Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Superficialreflexes 150609023712 Lva1 App6891
Uploaded by
Karthik TOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Superficialreflexes 150609023712 Lva1 App6891
Uploaded by
Karthik TCopyright:
Available Formats
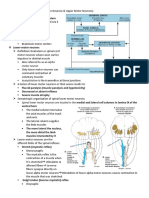
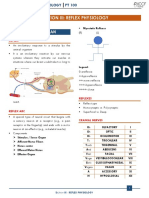
SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES
INTRODUCTION
– They are elcited by stimulation of certain parts of the skin or mucous membrane and the end result being
contraction of one or more muscles.
- They are polysynaptic reflexes.
- They are lost in lesions of corticospinal tract.
REFLEXES METHOD OF ELICITING RESPONSE
CORNEAL REFLEX
Afferent V cranial nerve Touch the cornea with wisp of cotton just below the pupil Reflex blinking of both eyelids.
reflex centre pons brought in from the side of the patient.
Efferent VII cranial nerve
CONJUNCTIVAL REFLEX
Afferent V cranial nerve This reflex is performed similar to the corneal reflex but Reflex blinking of both eyelids.
reflex centre pons the conjunctiva is touched.
Efferent VII cranial nerve
PHARYNGEAL REFLEX
Afferent IX cranial nerve Stimulating the posterior pharyngeal wall with a cotton Contraction of the pharynx and
Efferent X cranial nerve stick. elevation of the pharyngeal wall
SCAPULAR REFLEX
Afferent C4&C5 Stroking skin in interscapular area. Contraction of the scapular muscles.
Efferent is dorsal scapular nerve.
ABDOMINAL REFLEX
(Epigastric T 7-9, upper abdominal T9-11, lower Lightly stroke the abdomen from without inwards in all Contraction of abdominal muscles.
abdominal T11-L1) quadrants on both sides.
CREMASTERIC REFLEX – (L1 & L2)
Afferent femoral nerve. Upper part of the inner thigh is lightly stroked downward Pulling up of the testis and scrotum on
Efferent Genito femoral nerve and inward. that side.
BULBOCAVERNOUS REFLEX-(S3&4)
Afferent pudendal nerve Squeezing the tip of the glans penis. Contraction of the bulbocavernous
Efferent pudendal nerve muscle.
ANAL REFLEX-(S4&S5)
Afferent pudendal nerve Lightly scratching the perianal skin. Contraction of the external anal
Efferent pudendal nerve sphincter.
PLANTAR REFLEX-(L5&S1)
NERVE- Posterior tibial nerve Muscles of the lower limb should be relaxed. Flexor response -
Knee is flexed and thigh externally rotated. flexion of the toes.
The outer end of the sole of the foot is stimulated by
using a key or a blunt object along it from the heel upto Extensor response -
the ball of the great toe. dorsiflexion of the great toe,
fanning of the other toes,
dorsiflexion of the ankle,
flexion of the knee and hip &
contraction of tensor fascia lata.
OTHER METHODS OF ELICITING PLANTAR REFLEX
1. Squeezing the calf or pressing heavily along the inner border of the tibia (oppenheim’s Reflex)
2. Hard squeezed on the calf muscles (Gordon’s reflex)
3. Light stroke below the external malleous on the outer surface of the foot. (Chaddock Reflex)
4. Squeezing Achilles Tendon. (Schaefer’s Sign).
5. Pin pick on the dorsum of the foot. (Bing Sign).
CONDITIONS WHERE BABINSKI’S SIGN IS POSITIVE
1. U.M.N. LESIONS
2. DEEP SLEEP
3. INFANTS
4. COMA
5. POST ICTAL STATE
6. HYPOGLYCEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
7. HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY
8. HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
You might also like
- Babinski and Other Pyramidal Reflexes Without VideosDocument12 pagesBabinski and Other Pyramidal Reflexes Without VideosMaurizio SeverinoNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Cns Part ExaminationDocument68 pagesCns Part ExaminationHarshita CoolNo ratings yet
- Emailing SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES DR JAVERIA PDFDocument28 pagesEmailing SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES DR JAVERIA PDFNoor ZehraNo ratings yet
- Demonstration ReflexDocument40 pagesDemonstration Reflexnikita jainNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab No4Document5 pagesLab No4Usama JavedNo ratings yet
- Motor SystemDocument8 pagesMotor SystemEman LabNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesmishky19No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Lower LimbDocument6 pagesFlashcards - Lower LimbKhanNo ratings yet
- Plantar ReflexDocument5 pagesPlantar ReflexrazakmdpaedNo ratings yet
- Palm MusclesDocument41 pagesPalm MusclesRealmeNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFMohamed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Superficial and Deep ReflexesDocument28 pagesSuperficial and Deep ReflexesShilpa SNo ratings yet
- LAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighDocument8 pagesLAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighnanaNo ratings yet
- Plantar ReflexDocument19 pagesPlantar Reflexfidaafsal99No ratings yet
- REFLEXESDocument15 pagesREFLEXESSonali Soumyashree100% (2)
- NER4 and 5 NotesDocument11 pagesNER4 and 5 NotesjasminNo ratings yet
- Om Parkash AssignmentDocument5 pagesOm Parkash AssignmentMohini BaiNo ratings yet
- Reflexes and SignsDocument32 pagesReflexes and SignsKatrina Clarisse Hutalla100% (1)
- Palm MusclesDocument45 pagesPalm MusclesBandarupalli Akash Chowdary100% (1)
- Activity 6 - Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesActivity 6 - Nervous SystemJohn Ruel Sanchez IINo ratings yet
- Foot Region and Clinical Notes TransDocument14 pagesFoot Region and Clinical Notes Transchynne ongNo ratings yet
- Muscles EscanillaDocument9 pagesMuscles EscanillaESCANILLA CRISTINENo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Muscular System Part 4 StudentDocument41 pagesModule 6 - Muscular System Part 4 StudentLaw HacksNo ratings yet
- 02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEDocument18 pages02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEClaude ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaDocument4 pagesGluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaSteph SantosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Lower LimbDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Lower LimbahmedNo ratings yet
- LAB Reflex PhysiologyDocument4 pagesLAB Reflex PhysiologyCarl Cedrick FlojoNo ratings yet
- PGI May 2016 PaperDocument293 pagesPGI May 2016 PaperRohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Tendon ReflexDocument13 pagesTendon ReflexNurul Huda M ShahrinNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: DR Dyan Roshinta Laksmi Dewi, SP.S SMF Saraf Rsud DR Soedarso PontianakDocument19 pagesCranial Nerves: DR Dyan Roshinta Laksmi Dewi, SP.S SMF Saraf Rsud DR Soedarso PontianakVidia AsriyantiNo ratings yet
- Muscle Innervation Chart IIDocument7 pagesMuscle Innervation Chart IIkimsue9448No ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot Injuries in Sports MedicineDocument107 pagesAnkle and Foot Injuries in Sports MedicinebaoNo ratings yet
- Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist TablesDocument4 pagesPrimitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist TablesAmy EmylaNo ratings yet
- 10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionDocument36 pages10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionzelinaokiNo ratings yet
- Plantar ReflexDocument3 pagesPlantar Reflexhalu89No ratings yet
- Stretch ReflexDocument31 pagesStretch ReflexTots Enriquez Navarro100% (1)
- Extraocular Muscles and Common Tendinous RingDocument7 pagesExtraocular Muscles and Common Tendinous RingAliyu AishaNo ratings yet
- International Journalof Pediatricsand Neonatology Planter ReflexDocument4 pagesInternational Journalof Pediatricsand Neonatology Planter ReflexUmesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: General CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesCranial Nerves: General CharacteristicsRiki AntoNo ratings yet
- Reflex ExamDocument4 pagesReflex ExamDan Ali100% (1)
- Upper Limb MusclesDocument19 pagesUpper Limb MusclesVinod Sharma100% (1)
- Muscles and Nerves - Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesMuscles and Nerves - Origins and InsertionsLuke ThomsonNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument3 pagesReflexesJr LibetarioNo ratings yet
- Orbit - Head & NeckDocument57 pagesOrbit - Head & NeckNandini BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Project K Sciatic Nerve Pre Final Copy 2Document27 pagesProject K Sciatic Nerve Pre Final Copy 2Deepak NemaniNo ratings yet
- 6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesDocument3 pages6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Sciatica NotesDocument23 pagesSciatica NotesPruteanu VasileNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity - Muscle Summary ChartDocument9 pagesUpper Extremity - Muscle Summary ChartpoggerNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Testing Expected Normal Response Organic ReflexesDocument5 pagesProcedure For Testing Expected Normal Response Organic ReflexesMabel LynNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 3Document48 pagesالمحاضرة 3Anwer YahyaNo ratings yet
- Adult Reflexes Bicep ReflexDocument4 pagesAdult Reflexes Bicep ReflexChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Spine LectureDocument55 pagesSpine LectureLeoNo ratings yet
- Knee and Leg ReviewerDocument3 pagesKnee and Leg ReviewerKIARA VENICE DELGADONo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument32 pagesAnatomyShashanka PoudelNo ratings yet
- Reflex Tests Procedure For Testing Normal ResponseDocument4 pagesReflex Tests Procedure For Testing Normal ResponseMabel LynNo ratings yet
- Original For Recipient Duplicate For Transporter Triplicate For SupplierDocument1 pageOriginal For Recipient Duplicate For Transporter Triplicate For SupplierKarthik TNo ratings yet
- CIF Number 85121020802 Customer Name Talikota Karthik: Tds Details For The Year 2020-21Document1 pageCIF Number 85121020802 Customer Name Talikota Karthik: Tds Details For The Year 2020-21Karthik TNo ratings yet
- List of Igg Elisa/Clia Kits For Covid 19 Validated by Icmr Identified Validation CentresDocument2 pagesList of Igg Elisa/Clia Kits For Covid 19 Validated by Icmr Identified Validation CentresKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Nuclei TractsDocument1 pageSpinal Cord Nuclei TractsKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Adipokines 190521161751Document4 pagesAdipokines 190521161751Karthik TNo ratings yet
- Original For Recipient Duplicate For Transporter Triplicate For SupplierDocument1 pageOriginal For Recipient Duplicate For Transporter Triplicate For SupplierKarthik TNo ratings yet
- 15942381769000735ASO2Document1 page15942381769000735ASO2Karthik TNo ratings yet
- Retail Invoice / Bill: Your Total Savings: Rs.197.71Document2 pagesRetail Invoice / Bill: Your Total Savings: Rs.197.71Karthik TNo ratings yet
- Newer Therapies in COPD: Prem Parkash GuptaDocument6 pagesNewer Therapies in COPD: Prem Parkash GuptaKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Topics You Should Know:: Spinal CordDocument4 pagesTopics You Should Know:: Spinal CordKarthik TNo ratings yet
- SPIKES ProtocolDocument4 pagesSPIKES ProtocolKassem Gharaibeh100% (1)
- 16 Ra Thyro WeightDocument45 pages16 Ra Thyro WeightKarthik TNo ratings yet
- SPIKES ProtocolDocument4 pagesSPIKES ProtocolKassem Gharaibeh100% (1)
- Employee DetailsDocument81 pagesEmployee DetailsKarthik TNo ratings yet
- LP 160610182350Document25 pagesLP 160610182350Karthik TNo ratings yet
- 207Document5 pages207Satria 'arceus' DewantaraNo ratings yet
- CLASSWORK 7 2016112621158BRA 1° Medio AdjectiveDocument19 pagesCLASSWORK 7 2016112621158BRA 1° Medio AdjectivePatricio PerezNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Medicine For Erectile Dysfunction - Diabetes and Erectile DysfunctionDocument9 pagesAyurvedic Medicine For Erectile Dysfunction - Diabetes and Erectile DysfunctionYahu NewsNo ratings yet
- Lactose Intolerance: Diano, Gabriella Hilde Fanged, Paula Mandy Marrero, Xandra 9-KryptonDocument15 pagesLactose Intolerance: Diano, Gabriella Hilde Fanged, Paula Mandy Marrero, Xandra 9-KryptonArrianne AcopNo ratings yet
- Corbey 1993Document33 pagesCorbey 1993procrast3333No ratings yet
- A13 TalamusDocument37 pagesA13 TalamusDaniela GiorocNo ratings yet
- Zoo Book - Low-Res PDFDocument362 pagesZoo Book - Low-Res PDFAmmu Singh100% (1)
- Butterfly Diversity of District Nainital Uttarakhand (India)Document6 pagesButterfly Diversity of District Nainital Uttarakhand (India)NaveenNo ratings yet
- SUPPLIERS SPEED DIAL-UpdatedDocument2 pagesSUPPLIERS SPEED DIAL-Updatedlyn7387No ratings yet
- Balanced OcclusionDocument9 pagesBalanced OcclusionDrShweta Saini100% (1)
- 10-27-11 - Moneysaver - Palouse EditionDocument12 pages10-27-11 - Moneysaver - Palouse EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- De Kiem Tra Giua Ki II Tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart WorldDocument4 pagesDe Kiem Tra Giua Ki II Tieng Anh Lop 6 Ilearn Smart WorldNgọc HươngNo ratings yet
- Butterfly of The Day3 - Common MormonDocument3 pagesButterfly of The Day3 - Common MormonSimone VazNo ratings yet
- Snow Tails English RulesDocument11 pagesSnow Tails English RulesGabriel SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Chave de Identificação Das Espécies de Bagres Marinhos (Siluriformes, Ariidae) Da Costa BrasileiraDocument14 pagesChave de Identificação Das Espécies de Bagres Marinhos (Siluriformes, Ariidae) Da Costa Brasileirasafra82No ratings yet
- The Baiting of Wild Animals in RussiaDocument36 pagesThe Baiting of Wild Animals in RussiaZarya LaikaNo ratings yet
- Breast ExamDocument4 pagesBreast Exammoony_sasNo ratings yet
- STRATA PLAN LMS 2790 So Nest A Bylaws The Sonesta 1989 Dunbar Street, Vancouver, BC, CanadaDocument31 pagesSTRATA PLAN LMS 2790 So Nest A Bylaws The Sonesta 1989 Dunbar Street, Vancouver, BC, CanadaMike Stewart100% (1)
- Jin Shin Jyutsu Self Help - Main Central Energy FlowDocument6 pagesJin Shin Jyutsu Self Help - Main Central Energy Flowsale18100% (2)
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument12 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraAlunaficha Melody Kirania50% (2)
- IvermecDocument7 pagesIvermecApril Joy Yu-MateoNo ratings yet
- Fish50 Write UpDocument3 pagesFish50 Write UpSophia ManzanoNo ratings yet
- تجميع اسئله الاخصائين 1Document36 pagesتجميع اسئله الاخصائين 1Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Msapila PoutryDocument13 pagesMsapila PoutryEdgar Mugarura100% (2)
- Summative Test in TVL 12-Animal Production (Swine)Document4 pagesSummative Test in TVL 12-Animal Production (Swine)gemma salomon100% (9)
- The Debutante - by Leonora CarringtonDocument4 pagesThe Debutante - by Leonora CarringtonAimeNo ratings yet
- HC SVNT DRACONES - Core Rulebook - Extended PDFDocument205 pagesHC SVNT DRACONES - Core Rulebook - Extended PDFrasmusNo ratings yet
- The A To Z of Skeletal MusclesDocument238 pagesThe A To Z of Skeletal MusclesAspenPharma99% (161)
- Unit: 08 Placentation in Mammals: Developmental Biology Cr. Hours: 4 (3+1)Document30 pagesUnit: 08 Placentation in Mammals: Developmental Biology Cr. Hours: 4 (3+1)Task BirdNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemDavid DanielNo ratings yet