Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Desire For Reputation or Respect From Others (E.g., Status, Prestige) - Maslow Indicated That
Uploaded by
Jobelle Acena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesOriginal Title
SPIRITUAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThe Desire For Reputation or Respect From Others (E.g., Status, Prestige) - Maslow Indicated That
Uploaded by
Jobelle AcenaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
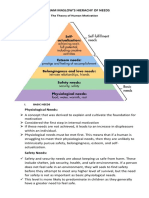
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a
motivational theory in psychology
comprising a five-tier model of human
needs, often depicted as hierarchical
levels within a pyramid.
Needs lower down in the hierarchy
must be satisfied before individuals
can attend to needs higher up. From
the bottom of the hierarchy upwards,
the needs are: physiological, safety,
love and belonging, esteem, and self-
actualization.
Maslow (1943, 1954) stated that
people are motivated to achieve
certain needs and that some needs take precedence over others.
Our most basic need is for physical survival, and this will be the first thing that motivates our
behaviour. Once that level is fulfilled the next level up is what motivates us, and so on.
1. Physiological needs - these are biological requirements for human survival, e.g. air, food,
drink, shelter, clothing, warmth, sex, sleep. If these needs are not satisfied the human body
cannot function optimally. Maslow considered physiological needs the most important as all the
other needs become secondary until these needs are met.
2. Safety needs - Once an individual’s physiological needs are satisfied, the needs for security
and safety become salient. People want to experience order, predictability and control in their
lives. These needs can be fulfilled by the family and society (e.g. police, schools, business and
medical care). For example, emotional security, financial security (e.g. employment, social
welfare), law and order, freedom from fear social stability, property, health and wellbeing (e.g.
safety against accidents and injury).
3. Love and belongingness needs - after physiological and safety needs have been fulfilled; the
third level of human needs is social and involves feelings of belongingness. The need for
interpersonal relationships motivates behaviour. Examples include friendship, intimacy, trust,
and acceptance, receiving and giving affection and love. Affiliating, being part of a group
(family, friends, work).
4. Esteem needs are the fourth level in Maslow’s hierarchy - which Maslow classified into
two categories: (i) esteem for oneself (dignity, achievement, mastery, independence) and (ii)
the desire for reputation or respect from others (e.g., status, prestige). Maslow indicated that
the need for respect or reputation is most important for children and adolescents and precedes
real self-esteem or dignity.
5. Self-actualization needs are the highest level in Maslow's hierarchy, and refer to the
realization of a person's potential, self-fulfilment, seeking personal growth and peak
experiences. Maslow (1943) describes this level as the desire to accomplish everything that one
can, to become the most that one can be. Individuals may perceive or focus on this need very
specifically. For example, one individual may have a strong desire to become an ideal parent. In
another, the desire may be expressed economically, academically or athletically. For others, it
may be expressed creatively, in paintings, pictures, or inventions.
SELF-ACTUALIZATION
Activities Objectives Strategies
Arts and crafts A creative outlet such as Watercolour painting outdoors or a knitting
art or crafts allows workshop to create scarves. Or take
participants to channel inspiration from your event’s surroundings
their energy into a and use nature to make art!
gratifying end result.
Sports Fest To showcase their talents Open for everyone who wants to express or
and to boost their self- display their talents.
confidence.
ESTEEM NEEDS
Activities Objectives Strategies
Beauty Pageants To empower people Open for everyone who wants to share their
through education by opinions and talents.
participating in charity
work therefore building
social awareness and
responsibility amongst
them.
Talent To showcase their talents Open for everyone who wants to express or
Competitions and to boost their self- display their talents.
confidence.
LOVE AND BELONGINGNESS NEEDS
Activities Objectives Strategies
Family Day To give family members Planning for different games that each family
and their children a could participate.
chance to celebrate the
meaning of being a
family and to spend
quality time with their
loved ones by
participating in fun
activities together.
SAFETY NEEDS
Activities Objectives Strategies
Medical missions To improve access to Free check-ups and medicines.
quality health care for the
homeless population by
providing direct,
continuous medical care
on the streets. To
promote health literacy,
healthier lifestyles, and
general well-being.
PHYSIOLOGIC NEEDS
Activities Objectives Strategies
Feeding Programs To reduce child hunger Selected barangay who has more cases of
or Outreach and improve child malnutrition is the target participants of this
programs nutrition. program.
Health teaching
Reference
https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html#needs5
You might also like
- The No B.S. Guide To Anterior Pelvic Tilt: In-Depth Assessment and 6-Week ProgramDocument39 pagesThe No B.S. Guide To Anterior Pelvic Tilt: In-Depth Assessment and 6-Week ProgramKosar83% (6)
- Case Study (Lung Cancer)Document17 pagesCase Study (Lung Cancer)Jobelle Acena100% (1)
- Advanced German Volume Training - Week 1Document9 pagesAdvanced German Volume Training - Week 1tactoucNo ratings yet
- Shaolin 18 Lohan HandsDocument9 pagesShaolin 18 Lohan HandsHero Gmr JonesNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Certify Baby'S Birth: Body TemperatureDocument9 pagesCertify Baby'S Birth: Body TemperatureJobelle Acena100% (1)
- Anti Psychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugscalfornianursingacadNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests PDFDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Tests PDFBenedict AlvarezNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument39 pagesMotivationnavin_tiwari_king100% (1)
- Geriatric Case StudyDocument15 pagesGeriatric Case StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Self-Determination Theory and The Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development and Well-BeingDocument11 pagesSelf-Determination Theory and The Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development and Well-BeingIsabelGuijarroMartinezNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Heirarchy of NeedsDocument4 pagesMaslow's Heirarchy of Needsnolan ryan alas-asNo ratings yet
- Case Study (ACS)Document12 pagesCase Study (ACS)Kristel Joy Cabarrubias Acena100% (1)
- Bioethics in Nursing Practice PDFDocument5 pagesBioethics in Nursing Practice PDFVhinny Macabontoc100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Grade 8 - P.E PPT (Week 1)Document30 pagesGrade 8 - P.E PPT (Week 1)Dave Sedigo100% (1)
- Neurophysiological Effects of Spinal ManipulationDocument15 pagesNeurophysiological Effects of Spinal ManipulationBojan AnticNo ratings yet
- Bed Making LectureDocument13 pagesBed Making LectureYnaffit Alteza Untal67% (3)
- Notes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Document22 pagesNotes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Jobelle Acena100% (1)
- ER Protocols in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesER Protocols in The PhilippinesJobelle Acena100% (1)
- Intrinsic MotivationDocument3 pagesIntrinsic MotivationdeenaismeehNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeDocument10 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Plan On Ncm-105 Psyhciatric NursingDocument13 pagesClinical Teaching Plan On Ncm-105 Psyhciatric NursingHazel RoseNo ratings yet
- Maslows Hierarchy of NeedsDocument13 pagesMaslows Hierarchy of NeedsNore Jane Parangue VillameroNo ratings yet
- Levels of Needs Motivation & BehaviorDocument5 pagesLevels of Needs Motivation & BehaviorDehajNo ratings yet
- Goal Theory - Reward & MotivationDocument2 pagesGoal Theory - Reward & Motivationkerang73No ratings yet
- "Molding Minds, Shaping Future": College of Public SafetyDocument22 pages"Molding Minds, Shaping Future": College of Public SafetyLeif SarmuyanNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Theory of Motivation - Hierarchy of NeedsDocument5 pagesMaslow's Theory of Motivation - Hierarchy of NeedsVinay NayakNo ratings yet
- Dlp1 Leadership Managemet Research Downloadable Ozawa Mariko Ann D. Au LegardaDocument6 pagesDlp1 Leadership Managemet Research Downloadable Ozawa Mariko Ann D. Au LegardaRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Maslows Hierarchy of NeedsDocument16 pagesMaslows Hierarchy of NeedsRam RamNo ratings yet
- 3 Joharis WindowDocument35 pages3 Joharis WindowPurbasha RoyNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument31 pagesMotivationIanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 11 - Week 4 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument10 pagesMODULE 11 - Week 4 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarsha MGNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Week 3-4Document13 pagesPersonal Development Week 3-4Edilene Rosallosa CruzatNo ratings yet
- Concept TheoriesDocument19 pagesConcept TheoriesGwendie Kaye GallardeNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy Theory: Needs), and The Top Level Is Known As Growth or Being Needs (B-Needs)Document12 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy Theory: Needs), and The Top Level Is Known As Growth or Being Needs (B-Needs)Suresh Kutty MNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow Pyramid of NeedsDocument1 pageAbraham Maslow Pyramid of NeedsZarida ArabainNo ratings yet
- HM AssigmentDocument19 pagesHM AssigmentZainab ImranNo ratings yet
- I MBA - II SEM - Soft Skills MotivationDocument3 pagesI MBA - II SEM - Soft Skills MotivationShaik Khalid 1234No ratings yet
- Dr. Sakshi Yadav - OBDocument10 pagesDr. Sakshi Yadav - OBSakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Physiological Needs - : Examples: - Air, Food, Drink, Shelter, Clothing, Warmth, Sex, SleepDocument2 pagesPhysiological Needs - : Examples: - Air, Food, Drink, Shelter, Clothing, Warmth, Sex, SleepKayes Mohammad Bin HossainNo ratings yet
- Group No - 07 - 20231117 - 022723 - 0000Document31 pagesGroup No - 07 - 20231117 - 022723 - 0000Mitali RoyNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter 123Document20 pagesResearch Chapter 123castro816761No ratings yet
- MASLOW'S Hierarchy of NeedsDocument2 pagesMASLOW'S Hierarchy of NeedsDavis TreyNo ratings yet
- 7.analyze The Importance of Abhraham Maslows Heirarchical TheoryDocument50 pages7.analyze The Importance of Abhraham Maslows Heirarchical TheoryAswathiNo ratings yet
- Theories Relevant To Nursing PracticeDocument51 pagesTheories Relevant To Nursing PracticeTRISHA MAE JOY ABAYONNo ratings yet
- Research in Psychology: Hierarchy of Human Needs"Document5 pagesResearch in Psychology: Hierarchy of Human Needs"Foxtrot DeltaNo ratings yet
- Basic Human NeedsDocument25 pagesBasic Human Needsenam professorNo ratings yet
- Pdev Lesson 3 Humanistic and Cognitive TheoryDocument21 pagesPdev Lesson 3 Humanistic and Cognitive TheoryMavNo ratings yet
- Learning To Do, Learning To Live Together and Learning To Be. Learning To Know by Combing A Sufficiently Broad Genera. Knowledge With The Opportunity To Work in Depth On Small Number of SubjectsDocument2 pagesLearning To Do, Learning To Live Together and Learning To Be. Learning To Know by Combing A Sufficiently Broad Genera. Knowledge With The Opportunity To Work in Depth On Small Number of SubjectsrubelynNo ratings yet
- Funda LectureDocument12 pagesFunda LectureWeng RamojalNo ratings yet
- 8 Basic NeedsDocument1 page8 Basic NeedsIamCcjNo ratings yet
- 4 - Theories of Behaviour ModificationDocument24 pages4 - Theories of Behaviour ModificationMahmoud KhalafNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Motivation: Riflan AhamedDocument10 pagesThe Theory of Motivation: Riflan AhamedAhamed ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Maslow Theory of Need Hierarchy: Presented By:-Mahendra Singh GarvaDocument23 pagesMotivation and Maslow Theory of Need Hierarchy: Presented By:-Mahendra Singh GarvamsgarwaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior - Module 3Document16 pagesConsumer Behavior - Module 3Dr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD GNo ratings yet
- HDPDDocument5 pagesHDPDAva Marie Lampad - CantaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 RLSD171 MASHUPYE M.LDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 RLSD171 MASHUPYE M.LbradfordNo ratings yet
- Psychology Assignment 3Document7 pagesPsychology Assignment 3Malaika ZubairNo ratings yet
- Part I. The Communication ProcessDocument6 pagesPart I. The Communication ProcessJonard FloresNo ratings yet
- Maslows Theory of Human Needs Transcript Additional NotesDocument3 pagesMaslows Theory of Human Needs Transcript Additional Notesrainbow. dreamzzNo ratings yet
- TFN (Week 12)Document38 pagesTFN (Week 12)Erica VelascoNo ratings yet
- Self-Determination Theory and The Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-BeingDocument14 pagesSelf-Determination Theory and The Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Beingjayson cajateNo ratings yet
- Lecture 42Document19 pagesLecture 42faisal waleedNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument11 pagesMaslowSehrishKhanNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs - Forensic PsychologyDocument14 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs - Forensic Psychologyvedika.uniNo ratings yet
- Holistic-Dynamic Theory: Hierarchy of NeedsDocument8 pagesHolistic-Dynamic Theory: Hierarchy of NeedsKenNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self LectureDocument54 pagesUnderstanding The Self LectureSARAH JANE CAPSANo ratings yet
- Psy1306 Sec3 Group-7 Mental-Health-PlanDocument13 pagesPsy1306 Sec3 Group-7 Mental-Health-Planhoneymae MiduraNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approach and ST Thomas AquinasDocument90 pagesHumanistic Approach and ST Thomas Aquinasmaylene marquezNo ratings yet
- Motivation Skills Dr. PoonamDocument67 pagesMotivation Skills Dr. PoonamJaibihari SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3Document10 pagesChapter - 3yugendran kumarNo ratings yet
- Assessment EthicsDocument7 pagesAssessment EthicsArturo MortelNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument4 pagesOutlineJayson IsidroNo ratings yet
- ALFRED ADLER - Week 4Document38 pagesALFRED ADLER - Week 4ruveydasatioglu02No ratings yet
- Personality 3Document36 pagesPersonality 3nonameNo ratings yet
- Self Determination TheoryDocument11 pagesSelf Determination TheorymarialeoyolagNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case StudyDocument21 pagesPediatric Case StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 SY 2020-2021: Legal and Ethical Consideration of Euthanasia in India: A Choice Between Life and DeathDocument8 pagesNCM 107 SY 2020-2021: Legal and Ethical Consideration of Euthanasia in India: A Choice Between Life and DeathJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Date/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeDocument2 pagesDate/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- GC ncp1Document2 pagesGC ncp1Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEDocument4 pagesNCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Union Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionDocument11 pagesUnion Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- GC ncp1 and 2Document4 pagesGC ncp1 and 2Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Online LectureDocument9 pagesOnline LectureJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Normal Cell GrowthDocument5 pagesNormal Cell GrowthJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument11 pagesNCPsJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- PHARMAfdDocument7 pagesPHARMAfdJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mechanism of Action of Cell Mediated Immune System and Humoral Mediated Immune SystemDocument4 pagesDifference Between Mechanism of Action of Cell Mediated Immune System and Humoral Mediated Immune SystemJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Er Drugs StudyDocument80 pagesEr Drugs StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing: Core Values of NursingDocument14 pagesNursing: Core Values of NursingJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Letter To ProfessorDocument3 pagesLetter To ProfessorAlannaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science and Technology InnovationDocument7 pagesPhilippine Science and Technology Innovationgabosara298No ratings yet
- Receiving and Storage PDFDocument12 pagesReceiving and Storage PDFshyamkattiNo ratings yet
- MMDSTDocument4 pagesMMDSTJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- Glycerol MsdsDocument6 pagesGlycerol MsdsJX Lim0% (1)
- L TyrosineDocument6 pagesL TyrosinecpullerNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics-AAP Guideline To SedationDocument18 pagesPediatrics-AAP Guideline To SedationMarcus, RNNo ratings yet
- AnsdDocument12 pagesAnsdAlok PandeyNo ratings yet
- Varma Practictioner GuideDocument9 pagesVarma Practictioner GuideGoutham PillaiNo ratings yet
- 12 2012 TriclabendazoleDocument16 pages12 2012 Triclabendazolenia suwartiningsihNo ratings yet
- Ramsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItDocument10 pagesRamsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItAdinda Putra PradhanaNo ratings yet
- LNG Hazards and SafetyDocument60 pagesLNG Hazards and SafetyFernando GrandaNo ratings yet
- Phytophthora InfestansDocument10 pagesPhytophthora Infestansvas2000No ratings yet
- H. Pylori IgA ELISA Package InsertDocument2 pagesH. Pylori IgA ELISA Package Inserttalha saleemNo ratings yet
- AICTE CorporateBestPracticesDocument13 pagesAICTE CorporateBestPracticesramar MNo ratings yet
- Working in A Lab Risk & AssessmentDocument10 pagesWorking in A Lab Risk & AssessmentMariam KhanNo ratings yet
- BECKER, Howard. Marihuana Use and Social ControlDocument11 pagesBECKER, Howard. Marihuana Use and Social ControlDanFernandes90No ratings yet
- Urbanization and HealthDocument2 pagesUrbanization and HealthsachiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis EssayDocument8 pagesSynthesis EssayWardah FarukNo ratings yet
- Essay 25.01.2021Document2 pagesEssay 25.01.2021Uyen TranNo ratings yet
- HSCA Vol10 RoseCheramieDocument9 pagesHSCA Vol10 RoseCheramiekanashane4794No ratings yet
- Estimation of Blood GlucoseDocument3 pagesEstimation of Blood Glucosepodcast gazalNo ratings yet
- Etp fOR Dasda PDFDocument6 pagesEtp fOR Dasda PDFDesignNo ratings yet