Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 10.1: mEIOSIS: Homologous Pairs Meiotic Divisions
Uploaded by
Kaleab GebreegizabiherOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 10.1: mEIOSIS: Homologous Pairs Meiotic Divisions
Uploaded by
Kaleab GebreegizabiherCopyright:
Available Formats
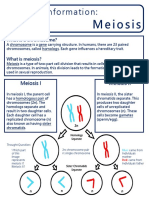
Topic 10.
1: mEIOSIS
Homologous Pairs Meiotic Divisions
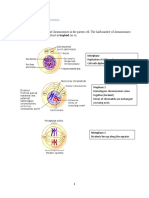
The chromosomes of sexually reproducing organisms Meiosis produces haploid gametes via two nuclear divisions:
are homologous (i.e. they exist in pairs) • Homologous pairs are separated during meiosis I
• There is a paternal copy and a maternal copy • Sister chromatids are separated during meiosis II
(sex chromosomes may not be homologous)
The final outcome of meiosis is four genetically distinct haploid
Chromosomes will replicate during interphase to form daughter cells (i.e. gametes)
genetically identical sister chromatids
• These chromatids are separated during meiotic
division to become autonomous chromosomes
sister
chromatids
homologous
chromosomes Interphase
Meiosis I
chromosome
Meiosis II
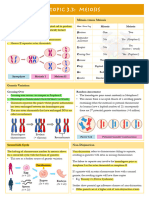
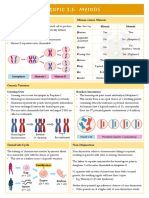
Random Assortment Crossing Over
During Metaphase I, homologous pairs of chromosomes During Prophase I, homologous pairs of chromosomes
line up in a random orientation along the equator form points of connection between non-sister chromatids
This means there is an equal chance of a gamete containing The connection points form via a process known as synapsis
either the maternal or paternal copy of a given chromosome and the resulting complex is called a bivalent (or tetrad)
The orientation of each homologous pair is independent to While in synapsis, non-sister chromatids may break and
the orientation of any other homologous pair recombine with their homologous partner (crossing over)
• Crossing over may result in the exchange of alleles
The number of potential chromosome combinations can be
determined by the formula: 2n (where n = haploid number) The non-sister chromatids remain physically connected at
points of exchange (chiasmata) until separated by anaphase
As humans have a haploid number of 23, they can produce
223 gamete combinations via random assortment
• 223 > 8 million different combinations Recombinants
The non-sister chromatids that have had genetic material
Possibility 1 Possibility 2
exchanged are called recombinants
• Recombination may result in novel allele combinations
Four gamete combinations are possible (2n) Chiasma Recombinants
You might also like
- Effect of Expectation On InterpretationDocument6 pagesEffect of Expectation On InterpretationKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Effect of Expectation On InterpretationDocument6 pagesEffect of Expectation On InterpretationKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Spacecraft Attitude Determination and ControlDocument495 pagesFundamentals of Spacecraft Attitude Determination and ControlCesar86% (7)
- An English Nyanja Dictionary of The Nyanja LanguageDocument253 pagesAn English Nyanja Dictionary of The Nyanja LanguageGarvey Lives100% (1)
- Topic 3.3: mEIOSIS: Mitosis Versus Meiosis MeiosisDocument3 pagesTopic 3.3: mEIOSIS: Mitosis Versus Meiosis Meiosis胡哲菁No ratings yet
- BIO150 CHAPTER 4 PT 3Document10 pagesBIO150 CHAPTER 4 PT 3hanaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocument4 pagesMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663Document20 pagesMeiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663María SalazarNo ratings yet
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument21 pages2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 Genetics HLDocument21 pagesCHP 10 Genetics HLSakthi SNo ratings yet
- 6.3 MeiosisDocument24 pages6.3 MeiosisPratika MNo ratings yet
- 10.1 MeiosisDocument15 pages10.1 MeiosisMrMidoo2020No ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- M1101-ISM-E2-General Embryology - Oocyte Sperm Cell PDF EditDocument48 pagesM1101-ISM-E2-General Embryology - Oocyte Sperm Cell PDF Editkavinduherath2000No ratings yet
- Meiosis 1 130327074711 Phpapp02Document42 pagesMeiosis 1 130327074711 Phpapp02Leigh JilianNo ratings yet
- Biosc 150 Exam 4 Study Guide: Chapter 13: MeiosisDocument23 pagesBiosc 150 Exam 4 Study Guide: Chapter 13: MeiosisKhusbu PatelNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document37 pagesMeiosis 1Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Cell Transp - Cell DiviDocument23 pagesWeek 2 - Cell Transp - Cell Divipilar gabriela hernandez fernandezNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Genetic Variation Pp193-196Document39 pagesMeiosis and Genetic Variation Pp193-196zohaibahmedNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument17 pagesMeiosisSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Fall 2021: Seminar 2: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisDocument24 pagesFall 2021: Seminar 2: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisChanceNo ratings yet
- Meiosis SlidesDocument14 pagesMeiosis SlidesbarsonsNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Sexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesMeiosis: Sexual ReproductionVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument13 pagesMeiosisapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document49 pagesMeiosis 2Rosalyn LucbanNo ratings yet
- Lec 5.3 - Meiosis-BBDocument38 pagesLec 5.3 - Meiosis-BBDuy An VoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanDocument7 pagesChromosomes: Karyotype of A Male HumanKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument113 pagesMeiosisSubhradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- Meiosis SummaryDocument8 pagesMeiosis SummaryShivanshu SiyanwalNo ratings yet
- Meiosis SBI3U1-C1 Revised Further 2022Document44 pagesMeiosis SBI3U1-C1 Revised Further 2022bxyrtbgyxcNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PDFDocument22 pagesMeiosis PDFEbook DownloadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ppt.2014Document48 pagesMeiosis ppt.2014Abdurraouf SaidNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ReductiodivisionDocument55 pagesMeiosis ReductiodivisionJelly Pearl ParzanNo ratings yet
- 3-Rajesh-Meiosis Class On 12th Feb 2013Document35 pages3-Rajesh-Meiosis Class On 12th Feb 2013Kanishk SinghNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument99 pagesLife ScienceDannydiorNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Meiosis NotesDocument3 pagesBio 1 - Meiosis NotesJayson RiveraNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsDocument19 pagesMeiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document38 pagesMeiosis 2RicardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Part2Document32 pagesChapter 8 - Part2Youssef MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Botany Module 3Document6 pagesBotany Module 3Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Division Genetic RecombinationDocument74 pagesReduction-Division Genetic Recombinationeden loredoNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisSachintha JayamahaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 MeiosisDocument1 page3.3 MeiosisMaeva SeneNo ratings yet
- 3.3 MeiosisDocument1 page3.3 MeiosisShannen IbayNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1Document47 pagesMEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1exitlagboysNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument46 pagesMeiosis PowerpointAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: General InformationDocument1 pageMeiosis: General Informationapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Common Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinDocument48 pagesCommon Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinJacky Lam JackyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument67 pagesMeiosisCliff Jhudielle D. CalaguiNo ratings yet
- 02 - MeiosisDocument4 pages02 - MeiosisAXA OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Similar To Mitosis Interphase. S Phase IdenticalDocument22 pagesSimilar To Mitosis Interphase. S Phase IdenticalEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- MeiosiSs Power PointDocument22 pagesMeiosiSs Power PointbanuroNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter 13 NotesDocument5 pagesAP Bio Chapter 13 NotesAndrew SongNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Science Chapter 6: Meiosis: BY: Ms Kasthuri JDocument35 pagesFoundation in Science Chapter 6: Meiosis: BY: Ms Kasthuri JKassyKasNo ratings yet
- DNA in Forensic: by Dr. Tiana MilandaDocument37 pagesDNA in Forensic: by Dr. Tiana MilandaAnnisa Aulia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument1 pageMeiosis and Sexual Life CyclesAChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument39 pagesMeiosisGrachiella JanenNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument27 pagesInheritanceAhmad RamiNo ratings yet
- Idenfity The Resulting Number of Chromosomes For The FollowingDocument58 pagesIdenfity The Resulting Number of Chromosomes For The FollowingLeah SorianoNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument47 pagesMeiosisSyrill PortugalNo ratings yet
- Topic 8.1: Metabolism: Metabolic PathwaysDocument1 pageTopic 8.1: Metabolism: Metabolic PathwaysKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Kaleab Mebratu Biology HomeworkDocument2 pagesKaleab Mebratu Biology HomeworkKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Application Form (Medicine) - 5Document2 pagesApplication Form (Medicine) - 5Kaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Kaleab Mebratu Gebreigziabher: Weep Not ChildDocument1 pageKaleab Mebratu Gebreigziabher: Weep Not ChildKaleab Gebreegizabiher0% (1)
- The Caloric-Kinetic Theory: By: Kaleab Mebratu, Tracy Owusu Aboagye, Francis Akwasi-Kuma, Rachel YamsonDocument6 pagesThe Caloric-Kinetic Theory: By: Kaleab Mebratu, Tracy Owusu Aboagye, Francis Akwasi-Kuma, Rachel YamsonKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Species - EcosystemsDocument1 page4.1 Species - EcosystemsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Examine The Extent To Which The Aims of Sustainable Tourism Might Be Achieved in Two Different Environments?Document5 pagesExamine The Extent To Which The Aims of Sustainable Tourism Might Be Achieved in Two Different Environments?Kaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.1: Chi-Squared Test: Worked ExampleDocument1 pageTopic 4.1: Chi-Squared Test: Worked ExampleKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Topic 11.2: Movement: Human Elbow Joint Movement SystemsDocument1 pageTopic 11.2: Movement: Human Elbow Joint Movement SystemsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Verstrepen2004 PreGli-Sac (Second)Document7 pagesVerstrepen2004 PreGli-Sac (Second)Kaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 5.3 BiodiversityDocument1 page5.3 BiodiversityKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Quartey Chemistry Gr4 EssumanDocument27 pagesQuartey Chemistry Gr4 EssumanKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Energy FlowDocument1 page4.2 Energy FlowKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.6: Stages of Mitosis: Stage Diagram Key EventsDocument1 pageTopic 1.6: Stages of Mitosis: Stage Diagram Key EventsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecular BiologyDocument1 page2.1 Molecular BiologyKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of LipidsDocument1 pageTopic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of LipidsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Eukaryotic CellsDocument1 page1.2 Eukaryotic CellsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Presentation Coloured SubstancesDocument9 pagesPresentation Coloured SubstancesKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: Topic 13 by Kaleab MebratuDocument6 pagesPeriodicity: Topic 13 by Kaleab MebratuKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Practical Guide Study Material English MediumDocument33 pages11th Physics Practical Guide Study Material English Mediumjeysonbegin4No ratings yet
- Geo Lower-Sec 1 0Document36 pagesGeo Lower-Sec 1 0Gelar T. KusumawardhanaNo ratings yet
- The Deisel Strength Mass ReportDocument45 pagesThe Deisel Strength Mass ReportNic Prince91% (11)
- MRS Bulletin TBCsDocument52 pagesMRS Bulletin TBCsLeandro Augusto SouzaNo ratings yet
- GMAT Verbal Reading Comprehension NotesDocument5 pagesGMAT Verbal Reading Comprehension NotesShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Wraith The Oblivion 20 - Paranormal Investigator's Handbook - Onyx PathDocument49 pagesWraith The Oblivion 20 - Paranormal Investigator's Handbook - Onyx Pathjigglepopper100% (1)
- Din 4 MM Standard and Dip CupsDocument7 pagesDin 4 MM Standard and Dip CupsDmitry_ucpNo ratings yet
- ES3 BSCpE2A Lab4 Group4Document5 pagesES3 BSCpE2A Lab4 Group4Daniel Melchizedek A. JimenezNo ratings yet
- MSC In: Machine Learning, Systems and ControlDocument2 pagesMSC In: Machine Learning, Systems and ControlMirza HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Quality Control Vernier CaliperDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 Quality Control Vernier CaliperAliNo ratings yet
- Blow Molding ProcessDocument184 pagesBlow Molding ProcessShubham ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference - WASH in School ConsultantDocument8 pagesTerms of Reference - WASH in School ConsultantilyasabibhNo ratings yet
- IoT in Agriculture Project Proposal by SlidesgoDocument46 pagesIoT in Agriculture Project Proposal by SlidesgoUyên Trịnh HoàngNo ratings yet
- ESC 3104 - Course OutlineDocument4 pagesESC 3104 - Course OutlineParbattie DannyNo ratings yet
- Trip To Marine National Park - Narara, Jamnagar, GujratDocument5 pagesTrip To Marine National Park - Narara, Jamnagar, GujratanandnaregalNo ratings yet
- Spec Citric Acid AnhyDocument1 pageSpec Citric Acid AnhyMaria StephanieNo ratings yet
- Safety Measures During Solar EclipseDocument8 pagesSafety Measures During Solar EclipseCristy Mae Catubag NialaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument11 pagesHypothesis TestingRitu KumariNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pertemuan 14 (Perilaku Organisasi)Document4 pagesTugas Pertemuan 14 (Perilaku Organisasi)REG.A/41921100002/DESI INDRIYANTINo ratings yet
- BKAT3023 Answer BookletDocument3 pagesBKAT3023 Answer BookletDik Ah SholehahNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument19 pagesThesisrichie sNo ratings yet
- Task 2 - Writing Task ForumDocument16 pagesTask 2 - Writing Task ForumDIEGO FELIPE GARCIANo ratings yet
- 1..write A Python Program To Swap Two Numbers Using A Third VariableDocument5 pages1..write A Python Program To Swap Two Numbers Using A Third VariablesainaveenNo ratings yet
- ASP QuestionsDocument25 pagesASP QuestionsMudassar Bin ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Udoh Anthony JosephDocument4 pagesUdoh Anthony JosephDAVIDNo ratings yet
- GEOGUIDE 3 (GUIDE TO ROCK AND SOIL DESCRIPTIONS) - GCO - The Government of The Hong Kong Special Administrative RegionDocument127 pagesGEOGUIDE 3 (GUIDE TO ROCK AND SOIL DESCRIPTIONS) - GCO - The Government of The Hong Kong Special Administrative Regionscpark9869gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Dixell XR60CDocument4 pagesDixell XR60CCarlos0% (1)
- Antenna Theory Analysis and Design (3rd Edition) PDFDocument1 pageAntenna Theory Analysis and Design (3rd Edition) PDFNarendra Jadhav40% (5)