Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 4 RESULTS-AND-DISCUSSION
Uploaded by
Czarina MasicatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 4 RESULTS-AND-DISCUSSION
Uploaded by
Czarina MasicatCopyright:
Available Formats
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
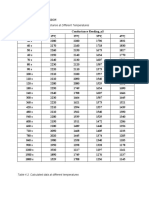
Table 4.1. Data from the titration of A-B with C.
Time Elapsed Conductance Reading
(s) 15℃ 25℃ 35℃ 45℃
30 2280 µS 2200 µS 1796 µS 1832 µS
40 2270 µS 2160 µS 1718 µS 1830 µS
50 2260 µS 2150 µS 1673 µS 1827 µS
60 2250 µS 2140 µS 1634 µS 1770 µS
70 2240 µS 2130 µS 1607 µS 1761 µS
80 2230 µS 2120 µS 1587 µS 1724 µS
90 2220 µS 2110 µS 1573 µS 1690 µS
100 2210 µS 2100 µS 1557 µS 1666 µS
110 2210 µS 2090 µS 1540 µS 1645 µS
120 2200 µS 2080 µS 1529 µS 1832 µS
180 2150 µS - 1472 µS 1521 µS
240 2100 µS - 1440 µS 1439 µS
300 2050 µS 1749 µS 1405 µS 1390 µS
360 2020 µS 1708 µS 1374 µS 1340 µS
420 1980 µS 1664 µS 1340 µS 1286 µS
480 1950 µS 1621 µS 1328 µS 1256 µS
540 1920 µS 1594 µS 1297 µS 1233 µS
600 1890 µS 1562 µS 1276 µS 1205 µS
660 1529 µS 1539 µS 1256 µS 1183 µS
720 1456 µS 1511 µS 1242 µS 1178 µS
780 1392 µS 1489 µS 1227 µS 1161 µS
840 2150 µS 1468 µS 1216 µS 1137 µS
900 2100 µS 1445 µS 1206 µS 1145 µS
1200 2050 µS 1358 µS 1158 µS 1137 µS
1500 2020 µS 1298 µS 1119 µS 1098 µS
1800 1980 µS 1227 µS 1094 µS 1071 µS
Table 4.2. Calculated data at different temperatures
Temp (℃) Rate Constant Go Activation Energy
15 0.049372
90619.88 J
25 0.196819
35 0.573558
Kinetics is the branch of chemistry or biochemistry concerned with measuring and studying the rates of
reactions. Generally, it tells how fast a reaction occur. Conductance (commonly denoted as L in Physics;
denoted as G in this experiment) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity (ohms). Conductivity is used to
measure the concentration of dissolved solids which have been ionized in a polar solution. The
saponification of ethyl acetate with sodium hydroxide is a second order, irreversible reaction; first order
with respect to CH3COOC2H5, and first order with respect to OH -. Hydroxide ions were consumed and
acetate ions were produced as the reaction happens. As a result, there would be an observed change in
conductance. Moreover, the molar conductivity of OH - ion is significantly larger than that of other ions
except for H+ ion, which is insignificant for the chemical reaction being studied.
In a presence of ions in a solution, it is said to conduct an electric current. The more ions present on the
solution gives higher conductance measurement. Also, sodium hydroxide dissolves and dissociates
completely so there are more ions that would be able to conduct. As a result, the measured
conductance is high. Meanwhile, ethyl acetate does not dissociate completely so there are fewer ions to
conduct which results to a relatively lower measured conductance. As the reaction happens, the number
of OH ions decreased (consumption of reactant) which lowered the overall conductance of the system.
Conductance was plotted against time for the values obtained during the first 2 minutes. The value of
the initial conductance, Go, was obtained (y-intercept). This was useful in calculating the rate of
1 Go−¿
reaction, k, for all temperatures using equation ¿= ( ) + 𝐺∞. In the experiment, it was evident
ak t
that the rate constant is directly proportional to temperature. The increase of kinetic energy of the
particles which increases the collisions between particles yields a faster reaction. As a rule of thumb,
reaction rates for many reactions double or triple for every 10 degrees Celsius increase in temperature,
as was observable in the chemical reaction being studied. Furthermore, Arrhenius equation,
Ea
ln k =ln A – , was used to determine the activation energy of the reaction. The experimental E a
RT
obtained was 90619.88 J which is the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical
reaction.
The errors that may have occurred in the experiment are usually from instrumental and personal errors.
An error present during the experiment was the fluctuation of temperature. During the experiment, the
temperature in the water bath varied by a degree or more. This error leads to inaccurate conductance
measurement since the conductance varies when the temperature changes. Another source of error is
the improper calibration of the conductance cell which would produce inaccurate results. These errors
may propagate throughout the calculation and duration of the experiment. Errors may also occur from
improper preparation of the solutions used. These errors present may be from the use of pipette, such
as from parallax errors.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Distillation Aspen HysysDocument66 pagesDistillation Aspen HysysCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Parcel History Final1Document8 pagesParcel History Final1sarthakjoshiNo ratings yet
- Dispersion-Modelling FinalDocument37 pagesDispersion-Modelling FinalCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Table 4.1. Values of Conductance at Different TemperaturesDocument6 pagesTable 4.1. Values of Conductance at Different TemperaturesCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Project Charter TemplateDocument1 pageProject Charter TemplateSyed Marwan AmeerNo ratings yet
- Sample Letter-Of-InterestDocument1 pageSample Letter-Of-InterestCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 SchematicDocument2 pagesExperiment 2 SchematicCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 SchematicDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 SchematicCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Plant Visit Report FormatDocument1 pagePlant Visit Report FormatCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Sample Cover-Letter 2Document1 pageSample Cover-Letter 2Czarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Seminar-Symposium Report FormatDocument2 pagesSeminar-Symposium Report FormatCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Sample Cover-LetterDocument1 pageSample Cover-LetterCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Sample Letter-Of-InterestDocument1 pageSample Letter-Of-InterestCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Alamin 2016Document9 pagesAlamin 2016Czarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- CSTR and Batch ReactorDocument1 pageCSTR and Batch ReactorCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Math Example PDFDocument18 pagesMath Example PDFAlexSilverSwordNo ratings yet
- Gaussian PlumesDocument7 pagesGaussian PlumesVeky PamintuNo ratings yet
- Plumed 4Document116 pagesPlumed 4Priya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Tables For Gaussian Plume ModelDocument1 pageTables For Gaussian Plume ModelCzarina MasicatNo ratings yet
- Gaussian PlumesDocument7 pagesGaussian PlumesVeky PamintuNo ratings yet
- Get Started Guide For New Users of Aspen HYSYSDocument23 pagesGet Started Guide For New Users of Aspen HYSYSudokasNo ratings yet
- Dist 003H ShortcutDocument7 pagesDist 003H ShortcutudokasNo ratings yet
- Production of Single Cell Protein Through FermentaDocument147 pagesProduction of Single Cell Protein Through FermentaSargam SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL SCIENCE 5 Q4 Week 9Document6 pagesGrade 5 DLL SCIENCE 5 Q4 Week 9Buena RosarioNo ratings yet
- Determination of HCV of Solid or Liquid Fuel Using Bomb CalorimeterDocument11 pagesDetermination of HCV of Solid or Liquid Fuel Using Bomb CalorimeterRavi PatilNo ratings yet
- Is - Iec .60079.20.1.2010 0 PDFDocument79 pagesIs - Iec .60079.20.1.2010 0 PDFAlex MtNo ratings yet
- Equations in PhysicsDocument2 pagesEquations in PhysicsDhruti MysoreNo ratings yet
- MEET 416 Module 1Document16 pagesMEET 416 Module 1Kian MoradosNo ratings yet
- Air Solubility in WaterDocument3 pagesAir Solubility in WaterSaverio GabrieleNo ratings yet
- Admission Brochure For PHD Admission Test: First Semester 2014-15 IndexDocument13 pagesAdmission Brochure For PHD Admission Test: First Semester 2014-15 IndexAnjnaKandariNo ratings yet
- Teknologi HurdleDocument39 pagesTeknologi HurdlenadiaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis M5 VTUDocument21 pagesPower System Analysis M5 VTUAndrewNo ratings yet
- Wenshuai ChenDocument36 pagesWenshuai ChenEstudiante2346No ratings yet
- Chroma TDocument73 pagesChroma TAnonymous XuiUo2ThNo ratings yet
- Chou19APR6 11304 Topological Quantum MaterialsDocument22 pagesChou19APR6 11304 Topological Quantum MaterialsQ. WangNo ratings yet
- F620-11 (Reapproved 2015)Document4 pagesF620-11 (Reapproved 2015)marcio de rossiNo ratings yet
- Control of Decarburization of Steel PDFDocument5 pagesControl of Decarburization of Steel PDFBhushan VermaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Schottky Diode Parameters From Forward Current-Voltage CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesExtraction of Schottky Diode Parameters From Forward Current-Voltage CharacteristicsChandu KakarlaNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment and Hardness of Tool SteelDocument14 pagesHeat Treatment and Hardness of Tool SteelStephen MirdoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S095006182300805X MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S095006182300805X Maind_diasol38No ratings yet
- Post-Second World War: 1945: Alsos MissionDocument1 pagePost-Second World War: 1945: Alsos MissionSkip JonesNo ratings yet
- Sakshi ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesSakshi Thermodynamicssakshi aroraNo ratings yet
- TCEWDocument14 pagesTCEWJose AquinoNo ratings yet
- Manual Kit Lamotte 5679-01Document24 pagesManual Kit Lamotte 5679-01ALVARO GOMEZ GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Pollutants (E-Waste) : Chemical Characteristics and Their Potential RisksDocument23 pagesPollutants (E-Waste) : Chemical Characteristics and Their Potential RisksRolly Fallorina SenangeloNo ratings yet
- C Series Wiper SystemsDocument2 pagesC Series Wiper SystemsJanaka ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- 1 Stress & StrainsDocument55 pages1 Stress & StrainsTechnautsNo ratings yet
- Exam1 04Document7 pagesExam1 04Rodney SalazarNo ratings yet
- Corrosion 1Document45 pagesCorrosion 1Lakshya Sadana100% (1)
- Classification of The ElementsDocument17 pagesClassification of The ElementsNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- Morison EquationDocument3 pagesMorison EquationChaidir TransmissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics - G. AruldhasDocument99 pagesEngineering Physics - G. Aruldhassubho0% (1)