100% found this document useful (1 vote)
488 views6 pagesCommunicating in Teams and Organizations
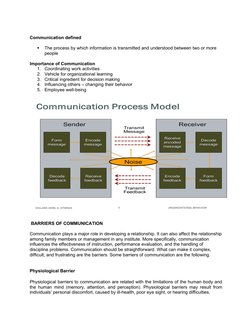
The document discusses barriers to effective communication. Some key barriers include physiological limitations, poor listening skills, information overload, inattention, emotions, poor memory retention, physical and environmental distractions, psychological factors, social and cultural differences, semantic issues like language or jargon, past negative experiences, organizational problems, technological failures, time pressures, complex organizational structures, unclear or inappropriate messages, stereotypes, using the wrong communication channel, and lack of feedback. Addressing these barriers can help improve communication.
Uploaded by
erielle mejicoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
488 views6 pagesCommunicating in Teams and Organizations
The document discusses barriers to effective communication. Some key barriers include physiological limitations, poor listening skills, information overload, inattention, emotions, poor memory retention, physical and environmental distractions, psychological factors, social and cultural differences, semantic issues like language or jargon, past negative experiences, organizational problems, technological failures, time pressures, complex organizational structures, unclear or inappropriate messages, stereotypes, using the wrong communication channel, and lack of feedback. Addressing these barriers can help improve communication.
Uploaded by
erielle mejicoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Communication Overview
- Communication Barriers
- Grapevine Communication