Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyperkalemia - ICU
Uploaded by
RithOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyperkalemia - ICU
Uploaded by
RithCopyright:
Available Formats
By Dr.
Kousama SJH 2020
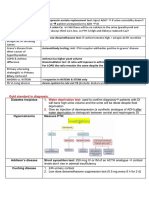
Hyperkalemia ECG Changes
‣ Peaked T wave
‣ Prolonged PR interval
‣ ST changes
Objectives: ‣ Wide QRS
1. Notice hyperkalemia (clinically)
‣ May progress to asystole
2. Understand ECG changes
3. Treat hyperkalemia on time
Goals of Rx
“AIRED”
Causes A add calcium
“MACHINE” I increase excretion (Kayexalate, Diuretics)
M medications (ACEIs, NSAIDS..)
R remove source (drugs..)
A acidosis (respiratory or metabolic)
E enhance K+ uptake (Insulin, Glucose,
C cellular damage (burns, trauma..)
NaCO3-..)
H hypoaldostronism, hemolysis
D dialysis
I intake (excessive of potassium)
N nephrons (renal failure)
E excretion (decrease)
Treatment
1. Ca2+ Gluconate (10ml):
‣ 1A IV over 2-3 mn
Signs ‣ Effect lasts 30-60 mn
“MURDER”
‣ If effect does not appear, use one again
M muscle weakness
5 mn later.
U urine (oliguria, anuria)
‣ Effect: prevent from V. Fib
R respiratory distress
‣ But if hyper-K+ from Digitalis (Digoxin)
=> use CaCl2 hydrate 2% (20ml)
D decreased cardiac contractility
2A IV 2-5 mn
E ECG changes
2. Glucose-Insulin:
R reflex (hyperreflexia or areflexia-flaccid)
‣ [Ins. 10 units (0.1ml) 1A] + [Glu. 50%
(10ml) 5A] inj. w/ IV in 30 mn
‣ If BG is 250 mg/dL, no need to IV Glu.
Remember “SHOCK” ‣ Effect appears 30 mn and last 2-6 hr
(shock + bradycardia) 3. Salbutamol:
S spinal cord injury (neurogenic shock)
‣ 10-20 mg by nebulizer over 10 mn
H hypo-endocrine (hypothyroidism, adrenal
‣ To promote k+ uptake into cells
insufficiency, Pituitary apoplexy)
4. NaCO3-:
O osborn (hypothermia)
‣ 1 mEq/kg DIV
C cardiogenic/cardiotoxic
‣ Effect lasts 2 hr
K potassium (hyperkalemia)
When to Start Rx
High risk patient w/ hyperkalemia (clinical
signs):
‣ w/ ECG changes => Rx immediately
‣ w/o ECG changes => confirm ABGs and
start Rx
You might also like
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- I. Definitions: Management of Hyperkalemia in AdultsDocument2 pagesI. Definitions: Management of Hyperkalemia in AdultsUpitFlowNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia Management Dec2010 PDFDocument6 pagesHyperkalemia Management Dec2010 PDFClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungDocument47 pagesKegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungEfa FathurohmiNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Myocardial InfarctionManju PillaiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs FileDocument29 pagesEmergency Drugs Filemmbire@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Potassium DisturbancesDocument23 pagesPotassium DisturbancesThien Nhan MaiNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument50 pagesChest PainGrafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Circulation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionDocument23 pagesCirculation Management: Hypovolemic Shock: Hemorrhagic Shock, Dehydration and CombustionYuni Sulistiyo WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic Crisis & Disaster NursingDocument80 pagesAcute Biologic Crisis & Disaster NursingprinceBel21No ratings yet
- Pembimbing: Dr. Ali Haedar, SP - EM: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas BrawijayaDocument26 pagesPembimbing: Dr. Ali Haedar, SP - EM: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Brawijayanoval hlfNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)Document58 pagesCase Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)tantsaNo ratings yet
- Episode 86 - HyperkalemiaDocument7 pagesEpisode 86 - HyperkalemiaAlok yadav100% (1)
- Necrotic LimbDocument16 pagesNecrotic LimbGladys PatulakNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HaemorrhageDocument16 pagesIntracranial HaemorrhageRizka Nurul FirdausNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument19 pagesManagement of Diabetic KetoacidosisSharafuddin SalimiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines and Protocols Of: Diabetes EmergenciesDocument36 pagesGuidelines and Protocols Of: Diabetes Emergenciesyassen hassanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Medical EmergenciesDocument24 pagesSummary of Medical Emergenciesbasharswork99No ratings yet
- Brugada SyndromeDocument3 pagesBrugada SyndromeBogdan ClujNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Hemorrhage Checklist: Safe Motherhood InitiativeDocument2 pagesObstetric Hemorrhage Checklist: Safe Motherhood InitiativejefeNo ratings yet
- ACLS PharmacologyDocument5 pagesACLS PharmacologyKuruva MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Test 38 Qid: 2819: Medicine - Renal, Urinary Systems & ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesTest 38 Qid: 2819: Medicine - Renal, Urinary Systems & Electrolyteskabal321No ratings yet
- Hemodialysis FXNDocument1 pageHemodialysis FXNSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Jaga 7 AprileditDocument18 pagesLaporan Jaga 7 ApriledithansenNo ratings yet
- (UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFDocument12 pages(UHL CHILDREN) Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) PDFRizki Ismi Arsyad IINo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document11 pagesLecture 7Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- DKA Guidelines PDFDocument111 pagesDKA Guidelines PDFzahra zymNo ratings yet
- TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardiaArvind SahniNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument16 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisffNo ratings yet
- Algoritma HiperkalemiaDocument1 pageAlgoritma HiperkalemiaanrihmNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionSajjad KabirNo ratings yet
- KKD Terapi CairanDocument35 pagesKKD Terapi CairanNeva Arunika UtamiNo ratings yet
- Morning Report: Physician in ChargeDocument3 pagesMorning Report: Physician in ChargeDoctoRides 46No ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromem3d1k100% (1)
- 22-11-22 RicuDocument316 pages22-11-22 RicuJhon WickNo ratings yet
- Potassium ManagementDocument28 pagesPotassium ManagementsiusiuwidyantoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Learning Session-Acute Coronary Syndromes Acs - 1Document31 pagesClinical Learning Session-Acute Coronary Syndromes Acs - 1api-611918048No ratings yet
- COMP 2 Exam NotesDocument19 pagesCOMP 2 Exam NotesMorgan PNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathophys NitesDocument28 pagesClinical Pathophys NitesDemianaNo ratings yet
- Neuro CaseDocument25 pagesNeuro CaseHainey GayleNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NotesDocument45 pagesPediatric NoteskkkssbbNo ratings yet
- Hipokalemia, Hipovolemia y Repercusión Electrocardiográfica Secundarias A Ingesta Prolongada de Furosemida. Caso ClínicoDocument7 pagesHipokalemia, Hipovolemia y Repercusión Electrocardiográfica Secundarias A Ingesta Prolongada de Furosemida. Caso ClínicoIvan TapiaNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalaemia FormularyDocument3 pagesHyperkalaemia FormularyMiguel SanJuanNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 A Review Random FinalDocument3 pagesNCM 118 A Review Random FinalRosel Vivien EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Feline Lower Urinary Tract DiseaseDocument6 pagesFeline Lower Urinary Tract DiseaseRob PNo ratings yet
- Pedia Handy NotesDocument18 pagesPedia Handy NotesCarl Donaire100% (2)
- Approach To Shock, Airway and FluidsDocument63 pagesApproach To Shock, Airway and FluidsJerry GohNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support PDFDocument9 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support PDFYulias YoweiNo ratings yet
- L4,5-Fluid Electrolytes Acid-BaseDocument74 pagesL4,5-Fluid Electrolytes Acid-BaseKhaled FrehatNo ratings yet
- General Census Nov 7Document5 pagesGeneral Census Nov 7Mark Angelo PonferradoNo ratings yet
- Addison Diseases LecDocument40 pagesAddison Diseases LecSalman RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia How To Recognize and How To ManageDocument26 pagesHyperkalemia How To Recognize and How To Managedhika2496No ratings yet
- Severe Sepsisand Septic Shock GuidelinesDocument17 pagesSevere Sepsisand Septic Shock GuidelinesdrquamrulNo ratings yet
- Tumor Lysis Oral Boards CasesDocument15 pagesTumor Lysis Oral Boards Casesczalesky66No ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan PerioperatifDocument35 pagesTerapi Cairan PerioperatifasepNo ratings yet
- Terminalia Arjuna (Arjun Bark) Benefits, Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsDocument22 pagesTerminalia Arjuna (Arjun Bark) Benefits, Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsManas Arora100% (1)
- NotiuniteoreticesipracticedeFiziologievegetala PDFDocument17 pagesNotiuniteoreticesipracticedeFiziologievegetala PDFJulian CatutzaNo ratings yet
- MAN5402 Assessment 2 S22023Document8 pagesMAN5402 Assessment 2 S22023Dorji TsheringNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Enhancement For PCMThermal Energy Storagein Triplex Tube Heat ExchangerDocument31 pagesHeat Transfer Enhancement For PCMThermal Energy Storagein Triplex Tube Heat ExchangerLam DesmondNo ratings yet
- Quick and Dirty Regression TutorialDocument6 pagesQuick and Dirty Regression TutorialStefan Pius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Outlook For Energy: A View To 2040Document17 pages2018 Outlook For Energy: A View To 2040manuel cabarcasNo ratings yet
- TM 2G3G4G Hardware Installation Guide V1.6 PDFDocument150 pagesTM 2G3G4G Hardware Installation Guide V1.6 PDFjacobus_louw4329No ratings yet
- Nf528t Rev.0Document1 pageNf528t Rev.0MZY Commercial EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Star Health and Allied Insurance Company Limited Tariff Statement - Mini SOC (FINALISED)Document1 pageStar Health and Allied Insurance Company Limited Tariff Statement - Mini SOC (FINALISED)Sanket Sahare100% (1)
- Column-I Column-II (Reactions) (Statements) : Organic Chemistry Enthuse DPP # 16Document3 pagesColumn-I Column-II (Reactions) (Statements) : Organic Chemistry Enthuse DPP # 16Arjun SabnisNo ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaDocument35 pages1 - Overview of The Transportation Sector in ZambiaPenelope Malilwe100% (1)
- Deadlock Avoidance For Multiple Tasks in A Self Organizing Production CellDocument10 pagesDeadlock Avoidance For Multiple Tasks in A Self Organizing Production CellsoniathalavoorNo ratings yet
- Tca 66-41.141Document266 pagesTca 66-41.141AlexDor100% (3)
- 09 Final Exam - Math Year 2 Paper 1Document8 pages09 Final Exam - Math Year 2 Paper 1bob yusufNo ratings yet
- 1.4301 Austenite Stainless SteelDocument3 pages1.4301 Austenite Stainless SteelSM Waqas ImamNo ratings yet
- Introduccion To SSA PDFDocument46 pagesIntroduccion To SSA PDFAlex RojasNo ratings yet
- CARESS 102 Module 1 Lesson 1 Innovation 1Document26 pagesCARESS 102 Module 1 Lesson 1 Innovation 1Micah PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Modern RiddlesDocument1 pageModern RiddlesHannah BautistaNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument26 pagesBiochemGhel GarciaNo ratings yet
- ActinobacillosisDocument16 pagesActinobacillosisMd Shamim AhasanNo ratings yet
- All She Wants To Do Is Dance (Henley) Chords & LyricsDocument1 pageAll She Wants To Do Is Dance (Henley) Chords & Lyricsben_davidson_27No ratings yet
- A9 Tech Book 1Document15 pagesA9 Tech Book 1DejanNo ratings yet
- RNA Columns NaOH Treatment RegenerationDocument7 pagesRNA Columns NaOH Treatment RegenerationVageeshbabu HanurNo ratings yet
- Equpment LayoutDocument6 pagesEqupment Layoutdasubhai100% (1)
- 003.ladders - Rev. 0Document25 pages003.ladders - Rev. 0narasimhamurthy414No ratings yet
- Kaur Et Al-2010-Journal of Pineal ResearchDocument9 pagesKaur Et Al-2010-Journal of Pineal ResearchElena Martínez CelisNo ratings yet
- TechometryDocument49 pagesTechometryMuhammad Usman RazaNo ratings yet
- Q.P. Code: 684884Document1 pageQ.P. Code: 684884Priyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- 107ME037 - Impact CrusherDocument7 pages107ME037 - Impact CrusherMohammed Abdo100% (1)
- Brochure XL - ArkemaDocument19 pagesBrochure XL - ArkemaCori_009No ratings yet