Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elliott Wave Handbook: Financial Freedom Trading
Uploaded by
Razak MwapachuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elliott Wave Handbook: Financial Freedom Trading
Uploaded by
Razak MwapachuCopyright:
Available Formats
Elliott Wave Handbook
Financial Freedom Trading
Table of Content
General Market Structure P. 3
Broad Concept
Complete Market Cycle
Compound Construction
Motive Waves P. 5
Impulse
Leading Diagonal
Ending Diagonal
Truncation
Extension
Corrective Waves P. 8
Zig-Zag
Regular Flat
Expanded Flat
Running Flat
Contracting Triangle
Barrier Triangle
Expanded Triangle
Double Three
Triple Three
Guidelines of Wave Formation P. 14
Alternation
Channeling
Wave Personality
Fibonacci & Ratio Analysis
Motive Wave Multiples
Corrective Wave Multiples
Summary P. 20
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 2
General Market Structure
Broad Concept
The Wave Principle was a phenomenon which was discovered by Ralph Nelson Elliott in the 1930s.
He analyzed the stock market and noticed, that the prices trend and behave in recognizable pattern.
In his research he discovered five primary pattern or waves, which link together to form a bigger
version of themselves. The Elliott Wave Theory was born.
The Elliott Wave Theory is primarily a tool to describe how markets behave. But it can be used
remarkably well as a forecasting tool, to identify the end of a movement and predict where the
market will turn.
Here at Financial Freedom Trading we use the Elliott Wave Theory as one building block of our
strategy. In combination with traditional support and resistance, Fibonacci level and Price Action
Signals it leads to great confluence and forms an edge in our trading.
On the following pages you will find a comprehensive collection of the basic and advanced Elliott
Wave elements, guidelines to follow and tips for the practical application.
Complete Market Cycle
First we have to take a look at the Complete
Market cycle. It consists of 8 waves, which
can be divided into two phases. In this whole
book we will only look at the bull market
variation, the bear market pattern are the
exact opposite.
• Phase 1 consists of five motive waves,
which are labelled with numbers.
• Phase 2 consists of three corrective
waves (or variations thereof) and are
labelled with letters.
Wave 1/3/5 are directional movements and
represent the primary trend. They are
separated by wave 2 and 4, which represent
countertrend corrections.
The biggest rules to follow about the basic pattern are:
• Wave 2 never goes below the beginning of wave 1
• Wave 3 is never the shortest wave
• Wave 4 never overlaps with Wave 1
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 3
Compound Construction
❗ You have to understand how the timeframes and cycles are interconnected. ❗
Take a look at the chart above. It contains the chart from the previous page with the waves (1) & (2).
But it is also a bigger, more detailed version of itself.
• One 5-wave pattern represents one part of a 5-waved pattern of a higher degree.
• It also can be subdivided into a 5-waved pattern of smaller degree.
Wave ② can also be subdivided into (A), (B), (C). Wave ② is a corrective wave on primary degree.
Its Wave (A) and (C) are motive waves, as they point of the trend direction of the correction.
• A 3-wave movement is a correction of a 5-wave pattern one degree higher.
• Wave (1), (2), (3), (4), (5) can also be subdivided into smaller versions of themselves.
❗ It’s crucial to understand, that these wave pattern are compounded in themselves. We could have a
nice trend on the 1 or 4-hour chart, which is only a correction of the daily chart.
It is not useful for everyday application to go too deep from a timeframe perspective.
A 5-waved motive pattern should be clearly visible one the 1h, 4h or daily chart.
When trading it’s best to look out for a continuation of the primary directional movement, as they are the
strongest with high momentum.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 4
Motive Waves
Impulse
Motives waves subdivide into five waves and always move in the same direction as the trend of one
degree higher. The countertrend wave 2 never moves beyond the beginning of wave 1 and wave 4
moves never beyond the beginning of wave 3.
There a 2 types of motive waves:
• The impulse
• The diagonal
The most common one is the impulse.
In an impulse wave 4 never overlaps with the high
of wave 1. Wave 1/3/5 are themselves motive.
Also wave 3 is never the shortest wave and
always an impulse.
Leading Diagonal
Leading Diagonals is a motive wave, but no
impulse as it also has corrective
characteristics.
Typically its wave 4 overlaps with the top of
wave 1.
It can be the Wave 1 of an Impulse or a Wave
A of an A-B-C Correction.
Its structure is either 3-3-3-3-3 or 5-3-5-3-5.
Rules:
• Wedge shape with parallel or contracting
trendlines
• Usually Wave 1 is the longest, Wave 3 must
be longer than Wave 5
• Wave 4 overlaps with wave 1 and has a smaller retracement than wave 2
• It is either followed by a wave 2 in a motive wave or by a wave B in an A-B-C correction.
❗ Often the fifth wave of the leading or ending diagonal makes a fake breakout above the trendline.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 5
Ending Diagonal
The Ending Diagonal is a pattern the occurs
when the preceding move as Elliott puts it
has gone „to far too fast“.
This pattern is mostly found in the fifth wave,
at the end of an impulse. It can also happen
as a final Wave C in a ABC-Correction.
Rules:
• Wedge shape with contracting trendlines
• Wave 4 overlaps with Wave 1, but does not
go beyond the start of wave 2
• Wave 1 is the longest wave and wave 3
can’t be shorter than wave 5
• Structure is normally 3-3-3-3-3, each
waves subdivides into a ZigZag a-b-c or
w-x-y
It is also accompanied by divergences in RSI
or MACD indicator.
❗ Watch out, often the fifth wave of the Ending Diagonal makes a fake breakout above the wedge
forming trendlines.
➔ Because Ending Diagonals only occur at the end of a move, the following trend change and new
direction of price action leads to great trade opportunities.
Truncation
A truncation is a „failure“ of the fifth wave to
move beyond the end of the third wave.
• It can usually be verified by identifying the
necessary five subwaves
• In classic technical analysis this wave
pattern can also be classified as a
common double top.
❗ A truncation usually happens after a really
strong extended third wave.
💡 Watch out for the subwaves to identify
the pattern early and be one step ahead.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 6
Extension
Most impulses contain what Elliott called an
extension. An extension is an elongated
wave with exaggerated subdivisions.
• The majority of impulses has one
extension.
• The most common extension is of wave 3,
although wave 1 and 5 are also possible
Have look at the chart on the right:
• Subwave 2 could not be labelled Wave 4,
because it overlaps with wave (1)
• Subwave 1 is shorter than wave (1)
→ If Subwave 1 is an impulse, than an
extended wave 3 is the most likely
expectation
❗ If wave 3 is the same size as wave 1, we would expect an extension of wave 5.
❗ Is wave 3 extended, Wave 5 often resemble Wave 1 in time and length.
Fifth Wave Extension of Fifth Wave Extension
An extension may also have an extension
within itself. This mostly happens in third of
fifth wave.
Normally you would expect a trend change
at the point of (1), because five waves took
place. But the trend remains intact and new
highs are made consistently.
→ This is where novices get eaten by the
market in one huge loss, as extensions tend
to go on forever.
❗ As only one Wave can be extended, if
wave 3 is the same size as wave 1, we would
expect an extension of wave 5.
„The trend is your friend“ - an old saying which is still true in today’s market. If most impulses have an
extension it is clever to ride the waves until a change of trend is clearly visible.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 7
Corrective Waves
Markets move against the trend of one greater degree only with struggle. This can be witnessed in
the frequently messy price action, as two forces are pulling in each direction. One clear rule for
corrections is, that they never have five waves. If they do, they are only a motive part of the overall
corrective pattern.
Corrections can be classified into two styles. There are the sharp corrections, which move sharply
against the major trend. Their angle is rather steep. On the other hand are sideways corrections, they
don’t retrace much in price, but can take a long time to finish.
Apart from the two styles are in general three correction pattern:
• Zig-Zag (5-3-5) (single, double, triple)
• Flat (3-3-5) (regular, expanded, running)
• Triangle (3-3-3-3-3) (contracting, barrier, expanding and running)
Combination of these pattern form either a double three or triple three correction. These prolonged
corrections are separated by a wave X.
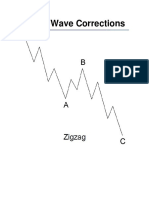
Zig-Zag Correction
A single Zig-Zag is a simple three-waved
corrective movement which is labelled A-B-
C.
It’s structure is 5-3-5, and top of wave B is
noticeable lower than the start of wave A.
Rules:
• Wave A has to be motive or diagonal
• Wave B can only be corrective pattern
• Wave B has to be shorter than Wave A
• Wave C has to be an impulse or ending
diagonal
This is the most common corrective pattern
in Elliott Wave Theory and is usually a sharp
correction.
The length of wave C is between
100%-161,8% of wave A.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 8
Zig-Zag’s appear most of the time as a wave 2,
but are also very common as a connective
wave in more complex corrections like a
double or triple three.
Occasionally Zig-Zag corrections will occur
two, sometimes even three times in a row.
This happens mostly, when the first Zig-Zag did
not correct far enough from a price
perspective.
❗ If a double Zig-Zag occurs, the single Zig-
Zags are separated by a three-waved
reactionary move, which is labelled Wave X
and is always corrective.
💡 Zig-Zag corrections often fit into a parallel
channel which is drawn between the highs of
wave A & B to determine the end of wave C.
Flat Correction
The Flat correction is the second most
common pattern and always has a 3-3-5
structure.
As wave A is not five-waved and powerful,
the retracement of wave B is rather strong.
Rules:
• Classic sideways movement, Wave A and
Wave B are corrective.
• Wave C is impulsive, but does not go
much below Wave A.
• Most of the time Wave B/C go some pips
above or below of Wave A ( just to trick
people into believing a breakout occurs).
• Although it is called the Regular Flat
Correction, it is not the most common one.
❗ Watch for overall market structure to avoid overtrading in corrections.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 9
Expanded Flat
The Expanded Flat is the most common one
under the flat corrections.
• Corrective wave pattern with an extended
wave B, which reaches higher than the
start of wave A.
• Wave B marks a fake breakout above the
last high.
• Wave C is also extended and goes deeper
than wave A.
• Structure of the correction is 3-3-5.
Rules:
• Wave B ends higher than the beginning of
wave A
• Wave C is an impulse or ending diagonal
and ends lower than the low of wave A
❗ Wave B/C over and over again catch traders on the wrong side, as fake breakouts take place just before the
market turns.
Running Flat
The last of the flat corrections is the running
variation. It is the least common one, but has the
same 3-3-5 structure.
Rules:
• Wave B ends high above the beginning of
wave A
• Wave C ends higher than the end of wave A
• Usually wave C is the same length as wave A.
→ This kind of correction happen in really strong
and fast markets. The fast and high push of
wave B and the short wave C are signs of a
strong primary trend.
A parallel channel regularly marks the low of
wave C.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 10
Contracting Triangle
Triangles represent a balance of the buying
and selling force in the market. They contain
five overlapping waves with a 3-3-3-3-3
structure.
The contracting triangle represents the most
frequently appearing.
Rules:
• Triangles have 5 Waves: A-B-C-D-E
• All of the waves are corrective
• Upper line is declining, lower line is rising
• Wave E frequently overshoots the
trendline and can also be a triangle
• Triangles only occur as a Wave 4/B/X/Y
• Never as a Wave 2/A
❗ Triangles represent a continuation pattern for the dominant trend.
Barrier & Expanded Triangle
The other two variations are the barrier and expanded triangle. They have the same characteristics as
the contracting triangle except their overall shape.
Usually triangles occur prior to the final push in the trend one degree higher. This final push is either a
wave 5 in an impulse or wave C in A-B-C correction. Often it travels the distance of the widest part of
the triangle.
They also occur in more complex corrections like the double or triple three, which are discussed in the
next chapter.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 11
Double Three
Apart from the normal and short corrections,
exist the more complex variations like the
double or triple three.
These pattern are combination of single
simple correction pattern like the zig-zag,
the flat or triangle variation.
These single corrections are linked by a
connecting „X“ Wave, which can take any
corrective form, but is usually a zig-zag.
Characteristic for complex corrections is the
sideways movement.
Rules:
• Zig-Zags and triangles only happen once
in these combination.
• Triangles only appear as Wave Y.
• The difference to a double Zig-Zag
correction apart from the elements, is the
horizontal orientation. A Zig-Zag corrects
sharper and more against the major trend.
→ It is possible that two flats are appearing,
but a flat followed by a triangle is a more
common example. As the single corrections
tend to alternate in form.
The count for a double three is W-X-Y.
Double three’s are common in the more
shallow wave 4.
❗ The purpose of double or triple threes is
to expand the duration of the correction.
❗ Watch out for a triangle or a final wave C
to catch the continuation of the primary
trend.
The pattern displayed show only some
possible variation the double three can take
due to reasons for clarity.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 12
Triple Three
Next to the double three exist the even more
complex or elongated corrections the triple
three.
The triple three correction is very similar to
the double three, it is just even more
extended.
The overall count is W-X-Y-X-Z, so the three
simple corrections are separated by two X
waves.
Similar to the double three, these X waves
are normally zig-zags, but can take any form.
A triangle is only valid as wave Z and
therefore represent the end of the correction.
As with the double three, the variation
displayed only show some possible forms.
In general the three simple corrective pattern
can take any shape (Flat, zig-zag, triangle),
but usually show alternation between
themselves.
A final notice about corrections:
Most traders loose money in these long
sideways corrections as the market does not
present a clear trend.
It is usually full of false breakouts and messy
price action. The experience shows, that
most of the time it is the best decision to stay
out of the market until a clear entry signal is
given.
In some cases a clear ranging market
(especially on higher timeframe) can be
traded, but this is only for experienced
traders.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 13
Guidelines of Wave Formation
The Elliott Wave pattern are conducted by rules, which can not be broken to classify one pattern. The two
most widely know are, that wave 3 can’t be the shortest wave, and wave 4 can’t overlap with wave 1.
Apart from the rules to classify the movements in the market, exist guidelines for identifying the correct
count. These guidelines can best be interpreted as a help to determine what is the most probable thing to
happen. But they are no rules, and therefore the possible must always be kept in mind.
In this chapter you will find additional concepts to make analysis easier and develop the right look.
Apart from the guidelines already described at the individual wave pattern, you will learn about alternation,
channeling, wave personality etc.
Alternation
When talking about guidelines, the concept
of alternation has to be discussed.
It basically states, that when analyzing the
markets, the most common pattern to expect
next, is one, that differs from the previous
related pattern.
To illustrate this concept, take a look at the
chart to the right. It shows a complete
impulse with five waves.
• Wave 2 corrects rather sharp against the
major trend und deep to the 61,8%
Fibonacci level.
• Wave 4 on the other hand is more of a
sideways correction and only corrects to
the 38,2% Fibonacci level.
Usually wave 2 is a zig-zag which corrects much of the price movement and wave 4 is either a flat,
triangle, double or triple three correction whose purpose lies in the extension of duration.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 14
Alternation within Corrective Waves
Not only does alternation take place
between different waves, but also within the
waves themselves.
Have a look at the two corrections shown.
They are both (A)-(B)-(C) pattern, but differ in
development.
In the first variation wave (A) is made of a
ABC Flat correction, which is followed by a
ABC Zig-Zag correction forming wave (B).
The second variation represents the exact
opposite. In both cases the second
component of the correction (Wave (B)),
varies from the first component.
→ Both corrections finish with a classic wave
(C), which is a five-wave countertrend
movement.
Channeling
As Elliott stated, a parallel channel often
occurs in the impulsive phase of the market
cycle and marks the lower and upper
boundaries of the impulse.
• For the initial channel we need three
reference points
• We can draw a channel when Wave 3 has
finished.
→ Draw a line between the high points of
Wave 1 and Wave 3 and make a parallel line
touching the base of Wave 2
→ The extension of this parallel line will determine the most likely ending point of Wave 4
❗ The final Wave 5 of the impulsive move has a target projection at the upper channel boundary.
💡 Wave 5 frequently forms a „throw-over“ which is a fake breakout above the channel line.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 15
Wave Personality
The price movements are the collective reflection of the beliefs of all market participants. They
represent mass psychology and the underlining dynamics from pessimism to optimism and back again.
Wave 1 is sometimes hard to spot, as the previous opposite trend is still intact. It also does not have
clear price action, looks choppy and the waves are overlapping, forming wedges/diagonals.
Wave 2 retraces a lot of the price movement made in wave 1. Most of the market participants still
speculate on the previous trend to continue and do not notice the ongoing trend change.
Wave 3 is usually the biggest move. It represents the finished trend change, as wave 2 made a higher
low followed by a higher high in wave 3. Also it is frequently extended, moving with strong momentum
without any major corrections to new highs.
Wave 4 can generally be predicted easily, as they tend to alternate to wave 2 and take more time to
finish. Most of the time it is a complex sideways movement, tricking traders into false signals.
Wave 5 represents the final push in the direction of the dominant trend. Usually wave 5 comes with
lower volume and often shows a clear divergence in indicators like the RSI, MACD etc.
Wave A can unfold in either three or five wave structure. It represents the exhaustion in the market and
is regularly not clearly visible as a lot of traders just think it is a normal pullback of the dominant trend.
Wave B is can take many shapes and are known for being a „bull-trap“. The can either retrace much
lower than wave A or they shoot back up fast, sometimes even above the last high, catching traders on
the wrong side as a fake breakout occurs. They always have there subwaves and in classical technical
analysis represent the right shoulder in Head-Shoulder formation.
Wave C is impulsive and has five waves against the dominant trend. Continually it has the length of
wave A, but an extension to the 161,8% or even greater is possible, making them fast and devastating
moves. It frequently catches traders on the wrong side of the market.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 16
Fibonacci & Ratio Analysis
When talking about Elliott waves, the proportional relationship between waves has to be considered. The
concept of the fibonacci numbers, which could be discussed in a book of its own, can often be applied
with exceptional accuracy.
In the following chapter we will take a look at the overall market structure, the retracement levels, motive
wave multiples and how to correctly apply the ratio analysis.
The practical application of Fibonacci level and Elliott waves can be divided into two groups.
• Retracements - identify probable targets for a corrective wave
• Extensions - identify probable targets for the next impulsive wave
The Retracement measures how far the correction retraces the previous wave.
Sharp corrections like a Zig-Zag as wave 2, wave B in a larger Zig-Zag, or a wave X correct time and again
to the 50%-61,8% level of the previous wave. If wave 1 is a leading diagonal it can even go travel to the
78,6% level.
Sideways corrections like a flat variation, double or triple three often correct only to the 23,6 / 38,2%
retracement. These shallow corrections regularly occur as a wave 4.
❗ In general wave 2 corrects deeply (e.g. 61,8%), while wave 4 is shallow and only reaches the 38,2%.
❗ IF daily price action candlestick signals occur, most of the time a retest and entry at 50% level is possible.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 17
Motive Wave Multiples
Apart from identifying a possible target for a retracement, it is very useful to determine a target for the
next impulse.
One way is to apply the Extension of the previous wave. To determine the extension you have to measure
the initial wave (e.g. Wave 1), and attach the multiples at the low of wave 2.
This can be seen at the diagram above.
• On the left, wave 3 is 161,8% of wave 1 which was laid at the low of wave 2.
• On the left, wave 5 is 161,8% of the length wave 1 to wave 3, attached to the low of wave 4.
→ Such a great extension of wave 5 only happens, if wave 5 is extended.
On the right is far more typical variation of an impulse:
• Wave 3 is 200% of wave 1, also attached to the low of wave 2.
• Wave 5 can be measured in different ways.
• Wave 5 = Wave 1 (100% of wave 1 attached to low of wave 4)
• Wave 5 = 61,8% extension of wave 1 to wave 3, attached to low of wave 4)
Motive Wave Multiples:
• Wave 1 - No target, initial wave
• Wave 3
• 161,8-261,8% extension of wave 1
• In rare cases over 261,8% extension of wave 1. (Extended wave within extended wave)
• Wave 5
• 100% of wave 1
• 100% of wave 3
• 61,8% of wave 1-3
• etc.
Always keep the overall right look in mind. Wave 3 is the most likely wave to be extended.
If so, wave 1 and 5 are probable to be similar in size and time. If wave 1 and 3 look very similar in size,
wave 5 most definitely will be extended. Always close some of your position at potential targets.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 18
Corrective Wave Multiples
The multiples of waves can also be applied to corrections. In a Zig-Zag Wave C repeatedly equals
Wave A in length. But other ratios like 161,8% or 61,8% do also occur. This ratio does also apply to the
first and the second zig-zag in a double zig-zag correction.
A regular flat correction, has Waves A/B/C which are quite equal. On the other hand, the extended flat
correction has different ratios applied. In this case wave C often represents the 161,8% extension of
wave A.
As you can see the waves are connected through a relationship in their ratio of magnitude and time.
But not only the degree of waves or timeframe you currently analyze, all degrees are operating at the
same time. Therefore have level with multiple Fibonacci relationships, more importance than a single
relationship.
BUT the concept of measuring the waves should always be the second part when analyzing the
markets. Do not expect to correctly measure a target for a wave, if the overall count is not valid and
rules were broken. The fibonacci numbers are complementary applied to the Elliott Wave theory.
Always be flexible in your approach and preserve capital if you are in doubt. Watch for clear pattern and
execute only if your edge appears in the market.
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 19
Summary
Dear Trader,
thanks for taking the time and reading my compendium about Elliott Waves. I hope you find some notable
insights in this guide.
In my own trading journey I discovered and adapted the Elliott waves, as I was stunned about the
accuracy this methodology applies to the markets. The waves represent one building block and are
combined with powerful price action trading to make my edge even greater.
You have to understand, that a methodology, may it be Elliott waves or something completely different, is
just one part of your successful trading.
A far greater element in becoming a successful trader, is the mindset you must obtain. You could have the
best strategies available, if you do not master the voice inside your head and the emotions which come
up while trading, it won’t be easy to reach mastery. I encourage you to take this journey serious and take
responsibility for your actions.
If you are openminded, disciplined and patient you can master the craft. Journal your trades, reflect your
thoughts and actions and you can reach your own financial freedom.
May your journey into trading be prosperous,
Phil
Founder of Financial Freedom Trading
www.financialfreedomtrading.com
www.instagram.com/financial_freedom_trading/
www.facebook.com/financialfreedomtrading/
www.tradingview.com/u/FinancialFreedomTrading/
© 2020 Financial Freedom Trading 20
You might also like
- Harmonic Elliott Wave: The Case for Modification of R. N. Elliott's Impulsive Wave StructureFrom EverandHarmonic Elliott Wave: The Case for Modification of R. N. Elliott's Impulsive Wave StructureRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 05 - Class 05 - Elliot Wave and FibonacciDocument11 pages05 - Class 05 - Elliot Wave and FibonacciChandler BingNo ratings yet
- Guideline 1: How To Draw Elliott Wave On ChartDocument6 pagesGuideline 1: How To Draw Elliott Wave On ChartAtul Mestry100% (2)
- Elliott Wave - Fibonacci High Probability Trading: Master The Wave Principle And Market Timing With Proven StrategiesFrom EverandElliott Wave - Fibonacci High Probability Trading: Master The Wave Principle And Market Timing With Proven StrategiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- GuideToElliottWaveAnalysisAug2012 PDFDocument5 pagesGuideToElliottWaveAnalysisAug2012 PDFvhugeat50% (2)
- Mastering Elliott Wave Principle: Elementary Concepts, Wave Patterns, and Practice ExercisesFrom EverandMastering Elliott Wave Principle: Elementary Concepts, Wave Patterns, and Practice ExercisesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Elliot Wave For Advanced UsersDocument9 pagesElliot Wave For Advanced UsersRazif Bahsir60% (5)
- Elliott Wave Patterns & Fibonacci Relationships GuideDocument30 pagesElliott Wave Patterns & Fibonacci Relationships Guidejorge perez100% (1)
- Tramline Trading: A practical guide to swing trading with tramlines, Elliott Waves and Fibonacci levelsFrom EverandTramline Trading: A practical guide to swing trading with tramlines, Elliott Waves and Fibonacci levelsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Elliott Wave Lesson 2: Cardinal Rules and GuidelinesDocument29 pagesElliott Wave Lesson 2: Cardinal Rules and Guidelinesfrancisblesson100% (1)
- Elliot Wave and Fibo All in OneDocument17 pagesElliot Wave and Fibo All in OneSATISH100% (4)
- Elliott GuideDocument42 pagesElliott GuideemreNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave and Fibonacci Ratios ManualDocument198 pagesElliott Wave and Fibonacci Ratios Manualstephane83% (6)
- Elliott Wave For BeginnersDocument11 pagesElliott Wave For Beginnersmytemp_0133% (3)
- Elliott Wave BasicsDocument16 pagesElliott Wave BasicsdeepakraoaNo ratings yet
- Elliott IndicatorDocument160 pagesElliott IndicatorEmmanuelUhuru100% (1)
- Using Elliot Wave For Advanced UsersDocument9 pagesUsing Elliot Wave For Advanced Usersokeke ekene100% (1)
- Elliott Wave Basics Impulse PatternsDocument12 pagesElliott Wave Basics Impulse Patternsjagadeesh44No ratings yet
- Elliott Wave Rules and GuidelinesDocument4 pagesElliott Wave Rules and Guidelineskacraj100% (1)
- 13 Elliott wave patterns guideDocument20 pages13 Elliott wave patterns guideDiepakk Upadhyay0% (1)
- The Elliot-Wave-Principle: Master and Ride The WavesDocument48 pagesThe Elliot-Wave-Principle: Master and Ride The WavesOburoh Bemigho Peter100% (1)
- 10.1 Elliot Wave Corrective Rules and CharacteristicsDocument23 pages10.1 Elliot Wave Corrective Rules and CharacteristicsJustin Lim100% (1)
- Corrective WaveDocument1 pageCorrective WaveMoses ArgNo ratings yet
- Advanced Level Elliott Wave Analysis GuideDocument64 pagesAdvanced Level Elliott Wave Analysis GuideMohd Harraz Abbasy100% (2)
- Practical Application of Elliott Wave Principle PDFDocument159 pagesPractical Application of Elliott Wave Principle PDFjorge perez100% (36)
- 1 5089578216180416934Document145 pages1 5089578216180416934Bruce wayne100% (3)
- Elliott Wave Final ProjectDocument81 pagesElliott Wave Final Projectrinekshj100% (2)
- Elliot Wave - The Ending Diagonal TriangleDocument9 pagesElliot Wave - The Ending Diagonal TriangleAngela WilsonNo ratings yet
- How to Trade Elliott Waves Like a ProDocument131 pagesHow to Trade Elliott Waves Like a ProShah Aia Takaful Planner100% (1)
- Elliot Wave TheoryDocument60 pagesElliot Wave TheoryMatt Hannan100% (3)
- Elliott & FibboDocument17 pagesElliott & FibboSATISH100% (2)
- Elliott Wave Cheat Sheet FINAL PDFDocument6 pagesElliott Wave Cheat Sheet FINAL PDFhawafiNo ratings yet
- 1001 Discovering EWPDocument11 pages1001 Discovering EWPJustin Yeo0% (1)
- 28 Elliot Wave PDFDocument14 pages28 Elliot Wave PDFRavikumar GandlaNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave Theory PDFDocument15 pagesElliott Wave Theory PDFupkumara100% (1)
- Practical Ew StrategiesDocument48 pagesPractical Ew Strategiesanudora100% (2)
- Eliot Waves E Book Part1 PDFDocument13 pagesEliot Waves E Book Part1 PDFByron Arroba0% (1)
- Elliott Wave CorrectionsDocument22 pagesElliott Wave CorrectionsBogdanC-tin100% (1)
- Elliott WAVe SimpleDocument22 pagesElliott WAVe Simplel3ohit100% (1)
- The Magic and Logic ofDocument72 pagesThe Magic and Logic ofKane Oo100% (2)
- ElliottWaveManual+G P@FBDocument71 pagesElliottWaveManual+G P@FBPranshu gupta100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet 1: Elliott Wave Dna: Wave 3 Buy Conservative SetupDocument12 pagesCheat Sheet 1: Elliott Wave Dna: Wave 3 Buy Conservative SetupPranshu gupta100% (2)
- Elliott Wave TheoryDocument13 pagesElliott Wave Theorymark adamNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave Rules, Guidelines and Basic StructuresDocument22 pagesElliott Wave Rules, Guidelines and Basic Structuresalok100% (1)
- Wave 4 Should Not Overlap Wave 1Document4 pagesWave 4 Should Not Overlap Wave 1James Roni100% (1)
- AWESOME GUIDE To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns and Rules!!Document20 pagesAWESOME GUIDE To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns and Rules!!SATISH100% (1)
- The Mystery of Elliott Wave AnalysisDocument6 pagesThe Mystery of Elliott Wave AnalysismgrreddyNo ratings yet
- Elliot Wave: by Noname Intermediate Elliot Wave Advanced Elliot WaveDocument30 pagesElliot Wave: by Noname Intermediate Elliot Wave Advanced Elliot WaveGlobal Evangelical Church Sogakope BuyingLeads100% (1)
- Completed Guide To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns PDFDocument14 pagesCompleted Guide To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns PDFQasim AnwarNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave PrincipleDocument41 pagesElliott Wave Principlecarlos mourao100% (1)
- Excerpts, Contents & Prices: Elliott Wave TradingDocument47 pagesExcerpts, Contents & Prices: Elliott Wave TradingCristian100% (1)
- Elliot Wave Ebook Compressed PDFDocument29 pagesElliot Wave Ebook Compressed PDFTimileyin Adediran88% (8)
- Ultimate Guide To Elliott Wave 1 1Document22 pagesUltimate Guide To Elliott Wave 1 1enver88% (8)
- Elliott Wave Structures Guide - Page 1Document2 pagesElliott Wave Structures Guide - Page 1Access LimitedNo ratings yet
- New Elliott Wave Rule PDFDocument40 pagesNew Elliott Wave Rule PDFSimon Eduerte100% (1)
- Elliott Wave - Elite Trader's SecretDocument83 pagesElliott Wave - Elite Trader's Secretisaac100% (2)
- Wave Theory - ComDocument26 pagesWave Theory - ComKevin Sula100% (2)
- Elliott Wave SummarizedDocument1 pageElliott Wave SummarizedNd Reyes100% (7)
- Medicard Phil Inc. vs. CIRDocument2 pagesMedicard Phil Inc. vs. CIRhigoremso giensdksNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Case StudyDocument7 pagesModule 1 Case StudyDivine ParagasNo ratings yet
- Facebook Black BookDocument23 pagesFacebook Black Bookwise_man1975100% (1)
- Question 1 - Adjusting EntriesDocument10 pagesQuestion 1 - Adjusting EntriesVyish VyishuNo ratings yet
- Ken Scott - Metal BoatsDocument208 pagesKen Scott - Metal BoatsMaxi Sie100% (3)
- Individual Learning Monitoring PlanDocument2 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring PlanJohnArgielLaurenteVictorNo ratings yet
- Annual Report-2018-19 (English)Document242 pagesAnnual Report-2018-19 (English)Alle de BeusNo ratings yet
- CS 401 Artificial Intelligence: Zain - Iqbal@nu - Edu.pkDocument40 pagesCS 401 Artificial Intelligence: Zain - Iqbal@nu - Edu.pkHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- Caren 4TH Q Finals MapehDocument3 pagesCaren 4TH Q Finals MapehDexter Lloyd Chavez CatiagNo ratings yet
- A Gringa in Oaxaca PDFDocument54 pagesA Gringa in Oaxaca PDFPeggy BryanNo ratings yet
- Essay 2Document13 pagesEssay 2Monarch ParmarNo ratings yet
- Maceda Vs Energy Reg BoardDocument4 pagesMaceda Vs Energy Reg BoardJay Mark Esconde100% (1)
- 555 and 556 Timer CircuitsDocument16 pages555 and 556 Timer Circuitssiddharthmohta100% (2)
- Part of Speech QuestionsDocument4 pagesPart of Speech QuestionsNi Luh Ari Kusumawati0% (1)
- CFLM-1 Chapter 5Document17 pagesCFLM-1 Chapter 5Rico T. MusongNo ratings yet
- Thời gian làm bài: 90 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề)Document8 pagesThời gian làm bài: 90 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề)Nguyễn KiênNo ratings yet
- Conciliar Post Reference GuideDocument9 pagesConciliar Post Reference GuideBenjamin WinterNo ratings yet
- EGNTDocument6 pagesEGNTTida Nicholas NyahunzviNo ratings yet
- Letter To Editor NDocument5 pagesLetter To Editor NNavya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Speidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.Document11 pagesSpeidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.oozdemirNo ratings yet
- Trust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDocument8 pagesTrust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDekweriz100% (1)
- Competences Needed in Testing - Handout Manual PDFDocument97 pagesCompetences Needed in Testing - Handout Manual PDFCristina LucaNo ratings yet
- Explore the City Centre in Salt Lake, KolkataDocument7 pagesExplore the City Centre in Salt Lake, Kolkataaishwarya raniNo ratings yet
- Swift Group Technical HandbookDocument8 pagesSwift Group Technical HandbookLukasz WilkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business ManagementDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Business ManagementZintle Mini0% (1)
- The Carb Cycling Codex ThibaudeuDocument30 pagesThe Carb Cycling Codex ThibaudeuOrlando Paez Cortazar100% (1)
- Human Rights EducationDocument149 pagesHuman Rights EducationLeonard MamergaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights DefinitionDocument2 pagesHuman Rights DefinitionFathiah MhNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 Module 1: Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Mountain RangesDocument38 pagesScience: Quarter 1 Module 1: Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Mountain RangesMaria LayupanNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - T - Basic Negotiation Skill Vol. 1Document5 pages2.2 - T - Basic Negotiation Skill Vol. 1Siva 93No ratings yet