Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M & A: Company A (Acquirer) Buys Company B (Acquired or Target Firm) Typically Creates A New Firm
Uploaded by
GaneshRathod0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views12 pagesOriginal Title
International MAs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views12 pagesM & A: Company A (Acquirer) Buys Company B (Acquired or Target Firm) Typically Creates A New Firm
Uploaded by
GaneshRathodCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
¡ M & A: Company A (Acquirer) buys Company B (Acquired
Or Target Firm)
¡ Typically Creates A New Firm
§ Daimler Benz and Chrysler Merged To Become Daimler-Chrysler
(New Identity)
¡ Volume of M & A
§ 1999 – US$ 3.3 Trillion
§ 2000 – US$ 3.5 Trillion
§ 2004 – 30,000 Acquisitions Globally (One Every 18 Minutes) Valued
at US$1.9 Trillion
§ 2007 – US$ 4.5 Trillion
▪ 47% of The $4.5 Trillion Involved Cross-Border
▪ M&A
¡ Technological change
§ Major companies jockeyed for position in rapidly evolving technologies
¡ Changes in regulatory environment
§ Examples liberalization of economies, opening up of FDIs, IJVs, etc.
¡ Globalization
§ Companies found they needed to be big to operate on the global stage: Markets,
Resources, Knowledge, Human/Social Capital
¡ Stock price appreciation
§ Bull market in late 1990s gave some companies the means to purchase others
§ 56% Of Acquiring Firm Managers Reported Meeting Pre-Acquisition
Performance Objectives
§ 70% Of Target Firm Managers Left Their Jobs within 5 Years
§ Both Managers Reported Acculturation Stress During Post Merger
¡ Market Power – Merged Firm Has Greater Power Over
Consumers (Transfer of Wealth from Consumers to Firm)
¡ Efficiency – Focuses On Cost Side
¡ Resource Deployment – Redeployment of Competencies and
Assets To Generate Economies of Scope
¡ Market Discipline – Protects Shareholders from Poor
Management
¡ Compensation – Firm Size Positively Correlated With
Executive Compensation
¡ Managerial Hubris – Managerial Ego and Exaggerated Self-
Confidence
¡ Environmental Uncertainty– Less Diversified Firms Pursue
Acquisitions to Reduce Uncertainty
¡ Resource Dependence – Firms Acquire Other Firms To Reduce
Dependence On Scarce Resources
¡ Acquisition Experience – Prior Experience In Acquisitions
Increases Likelihood of Subsequent Acquisition
¡ Firm Strategy – Companies Following A Global Strategy Have
Higher Proportion of Greenfield Developments than
Companies Following Multi-Domestic Strategies
¡ Firms Facing Strategic Hurdles (Lack of Resources, etc.,) More
likely Targets for Acquisitions
¡ Value Creation Refers To Short-Term and Long-Term Stock
Holder Returns to
§ Acquiring Firms’ Shareholders
§ Acquired Firms’ Shareholders
§ Performance of the Firm After Mergers and Acquisitions
§ Yes, M & A Creates Value for Shareholders
¡ Company A (Acquiring Firm) Buys Company B (Target or
Acquired Firm)
§ Return To A’s Shareholders Either None or Negative
§ Return to B’s Shareholders Positive
¡ Over Payment for Target Firms
¡ Lack of Integration Of Target Firm and Acquiring Firm
(Systems and Processes)
¡ Strategic Misfit Post-Acquisition
¡ Post Acquisition Loss of Talented Managers and Human
Capital
¡ Cultural Conflict Between Acquiring and Target Firms
¡ Growth To Be By-Product of Profitability Not An End In Itsel
You might also like
- Chap 7 - SummaryDocument12 pagesChap 7 - SummaryMimi HassanNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Corporate RestructuringDocument5 pagesReasons For Corporate RestructuringRikardasNo ratings yet
- Jitendra Mohananey B. Com., LL.B., ACA, ACS +91 9810287311Document35 pagesJitendra Mohananey B. Com., LL.B., ACA, ACS +91 9810287311rahulmohiniNo ratings yet
- Inbound Mergers and Acquisitions Financing, IPE, HYDERABADDocument20 pagesInbound Mergers and Acquisitions Financing, IPE, HYDERABADsushantsaahaji100% (1)
- Project On ICICI and BOR Merger and AcquistionsDocument32 pagesProject On ICICI and BOR Merger and Acquistionssourbh_brahma100% (1)
- 7.merger and AcquisitionsDocument32 pages7.merger and AcquisitionsNatani Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Submitted To Course InstructorDocument15 pagesSubmitted To Course InstructorAmitesh TejaswiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Class 8: Corporate Mergers & AcquisitionsDocument22 pagesWelcome To Class 8: Corporate Mergers & AcquisitionsKEREN MILLETNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Introduction To M and ADocument28 pagesChapter 01 Introduction To M and ASattagouda M PatilNo ratings yet
- Corporate RestructuringDocument16 pagesCorporate Restructuringdeepakpatel4u100% (1)
- External Growth Strategies: Mergers and Acquisitions: Prof. Supriti MishraDocument41 pagesExternal Growth Strategies: Mergers and Acquisitions: Prof. Supriti MishraSiddharth Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Title Page: Valuation of Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument58 pagesTitle Page: Valuation of Mergers and Acquisitionsgirish8911No ratings yet
- Murdoch MBS 608 Strategy To Operations Week 4b Slides For StudentsDocument55 pagesMurdoch MBS 608 Strategy To Operations Week 4b Slides For StudentsstgregNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To M ADocument17 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To M Aappu.sreeraj6580No ratings yet
- Kone Germany StrategyDocument131 pagesKone Germany StrategyAtila Kemal Oguz100% (1)
- Topic 6.0 - Corporate Restructuring - M ADocument54 pagesTopic 6.0 - Corporate Restructuring - M ANannet WakariNo ratings yet
- Acquisition and MergingDocument19 pagesAcquisition and MergingTeerraNo ratings yet
- Title of The Paper:: Mergers and Acquisitions Financial ManagementDocument25 pagesTitle of The Paper:: Mergers and Acquisitions Financial ManagementfatinNo ratings yet
- 6 Unit 8 Corporate RestructureDocument19 pages6 Unit 8 Corporate RestructureAnuska JayswalNo ratings yet
- Chief Financial Officer in Toronto Canada Resume Gregory ScottDocument3 pagesChief Financial Officer in Toronto Canada Resume Gregory ScottGregoryScott1No ratings yet
- Mergers, Acquisitions & Corporate RestructuringDocument44 pagesMergers, Acquisitions & Corporate RestructuringkayNo ratings yet
- Agency Theory: Duncan AngwinDocument18 pagesAgency Theory: Duncan AngwinAmin LalaniNo ratings yet
- Cross Border M & AquisitionsDocument39 pagesCross Border M & AquisitionsJoel ChikomaNo ratings yet
- 2,3 M&aDocument17 pages2,3 M&areysinghania7No ratings yet
- Corporate Restructuring 2015Document25 pagesCorporate Restructuring 2015vaibhav100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To M ADocument29 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To M ASofiaLimantaraNo ratings yet
- Cours MA Private EquityDocument198 pagesCours MA Private EquityOmar MechyakhaNo ratings yet
- M&a BasicsDocument26 pagesM&a BasicsSpace MuskNo ratings yet
- Acquisitions: MergersDocument78 pagesAcquisitions: Mergersakhil reddy kalvaNo ratings yet
- Small-Cap Investor Activism in Canada and Crescendo Partners - Nov 2010Document29 pagesSmall-Cap Investor Activism in Canada and Crescendo Partners - Nov 2010davidjlNo ratings yet
- Corporate Restructuring 2014Document19 pagesCorporate Restructuring 2014manish9890No ratings yet
- 501ppt Strategy For Merger and AcquisitionDocument31 pages501ppt Strategy For Merger and AcquisitionJitender ThakurNo ratings yet
- History of Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument23 pagesHistory of Mergers and AcquisitionsZeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Chpater 6Document34 pagesChpater 6starshine.jimenezNo ratings yet
- Chpater-6 2Document27 pagesChpater-6 2starshine.jimenezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Management Pt. 1: Prepared By: Erica B. EvangelistaDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Financial Management Pt. 1: Prepared By: Erica B. EvangelistaKarl Adrian PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage and Capital Allocation - Dorsey Asset Management 1Document30 pagesCompetitive Advantage and Capital Allocation - Dorsey Asset Management 1bsaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Corporate RestructuringDocument18 pagesCorporate Restructuringbhavya_bajaj968No ratings yet
- SM CH - 2Document23 pagesSM CH - 2Thë FähãdNo ratings yet
- Business Finance - Lesson 1Document49 pagesBusiness Finance - Lesson 1joesNo ratings yet
- Chap1 StratMgmt PPDocument31 pagesChap1 StratMgmt PPmohasacaliNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Acquisition and Restructuring StrategiesDocument20 pagesCH 7 Acquisition and Restructuring Strategiesbk gautamNo ratings yet
- Growth Through Acquisition (Anslinger Copeland)Document15 pagesGrowth Through Acquisition (Anslinger Copeland)Andre Bigo100% (1)
- Introduction To Mergers and AcquisitionDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Mergers and AcquisitionBishop SinghNo ratings yet
- Acquisition and Restructuring StrategiesDocument20 pagesAcquisition and Restructuring Strategiespolaris2184No ratings yet
- wxvX1zXpQ1eBenF4P20l HAMISH S STOCK ANALYSIS CHECKLISTDocument6 pageswxvX1zXpQ1eBenF4P20l HAMISH S STOCK ANALYSIS CHECKLISTAndy NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Goals of The Firm - 6Document21 pagesGoals of The Firm - 6Dhruv SoodNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis & Valuation: Using Financial StatementsDocument67 pagesBusiness Analysis & Valuation: Using Financial StatementsVan-Hu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Turnaround ManagementDocument29 pagesTurnaround ManagementNeha KalloliNo ratings yet
- Arnaud Ajdler Investing in ChangeDocument44 pagesArnaud Ajdler Investing in ChangeValueWalk100% (5)
- Week 7 Lecture Notes-1-1Document48 pagesWeek 7 Lecture Notes-1-1Hamada BakheetNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument3 pagesSynopsisRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mergers & AcquisitionDocument25 pagesMergers & AcquisitionBharath Pavanje100% (1)
- Mergers & Acquisitions KSLUDocument51 pagesMergers & Acquisitions KSLUHans TalawarNo ratings yet
- Corporate Restructuring: Prof Ashish K MitraDocument18 pagesCorporate Restructuring: Prof Ashish K MitraSanchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- SM UNIT - IIIBDocument11 pagesSM UNIT - IIIBrammohan33No ratings yet
- Business Finance NotesDocument6 pagesBusiness Finance Notesclaire juarezNo ratings yet
- Mit Sloan Investment Conference Competitive Advantage and Capital Allocation Dorsey Asset Management March 2017Document30 pagesMit Sloan Investment Conference Competitive Advantage and Capital Allocation Dorsey Asset Management March 2017JeffStelling1No ratings yet
- Theories in Merger and AcquisitionDocument123 pagesTheories in Merger and Acquisitiongoel76vishal100% (3)
- Lessons from Private Equity Any Company Can UseFrom EverandLessons from Private Equity Any Company Can UseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Electives Term 5&6Document28 pagesElectives Term 5&6GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- SESSION 4. Role of People in ServicesDocument58 pagesSESSION 4. Role of People in ServicesGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation at Brazilian Retailer Magazine: Presented By: Group A5Document7 pagesDigital Transformation at Brazilian Retailer Magazine: Presented By: Group A5GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Summary Part 2Document1 pageSummary Part 2GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Wawa: Retailing Reinvented Through Blue Ocean StrategyDocument6 pagesWawa: Retailing Reinvented Through Blue Ocean StrategyGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- AIG (American International Group)Document24 pagesAIG (American International Group)GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- International Business Assignment # 2 August 2020Document2 pagesInternational Business Assignment # 2 August 2020GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Session 17 ADocument48 pagesSession 17 AGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- CSR Activities at Wipro: Group 3Document6 pagesCSR Activities at Wipro: Group 3GaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Identifying Affluent Tehsils in Rural India Approach To The ProjectDocument76 pagesIdentifying Affluent Tehsils in Rural India Approach To The ProjectGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Case Solution: Dear Diary: My Heart Is Racing To Buy A CarDocument2 pagesCase Solution: Dear Diary: My Heart Is Racing To Buy A CarGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- Vigilance Week PosterDocument1 pageVigilance Week PosterGaneshRathodNo ratings yet
- The Holy Rosary 2Document14 pagesThe Holy Rosary 2Carmilita Mi AmoreNo ratings yet
- Actividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.Document4 pagesActividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.jamesNo ratings yet
- 2020 Rattlers Fall Sports ProgramDocument48 pages2020 Rattlers Fall Sports ProgramAna CosinoNo ratings yet
- La Bugal BLaan Tribal Association Inc. vs. RamosDocument62 pagesLa Bugal BLaan Tribal Association Inc. vs. RamosAKnownKneeMouseeNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Salford Estates (No. 2) Limited V AltoMart LimitedDocument2 pagesCase Report On Salford Estates (No. 2) Limited V AltoMart LimitedIqbal MohammedNo ratings yet
- Specific Relief Act, 1963Document23 pagesSpecific Relief Act, 1963Saahiel Sharrma0% (1)
- Retail Strategy: MarketingDocument14 pagesRetail Strategy: MarketingANVESHI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Solar - Bhanu Solar - Company ProfileDocument9 pagesSolar - Bhanu Solar - Company ProfileRaja Gopal Rao VishnudasNo ratings yet
- Account Number:: Rate: Date Prepared: RS-Residential ServiceDocument4 pagesAccount Number:: Rate: Date Prepared: RS-Residential ServiceAhsan ShabirNo ratings yet
- Anglais OverconsumptionDocument3 pagesAnglais OverconsumptionAnas HoussiniNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire of Personal and Organizational Values Congruence For Employee (Q-POVC-115)Document6 pagesQuestionnaire of Personal and Organizational Values Congruence For Employee (Q-POVC-115)Kowshik SNo ratings yet
- Principles of Natural JusticeDocument20 pagesPrinciples of Natural JusticeHeracles PegasusNo ratings yet
- ,وثيقة تعارفDocument3 pages,وثيقة تعارفAyman DarwishNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: The Entrepreneur, The Individual That SteersDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship: The Entrepreneur, The Individual That SteersJohn Paulo Sayo0% (1)
- PDF Issue 1 PDFDocument128 pagesPDF Issue 1 PDFfabrignani@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Hatch Waxman Act OverviewDocument7 pagesHatch Waxman Act OverviewPallavi PriyadarsiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Study GuidejoeNo ratings yet
- CTC VoucherDocument56 pagesCTC VoucherJames Hydoe ElanNo ratings yet
- Iraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Document29 pagesIraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Beatriz RosenburgNo ratings yet
- Module 2 2023Document14 pagesModule 2 2023ubpi eswlNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet: Unit Test Study GuideDocument8 pagesRomeo and Juliet: Unit Test Study GuideKate Ramey100% (7)
- Impact of Money Supply On Economic Growth of BangladeshDocument9 pagesImpact of Money Supply On Economic Growth of BangladeshSarabul Islam Sajbir100% (2)
- Lord Chief Justice Speech On Jury TrialsDocument10 pagesLord Chief Justice Speech On Jury TrialsThe GuardianNo ratings yet
- Inversion in Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesInversion in Conditional SentencesAgnieszka M. ZłotkowskaNo ratings yet
- OECD - AI Workgroup (2022)Document4 pagesOECD - AI Workgroup (2022)Pam BlueNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Document4 pagesFlipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Giri KanyakumariNo ratings yet
- The Giver Quiz 7-8Document2 pagesThe Giver Quiz 7-8roxanaietiNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Inderstanding Ups and GoldcoastDocument3 pagesMemorandum of Inderstanding Ups and Goldcoastred_21No ratings yet
- Basic Priciples of GuidanceDocument6 pagesBasic Priciples of GuidanceRuth ApriliaNo ratings yet
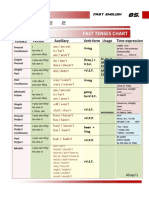
- Table 2: Fast Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesTable 2: Fast Tenses ChartAngel Julian HernandezNo ratings yet