Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dept. of Mathematics, BMSCE Unit 5: Calculus of Variations: I Fxyydx
Uploaded by
Nikhil PrasannaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dept. of Mathematics, BMSCE Unit 5: Calculus of Variations: I Fxyydx
Uploaded by
Nikhil PrasannaCopyright:
Available Formats
Dept.
of Mathematics, BMSCE Unit 5: Calculus of Variations
CALCULUS OF VARIATIONS:
x2
EULER’S EQUATION: A necessary condition for I f ( x, y, y ')dx to be an extremum is that
x1
f d f
0
y dx y
Other forms of Euler’s equation:
d f f
i. If f is a function of x, y, y’ then Euler’s equation will be of the form f y 0
dx y x
ii. If f is a function of x, y, y’ then Euler’s equation will be of the form
f 2 f 2 f 2 f
y y 0
y x y y y y
2
1. Find the extremal of the following functionals:
x2
( y ' x
2
a) y '2 ) dx . (Grewal)
x1
x2
(y y '2 2 ye x ) dx .
2
b) (Grewal)
x1
b
(x y '2 2 y 2 2 xy ) dx . (Grewal)
2
c)
a
x2
(y' y 2 2 y sec x ) dx .
2
d)
x1
x1
e) ( x y) ydx . (Grewal)
x0
x1
(1 x
2
f) y ') y ' dx . (Grewal)
x0
g)
2 0 .
2
h) (y
2
y '2 2 y sin x) dx, y (0) y (Grewal)
0
2
i) (y' y
2 2
4 y cos x) dx, y (0) y 0 . (Grewal)
0
1 y2
x1
j) y '3 dx (Grewal)
x0
2
x3
k) dx ; y 1 0 & y 2 3. (Grewal)
1
y'2
2
1 y'2
l) dx ; y 1 0 & y 2 1. (Grewal)
1
x
x1
y'2
m) x3
dx (Grewal)
x0
Applied Mathematics Page 1
Dept. of Mathematics, BMSCE Unit 5: Calculus of Variations
2
x3
n) dx ; y 1 0 & y 2 3. (Grewal)
1
y'2
o)
y'
2
p) On which curve the functional 2
y 2 2 xy dx with y 0 0 & y / 2 0 be
0
extremized?
y'
1
q) Find the curves on which the functional 2
12 xy dx with y 0 0 & y 1 1 .
0
2
1
2. Show that the curve joining the points 1, 0 and 2,1 for which I 1 y 2 dx is an extremum
1
x
is a circle.
y
2
3. Solve the variational problem 2
y ' 2 dx under the conditions y 0 0 & y / 2 0 .
0
4. Find the path on which a particle in the absence of friction will slide from one point to another in
the shortest time under the action of gravity. (Brachistochrone problem )
5. A heavy cable hangs freely under gravity between fixed points. Show that the shape of the cable
is catenary. (Hanging chain problem)
1
( y ' 12 xy )dx with y(0) 0 and y (1) 1 can be
2
6. Find the curve on which the functional
0
extremized?
1
( x y y ' )dx 0 under the conditions y(0) 1 and y(1) 2 .
2
7. Solve the variational problem
0
1
Show that the general solution of the Euler’s equation for the integral y 3x( y ' 1) yy ' dx
2 2 3
8.
0
under the conditions y(0) 0 and y(1) 2 is x 2 y 2 5 x 0
b
1
9. Show that the general solution of the Euler’s equation for the integral 1 ( y ') 2 dx is
a
y
( x h) 2 y 2 k 2 .
Applied Mathematics Page 2
You might also like
- MGEC06 Topics in Macroeconomic Theory (Intermediate Macroeconomics II) Summer 2020Document6 pagesMGEC06 Topics in Macroeconomic Theory (Intermediate Macroeconomics II) Summer 2020Mick MendozaNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - Class Handout PDFDocument39 pagesTechnical Drawing - Class Handout PDFRicardo Rincon VegaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Worksheet On Multiple IntegralDocument3 pagesCH 2 Worksheet On Multiple IntegralSuleiman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vector IntegrationDocument38 pagesVector IntegrationPreetham N KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Document9 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.1 Double Integral)Hafzal GaniNo ratings yet
- U2-Two Marks Q & ADocument13 pagesU2-Two Marks Q & A217 LiansangkimaNo ratings yet
- XII Differential Equations AssignmentDocument2 pagesXII Differential Equations AssignmentCRPF SchoolNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Unit - I Multiple IntegralsDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank: Unit - I Multiple IntegralsRangan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Diff Eq SSVV 2324Document2 pagesDiff Eq SSVV 2324tisyadhruvNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation of Order One: Dy P (X) y Q (X) DXDocument2 pagesLinear Equation of Order One: Dy P (X) y Q (X) DXConchito Galan Jr IINo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 3 (Multiple Integrals)Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet - 3 (Multiple Integrals)Dipankar NathNo ratings yet
- M9 PDFDocument8 pagesM9 PDFabasNo ratings yet
- University of Technology, Jamaica: Tutorial Sheet #3: Double IntegralsDocument3 pagesUniversity of Technology, Jamaica: Tutorial Sheet #3: Double IntegralsDrake BroownNo ratings yet
- Review Integral GandaDocument22 pagesReview Integral GandaTEGUH PRASETYONo ratings yet
- Cfe Assignment Module5Document3 pagesCfe Assignment Module5Nandan AnnamrajuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4a (Prerequisite) Calculus of Variation: DX Dy X y DX X X y X y F JDocument13 pagesChapter 4a (Prerequisite) Calculus of Variation: DX Dy X y DX X X y X y F JAwuraris AbireNo ratings yet
- Multiple Integrals of Multivariable FunctionsDocument26 pagesMultiple Integrals of Multivariable FunctionsPrateek SInghNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument11 pagesDifferential EquationMapple VergaraNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Complete Manual PDFDocument71 pagesDifferential Equations Complete Manual PDFJames Carl BelgaNo ratings yet
- Double IntegralDocument1 pageDouble Integralyw89407No ratings yet
- Mathematical AnalysisDocument143 pagesMathematical AnalysisAna AmootNo ratings yet
- CH 09 (9.10-9.17)Document158 pagesCH 09 (9.10-9.17)Lam WongNo ratings yet
- RT I TJ TK RT T T RT TT RT: Part (A) : SolutionsDocument4 pagesRT I TJ TK RT T T RT TT RT: Part (A) : SolutionsAnees Ur Rehman50% (2)
- Practice 4.2 (Solution) : 1. Change To Standard Form, We Have - A Second Solution Is Given byDocument1 pagePractice 4.2 (Solution) : 1. Change To Standard Form, We Have - A Second Solution Is Given byckithoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 3 - Multiple IntegralsDocument56 pagesChapter 2 - 3 - Multiple IntegralsSafi FouadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 1.2 Limit and Continuity) PDFDocument5 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 1.2 Limit and Continuity) PDFSyamim Hamizan100% (1)
- Applied Maths II Chap 4Document24 pagesApplied Maths II Chap 4qashtikiyya65No ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional de CajamarcaDocument6 pagesUniversidad Nacional de Cajamarcavictor hugoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document10 pagesTutorial 2Faris HishamNo ratings yet
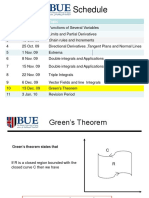
- Schedule: Week Date TopicDocument9 pagesSchedule: Week Date TopicmostafaNo ratings yet
- Home Take Exam Os Calculus of Several VariablesDocument2 pagesHome Take Exam Os Calculus of Several Variableszerihun MekoyaNo ratings yet
- MA2001 - Differential Calculus of Multivariable Functions 1314ADocument48 pagesMA2001 - Differential Calculus of Multivariable Functions 1314AMatthew LauNo ratings yet
- Differential Eqn - PDF ProblemDocument9 pagesDifferential Eqn - PDF ProblemAbhijit NathNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of A Wing Fundamentals of The Lifting-Line TheoryDocument25 pagesAerodynamics of A Wing Fundamentals of The Lifting-Line TheoryCarolina Guthemberg JacomeNo ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodsDocument10 pagesFinite Element MethodsChiranjit SauNo ratings yet
- Physics 430: Lecture 15 Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryDocument16 pagesPhysics 430: Lecture 15 Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- The Calculus AB BibleDocument14 pagesThe Calculus AB BiblecaddlemanNo ratings yet
- CA2123-Lec-6 R-1Document29 pagesCA2123-Lec-6 R-1tak752951No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Roop KishorNo ratings yet
- 1) Method of Undetermined Coefficients 2) Variation of Parameters 3) Inverse OperatorDocument9 pages1) Method of Undetermined Coefficients 2) Variation of Parameters 3) Inverse Operatorbndgdd cncncjNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2323 Maths Assignment PaperDocument10 pagesALPS 2323 Maths Assignment PaperAryan GoelNo ratings yet
- 1 2x x−y π xDocument9 pages1 2x x−y π xjinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 SSCE1993Document15 pagesTutorial 2 SSCE1993محمد ابو جرادNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument2 pagesEcuaciones DiferencialesFabian GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus of Functions of Several VariablesDocument28 pagesDifferential Calculus of Functions of Several VariablesWESTON MALAMANo ratings yet
- Calculus 10th Edition H. Anton Chapter 13Document12 pagesCalculus 10th Edition H. Anton Chapter 13Saniat Hossain100% (1)
- MYE Timed Trial 1 - SolutionsDocument15 pagesMYE Timed Trial 1 - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- NSS M2V2 09 FS EngDocument41 pagesNSS M2V2 09 FS EngWong TonyNo ratings yet
- Schedule: Week Date TopicDocument7 pagesSchedule: Week Date TopicmostafaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - PYQ Practice SheetDocument11 pagesDifferential Equations - PYQ Practice Sheetabhaysingh785124No ratings yet
- Integrating FactorsDocument25 pagesIntegrating FactorsWASEEM_AKHTERNo ratings yet
- Mss 212 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMss 212 Tutorial 1Fahad MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Otherwise y X y X C y X F C (B) FindDocument2 pagesOtherwise y X y X C y X F C (B) FindAshutosh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Previous Years QuestionsDocument14 pagesDifferential Equations Previous Years QuestionsKunish GargNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Dragged) 3Document1 pageLecture Notes (Dragged) 3yawas50511No ratings yet
- CH 3 Math of ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesCH 3 Math of Thermodynamicsmailsk123No ratings yet
- التحليلات الهندسية المحاضرة رقم 5 PDFDocument6 pagesالتحليلات الهندسية المحاضرة رقم 5 PDFابومحمد المرزوقNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems-2Document3 pagesPractice Problems-2Bantu AadhfNo ratings yet
- Beta Function:: M N MN X X DX MN NMDocument43 pagesBeta Function:: M N MN X X DX MN NMSanthosh SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Mate IV PDFDocument4 pagesTaller 1 Mate IV PDFhamiltonNo ratings yet
- MTH404 Assignment 1 Abdul Hadi E ServicesDocument2 pagesMTH404 Assignment 1 Abdul Hadi E ServicesAhmeddedNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- ErgonomicsDocument18 pagesErgonomicsbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Osama Mehmood Ali1 Erp Modules Alexis LeonDocument44 pagesChapter 5 Osama Mehmood Ali1 Erp Modules Alexis LeonNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Mba II Sem IV 404 Oscm - Industry4.0 Pattern-2019 MCQDocument13 pagesMba II Sem IV 404 Oscm - Industry4.0 Pattern-2019 MCQNikhil Prasanna100% (1)
- Introduction To Workplace Ergonomics: Prosafety Culinary Arts Curriculum Unit 7Document16 pagesIntroduction To Workplace Ergonomics: Prosafety Culinary Arts Curriculum Unit 7Nikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Accentra Pharmaceuticals: Thrashing Through ERP Systems: Teaching CaseDocument9 pagesAccentra Pharmaceuticals: Thrashing Through ERP Systems: Teaching CaseNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Consumer Behaviour: Ordinal Approach: StructureDocument33 pagesUnit 5 Consumer Behaviour: Ordinal Approach: StructureNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Dnyansagar Institute of Management and Research: Artificial Intelligence Is AboutDocument24 pagesDnyansagar Institute of Management and Research: Artificial Intelligence Is AboutAbhishek A. NadgireNo ratings yet
- Medical Shop MGTDocument24 pagesMedical Shop MGTSonia SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Medical Erp Buyer S GuideDocument16 pagesMedical Erp Buyer S GuideNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning System in Health CareDocument15 pagesImpact of Enterprise Resource Planning System in Health CareNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- ERP Integration in A Healthcare Environment: A Case Study: Journal of Enterprise Information Management January 2006Document17 pagesERP Integration in A Healthcare Environment: A Case Study: Journal of Enterprise Information Management January 2006Nikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Consumer Behaviour: Cardinal Approach: 4.0 ObjectivesDocument19 pagesUnit 4 Consumer Behaviour: Cardinal Approach: 4.0 ObjectivesMaadhavNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning Systems: Digitization of Healthcare Service QualityDocument12 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning Systems: Digitization of Healthcare Service QualityNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Boonstra Govers FullDocument8 pagesBoonstra Govers FullNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Indg90 PDFDocument10 pagesIndg90 PDFajaymechengineerNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 MDID PDFDocument59 pagesChapter-4 MDID PDFgraymondrNo ratings yet
- ERP in HealthcareDocument10 pagesERP in HealthcaredsshhkNo ratings yet
- Unit Working Environment and Human Productivity: StructureDocument25 pagesUnit Working Environment and Human Productivity: StructureNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Mba Ii/ Sem Iii 313 BA: Industrial Internet of The Things Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesMba Ii/ Sem Iii 313 BA: Industrial Internet of The Things Multiple Choice QuestionsNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Kanban TutorialDocument29 pagesKanban TutorialI Kailash Rao100% (2)
- Unit 15 Man-Machine Systems: StructureDocument21 pagesUnit 15 Man-Machine Systems: StructureNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 2Document60 pagesStrength of Materials 2shekhar_raghav15640% (1)
- Fine Blanking and Forming in One Pass: 25 MM For Parts From 150 To 200 Sq. MM Unlike Conventional Stamping, Fine BlankingDocument11 pagesFine Blanking and Forming in One Pass: 25 MM For Parts From 150 To 200 Sq. MM Unlike Conventional Stamping, Fine BlankingNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials Technology InsertionDocument15 pagesAdvanced Materials Technology InsertionNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- General KnowlwdgeDocument115 pagesGeneral KnowlwdgeMUDASSAR IDRIS98% (44)
- CostingDocument60 pagesCostingNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Milling: History of The Milling MachineDocument11 pagesMilling: History of The Milling MachineNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Dip ProdTech (Mould Tech)Document2 pagesDip ProdTech (Mould Tech)Nikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 BendingDocument16 pagesChapter-2 BendingNikhil PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument6 pagesBed BathKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- (Nand Flash Memory) HY27 (U - S) S (08 - 16) 121M (Rev0.6)Document43 pages(Nand Flash Memory) HY27 (U - S) S (08 - 16) 121M (Rev0.6)jituelectNo ratings yet
- Bacanie 2400 Articole Cu Cod de BareDocument12 pagesBacanie 2400 Articole Cu Cod de BareGina ManolacheNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Accounting & Finance Chapter 5Document27 pagesResearch Methods in Accounting & Finance Chapter 5bikilahussenNo ratings yet
- 10-02-20. Deed of Donation SSF Equipment - SSF On Vermicomposting (Formerly Large Scale Vermi Composting Production)Document3 pages10-02-20. Deed of Donation SSF Equipment - SSF On Vermicomposting (Formerly Large Scale Vermi Composting Production)Catherine BenbanNo ratings yet
- HSG 9 Tienganh 2019Document7 pagesHSG 9 Tienganh 2019Bảo HoàngNo ratings yet
- Disciplinary Literacy Strategies To Support Transactions in Elementary Social StudiesDocument11 pagesDisciplinary Literacy Strategies To Support Transactions in Elementary Social Studiesmissjoseph0803No ratings yet
- Case Study GingerDocument2 pagesCase Study Gingersohagdas0% (1)
- ISCOM5508-GP (A) Configuration Guide (Rel - 02)Document323 pagesISCOM5508-GP (A) Configuration Guide (Rel - 02)J SofariNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Management - Traditional Building Part#2Document194 pagesFire Safety Management - Traditional Building Part#2Yoyon Haryono100% (1)
- Agreement of PurchaseDocument8 pagesAgreement of PurchaseAdv. Govind S. TehareNo ratings yet
- AP Online Quiz KEY Chapter 8: Estimating With ConfidenceDocument6 pagesAP Online Quiz KEY Chapter 8: Estimating With ConfidenceSaleha IftikharNo ratings yet
- CDS11412 M142 Toyota GR Yaris Plug-In ECU KitDocument19 pagesCDS11412 M142 Toyota GR Yaris Plug-In ECU KitVitor SegniniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Document4 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Azfar RashedNo ratings yet
- Unibertsitaterako Hautaproba Ingelesa EHU/UPVDocument2 pagesUnibertsitaterako Hautaproba Ingelesa EHU/UPVdabidNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Previewing and PredictingDocument8 pagesUNIT 1 Previewing and PredictingRisa nurlailiNo ratings yet
- RMC No. 23-2007-Government Payments WithholdingDocument7 pagesRMC No. 23-2007-Government Payments WithholdingWizardche_13No ratings yet
- Marina AbramovićDocument2 pagesMarina AbramovićTatiana AlbuNo ratings yet
- Apply Study and Learning SkillsDocument58 pagesApply Study and Learning SkillsSelf-DeveloperNo ratings yet
- 09 - Arithmetic Progressions - 16 PDFDocument16 pages09 - Arithmetic Progressions - 16 PDFShah RukhNo ratings yet
- SAi Sankata Nivarana StotraDocument3 pagesSAi Sankata Nivarana Stotrageetai897No ratings yet
- HARRISON 1993 - The Soviet Economy and Relations With The United States and Britain, 1941-45Document49 pagesHARRISON 1993 - The Soviet Economy and Relations With The United States and Britain, 1941-45Floripondio19No ratings yet
- PT3 Liste PDFDocument2 pagesPT3 Liste PDFSiti KamalNo ratings yet
- DentinogenesisDocument32 pagesDentinogenesisNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Jane AustenDocument2 pagesJane Austendfaghdfo;ghdgNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Concept MappingDocument34 pagesMyocardial Concept MappingTHIRD YEARNo ratings yet
- PFASDocument8 pagesPFAS王子瑜No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Financial Management and Financial Objectives: Answer 1Document9 pagesChapter 12 Financial Management and Financial Objectives: Answer 1PmNo ratings yet
- Exeter: Durance-Class Tramp Freighter Medium Transport Average, Turn 2 Signal Basic Pulse BlueDocument3 pagesExeter: Durance-Class Tramp Freighter Medium Transport Average, Turn 2 Signal Basic Pulse BlueMike MitchellNo ratings yet