaphenath-paneah ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document262 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2Israk Mustakim IslamNo ratings yet
- My Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalideDocument4 pagesMy Faculty Is Downloading Question Paper Alkyl HalidesanskritiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry s6 AllDocument213 pagesChemistry s6 AllAKAYEZU Body santiveNo ratings yet
- Janahi 12 Unit11Document62 pagesJanahi 12 Unit11anup20janNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Reactions of AlcoholsDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Reactions of AlcoholsRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument36 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EtherRajdeep GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument37 pagesChemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFMohammed RafiuddinNo ratings yet
- OC - Halogen Derivatives - E - CE PDFDocument42 pagesOC - Halogen Derivatives - E - CE PDFAbhinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Distillation (Exercise 1) - Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesDistillation (Exercise 1) - Organic ChemistryDoxa Dave RotapNo ratings yet
- Organic 2 PDFDocument864 pagesOrganic 2 PDFaisyahNo ratings yet
- CBSE 2018 12th Chemistry Sample Question PaperDocument8 pagesCBSE 2018 12th Chemistry Sample Question PapermisostudyNo ratings yet
- 2004 Nasional BelarusDocument14 pages2004 Nasional BelarusFeni Utari BasyarNo ratings yet
- Organic 6 CDocument26 pagesOrganic 6 CDr.Rajarshi PatelNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexane Conformational AnalysisDocument17 pagesCyclohexane Conformational AnalysiscclatrumNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document1 pageTest 3Windellea WongNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry of CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesStereochemistry of CarbohydratesRabia Hussain100% (1)
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Document67 pagesChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNo ratings yet
- Reactive Intermediates - LecturesDocument24 pagesReactive Intermediates - Lecturesapi-3771395100% (1)
- Alkadienes & Its PropertiesDocument24 pagesAlkadienes & Its PropertiesShivam Gupta67% (3)
- IB Chemistry BioChem WS 1Document8 pagesIB Chemistry BioChem WS 1whalerfishNo ratings yet
- EAMCET QR Chemistry SR Chem 17.organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesEAMCET QR Chemistry SR Chem 17.organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidsJagadeesh Goli100% (2)
- H.D.A. 2021Document54 pagesH.D.A. 2021Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- Cracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionDocument1 pageCracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionZhering RodulfoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Structural Formulae Section - 1Document108 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry: Structural Formulae Section - 1SUKH RAM VAISHNAVNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry - Heterocyclic CompoundsDocument37 pagesMedicinal Chemistry - Heterocyclic CompoundsnasibdinNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction Reagent Assignment PDFDocument21 pagesName Reaction Reagent Assignment PDFSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Complex CoumpoundsDocument37 pagesComplex CoumpoundsGirish Jha100% (1)
- Transition Metals and Coordination ChemistryDocument80 pagesTransition Metals and Coordination ChemistryVincent Choo100% (1)
- TH TH TH TH: 8 Theoretical Problems 2 Practical ProblemsDocument17 pagesTH TH TH TH: 8 Theoretical Problems 2 Practical Problemslos sabiosNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-OctDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers-31-Octolivia.benson9331No ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholssumitNo ratings yet
- Constitution of AlloysDocument4 pagesConstitution of AlloysKancharla KiranNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem U-3Document51 pagesOrganic Chem U-3sinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Join @iitwale On Telegram: Physical Chemistr y Inorganic Chemistr y Organic Chemistr yDocument51 pagesJoin @iitwale On Telegram: Physical Chemistr y Inorganic Chemistr y Organic Chemistr yK GhatageNo ratings yet
- Isolobal AnalogyDocument11 pagesIsolobal AnalogyGA GANo ratings yet
- Alcohols Ethers and Phenol-03 - Assignments (New)Document26 pagesAlcohols Ethers and Phenol-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Organized By: Badahdah, M. S. & Alghazzawi, W. M. 1Document17 pagesChromatography: Organized By: Badahdah, M. S. & Alghazzawi, W. M. 1sivaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy and ChromatographyPa GesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Oxidation Numbers Through Electronegativity and Partial ChargesEricNo ratings yet
- 6-2103471 Fuel and Fuel-Air CombustionDocument117 pages6-2103471 Fuel and Fuel-Air Combustiondinosaur x-drakeNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane - Haloarene NotesDocument38 pagesHaloalkane - Haloarene NotesPadmalaya palo100% (1)
- Molecular Polarity: AP ChemistryDocument13 pagesMolecular Polarity: AP ChemistryArvie Guevarra ToqueroNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-01 - TheoryDocument32 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11Document58 pagesVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11superfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free EnergyDocument4 pagesGibbs Free EnergyFernando100% (1)
- Valency TableDocument2 pagesValency TableashokNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-JeeDocument33 pagesOrganic Chemistry-JeeRamesh Babu GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- FunctionalGroups AnswersDocument2 pagesFunctionalGroups AnswerstaylorNo ratings yet
- 7 Oxidation Ladder 2019 PDFDocument1 page7 Oxidation Ladder 2019 PDFNoel SibyNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Ella EH EH ÉDocument19 pagesHydrocarbons: Ella EH EH ÉIsabella LopezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry SummaryDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument78 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidSwapnil MandalNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Ethers 19-23 PDFDocument5 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives - Ethers 19-23 PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives-Aldehydes - Ketones 31 - 35 PDFDocument5 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives-Aldehydes - Ketones 31 - 35 PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Ethers 19-23 PDFDocument5 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives - Ethers 19-23 PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Amides: Organic Compounds with Nitrogen AtomsDocument4 pagesAmides: Organic Compounds with Nitrogen AtomsAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
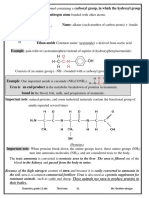
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Document6 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Ahmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDocument49 pagesUnit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDwiyasa Irin100% (2)
- Hydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Document6 pagesHydrocarbons Derivatives - Alcohols 13-18Ahmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument23 pagesDocument PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Test2 Ch17a Acid-Base Practice Problems PDFDocument12 pagesTest2 Ch17a Acid-Base Practice Problems PDFRaphael CastilloNo ratings yet
- Everything Multiple Choice Student PDFDocument11 pagesEverything Multiple Choice Student PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria ProblemsDocument27 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria ProblemsBen NarvarteNo ratings yet
- Everything Multiple Choice Student PDFDocument11 pagesEverything Multiple Choice Student PDFAhmed HammadNo ratings yet
- 4.207 S.Y.B.sc - Chemistry Sem III IVDocument36 pages4.207 S.Y.B.sc - Chemistry Sem III IVpratikNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and HalogenoalkanesDocument67 pagesAlkanes and HalogenoalkanesFunmi AbariNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Benzene and Its DerivativeDocument46 pagesReactions of Benzene and Its Derivativequyenda08hhaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument34 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesManshu GargNo ratings yet
- A-Halo Boronic Esters: Intermediates For Stereodirected SynthesisDocument17 pagesA-Halo Boronic Esters: Intermediates For Stereodirected SynthesisludoNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry: Alkene Properties and ReactionsDocument19 pagesSPM Chemistry: Alkene Properties and ReactionsVinnySha SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I Problems on Functional Groups and IsomerismDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Problems on Functional Groups and IsomerismMonica BravoNo ratings yet
- Electron Delocalization and Resonance Structures in BenzeneDocument38 pagesElectron Delocalization and Resonance Structures in BenzenemaulidyaNo ratings yet
- Alkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFPrasad Yarra100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Practice QuestionsMarlon PeterosNo ratings yet
- Halogenated Organic Compounds Classification and PropertiesDocument116 pagesHalogenated Organic Compounds Classification and PropertiesSam.CareleoneNo ratings yet
- DGT Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument50 pagesDGT Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSYAMALA GIRINo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 1-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument16 pagesHydrocarbon 1-Jeemain - Guru PDFPIYUSH MADANNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Eugenyl Cinnamate from Clove Oil via Bromination MethodsDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Eugenyl Cinnamate from Clove Oil via Bromination MethodsAnonymous g7yHQeB36No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-The Study of Chemical ReactionsDocument20 pagesChapter 4-The Study of Chemical Reactions張湧浩No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Waste MinimizationDocument19 pagesChemistry of Waste MinimizationAlfred BanghkokNo ratings yet
- M.sc. (Chemistry) Part I (Semester i&II) PapersDocument21 pagesM.sc. (Chemistry) Part I (Semester i&II) Papersਗਗਨ ਦੀਪ ਸਿੰਘNo ratings yet
- Unacademy Organic Chemistry QuestionsDocument16 pagesUnacademy Organic Chemistry QuestionsSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons One Shot BouncebackDocument172 pagesHydrocarbons One Shot BouncebackHarishNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1 - Introduction and FunctionalizationDocument57 pagesPertemuan 1 - Introduction and FunctionalizationGhina IzdiharNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@ejoc 201900449Document9 pages10 1002@ejoc 201900449Md. Sohanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2327 Chemistry Assignment Paper PDFDocument11 pagesALPS 2327 Chemistry Assignment Paper PDFAyushNo ratings yet
- Student - S Guide - Chapter 4 - Q & ADocument70 pagesStudent - S Guide - Chapter 4 - Q & AmoastNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Technology PDFDocument579 pagesChemical Reaction Technology PDFprashant_cool_4_u100% (2)
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument7 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesMuhammad Hasnain AliNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument4 pagesPreviewrihana yadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Alkanes PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Alkanes PDFSITI NUR ALISSA BINTI AHMAD RASMANNo ratings yet
- A Greener Bromination of StilbeneDocument13 pagesA Greener Bromination of StilbeneLuis Alvarez100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Mcqs Part 1Document51 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mcqs Part 1omama choudhryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Tests for Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemistry Tests for Organic CompoundsVarun Sharma0% (1)