Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Minerals: Mineral Major Dietary Deficiency Other Info Functions Source Symptoms
Uploaded by
teenwolf4006Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Major Minerals: Mineral Major Dietary Deficiency Other Info Functions Source Symptoms
Uploaded by
teenwolf4006Copyright:
Available Formats
Major Minerals
Mineral Major Dietary Deficiency Other info
Functions Source Symptoms
Calcium 99% of calcium: •milk and To decrease bone loss:
•Structure of bones, teeth milk products •silent disease till • (walking and
abundant 1% dissolved in blood for: •soy milk elderly _________________
mineral in •Muscle contraction •____________ • ______________ • Adequate ____________
the body •Nerve transmission •____________ • Adequate ____________
•Blood ___________ _____________ • _____________________
•____________ regulation •fish with bones • after menopause
(sardines) • Bone mass peaks ~20 yrs
______________________
Phosphorus •______________________ • Deficiency is rare •High phosphorous
2nd most •Major ________________ •animal protein (e.g. )
abundant •Part of _________________ •legumes decreases Ca absorption
mineral •Role in metabolism •dairy products
in the body • •fish
Magnesium •Component of bones •dark green Deficiency is
•Important to ____________ foods
•_______________________ •legumes • Weakness
• muscle •whole grains • Muscle pain
contraction,blood clotting •nuts • Poor heart function
•Prevents_______________ •_____________
•Protects against
hypertension
Sodium •________________(+) •_________ foods • muscle cramps •Salt pill ______________
___________ of cell (=_____of intake) for endurance athletes
•Fluid/electrolyte balance •table salt (use _________________)
•Nerve transmission •condiments
•Muscle contraction •sauces •Diets rarely lack sodium
•If “__________________”, •soups
Na+ intake increases the
risk of _______________
Potassium •______________________ •fresh fruits,veg Dietary deficiency Toxicity: _______________
______________________ •meat, milk is ________ ___________________
•Fluid/electrolyte balance •whole grains (e.g. heart patients)
•Nerve transmission •Muscle weakness ______________________
•Muscle contraction Pot ____and Sodium ___
Chloride •______________________ •table salt
the cell •processed Rare
•Fluid/electrolyte balance foods
•_______ (hydrocholoric acid) •some veg
_____________________
Sulfur •Sulfur is not used as a •all protein
nutrient by itself, but is containing Deficiency is
____________________ foods unknown
•“Bridges” in ________,
_______________________
•Acid/Base balance
When Blood Calcium is low: *Intestines absorb more Ca, *Bones release Ca, *Kidneys excrete less Ca (* need Vit D)
Blood calcium is maintained at the expense of bones
Trace Minerals
• Trace mineral content of food _________________________________________
• Deficiencies are typically failure to thrive and grow; TM used in all body systems
• TM ___________ at intakes _________________________________________
•________________________________…FDA cannot limit amounts in supplements
• ________________ among them ______________…if take too much can lead to deficiencies of others
Iodine
• Functions: component of thyroid hormone
• Deficiency: Goiter (=enlargement of Thyroid gland), Cretinism (=def during pregnancy --> retardation)
• Sources: iodized salt, seafood, ______________(=world’s major source)
Iron
• Functions: part of ___________ and __________…carry and release ___________
• Forms of Iron: Nonheme and Heme
• __________ is found in _______________ and is absorbed ___________
• ________ is found in ________(meat, fish etc) and is __________________than nonheme
• Deficiency: ______________________________________________________
• ___________: _________________ of iron stores with low hemoglobin concentration
• Absorption increased by __________________________ and decreased by ______________________
• Toxicity: “hemochromatosis” = ___________________________________
• Iron Poisoning: children accidentally taking iron (eg.mother’s) pills…
_________________________________________________ (as few as 5 pills)
• Sources: meat, fish, enriched grains/cereals, green leafy veggies
Zinc
• Functions: important in: many enzymes, insulin,______________, immune system, vitamin A
___________________________________________________________
• Deficiency: growth retardation, arrested sexual maturation, impaired: immune function,
brain function, thyroid, taste, wound healing, vitamin A
• Sources: shellfish, meats, poultry, liver, whole grains
Selenium
• Functions: works as an ____________, makes ________________ active
• Deficiency: may increase risk for heart disease
• Sources: meats and other animal products, whole grains
Fluoride
• Functions: forms crystal structure of ________
• Deficiency: increased risk of dental caries: ____________________________________
• Toxicity: in communities where water Fl is too high see _____________________
• Sources: best source is ___________________ (~75% of US has access to Fl drinking water)
Chromium
• Functions: associated with insulin to ____________________________ into cells
• chromium supplements _________help lose fat and build muscle; but does help with diabetes
• Sources: meats, egg yolks, whole grains, veg oils, nuts
Copper
• Functions: __________________________, collagen synthesis, works with many antioxidant enzymes
• Deficiency: rare
• Sources: legumes, whole grains, nuts, organ meats, seeds, dried fruits
Water Balance:
_____________(from Adrenal Glands) and Antidiruetic Hormone (ADH) from _____ act on kidneys to retain water
Electrolytes = Salts that dissolve in water and dissociate (separate)
Electrolytes: Attract ___________; Examples are Sodium, Potassium, Chloride
Electrolytes create ________________; pressure caused by water following electrolytes within or between cells
You might also like
- Biology: Alex ColladoDocument39 pagesBiology: Alex Colladoalex colladoNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument5 pagesDigestionJoseph MitchellNo ratings yet
- Copy of Life Cycle Nutrition NotesDocument6 pagesCopy of Life Cycle Nutrition NotesSirly Guevara-Mejia Student - SandersonHSNo ratings yet
- IronRichFoods TRHDocument10 pagesIronRichFoods TRHxaenirNo ratings yet
- Biology (Nutrition)Document44 pagesBiology (Nutrition)alex colladoNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument4 pagesWorksheetShannara ElliseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Diet and Growth StudentDocument12 pagesChapter 7 Diet and Growth StudentUsha PerumalNo ratings yet
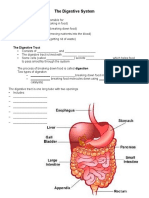
- The Digestive System Note TemplateDocument11 pagesThe Digestive System Note Templateapi-534401949No ratings yet
- Pfeiffer 5 Ppts Chapter06 - Nutritional Considerations (Student Copy)Document28 pagesPfeiffer 5 Ppts Chapter06 - Nutritional Considerations (Student Copy)api-287615830No ratings yet
- Atp Hormones VitaminsDocument8 pagesAtp Hormones VitaminssugleebruNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Digestive SystemLaci PryorNo ratings yet
- PROJECT-Biomolecules: Name: - Period: - Reading GuideDocument8 pagesPROJECT-Biomolecules: Name: - Period: - Reading Guidejennifer nogueraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition NotesDocument5 pagesNutrition Notesdrng48No ratings yet
- Initial Assessment FormDocument2 pagesInitial Assessment FormMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Healthy EatingDocument15 pagesHealthy EatingDurgasiri SithanNo ratings yet
- Cattle Rising ActivityDocument5 pagesCattle Rising ActivityLuz Adriana Flórez MontesNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Student HandoutDocument2 pagesCarbohydrate Student HandoutAlyssa Gian CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System KNP Note Taking SheetDocument5 pagesDigestive System KNP Note Taking Sheetmelindamd8100% (1)
- Nutrition QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesNutrition QuestionnaireHafiz RathodNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients: Essential Minerals and VitaminsDocument21 pagesMicronutrients: Essential Minerals and VitaminsRandy MaynagcotNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules.Document94 pagesBiological Molecules.yugkamatNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care Process: Maria Sheila A. Clanor RN, MANDocument75 pagesNutrition Care Process: Maria Sheila A. Clanor RN, MANyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Vitamins Minerals and WaterDocument29 pagesLesson 8 Vitamins Minerals and WaterArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION TEST 2024Document6 pagesNUTRITION TEST 2024lecie4lecieNo ratings yet
- English Writing Page 1Document1 pageEnglish Writing Page 1ZhenZhen LeeNo ratings yet
- Ace HHQDocument4 pagesAce HHQbojanNo ratings yet
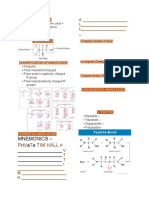
- Mnemonics - Ri A E: P V T Tim HallDocument6 pagesMnemonics - Ri A E: P V T Tim HallEshiebel OrganistaNo ratings yet
- PortfolioDiet TRHDocument12 pagesPortfolioDiet TRHНадя КрыжановскаяNo ratings yet
- Nursing Aast Chap # 1Document17 pagesNursing Aast Chap # 1Shaheen KhowajaNo ratings yet
- Iron Lab Part 2Document3 pagesIron Lab Part 2YoNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency in Children (8 Years or Younger) : Key Points To RememberDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency in Children (8 Years or Younger) : Key Points To Rememberinggrit06No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 NotesshamptonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Human NutritionDocument45 pagesChapter 7 Human Nutritionjzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Electrolytes NclexDocument2 pagesFluids - Electrolytes NclexDilNo ratings yet
- Cut Your Sugar IntakeDocument6 pagesCut Your Sugar IntakeNathan MoyerNo ratings yet
- Di CiwpresentationDocument18 pagesDi Ciwpresentationapi-460873300No ratings yet
- Lifestyle Patient FormDocument3 pagesLifestyle Patient FormJohn CabilanNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Webquest in The Worldbook StudentDocument8 pagesNutrient Webquest in The Worldbook Studentabc378hotmailcomNo ratings yet
- Paul Michael G. Baguhin - PonrDocument9 pagesPaul Michael G. Baguhin - PonrPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHINNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Water and Body FluidsDocument4 pagesMinerals: Water and Body FluidsbrooklynNo ratings yet
- Unit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .Document14 pagesUnit 8A Food and Digestion: Name: .rickyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Form: Shiza Gull Gcuf Bs HNDDocument7 pagesAssessment Form: Shiza Gull Gcuf Bs HNDAnas siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument16 pagesAnimal NutritionShop AliceNo ratings yet
- Intro To Animals Student NotesDocument2 pagesIntro To Animals Student Noteschaine1No ratings yet
- Worksheet FoodDocument2 pagesWorksheet FoodSofiaMartinsNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential Nutrients PDFDocument15 pages6 Essential Nutrients PDFJuan Rodriguez Jr100% (1)
- The Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterDocument21 pagesThe Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterCharity Faith EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes P2Document35 pagesElectrolytes P2Jainee Chen JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Nutrient QuizDocument4 pagesNutrient Quizapi-297371665No ratings yet
- Initial Nutrition Assessment FormDocument3 pagesInitial Nutrition Assessment FormAmina HaiderNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 1)Document29 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 1)qq23595% (37)
- Lesson 3 - Beef Cuts - Student NotesDocument23 pagesLesson 3 - Beef Cuts - Student NotesHeijz RaguinganNo ratings yet
- Grains GuideDocument5 pagesGrains GuideKristi HauseNo ratings yet
- Measuring Diet 2006Document49 pagesMeasuring Diet 2006anisahNo ratings yet
- Potassium-sparing diuretics: functions, indications and nursing responsibilitiesDocument9 pagesPotassium-sparing diuretics: functions, indications and nursing responsibilitieschelseyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Student Note Taking, 15th EditionDocument6 pagesChapter 13 Student Note Taking, 15th Editionjoanne libedNo ratings yet
- 17.0 - Food and NutritionDocument16 pages17.0 - Food and NutritionBuddhini JNo ratings yet
- Essential Minerals and Their FunctionsDocument22 pagesEssential Minerals and Their Functionsm.umair mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Bone Broth Magic: Easy and Healthy Recipes for Beginners to Lose Weight, Reduce Inflammation, Fight Infections and Much More!: Broths & SoupsFrom EverandBone Broth Magic: Easy and Healthy Recipes for Beginners to Lose Weight, Reduce Inflammation, Fight Infections and Much More!: Broths & SoupsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- M1 Lecture1 Meet+the+nutrientsDocument42 pagesM1 Lecture1 Meet+the+nutrientsteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Madeleine Baker ReferencesDocument2 pagesMadeleine Baker Referencesteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Clicker-Questions-Chapter 8-April-28thDocument5 pagesClicker-Questions-Chapter 8-April-28thteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- BIOL 1104 Organismal Biology Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesBIOL 1104 Organismal Biology Course Syllabusteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Densities V Sugar PercentagesDocument2 pagesDensities V Sugar Percentagesteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- What Is Serveuga?: TH NDDocument2 pagesWhat Is Serveuga?: TH NDteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- In The Wee Small Hour of The Morning Lead Sheet PDFDocument1 pageIn The Wee Small Hour of The Morning Lead Sheet PDFteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- M1 Lecture1 Meet+the+nutrientsDocument42 pagesM1 Lecture1 Meet+the+nutrientsteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- PSYC 1101 Spring 2019 SyllabusDocument5 pagesPSYC 1101 Spring 2019 Syllabusteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Reflection 2Document2 pagesReflection 2teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Mock Interview - Public SpeakingDocument1 pageMock Interview - Public Speakingteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Vaccine Brochure Assignment and RubricDocument2 pagesVaccine Brochure Assignment and Rubricteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Table 1: Fall 2016 Spring 2017 Fall 2017 Spring 2018 Fall 2018 Spring 2019 Fall 2019Document4 pagesTable 1: Fall 2016 Spring 2017 Fall 2017 Spring 2018 Fall 2018 Spring 2019 Fall 2019teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- 1211 Exam 2 Review Questions-wt-SolutionsDocument37 pages1211 Exam 2 Review Questions-wt-Solutionsteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- FYOS Final ReflectionDocument2 pagesFYOS Final Reflectionteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Mock Interview - Public SpeakingDocument1 pageMock Interview - Public Speakingteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Reflection 1Document2 pagesReflection 1teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Scientific SourceDocument2 pagesScientific Sourceteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech ReviewsDocument2 pagesPersuasive Speech Reviewsteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Brochure 2 PDFDocument4 pagesBrochure 2 PDFteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure PDFteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Acknowledgements Rating: 1 Needs Work 3 Adequate 5 ExcellentDocument1 pageAcknowledgements Rating: 1 Needs Work 3 Adequate 5 Excellentteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Immunity Individual Dropbox Assignment-Functions of The Immune SystemDocument2 pagesImmunity Individual Dropbox Assignment-Functions of The Immune Systemteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Brochure 3 PDFDocument5 pagesBrochure 3 PDFteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- COMM 1110 - Public Speaking Syllabus Fall 2019 (TTH)Document8 pagesCOMM 1110 - Public Speaking Syllabus Fall 2019 (TTH)teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Maids Everyone 52-54Document2 pagesMaids Everyone 52-54teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- SNP StudyDocument3 pagesSNP Studyteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Artikel Bahasa Inggris Dengan Topik BerbedaDocument2 pagesArtikel Bahasa Inggris Dengan Topik Berbedaputra haqiqiNo ratings yet
- Addicted To Phones - Reading AssignmentDocument4 pagesAddicted To Phones - Reading AssignmentLilith PersephoneNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Subjectivity and IntersubjectivityDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Human Subjectivity and IntersubjectivityKimchiiNo ratings yet
- January 2022 BehavioursDocument8 pagesJanuary 2022 Behavioursdhopat kalpeshNo ratings yet
- Instability of The Distal Radioulnar JointDocument12 pagesInstability of The Distal Radioulnar JointOryza SatriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.3: Erection III: Steel Construction: Fabrication and ErectionDocument4 pagesLecture 3.2.3: Erection III: Steel Construction: Fabrication and ErectionMihajloDjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- SV The Coronation of King Charles IIIDocument9 pagesSV The Coronation of King Charles IIIMaria GromovaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of T-Piece Resuscitator Versus Self-Inflating Bag During Birth Resuscitation in Very Low Birth Weight InfantsDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of T-Piece Resuscitator Versus Self-Inflating Bag During Birth Resuscitation in Very Low Birth Weight InfantsRaja SekarNo ratings yet
- Charity Marathon Risk AssessmentDocument9 pagesCharity Marathon Risk Assessmentamarnadh100% (1)
- College of Liberal Arts University of LuzonDocument9 pagesCollege of Liberal Arts University of LuzonChristianne Joyse MerreraNo ratings yet
- Role Play Script BHS INGGRISDocument6 pagesRole Play Script BHS INGGRISardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Sports Day Narrative Report 2022-2023Document6 pagesSports Day Narrative Report 2022-2023Bloom Sarinas100% (1)
- Effective Leadership Theory Cases and Applications 1st Edition Humphrey Test BankDocument9 pagesEffective Leadership Theory Cases and Applications 1st Edition Humphrey Test Bankhillyobsidian8hi42g100% (36)
- How To Negotiate With Nursing Authority Figures (Rough)Document2 pagesHow To Negotiate With Nursing Authority Figures (Rough)Meet DandiwalNo ratings yet
- 1023 3581 1 PBDocument4 pages1023 3581 1 PBfitriNo ratings yet
- Implant Abutment Emergence Angle and Profile in Relation To Peri Implantitis A Systematic ReviewDocument12 pagesImplant Abutment Emergence Angle and Profile in Relation To Peri Implantitis A Systematic ReviewValentinaNo ratings yet
- The Hall Technique 10 Years On: Questions and Answers: GeneralDocument6 pagesThe Hall Technique 10 Years On: Questions and Answers: GeneralamilescoNo ratings yet
- Employee Perceptions of HR Practices & Organizational CultureDocument45 pagesEmployee Perceptions of HR Practices & Organizational CultureJatin Gupta100% (1)
- Privacy NurseDocument62 pagesPrivacy NurseGerryNo ratings yet
- Six Major Schools of Thought in PsychologyDocument2 pagesSix Major Schools of Thought in PsychologyAnonymous 4qEPpyx100% (1)
- 18.20.04 - BSSL Seafarers Health Self Declaration With COVID 19 Test And... (1) - 3Document3 pages18.20.04 - BSSL Seafarers Health Self Declaration With COVID 19 Test And... (1) - 3Dean IL RE JamesNo ratings yet
- Modals of Suggestion HomeworkDocument2 pagesModals of Suggestion HomeworkmateoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Penelitian KBDocument6 pagesJurnal Penelitian KBMaya Ulfah apriliyaNo ratings yet
- Shift Manager ResumeDocument2 pagesShift Manager ResumeAbdul NaeemNo ratings yet
- WKF Para-Karate Kata Competition RulesDocument14 pagesWKF Para-Karate Kata Competition RulesMohamad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Annual Record of Homœopathic Literature.1875Document395 pagesAnnual Record of Homœopathic Literature.1875GustavoMarceloDareNo ratings yet
- 20 Đề tham khảo tuyển sinh vào lớp 10 2022Document87 pages20 Đề tham khảo tuyển sinh vào lớp 10 2022nguyethuhang.hnNo ratings yet
- Evidence Plan: Prepare/Stake Out Building LinesDocument2 pagesEvidence Plan: Prepare/Stake Out Building LinesJulius Pecasio100% (1)
- HOPE 1 Module 8Document2 pagesHOPE 1 Module 8Kevin Viernes Garais100% (2)
- Pa RewriteDocument6 pagesPa Rewriteapi-611938804No ratings yet