Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Area and Volume of Right Prisms
Uploaded by
Alex0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageSurface Area and Volume of Right Prisms
Uploaded by
AlexCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
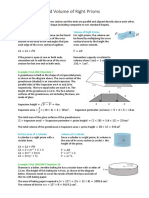
Surface Area and Volume of Right Prisms
Right Prism
A 3D shape with a uniform cross section and the ends are parallel and aligned directly above each other.
The cross section can be any shape (including composite or non-standard shapes).
Surface Area of Right Prisms Volume of Right Prisms
For right prisms, the surface area can be found For right prisms, the volume can
by adding two lots of the area of the cross be found by multiplying the cross
section to the area of the rectangles that join sectional area by the height the
each edge of the cross sections together. cross section extends.
𝑆𝐴 = 2𝐴 + 𝑃𝐻 𝑉 = 𝐴𝐻
If the prism is open at one or both ends, Remember: capacity is related to
remember not to add the area of the cross volume where 1 mL = 1 cm ,
section for that one end or both ends. 1 kL = 1 m .
Example VCAA 2013 Question 7
A greenhouse is built in the shape of a trapezoidal prism,
as shown in the diagram above. The cross-section of the
greenhouse (shaded) is an isosceles trapezium. The
parallel sides of this trapezium are 4 m and 10 m
respectively. The two equal sides are each 5 m. The
length of the greenhouse is 12 m. The five exterior
surfaces of the greenhouse, not including the base, are
made of glass.
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
trapezium height = 5 − 3 = 4 m
1
trapezium area = ⎯⎯× (10 + 4) × 4 = 28 m , trapezium perimeter (no base) = 5 + 4 + 5 = 14 m
2
The total area of the glass surfaces of the greenhouse is
(2 × trapezium area) + (trapezium perimeter × prism height) = (2 × 28) + (14 × 12) = 224 m
The total volume of the greenhouse is trapezium area × prism height = 28 × 12 = 336 m
Surface Area of a Cylinder Volume of a Cylinder
A cylinder is a right prism with a Since a cylinder is a right prism, its volume is
circular base. the area of its cross section (a circle) × the
height of the prism.
𝑆𝐴 = 2𝐴 + 𝑃𝐻
𝑆𝐴 = 2 × 𝜋𝑟 + 𝐶 × ℎ 𝑉 = 𝐴𝐻
𝑆𝐴 = 2𝜋𝑟 + 2𝜋𝑟ℎ 𝑉 = 𝜋𝑟 × ℎ
𝑆𝐴 = 2𝜋𝑟(𝑟 + ℎ) 𝑉 = 𝜋𝑟 ℎ
Example VCAA 2018 NHT Question 1b
Shannon is a baker. Another baking tin has a circular base with a radius of
12 cm. The height of this baking tin is 8 cm, as shown in the diagram
below. Shannon needs to cover the inside of both the base and side of
this tin with baking paper.
The area of baking paper required is 𝜋 × 12 + (2𝜋 × 12 × 8) = 1055.6 cm .
The volume of this tin is 𝜋 × 12 × 8 = 3619.1 cm .
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Surface Area and Volume of Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresDocument2 pagesSurface Area and Volume of Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresAlexNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume PDFDocument1 pageSurface Area and Volume PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Composite SolidsDocument1 pageComposite SolidsAlexNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume of Right PrismsDocument1 pageSurface Area and Volume of Right PrismsAlexNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument1 pageSurface Area and VolumeAlexNo ratings yet
- Composite SolidsDocument1 pageComposite SolidsAlexNo ratings yet
- Mercy Mercy Mercy Full Score and Individual Parts PDFDocument43 pagesMercy Mercy Mercy Full Score and Individual Parts PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Monsters Inc Full Score and Individual Parts PDFDocument53 pagesMonsters Inc Full Score and Individual Parts PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume of Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresDocument2 pagesSurface Area and Volume of Pyramids, Cones, and SpheresAlexNo ratings yet
- Transition Matrices With Culling and RestockingDocument1 pageTransition Matrices With Culling and RestockingAlexNo ratings yet
- Steady State For 2×2 Transition Matrices Using A RuleDocument1 pageSteady State For 2×2 Transition Matrices Using A RuleAlexNo ratings yet
- Mercy Mercy Mercy Full Score and Individual Parts PDFDocument43 pagesMercy Mercy Mercy Full Score and Individual Parts PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Matrices Technology (Casio)Document1 pageMatrices Technology (Casio)AlexNo ratings yet
- Steady State and The Long TermDocument1 pageSteady State and The Long TermAlexNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Rules of IntegrationDocument3 pagesRules of IntegrationChang Seng SinNo ratings yet
- Q1-W1-L5 DLP - Factoring General Quadratic TrinomialsDocument2 pagesQ1-W1-L5 DLP - Factoring General Quadratic TrinomialsArela Jane TumulakNo ratings yet
- Eves, Howard, (BF) Great Moments in Mathematics Before 1650Document283 pagesEves, Howard, (BF) Great Moments in Mathematics Before 1650Federico100% (1)
- Past Exam Questions Workbook (2H)Document16 pagesPast Exam Questions Workbook (2H)bonyantunNo ratings yet
- Calculo de Potencia para Evaporadores de Pelicula Agitada Mckenna 1995Document15 pagesCalculo de Potencia para Evaporadores de Pelicula Agitada Mckenna 1995Sebastian PinzonNo ratings yet
- MM16 Module 1Document13 pagesMM16 Module 1Jayson PajaresNo ratings yet
- Math 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDocument3 pagesMath 21 Written Homework Chapter 5 ReviewDavidsLockNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFUday kiranNo ratings yet
- Maths4 Nov09Document24 pagesMaths4 Nov09jrfrancisNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAhmed AmanNo ratings yet
- cs8383 Object Oriented Programming LaboratoryDocument138 pagescs8383 Object Oriented Programming LaboratoryShrijith NairNo ratings yet
- The Van Hiele Analysis of Curricular Materials - A Comparative StuDocument156 pagesThe Van Hiele Analysis of Curricular Materials - A Comparative StuhasanNo ratings yet
- J. Measuring Square FeetDocument39 pagesJ. Measuring Square FeetashevillerealestateNo ratings yet
- January 2019 (R) QP - Paper 1H Edexcel Maths (A) IGCSEDocument28 pagesJanuary 2019 (R) QP - Paper 1H Edexcel Maths (A) IGCSEShadi ShokryNo ratings yet
- Triangle, Trapezoid, Parallelogram AreaDocument2 pagesTriangle, Trapezoid, Parallelogram AreaAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- Physiological Reviews: MAX KleiberDocument31 pagesPhysiological Reviews: MAX KleiberFetcu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 MELC CompilationDocument46 pagesGrade 5 MELC CompilationAnne DeteraNo ratings yet
- HCP crystal structure packing factorDocument4 pagesHCP crystal structure packing factorBahroz RashidNo ratings yet
- FEDEL MALOLOY-ON CONVERSION PROBLEMSDocument10 pagesFEDEL MALOLOY-ON CONVERSION PROBLEMSStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Handouts - Trigonometry and GeometryDocument5 pagesHandouts - Trigonometry and GeometryTrisha Rañada100% (1)
- Areaand Volumesof Similar SolidsDocument4 pagesAreaand Volumesof Similar SolidsBrian CruzNo ratings yet
- Homework Set #3: EE6412: Optimal Control January - May 2023Document2 pagesHomework Set #3: EE6412: Optimal Control January - May 2023kapali123No ratings yet
- Riemann SumsDocument18 pagesRiemann Sumsapi-285947070No ratings yet
- Area Measurement by TapeDocument22 pagesArea Measurement by TapeMike SyNo ratings yet
- Percetages TDY-302Document36 pagesPercetages TDY-302madhu jhaNo ratings yet
- Keo Sodara - High School Math Contest I (From Carolina)Document526 pagesKeo Sodara - High School Math Contest I (From Carolina)Felipe GallegosNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Practice Problems-Answer KeyDocument5 pagesSession 2-Practice Problems-Answer KeyMuskaan MusicidNo ratings yet
- Circle WikiDocument51 pagesCircle Wikidata xlNo ratings yet
- 12th MathematicsDocument6 pages12th MathematicsUnwantedNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extended © Cambridge University Press, 2015 GlossaryDocument6 pagesGlossary: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extended © Cambridge University Press, 2015 GlossarySyed Waqas AhmedNo ratings yet