Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endometriosis
Uploaded by
Isabel CastilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endometriosis
Uploaded by
Isabel CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
LECTURE OUTLINE • Adolescents with obstructive Mullerian Anomalies
• Incidence • Most commonly in dependent portions of the pelvis
• Pathophysiology
• Clinical presentation Coelomeic Metaplasia Theory
• Diagnosis • Coelomic epithelium ( where mullerian ducts are derived)
• Management retains the ability for multipotential development
o Medical
Coelomic epithelium which
o Surgical
makes up the peritoneal
surface is a multipotential cell,
ENDOMETRIOSIS which when induced by
Endometriosis afflicts women of the reproductive age. It is estrogen and progesterone,
a benign disease yet it is locally infiltrating and a very
undergoes metaplasia and
progressive disease, perplexing obstetrician- gynecologists becomes endometrial cells with
treating it. continued stimulation by
• Presence and growth of endometrial glands and stroma in hormones (estrogen and
an abberant or heterotropic location progesterone) these
endometrial cells proliferate
Incidence just like the endometrium
• 11 % reproductive aged woman
• 5-15 % of laparotomies performed on reproductive aged • Metaplasia occur after an induction phenomenon
women for other indications (Induction substance: combination of menstrual debris
• 33-82 % in women with chronic pelvic pain and estrogen and progesterone) has stimulated the
• 30-45 % in patients with infertility multipotential cell
The incidence of endometriosis has increased over the past • Metaplastic cells transform to endometrial cells
years secondary to increased awareness of mild forms of • Endometriosis in premenarcheal girls
the disease diagnosed by the increasing use of This explains why even in premenarcheal girls, who never
laparoscopy. The exact incidence of the disease is not menstruated (therefore cannot be explained by Sampson’s
known and is only estimated. theory), endometriosis is sometimes found.
Pathophysiology Lymphatic and Vascular Metastasis
1. Retrograde menstruation (Sampson’s) • Endometrium transplanted via lymphatic channels and the
2. Coelomic metaplasia vascular system to different parts of the body
3. Lymphatic and vascular metastases • Endometriosis has been observed in the pelvic lymph
4. Iatrogenic dissemination nodes of approximately 30 % of women
5. Immunologic Changes • Endometriosis of the forearm, thigh, and multiple lesions
6. Genetic Predisposition in the lungs and nose
7. Hormonal Influences Hematogenous dissemination of the endometrium is the
8. Environmental Factors best theory to explain the presence of endometriosis in
There are several theories to explain the pathogenesis of rare and remote sites.
Endometriosis. However, no single theory explains all the
manifestations of the disease. Iatrogenic Dissemination
• Endometrial glands and stroma are implanted during the
Retrograde Menstruation (Sampson’s Theory) performance of an operation
there is increasing evidence that environmental factors
plays a role specially dioxin and other endocrine disruptors Examples:
• Most popular theory endometriosis at the
• Reflux of menstrual blood and endometrial cells at the anterior abdominal wall
tubal ostia during menstruation attach to the pelvic or episiotomy scar
peritoneum and under hormonal influence grow as
homologous grafts
Immunologic Changes
• Primary immunologic change: alteration in the function of
the peritoneal macrophages in the peritoneal fluids of the
patients with endometriosis
More Enhance
Secrete
peritoneal development
multiple
macrophages of
growth factors
that are larger endometriosis
and cytokines
and hyperactive
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 1
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
One of the observations of experts is that some women Pathology: Ovary
with retrograde menstruation develop endometriosis while Endometrioma/ Endometriotic Cysts:
majority do not. Investigations suggested that changes in • Chocolate Cyst
the immune function are directly related to the
pathogenesis of endometriosis.
Genetic Predisposition
• 7x increase incidence of endometriosis in relatives of
women with the disease
• 1/10 women with severe endometriosis will have a sister
or mother with clinical manifestations of the disease
• Women who have a family history of endometriosis are
likely to develop the disease earlier in life and to have
more advanced disease
• Several candidate gene and gene products are abberantly
expressed in patients with endometriosis
Several studies have shown clustering of endometriosis in
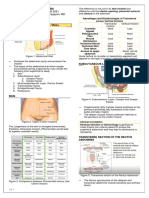
Peritoneal Endometriosis
families like mother and daughter
• Gross Appearance
o powder burn, puckered black lesions
o vascularized glandular papules
o vesicular lesions
o red, flamelike
o petechial peritoneum
o discolored areas
The gross appearance of the implant depends on the site,
activity, relationship to the day of the menstrual cycle, and
chronicity of the area involved.
• Small bleb like appearance
Endometriosis most commonly affects the most dependent
portion of the pelvis
Common sites Rare Sites
Ovaries Umbilicus
Pelvic peritoneum Episiotomy scar
Ligaments of the uterus Bladder
Pelvic lymph nodes – 30% Kidney
Rectosigmoid – 10 to 15% Lungs
Appendix Arms and legs
Vagina Nasal mucosa
Cervix Spinal column
Fallopian tubes
Small, bleblike implants that are raised above the
surrounding tissues, less than 1 cm in diameter are new
lesions.
Very subtle. Represents the earliest form of the disease
• Red Blood-filled lesions
• red, flamelike
• petechial peritoneum
Red, blood-filled lesions are the most active phase of the
disease.
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 2
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
The associated adhesions may be minimal or extensive,
filmy or dense, and avascular or vascular
• powder burn, puckered black lesions
These lesions will later on progress to? Scripted na tanong
to ni Doc bale check nyo na lang sagot sa book. Powder Minimal filmy adhesions
burn lesions are the older lesions and usually are the deep
infiltrating lesions
• White lesions/ scar
The older lesions are white, have more intense scarring,
and are usually puckered or retracted from the
surrounding tissue.
White or mixed colored lesions are more likely to provide
histologic confirmation of endometriosis.
The progression from red to white lesions also seems to
Minimal-mild form of the disease with normal anatomy of
correlate with age.
the reproductive organs ----- severe form of the disease
with the cul de sac obliterated due to dense adhesions
Three Cardinal Histologic Features and Symptoms
1. Ectopic endometrial glands
2. Ectopic endometrial stroma
3. Hemorrhage into the
adjacent tissue
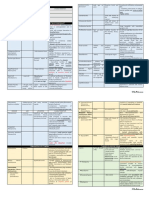
Endometriosis: A Disease of Clinical Contrasts
Characteristics Contrasts
Benign Disease Locally invasive
Widespread disseminated foci
Proliferates in pelvic lymph
nodes
Minimal Disease Severe pain
Many large endometriomas Asymptomatic patient
Pathology: Adhesions Cyclic hormones cause growth Continuous hormone reverse
the growth pattern
The symptomatology does not correspond to the severity
of the disease.
• Classic Symptoms:
o Cyclic pelvic pain
o Infertility
• Other symptoms:
o Secondary dysmenorrhea
o Dyspareunia
o Abnormal bleeding
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 3
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
o Urinary symptoms: Diagnosis
§ Urinary frequency History and Physical Examination
§ Hematuria • Cyclic or chronic pelvic pain, deep dyspareunia presenting
§ Dysuria with subfertility
o GI symptoms: • Rectovaginal examination performed during the
§ Cyclic abdominal pain menstrual phase (D1-D2) may aid in the diagnosis as it is
§ Intermittent constipation the time of maximal swelling and tenderness in the areas
§ Diarrhea of endometriosis
§ Dyschezia o Pelvic tenderness
It is important to emphasize that 1/3 women with o Fixed retroverted uterus
endometriosis are asymptomatic and are diagnosed o Tender and thickened uterosacral ligaments
incidentally during operation due to other causes. o Enlarged ovaries
Symptoms: Pain
• The cyclic pelvic pain is related to the sequential swelling History and PE :
and the extravasation of blood and menstrual debris into
the surrounding tissue It should be suspected in patients
• Mechanism of Pain: with cyclic or chronic pelvic pain
o Production of substances like prostaglandins, and infertility or dyspareunia.
growth factors and cytokines by macrophages Rectovaginal examination
o Direct and indirect effects of active bleeding examination should be done and
from the implants preferably during the menstrual
o Irritation and direct invasion of nerves by cycle to detect nodulations and
infiltrating endometriotic implants scarring in the USL which
The chemical mediators of this intense sterile inflammation suggests the presence of
and pain are believed to be prostaglandins and cytokines endometriosis..
Symptoms: Secondary Dysmenorrhea
• varies from a dull ache to severe pelvic pain Diagnosis: Ultrasound
• unilateral or bilateral radiating to the lower back, legs, and • detect endometriotic cysts but not peritoneal
groin endometriosis
• Pelvic heaviness or a perception of their internal organs o Unilocular cyst with low to medium level echoes
being swollen within
• Pain may last for many days, including several days before
and after the menstrual flow.
Symptoms: Dyspareunia
• pain deep in the pelvis during intercourse
• Due to immobility of the pelvic organs during coital activity
or direct pressure on areas of endometriosis in the
uterosacral ligaments or the cul-de-sac.
• The acute pain may continue for several hours following
intercourse.
Diagnosis: Laparoscopy
Signs • “Gold Standard” in diagnosis
• Classic Sign: • Offers an addititional benefit of treatment at the time of
o Fixed, retroverted uterus w/ scarring & diagnosis
tenderness posterior to the uterus • Visual Inspection with histologic confirmation is the
• Others: definitive means to establish the diagnosis of pelvic
o nodularity of uterosacral ligaments & cul de sac endometriosis.
o ovaries may be enlarged & tender and often Although laparoscopy is the gold
fixed to the broad ligament or lateral pelvic wall standard in diagnosisng
• Nodularity of the uterosacral ligaments and cul-de-sac may endomet, its natiure and extent
be palpated on rectovaginal examination in approximately of the disease, this is not always
one third of women with the disease. possible specially in young
• Advanced cases have nulliparous pxs…
o extensive scarring and If we ruled out the possibily of
o narrowing of the posterior vaginal fornix infection and malignancy, and
highly suspect endometriois by
history and PE, then it is prudent
to do trial of medical
management for 3 months..
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 4
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
Diagnosis: CT Scan or MRI GnRH Agonist
• Not a practical modality for endometriosis diagnosis • Leuprolide acetate (Lupron, injectable)
o 3.75 mg intramuscularly once per month or
Diagnosis: CA 125 11.25 mg depot injection every 3 months
• Has NO value in the diagnosis of endometriosis • Nafarelin acetate (Synarel, intranasal)
o one spray (200 mg) in one nostril in the morning
Management and one spray (200 mg) in the other nostril in the
• Primary short term goals evening up to a maximum of 800 mg daily
o relief of pain • Goserelin acetate (Zoladex, subcutaneous implant)
o promotion of fertility o 3.6 mg every 28 days in a biodegradable
• Primary long term goal subcutaneous
o prevent progression or recurrence of disease • MOA: Down regulates and desensitizes pituitary gland to
• Choice of therapy, depends on patient's age, her future produce extremely low levels of FSH & LH ----- Low
reproductive plans, location and extent of the disease, the estrogen and progesterone
severity of symptoms, and associated pelvic pathology. • “medical oophorectomy”
• Primary goal of the hormonal treatment: Induction of • No effect on sex-hormone binding globulin
amenorrhea • Side effects:
o hot flushes,
o vaginal dryness
Recurrent bleeding in the ectopic implants is one of the o insomnia
most important pathophysiologic processes to interrupt o decrease bone density
• Medical: • Advantage: better patient compliance
o NSAIDS Can only be used for 6 months for its Side effects to be
o Danazol reversible after discontinuation.
o GnRH Agonist
o Combined oral contraceptive pills Combined Oral Contraceptive Pills
o Progestins: • Produce amenorrhea
§ Medroxyprogesterone • “pseudopregnancy”
§ Depomedroxyprogesterone • Continuous low dose monophasic OCP
§ Levonorgestrel Intrauterine system As in other oral hormonal regimen, amenorrhea is the
o Aromatase inhibitors desired endpoint continuous daily oral contraceptives for 6
• Surgical: to 12 months beginning on the third day of the patient's
o Laparotomy (Open) period
o Laparoscopy (Minimally invasive) • Others:
Induction of amenorrhea is the primary goal of the o Aromatase inhibitors
hormonal treatment because recurrent bleeding in the o Medroxyprogesterone
ectopic implants is one of the most important § 30mg/day
pathophysiologic processes to interrupt o Depomedroxyprogesterone
§ 150mg IM every 3 months- 200 mg
Medical every month
Danazol o Levonorgestrel-containing Intrauterine device
• Dosage: 400-800mg/day for 6 months system
• hypoestrogenic & hyperandrogenic As in other oral hormonal regimen, the amenorrhea is the
• MOA: binds to androgen and progesterone receptors and desired endpoint
sex hormone-binding globulin.
Rarely used now because of its side-effects that does not Surgery
resolve after discontinuation.. Main Role:
• Adverse effects: There has been a shift in the management of
o menopausal hot flushes endometriosis especially in the presence of ART
o atrophic vaginitis
o emotional lability Previous Years Present
o weight gain Large endometriomas >3-4 cms Provide symptomatic relief of
o fluid retention pain
o migraine headaches Improve Fertility Outcomes
o deepening of voice Failed medical management
Adverse affects of danazol is irreversible Acute rupture endometriomas
• The recommended doses of Danazol for the treatment of
endometriosis have substantial androgenic and Conservative Surgery
hypoestrogenic side effects that limit the clinical utility of • resection or destruction of endometrial implants, lysis of
the drug adhesions, and attempts to restore normal pelvic anatomy
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 5
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
Definitive Surgery Standard Criterion for the diagnosis of
• removal of both ovaries, the uterus, and all visible ectopic Adenomyosis
foci of endometriosis
• Address 3 main categories of the lesion : Endometrial glands and stroma more
o Superficial than one low-powered field (2.5 mm)
o Endometrioma from the basalis layer of the
o DIE endometrium
Laparoscopic Excision
• Is currently the “GOLD STANDARD” approach for the
management of endometriosis
Manifestation
Minimally Invasive Surgery • Asymptomatic
• Is preferred: • Parous, more than 35 years old
o Laparoscopy • Classic Symptom:
o Robotic surgery o Secondary dysmenorhhea
• Advantages: o HMB (Menorrhagia)
o Improved visualization • Sign: globularly enlarged uterus, 2-3x normal size
o Shorter recovery period
o Decrease blood loss
o Decreased risk of complication
Minimally invasive Surgery has largely replaced the need
to open surgery
Endometriosis- Associated Infertility
• Surgical therapy- preferred approach
• Surgical removal of all endometriotic lesion is the only
Adenomyosis Myoma
treatment that improves spontaneous conception rates in
infertile patients with endometriosis • The diagnosis of adenomyosis is usually confirmed
following histologic examination of the hysterectomy
• Pregnancy rates after surgery:
specimen
o Laparoscopy= 54-66%
o Laparotomy (open) = 36-45%
Diagnosis
There is no evidence that medical therapy can improve
pregnancy rates of patients with endometriosis associated • Transvaginal Examination (Left photo)
infertility • MRI (Right photo)
Hidden powerpoint slide to ni Doc guys, pero nilagay ko na
lang din.
Adenomyosis
• Growth of endometrial glands & stroma within the
myometrium to a depth of 2.5 mm from the basalis layer
Currently not considered a variant of endometrios
Pathology
• Cut surface protrudes convexly and has a spongy Treatment
appearance • There is no satisfactory proven medical treatment for
• Cut surface is darker than the white cut section of a adenomyosis
myoma o GNRH Agonists
• There is NO distinct cleavage plane around focal o Cyclic hormones
adenomyoma compared to myoma o Prostaglandin inhibitors
• Hysterectomy
o definitive treatment if this therapy is appropriate
for the woman's age, parity, and plans for future
reproduction
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 6
GYNECOLOGY EXIMIUS
ENDOMETRIOSIS 2021
Jacqueline Banatao- Pua, MD, FPOGS, FPSREI, FP May 2020
TRANSCRIBERS CABALZA, JKB. 7
You might also like
- GYNE 4.01a EndometriosisDocument4 pagesGYNE 4.01a EndometriosisGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.06-Benign and Malignant Lesions of UterusDocument7 pagesGYNE 4.06-Benign and Malignant Lesions of UterusGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Abortion and Sterilization: Medical and Social AspectsFrom EverandAbortion and Sterilization: Medical and Social AspectsJane E. HodgsonNo ratings yet
- OSCE Reviewer 2013Document4 pagesOSCE Reviewer 2013rere choiNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.01b InfertilityDocument4 pagesGYNE 4.01b InfertilityGray SnellNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.04 Pelvic Organ DisordersDocument7 pagesGYNE 4.04 Pelvic Organ DisordersGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Systems Review MnemonicsDocument4 pagesSystems Review MnemonicsNatasha JuchkovNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.03 Urinary IncontinenceDocument7 pagesGYNE 4.03 Urinary IncontinenceGray SnellNo ratings yet
- (Gyne) 2.1 PCOS, Hyperandrogenism & Hyperprolactenemia (OnaCruz) - WiniDocument10 pages(Gyne) 2.1 PCOS, Hyperandrogenism & Hyperprolactenemia (OnaCruz) - WiniDexter IanNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.05a Bening Ang Malignant Lesions of The VulvaDocument11 pagesGYNE 4.05a Bening Ang Malignant Lesions of The VulvaGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sex Development (DSD) DevelopmentDocument40 pagesDisorders of Sex Development (DSD) DevelopmentAndi AdityaNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.02 - Lower and Upper Genital InfectionDocument12 pagesGYNE 4.02 - Lower and Upper Genital InfectionGray Snell100% (1)
- Gyne ReflectionDocument18 pagesGyne ReflectionKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Management of CA Vulva 2Document33 pagesManagement of CA Vulva 2api-3705046No ratings yet
- Pathology 5.05b Vagina and Vulva - DR - Dy (Final Edit)Document11 pagesPathology 5.05b Vagina and Vulva - DR - Dy (Final Edit)Dranreb Berylle MasangkayNo ratings yet
- 002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFDocument11 pages002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFale_fearNo ratings yet
- Distal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesDocument8 pagesDistal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: (Hydatidiform Mole)Document12 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease: (Hydatidiform Mole)Gylle Marie PlazaNo ratings yet
- HERNIADocument34 pagesHERNIAAtiqah ShahNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument7 pagesABORTIONChristine Evan Ho100% (1)
- B - Embyrology HomologuesDocument1 pageB - Embyrology HomologuesS ParekhNo ratings yet
- Neonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Document15 pagesNeonatology I: Pediatrics 1.1Kurt ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic LesionsDocument103 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions201286% (7)
- Medicine 6.1b Approach To Cancer Patients - FernandoDocument7 pagesMedicine 6.1b Approach To Cancer Patients - FernandoAbigail LausNo ratings yet
- Phyllodes TumorDocument20 pagesPhyllodes TumorManuela KarinaaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ob2 s1t15 Preterm Labor and BirthDocument12 pages2022 Ob2 s1t15 Preterm Labor and BirthmedicoNo ratings yet
- 4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersDocument5 pages4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersRainy Liony DuhNo ratings yet
- Gynecology: 3.09 - AmenorrheaDocument13 pagesGynecology: 3.09 - AmenorrheaAnna Mae MarantanNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic Lesions: Urethral Caruncle, Cyst, Nevus, Hemangioma, Fibroma, Lipoma, Endometriosis, Urethral DiverticulumDocument158 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions: Urethral Caruncle, Cyst, Nevus, Hemangioma, Fibroma, Lipoma, Endometriosis, Urethral DiverticulumArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- Topic: Asthma and Copd: Internal Medicine IiDocument8 pagesTopic: Asthma and Copd: Internal Medicine IicarlosNo ratings yet
- Examination of Breast Lump PDFDocument2 pagesExamination of Breast Lump PDFDanaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Surgery NuggetsDocument17 pagesSystemic Surgery NuggetsAhmad UsmanNo ratings yet
- VulvaDocument7 pagesVulvaJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Benign Breast DiseasesDocument24 pagesBenign Breast DiseasesNur Hanani KhanNo ratings yet
- Hormone Regulation of the Menstrual CycleDocument8 pagesHormone Regulation of the Menstrual CycleRj PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Penile CaDocument76 pagesPenile CaUsmle GuyNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesCervical CancerCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- (DERMA) 03 TineasDocument9 pages(DERMA) 03 TineasJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- 1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyDocument6 pages1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyIrene FranzNo ratings yet
- Normal Conduct of LaborDocument62 pagesNormal Conduct of LaborFaye Cabotaje LinganNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesEndometrial Cancer Diagnosis and TreatmentAhmed Butt100% (1)
- Postpartum CollapseDocument54 pagesPostpartum Collapsemedical chroniclesNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Achalasia DysphagiaDocument14 pagesEsophageal Achalasia DysphagiaTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- RISE REVIEW - Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesRISE REVIEW - Female Reproductive SystemGerben Villanueva100% (1)
- Benign Gyne LesionsDocument133 pagesBenign Gyne LesionsJulie Ann ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDocument6 pagesGynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDawn Marco100% (1)
- Abnormal Labor and Dystocia Causes, Evaluation and ManagementDocument63 pagesAbnormal Labor and Dystocia Causes, Evaluation and ManagementJoan LuisNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Fetal AssessmentDocument52 pagesIntrapartum Fetal AssessmentAditya TejabaswaraNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument5 pagesObstetrics - Operative Vaginal DeliveryJonathanNo ratings yet
- Contraction Stress Test complicationsDocument5 pagesContraction Stress Test complicationsPao Ali100% (1)
- POGS PB Dystocia Sept 2022Document6 pagesPOGS PB Dystocia Sept 2022John Piox Badiang100% (1)
- Dengue Fever and Pregnancy-A Review and CommentDocument6 pagesDengue Fever and Pregnancy-A Review and CommentRolando AgustianNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic Lesions FinalDocument11 pagesBenign Gynecologic Lesions Final2012100% (4)
- Pedia Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesPedia Finals ReviewerMarron Jane GanoticeNo ratings yet
- OB 1S 1 Maternal AnatomyDocument6 pagesOB 1S 1 Maternal AnatomyKiara Loren DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Ob-Gyn Review Part 3Document101 pagesOb-Gyn Review Part 3filchibuffNo ratings yet
- Missed AbortionDocument45 pagesMissed AbortionMarest AskynaNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis and Adenomycosis - CaramelMacchiatoDocument6 pagesEndometriosis and Adenomycosis - CaramelMacchiatoJanelle MatamorosaNo ratings yet
- SURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableDocument4 pagesSURGICAL PATHOLOGY SOFT TISSUES TableIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - Peripheral NervesDocument1 pageSurgical Pathology - Peripheral NervesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ok Ok Notes PediaDocument10 pagesOk Ok Notes PediaIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Guide to PrescriptionsDocument54 pagesDoctor's Guide to PrescriptionsNo Longer HumanNo ratings yet
- CNS Tumors - Types, Grades and Key Imaging FeaturesDocument2 pagesCNS Tumors - Types, Grades and Key Imaging FeaturesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - Bones and JointsDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - Bones and JointsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY - Cuteneous Candidiasis, PityrosporumDocument4 pagesDERMATOLOGY - Cuteneous Candidiasis, PityrosporumIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument6 pagesDermatology - Exanthematous Viral DiseasesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY - Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument6 pagesDERMATOLOGY - Sexually Transmitted DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- TemperamentsDocument2 pagesTemperamentsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - Skin NeoplasmsDocument12 pagesDermatology - Skin NeoplasmsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Implantation and Placental DevelopmentDocument62 pagesImplantation and Placental DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Child Growth and DevelopmentDocument60 pagesChild Growth and DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Embryo and Fetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesEmbryo and Fetal DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- Pneumonia Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesPneumonia Diagnosis and TreatmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Genetic Basis of Congenital DisordersDocument87 pagesGenetic Basis of Congenital DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Newborn Diseases Pediatrics IIDocument17 pagesNewborn Diseases Pediatrics IIIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- PEDIATRIC CHAIN OF SURVIVALDocument10 pagesPEDIATRIC CHAIN OF SURVIVALIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseDocument4 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pedia Pre School NewsDocument3 pagesPedia Pre School NewsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument3 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Interatitial Lung DiseaseDocument2 pagesInteratitial Lung DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Medicine: Early AdolescenceDocument2 pagesAdolescent Medicine: Early AdolescenceIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Document13 pagesPediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Isabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankDocument4 pagesAcute Appendicitis and Peritonitis: RLQ, To The Pelvis, Right FlankIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesAcute and Chronic PancreatitisIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pack-Years of Cigarette Smoking Is The Most HighlyDocument5 pagesPack-Years of Cigarette Smoking Is The Most HighlyIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Listado 2 4ghzDocument4 pagesListado 2 4ghzRogerNo ratings yet
- Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti Language UniversityDocument30 pagesKhwaja Moinuddin Chishti Language UniversityShivam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Biotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainDocument8 pagesBiotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- K Park 24 TH Edition ChangesDocument8 pagesK Park 24 TH Edition ChangesAnkit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 255 Introduction Vocational Service enDocument12 pages255 Introduction Vocational Service enDmitri PopaNo ratings yet
- Review Relative Clauses, Articles, and ConditionalsDocument10 pagesReview Relative Clauses, Articles, and ConditionalsNgoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Otr Product CatalogDocument116 pagesOtr Product CatalogIwan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 6Document4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 6darshilsinghgharwarNo ratings yet
- Lean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesDocument60 pagesLean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesKaio Sol100% (6)
- Social Engineering For Pentester PenTest - 02 - 2013Document81 pagesSocial Engineering For Pentester PenTest - 02 - 2013Black RainNo ratings yet
- Small BusinessDocument22 pagesSmall BusinessAngelie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Of Our TimesDocument84 pagesOf Our TimesThe Journal of Music100% (1)
- Transcricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingaleDocument62 pagesTranscricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingalepauloalaraNo ratings yet
- Growatt Warranty Procedure - 07-09-2020Document9 pagesGrowatt Warranty Procedure - 07-09-2020Design TeamNo ratings yet
- 2narrative Essay - My Favorite TeacherDocument9 pages2narrative Essay - My Favorite TeacherHerbertKoh100% (1)
- GCMS-QP2010 User'sGuide (Ver2.5) PDFDocument402 pagesGCMS-QP2010 User'sGuide (Ver2.5) PDFnguyenvietanhbtNo ratings yet
- How English Works - A Grammar Handbook With Readings - Answer Key PDFDocument38 pagesHow English Works - A Grammar Handbook With Readings - Answer Key PDFAlessio Bocco100% (1)
- Company Introduction PT GEADocument8 pagesCompany Introduction PT GEABegawan Half DoneNo ratings yet
- Rulings On Healing and RukiyaDocument324 pagesRulings On Healing and RukiyatheproboxerNo ratings yet
- Capstone Presentation 2020Document12 pagesCapstone Presentation 2020api-539629427No ratings yet
- Arm Cortex InstructionsDocument14 pagesArm Cortex InstructionsHamsini ShreenivasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines On Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: An Executive Summary and Recommendations - Update 2019-2020Document17 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines On Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: An Executive Summary and Recommendations - Update 2019-2020Marwa YassinNo ratings yet
- Group L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedDocument10 pagesGroup L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedMani ThomasNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee Word ListDocument26 pagesSpelling Bee Word Listsan_6303No ratings yet
- Romeo and Julliet - Close Read AnalysisDocument5 pagesRomeo and Julliet - Close Read Analysisapi-514407929No ratings yet
- Oromia State UniversityDocument65 pagesOromia State UniversityEYOB AHMEDNo ratings yet
- G25M R TransmissionDocument29 pagesG25M R TransmissionMaksym VovkNo ratings yet
- Last Lesson: How Did Franz Feelings About M Hamel and School Change ?Document4 pagesLast Lesson: How Did Franz Feelings About M Hamel and School Change ?RitikaNo ratings yet
- How To Make Lampblack - AllDocument6 pagesHow To Make Lampblack - AllclaudjiuNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)