Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial of Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters in Discontinuous Mode (Benny Yeung) PDF
Tutorial of Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters in Discontinuous Mode (Benny Yeung) PDF
Uploaded by
Yimy GarciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial of Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters in Discontinuous Mode (Benny Yeung) PDF
Tutorial of Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters in Discontinuous Mode (Benny Yeung) PDF
Uploaded by
Yimy GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
THE HONG KONG
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY_________________________________________________ ___
Department of Electrical Engineering
TUTORIAL OF NON-ISOLATED DC/DC CONVERTERS
IN DISCONTINUOUS MODE
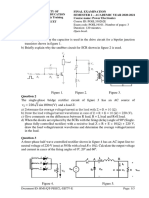
(1) Fig. Q1 represents a circuit diagram of
buck converter. It is driven by a
constant input voltage 50V. Switching
frequency is 20kHz. Inductance L and
load resistance R of the converter are
2mH and 200Ω, respectively. Assuming
the diode and the transistor of the
converters are ideal and output filtering
capacitor is large enough. Fig. Q1
(a) Select the right components for 1, 2, and 3 items 1 2 3
from the choices of A, B and C as shown in Fig. T
D L
Q1 (a). A
(b) Evaluate the duty ratio D when the buck
converter operates at the boundary condition T
L D
between continuous and discontinuous modes. B
(c) Calculate the average current of the load resistor
Io when the duty ratio D = 0.4. T
L D
C
(d) Draw the waveforms of iL, vT and iD of the
above condition with detailed parameters for the Fig. Q1 (a)
X-axis (time).
(e) If the duty ratio D is 0.2, evaluate the minimum
inductance of L to maintain continuous mode
operation while all other parameters remain the
same.
ANS:
(a) C
2L 2 (2m)
(b) K 0.4
RTs 200 (1 / 20k )
Since the boundary condition of a buck converter is:
K 1 D , hence,
D 0.6
(c) When D = 0.4, K 1 D . The buck converter is operating in discontinuous mode. The
Vo 2 2 2
0.4633
Vin 1 1 4 K / D 2 1 1 [( 4 0.4) / 0.4 2 ] 1 11
Vo 0.4633Vin 23.165V
I o Vo / R 115.82mA
EE4211 Advanced Power Electronics Page 1
THE HONG KONG
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY_________________________________________________ ___
Department of Electrical Engineering
(Vin Vo ) D
(d) 0.4634
Vo
DTs 20ms, Ts 23.17ms, (1 D )Ts 6.83ms
23.17ms
20ms 6.83ms
(e) In boundary condition,
2L
K min 1 D
RTs
(1 D ) RTs (1 0.2) 200
Lmin 4mH
2 2(20k )
EE4211 Advanced Power Electronics Page 2
THE HONG KONG
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY_________________________________________________ ___
Department of Electrical Engineering
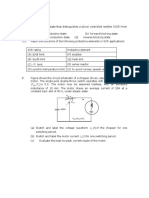
(2) A boost converter as shown in Fig. Q2 (a) vL iL vD iD
operates at 100kHz switching frequency with the
L D
resistance of the load R = 1kΩ. Fig Q2 (b) show iC
a graph of the voltage conversion ratio Vo/Vin (Y- +
+
Vin T vT C R Vo
axis) of the converter as duty ratio of the gate -
signal D (X-axis) varies from 0.5 to 0.8 while iT
the curve changes its shape when D is 0.6.
Fig. Q2 (a)
Fig. Q2 (b)
(a) Based on the information from the graph, evaluate the value of L.
(b) Calculate the value of Vo/Vin when D=0.5 and 0.7 respectively.
(c) If the value of R increases slightly, describe the change of the Vo/Vin curve in the graph, draw
the new curve roughly, and explain the change of the curve.
ANS:
(a) According to Fig. Q2, boundary condition is at the duty ratio of the gate signal D = 0.6. For boundary
condition:
2L
K D(1 D) 2
RTs
RTs D(1 D) 2 (1000)(0.6)(1 0.6) 2
L
2 2(100k )
L 480H
(b) When D = 0.5, the boost converter operates in discontinuous mode. Voltage conversion ratio is:
Vo 1 1 4 D 2 / K 1 1 (4)(0.52 ) / 0.096
2.1894
Vin 2 2
When D=0.7, the boost converter operates in continuous mode. Voltage conversion ratio is:
Vo 1
3.3333
Vin 1 D
EE4211 Advanced Power Electronics Page 3
THE HONG KONG
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY_________________________________________________ ___
Department of Electrical Engineering
(c) K is slightly smaller when R slightly higher. The duty ratio of the gate signal for boundary condition
is changed from 0.6 to a higher ratio. From the equation of voltage conversion ratio of the converter
in discontinuous mode, the voltage conversion ratio is higher while R is higher. In continuous mode,
the voltage conversion ration remains unchanged while K or R is changed because the output voltage
is load independent and is no effect from the value of TS or L.
In short, when R is higher, the duty ratio of boundary condition is higher and the voltage conversion
ratio is higher until the new curve aligns the original curve. The revised curve of voltage conversion
ratio (Y-axis) vs duty ratio of the gate signal (X-axis) is:
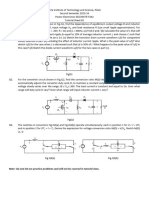
(3) A non-isolated single-inductor hard-switching DC/DC converter generates a range of output
voltage from 8V to 15V in continuous mode. Its input voltage is 12V.
(a) Suggest a topology for this DC/DC conversion. Sketch the circuit diagram of the suggested
circuit. Mark the polarity of the output voltage in the circuit diagram.
(b) Evaluate the duty ratios of the gate signal for generating 8V and 18V output voltage,
respectively.
(c) Calculate the minimum inductance of the inductor of the suggested converter for the same
condition of operation when the switching frequency is 1kHz and the resistance of the load is
1Ω.
(d) With the calculated minimum inductance and the specification of the converter in (c), calculate
the output voltage of the converter when the duty ratio of the gate signal is 0.1.
ANS:
(a) Buck-boost converter is suggested. The output voltage is inversed.
vT i vD i
T D
D
+ T L vL
Vin - C R Vo
+
iL iC
EE4211 Advanced Power Electronics Page 4
THE HONG KONG
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY_________________________________________________ ___
Department of Electrical Engineering
(b) Voltage conversion ratio of a buck-boost converter in continuous mode is:
Vo D Vo
D
Vin 1 D Vin Vo
For output voltage is 8V, the duty ratio of the gate signal is:
8
D8V 0.4
12 8
For output voltage is 18V, the duty ratio of the gate signal is:
18
D15V 0.6
12 18
(c) For continuous mode,
2L
K (1 D) 2
RTS
The duty ratio of the gate is the lowest when the output voltage is 8V in the range of the output voltage,
2L
(1 D8V ) 2
RTS
R (1 D8V ) 2 (1)(1 0.4) 2
L
2 fS 2(1k )
L 180 H Lmin 180 H
(d) With the specification of (c) and L = 180µH, the converter is in discontinuous mode while D = 0.1.
Hence the output conversion ratio is:
Vo D 2 L (2)(180 )(1k )
where K 0.36
Vin K RTS (1)
(0.1)(12)
Vo 2V
0.36
EE4211 Advanced Power Electronics Page 5
You might also like
- Probs CH 2Document2 pagesProbs CH 2Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- GATE (1991-2010) Solved Papers EEDocument261 pagesGATE (1991-2010) Solved Papers EEqwer0% (1)
- PDFDocument25 pagesPDFDEEPIKA PANTNo ratings yet
- T S Ia SDocument7 pagesT S Ia S1nshsankritNo ratings yet
- Classical DCDocument27 pagesClassical DCPierre Jean SichonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)Document8 pagesChapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)dummymail6383No ratings yet
- Aris 01Document8 pagesAris 01zaid aihsanNo ratings yet
- S D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PDocument5 pagesS D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PPankajSinghBhatiNo ratings yet
- 02 - Alternating Current - QuestionDocument5 pages02 - Alternating Current - Questionbest badmintonNo ratings yet
- Ee270 HW2Document7 pagesEe270 HW2saiedali2005No ratings yet
- Eee F342 T2Document1 pageEee F342 T2f20212653No ratings yet
- Dual Feed Forward ControlDocument6 pagesDual Feed Forward ControlSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Pe Chapter 6 DC Ac 1Document32 pagesPe Chapter 6 DC Ac 1Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Diode Bridge Rectifier With Improved Power Quality Using Capacitive NetworkDocument6 pagesDiode Bridge Rectifier With Improved Power Quality Using Capacitive NetworkShashi ShekharNo ratings yet
- H.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inDocument8 pagesH.O. 92, Rajeev Gandhi Nagar, Kota (Raj.) Mob. 97831-97831, 70732-22177, Ph. 0744-2423333 WWW - Nucleuseducation.inB AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 200809Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 1 200809Kung ChinHanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Part ADocument13 pagesLecture 4 Part AAbd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PDFDocument41 pagesPower Electronics PDFAnand KalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04 Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesAssignment 04 Power ElectronicsTayyab Hussain0% (1)
- A Novel Loss Estimation Technique For Power ConverDocument7 pagesA Novel Loss Estimation Technique For Power ConverSridhar MNo ratings yet
- QUT Digital Repository:: Conference (IPEC 2007), Pages Pp. 661-665, SingaporeDocument6 pagesQUT Digital Repository:: Conference (IPEC 2007), Pages Pp. 661-665, SingaporeSheetal VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 3: Isolated ConverterDocument28 pagesChapter 2 - Part 3: Isolated ConverterWeehao SiowNo ratings yet
- PT 1Document5 pagesPT 1Karthik BolluNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis Bi-Directional DC-DC Converters: of Non-IsolatedDocument6 pagesA Comparative Analysis Bi-Directional DC-DC Converters: of Non-IsolatedTeam RaagNo ratings yet
- EE254: D2 Buck ConverterDocument13 pagesEE254: D2 Buck ConverterNeil Hildick-SmithNo ratings yet
- Interleaved Boost Converter For Photovoltaic Power-GenerationDocument11 pagesInterleaved Boost Converter For Photovoltaic Power-GenerationRihab HamdiNo ratings yet
- Eee 513 Lecture Module IiDocument30 pagesEee 513 Lecture Module Iistephenhuncho22No ratings yet
- Class Test 2 Question PaperDocument1 pageClass Test 2 Question Paperbrahma2deen2chaudharNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Measure Volt AmpDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Measure Volt AmpShreyes GedamNo ratings yet
- Exam - EC3032 Power Electronics 2019Document6 pagesExam - EC3032 Power Electronics 2019sadeepa sooriyaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 PDFDocument23 pagesLecture 01 PDFAbd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Set A1880Document16 pagesApgenco Set A1880Srimannarayana NandamNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction With Boost Rectifier: I J A R E E I EDocument15 pagesPower Factor Correction With Boost Rectifier: I J A R E E I EtejaNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004Mohd ShanuNo ratings yet
- BUCK and BoostDocument8 pagesBUCK and Boostkingsuk majumdarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Steady-State Converter Analysis: (T) As Illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The Voltage V (T) Is Equal ToDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Steady-State Converter Analysis: (T) As Illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The Voltage V (T) Is Equal ToSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Steady-State Converter Analysis: (T) As Illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The Voltage V (T) Is Equal ToDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Steady-State Converter Analysis: (T) As Illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The Voltage V (T) Is Equal TohassanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 NotesDocument24 pagesCH 2 NotesJahangeer SoomroNo ratings yet
- Polozec, Cockcroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier, Nov. 2016, 10.13140RG.2.2.35788.82564Document9 pagesPolozec, Cockcroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier, Nov. 2016, 10.13140RG.2.2.35788.82564Denis JaissonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayTấn Long Đoàn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- EE 5021: Power Converter Analysis and Design Sept2020-Jan2021 Assignment 3Document3 pagesEE 5021: Power Converter Analysis and Design Sept2020-Jan2021 Assignment 3Raj JhaNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004Pradeepan PoothattaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of D Converter: K. K. Phanisri KruthiventiDocument6 pagesAnalysis of D Converter: K. K. Phanisri KruthiventiTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004hazem ab2009No ratings yet
- Ee Power-Electronics PDFDocument42 pagesEe Power-Electronics PDFPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Spectral Analysis of Buck and Sepic ConvertersDocument7 pagesSpectral Analysis of Buck and Sepic ConvertersMuhammad Kamran MustafaNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Based High Gain DC-DC Boost Converter For Microgrid ApplicationDocument7 pagesFuzzy Logic Based High Gain DC-DC Boost Converter For Microgrid ApplicationNishanthi BheemanNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument51 pagesRectifiersfa21-bee-015100% (1)
- Gate 2015 PDFDocument81 pagesGate 2015 PDFsameer meshramNo ratings yet
- Project On Full Wave Rectifier!Document51 pagesProject On Full Wave Rectifier!Aniket DasNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #1 Basic Converter Analysis Due at 10 Am MDT On Friday, September 7, 2017Document3 pagesHomework Assignment #1 Basic Converter Analysis Due at 10 Am MDT On Friday, September 7, 2017ollata kalanoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Sensor Principles Part 2Document30 pagesLec 4 - Sensor Principles Part 2Mohsin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Review of Power Electronics-Chapter - 6Document17 pagesReview of Power Electronics-Chapter - 6ee mce dataNo ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47Document134 pagesElectronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47dixitratan68No ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter - QuadraticDocument11 pagesDC-DC Converter - Quadraticvasu.jain20022002No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Computer Memories and StorageDocument6 pagesComputer Memories and StorageShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- The AVR Microcontroller and Embedded Systems (PDFDrive)Document118 pagesThe AVR Microcontroller and Embedded Systems (PDFDrive)Shah ZaibNo ratings yet
- Defining Intelligence: Shahzaib ShahDocument2 pagesDefining Intelligence: Shahzaib ShahShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- A4955 DatasheetDocument11 pagesA4955 DatasheetShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheets Complete 2016-17Document6 pagesAssignment Sheets Complete 2016-17Shah ZaibNo ratings yet
- Continuity of ProphethoodDocument11 pagesContinuity of ProphethoodShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- Averaged Switch Modeling,: AC Equivalent Circuit ModelingDocument12 pagesAveraged Switch Modeling,: AC Equivalent Circuit ModelingJulián RincónNo ratings yet
- Implementation of ZVT-ZCT-PWM Boost ConverterDocument87 pagesImplementation of ZVT-ZCT-PWM Boost Converterrajat nimjeNo ratings yet
- A Single Switch Continuous Input Current Buck-Boost Converter With Non-Inverted Output VoltageDocument10 pagesA Single Switch Continuous Input Current Buck-Boost Converter With Non-Inverted Output VoltageSureshkumar AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- Primary-Side Control, Offline LED Controller With Active PFC, NTC and PWM DimmingDocument19 pagesPrimary-Side Control, Offline LED Controller With Active PFC, NTC and PWM Dimmingzuffflor_925748656No ratings yet
- Study On Interleaved Three Switch Buck Boost Converters With Co Directional Coupling InductorDocument11 pagesStudy On Interleaved Three Switch Buck Boost Converters With Co Directional Coupling Inductorbilalshahid2338No ratings yet
- Buck Boost ConverterDocument32 pagesBuck Boost ConverterJanmejay MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Maximum Power Point Tracking For PV ArrayDocument68 pagesMaximum Power Point Tracking For PV ArraySamar El-lethyNo ratings yet
- Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiDocument11 pagesInstitute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiQuratulain AnwarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet HV9910 Universal High Brightness LED DriverDocument11 pagesDatasheet HV9910 Universal High Brightness LED Driverthierry42No ratings yet
- Buck Boost ProjectDocument24 pagesBuck Boost ProjectRonald LugwireNo ratings yet
- Average and Small-Signal Modeling of Self-Oscillating Flyback Converter With Applied Switching DelayDocument8 pagesAverage and Small-Signal Modeling of Self-Oscillating Flyback Converter With Applied Switching DelayMohamed HaddadNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Converters Modeling and ControlDocument8 pagesPower Electronics Converters Modeling and ControlXergio Velarde GomezNo ratings yet
- High-Efficiency, High Step-Up DC-DC ConvertersDocument9 pagesHigh-Efficiency, High Step-Up DC-DC ConvertersC_hakan_CNo ratings yet
- Ece 485 Lect4Document17 pagesEce 485 Lect4saleh almutawaNo ratings yet
- Bridgeless AC-DC Buck-Boost Converter WithDocument5 pagesBridgeless AC-DC Buck-Boost Converter WithJishnu VenugopalNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConverterDocument25 pagesDC DC ConverterpugazhendiraNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage, Ultra-Low IQ Buck-BoostDocument28 pagesLow Voltage, Ultra-Low IQ Buck-BoostRadu MititeluNo ratings yet
- PE AssignmentsDocument11 pagesPE AssignmentsVinayaniv YanivNo ratings yet
- Peres Unit 3Document86 pagesPeres Unit 3ulaganathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - DSPDocument58 pagesChapter 16 - DSPMaira HaiderNo ratings yet
- TPS65133 5-V, 250-Ma Dual-Output Power Supply: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument27 pagesTPS65133 5-V, 250-Ma Dual-Output Power Supply: 1 Features 3 DescriptionCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- C. AppendixDocument20 pagesC. AppendixgechnetNo ratings yet
- CCM To DCM Boundary Conditions: IN OUTDocument25 pagesCCM To DCM Boundary Conditions: IN OUTsree_cyberNo ratings yet
- Sree Sai MahiDocument82 pagesSree Sai MahiKalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- PX4212 4Document2 pagesPX4212 4kalpanaNo ratings yet
- MPPT Project DocumentationDocument115 pagesMPPT Project DocumentationJeferson AraujoNo ratings yet
- Chopper Notes1Document7 pagesChopper Notes1Ruthra DeviNo ratings yet
- 001-15223 AN2344 Power Management Battery Charger With Cell Balancing and Fuel Gauge Function SupportDocument14 pages001-15223 AN2344 Power Management Battery Charger With Cell Balancing and Fuel Gauge Function SupportCONG TRAN NGOCNo ratings yet
- DC dc081113Document70 pagesDC dc081113G.MUTHURAM HICET STAFF EEENo ratings yet
- LNK304 PDFDocument20 pagesLNK304 PDFnourtal2013No ratings yet