Professional Documents
Culture Documents
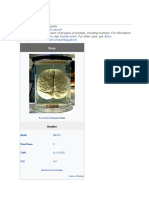
Brain
Uploaded by
ANMOL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagebrain
Original Title
brain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbrain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBrain
Uploaded by
ANMOLbrain
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and
most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs
for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human,
the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons,[1] and the estimated number of
neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion.[2] Each neuron is connected by synapses to several
thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of
long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant
parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.
Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest
of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of
chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to
changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be
mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of
behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a
centralized brain.
The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way
they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved.[3] Recent models in modern
neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an
electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding
world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways.
This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the
greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties
of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the
human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there
because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain
disease and the effects of brain damage, that are covered in the human brain article.
You might also like
- Super Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingFrom EverandSuper Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingNo ratings yet
- Brain: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesBrain: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchFrances camille TumbagaNo ratings yet
- PT ScribdDocument1 pagePT ScribdHopeNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument1 pageThe Brainveronica pirelaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument32 pagesBrainJulianNo ratings yet
- Assignment NAME: Sana SohailDocument8 pagesAssignment NAME: Sana SohailMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment NAME: Sana SohailDocument8 pagesAssignment NAME: Sana SohailMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Brain EssayDocument1 pageBrain EssaydjduganatorNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument14 pagesClass NotesKovács EnikõNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search Human Brain Brain (Disambiguation)Document11 pagesNavigation Search Human Brain Brain (Disambiguation)keola greavesNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument2 pagesBrainMiraat GuptaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument37 pagesBrain呂布No ratings yet
- A Chimpanzee BrainDocument21 pagesA Chimpanzee BrainKevin ChenNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument27 pagesBraincviymqty7No ratings yet
- The MindDocument3 pagesThe MindWiam MardianaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemMac Gab100% (3)
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourRichard ManuelNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- Chapter 2 - The Brain and BehaviorDocument40 pagesChapter 2 - The Brain and BehaviorKaiNo ratings yet
- The Human BrainDocument6 pagesThe Human BraindamanzurNo ratings yet
- MBBC 2018 Notes 1Document14 pagesMBBC 2018 Notes 1Dimitri KhooNo ratings yet
- Criminal Psychology Mod 2 by EdxDocument8 pagesCriminal Psychology Mod 2 by EdxAlexandra SfNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomical Divisions of The Nervous SystemDamianNo ratings yet
- Imlementation of ANN On FPGADocument76 pagesImlementation of ANN On FPGAthomagtNo ratings yet
- What Chat GPT Think of Human BrainDocument2 pagesWhat Chat GPT Think of Human BrainbigthinkinganddoNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesRelationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleObi TomaNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesThe Brain: Learning Objectivessaswati biswalNo ratings yet
- Preparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiDocument8 pagesPreparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiKielNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument15 pagesBrainŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- How Does Brain WorkDocument1 pageHow Does Brain WorkMujeeb joyiaNo ratings yet
- Biology and BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiology and BehaviorDanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesChapter 3 NeuroscienceskateboardinglivNo ratings yet
- (16-17) Brain SummaryDocument57 pages(16-17) Brain SummarybartNo ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- Brain and NeuronDocument2 pagesBrain and NeuronMuhammad Ilham UtamaNo ratings yet
- 121 Veterinary Physiology - II (Neuromuscular Digestive & Respiratory Systems)Document346 pages121 Veterinary Physiology - II (Neuromuscular Digestive & Respiratory Systems)Vaidika YadavNo ratings yet
- What Is Cognitive Neuroscience?Document9 pagesWhat Is Cognitive Neuroscience?Neus Sangrós VidalNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 08 33 EtextDocument13 pagesKepy 01 08 33 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- Brain and MindDocument5 pagesBrain and MindMubashir AminNo ratings yet
- The Brain - NobaDocument21 pagesThe Brain - NobaMarNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument1 pageThe BrainMonica LoiseNo ratings yet
- Ap Psychology Chapter 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesAp Psychology Chapter 2 SummaryAllyOuNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument12 pagesHuman BrainJashwanthNo ratings yet
- The Study About Brain Wave Extreme Low Frequency and WorksDocument6 pagesThe Study About Brain Wave Extreme Low Frequency and WorksCraciun Fadei AndreiNo ratings yet
- Axon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyDocument6 pagesAxon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyshashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Week 1: The Brain: Learning ObjectivesDocument16 pagesWeek 1: The Brain: Learning ObjectivesCrystel AgardNo ratings yet
- PYC1501 Unit 1 Human Nervous System OERDocument18 pagesPYC1501 Unit 1 Human Nervous System OERjulia.mokoenadjNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument27 pagesBiological Basis of Human BehaviorAnanta ChaliseNo ratings yet
- 1XX3 Neuroscience 2Document7 pages1XX3 Neuroscience 2Michelle RiveraNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Saraf Manusia A.S. Muhammad Arhamar, 2023Document9 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem Saraf Manusia A.S. Muhammad Arhamar, 2023Vansh SayaniNo ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408012Document2 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408012Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Biology For EngineersDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Biology For Engineers20me006No ratings yet
- Mind Blowing BrainDocument16 pagesMind Blowing BrainTrance CrossingNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Finals ExamDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Finals ExamJohn Lloyd BallaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- โท the BrainDocument39 pagesโท the BrainFadil Wanna-mart100% (1)
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.From EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.No ratings yet
- OrionDocument2 pagesOrionANMOLNo ratings yet
- Turmeric: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 pagesTurmeric: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Hibiscus: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 pagesHibiscus: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Ocimum Tenuiflorum: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesOcimum Tenuiflorum: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Tinospora Cordifolia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 pagesTinospora Cordifolia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument3 pagesAloe Vera: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Magic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionDocument1 pageMagic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionANMOLNo ratings yet
- Pedal: Computers and Other EquipmentDocument1 pagePedal: Computers and Other EquipmentANMOLNo ratings yet
- OrionDocument2 pagesOrionANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus: COVID-19 Pandemic COVID-19 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Document2 pagesCoronavirus: COVID-19 Pandemic COVID-19 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2ANMOLNo ratings yet
- Pedal: Computers and Other EquipmentDocument1 pagePedal: Computers and Other EquipmentANMOLNo ratings yet
- Magic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionDocument1 pageMagic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionANMOLNo ratings yet
- rɪ Neɪsəns/ / Rɛnəsɑ NS/ Period European History Middle Ages Modernity Crisis of The Late Middle Ages Social Change Early ModernDocument1 pagerɪ Neɪsəns/ / Rɛnəsɑ NS/ Period European History Middle Ages Modernity Crisis of The Late Middle Ages Social Change Early ModernANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- Magic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionDocument1 pageMagic (Supernatural) Magic (Illusion) Magical Thinking Magic in FictionANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- SpaceDocument1 pageSpaceANMOLNo ratings yet
- Classical MusicDocument1 pageClassical MusicANMOLNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument1 pageMusicANMOLNo ratings yet
- Romanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyDocument1 pageRomanian ( Starʲɪt S) Eastern Orthodox Ascetic Struggle Hesychasm Holy Spirit Heal ProphesyANMOLNo ratings yet
- rɪ Neɪsəns/ / Rɛnəsɑ NS/ Period European History Middle Ages Modernity Crisis of The Late Middle Ages Social Change Early ModernDocument1 pagerɪ Neɪsəns/ / Rɛnəsɑ NS/ Period European History Middle Ages Modernity Crisis of The Late Middle Ages Social Change Early ModernANMOLNo ratings yet
- Solidago Virgaurea: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesSolidago Virgaurea: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Cinchona Officinalis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesCinchona Officinalis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Digitalis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesDigitalis: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Strychnos Ignatii: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesStrychnos Ignatii: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet
- Arnica Montana: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesArnica Montana: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchANMOLNo ratings yet