Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
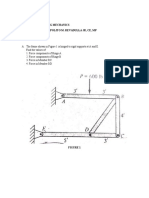
1. Determine the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shaded area shown in Figure below.
2. Locate the centroid of the plane area shown in Figure below with respect to the x and y axis.
3. Determine the centroid of the shaded area of the Figure shown below with respect to the
given X and Y axis.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
4. For the shaded area shown in Figure below, determine centroid position of the shaded area
with respect to x and y axes.
5. For the shaded area shown in Figure below, determine centroid position of the shaded area
with respect to x and y axes.
6. Determine centroid of the shaded area shown in Fig 2a with respect to OX and OY axes
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
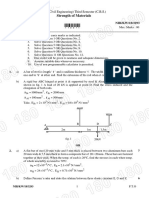
Section: X
7. Determine centroid of the shaded area shown in Figure below with respect to OX and OY
axes.
8. For the shaded area shown in Fig.2B, determine centroid position of the shaded area with
respect to x and y axes.
9. Determine the moment of inertia and radius of gyration of the shaded area shown in Figure
below with respect to the x and y axis.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
10. Determine the moments of inertia and radius of gyration of the shaded area shown in Figure
shown below with respect to the x axis.
11. Determine the moment of inertia of the composite area shown in Figure below with respect
to X axis.
� Engineering Mechanics
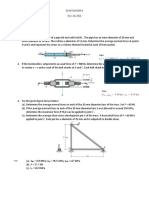
Assignment - 05
Section: X
12. Determine moments of inertia of the I-shape section shown in Figure below with respect to
its centroidal axes XX and YY. Also, determine polar moment of inertia about an axis which
is perpendicular to centroidal XX and YY axes.
13. Determine the moments of inertia of the area shown in Figure below with respect to side AB
and about an axis which is the perpendicular bisector to AB.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
14. Determine area moment or inertia for the section as shown in Figure below about centroidal
axis XX.
15. Determine area moment of inertia of the stepped area as shown in Figure below about
reference axes XX and YY.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
16. For the area shown in Figure below, determine area moment of inertia about centroidal axis.
17. A cast iron beam 20 mm × 20 mm in section and 1 m long is simply supported at the ends. It carries a point
load of W N at centre. The maximum bending stress induced is 120 N/mm2. Calculate the value of point load
W. What uniformly distributed load will break a cantilever of the same material 50 mm wide, 100 mm deep
and 2 m long?
18. A symmetrical section 300 mm deep has a moment of inertia of 8 × 106 mm4 about its neutral axis. Determine
the longest span over which, when simply supported, the beam would carry a u.d.l. of 3.2 kN/m run without
the stresses due to bending exceeding 120 N/mm2.
19. A timber beam of rectangular section, simply supported over a span of 4 m, is carrying a u.d.l. of 5.1 kN/m
over the entire span. Calculate the width and depth of the beam if the stress is not to exceed 8 N/mm2. Take
ratio of depth to width as 1.5.
20. A T-section is simply supported over a span of 10 m. The beam carries a concentrated load of 2500 N at mid-
span. Calculate the safe u.d.l. which the beam can carry if the maximum allowable stress is 100 N/mm2.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
140 mm
10 mm
140 mm
10 mm
21. A cast iron pipe 300 mm bore, metal thickness 15 mm, is supported at two points 6 m apart. Find the
maximum stress in the metal of pipe when it is running full of water. Density of cast iron is 70.63 kN/m3 and
that of water is 9.81 kN/m3.
22. Calculate the dimensions of the strongest rectangular beam that can be cut out of log of a wood 500 mm in
diameter.
23. A horizontal beam as shown in Fig. below is 3 m long is simply supported at ends. Find the maximum u.d.l. it
can carry if the compressive and tensile stresses must not exceed 56 N/mm2 and 30 N/mm2, respectively.
Draw a diagram showing the variation of stress over the mid span section of the beam.
25 mm 25 mm
120 mm
150 mm
24. For a given stress, compare the moments of resistance of a beam square section, when placed
i. With its two sides horizontal
ii. With its diagonal horizontal
25. Draw the shear stress distribution of the following sections under a shear force of F:
i. Rectangular section having width, b and depth, d
ii. Circular section having diameter of, d
iii. Hollow rectangular section having outer width, B and outer depth, D with inner width, b and
inner depth, d.
26. A timber beam 150 mm × 300 mm in cross-section is simply supported at its ends and has a span of 4 m. The
maximum safe allowable stress in bending is 8 N/mm2. Find the maximum safe u.d.l. which the beam can
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
carry. What is the maximum shear stress in this beam for u.d.l. calculated? Draw the bending and shear stress
diagram.
27. A 3 m long beam of rectangular section is loaded by a concentrated load of 8000 N at its mid span. Determine
the maximum shear stress and average shear stress on the section subjected to maximum shear force. Also,
draw the shear stress diagram across the section. The size of the beam is 100 mm × 200 mm.
28. At certain cross-section of a beam of rectangular section 120 mm × 300 mm, the bending moment is 180 kN-
m while the shear force is 24 kN. Calculate the bending and shear stresses at 150 mm, 100 mm, 50 mm and
0 mm from the neutral axis. Draw the bending and shear stress diagram across the section.
29. A T-beam of flange size 80 mm × 10 mm and web size of 120 mm × 10 mm is subjected to shear force of 10
kN. Compute and draw the variation of shear force over the depth of the section.
30. For a beam having the section shown in Figure below (dimensions are in mm). Determine the largest allowable
vertical force if the allowable shear is 60 MPa.
31. Draw the shear stress distribution across the depth of a C - section as shown in Figure below for a shear force of
50 kN.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
32. A torque of magnitude T = 4 kNm is applied at end A of the composite shaft shown in Figure below. Modulus
of rigidity is 77 GPa for steel and 27GPa for aluminum. Determine the maximum shearing stress in the steel
core. (ii) maximum shearing stress in the aluminum jacket and (iii) the angle of twist at A.
33. A composite shaft consists of copper rod 30 mm in diameter enclosed in a tube of 40 mm external diameter
and 5 mm thickness. There is no relative motion between the two and shafts are co axially fixed. Determine
the shear stresses developed in copper and steel rods if both the shafts have equal lengths. Take shear
modulus for copper as 40 GPa and shear modulus of steel 80 GPa. The shaft is required to transmit a torque
of 5 kN-m.
� Engineering Mechanics
Assignment - 05
Section: X
34.