Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Models of Organisation Behaviour
Uploaded by
SUPRIMAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Models of Organisation Behaviour
Uploaded by
SUPRIMACopyright:
Available Formats
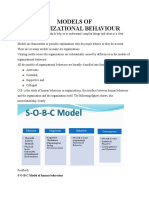
MODELS OF ORGANISATION BEHAVIOUR
The Autocratic Model
The basis of this model is power with a managerial orientation of authority. It depends upon strength, power and formal authority. The employees in turn are
oriented towards obedience and dependence on the boss. The employee need that is met is subsistence. The performance result is minimal.
In case of an autocratic model, the managerial orientation is doctorial. The managers exercise their commands over employees. The managers give orders and
the employees must obey the orders. Thus, the employees’ orientation towards the managers/bosses is obedience and dependence. Under autocratic
conditions, employees give higher performance either because of their achievement drive or their personal liking to the boss or because of some other factor.
Example: Defence team since here the officer holds power and authority to obey them and thus the soldiers are obedient to execute the officers order.
The Custodial Model
The basis of this model is economic resources with a managerial orientation of money. The employees in turn are oriented towards security and benefits and
dependence on the organization. The employee need that is met is security. The performance result is passive cooperation. The basis of this model is
partnership with a managerial orientation of teamwork.
While studying the employees, the managers realized and recognized that although the employees managed under autocratic style do not talk back to their
boss they certainly think back about the system. Such employees filled with frustration and aggression vent them on their co-workers, families and
neighbours. This made the managers think how to develop better employee satisfaction and security. It was realized that this can be done by dispelling
employees' insecurities, frustration and aggression.
Example: Garments factory since it is based on economical resources. Labours execute their job for security and benefits. If the organisation does well then,
the employee gets the benefit.
The Supportive Model
The basis of this model is leadership with a managerial orientation of support. The employees in turn are oriented towards job performance and
participation. The employee need that is met is status and recognition. The performance result is awakened drives.
The supportive model is founded on leadership, not on money or authority. In fact, it is the managerial leadership style that provides an atmosphere to help
employees grow and accomplish their tasks successfully. The managers recognize that the workers are not by nature passive and disinterested to
organizational needs, but they are made so by an inappropriate leadership style. The managers believe that given due and appropriate changes, the workers
become ready to share responsibility, develop a drive to contribute their mite and improve themselves. Thus, under supportive approach, the management's
orientation is to support the employee's job performance and participation for meeting both organizational and individual goals.
Example: Software Firm because here the leaders support their employees to perform their task/ project.
The Collegial Model
The collegial model is an extension of the supportive model. As the literal meaning of the work 'college' means a group of persons having the common
purpose, the collegial model relates to a team work/concept. The foundation of the collegial model lies on management's building a feeling of partnership
with employee. Under collegial approach, employees feel needed and useful. They consider managers as joint contributors to organizational success rather
than as bosses.
Its greatest benefit is that the employee becomes self-discipline. Feeling responsible backed by self-discipline creates a feeling of team work just like what the
members of a football team feel. The research studies report that compared to traditional management model, the more open, participative, collegial
managerial approach produced improved results in situations where it is appropriate.
Example: Social organisations such as willingly blood donation BADHON organisations because here everyone works as a team and takes responsibility for
organisational goal.
System model
The final organisational model is referred to as the system model. This is the most contemporary model of the five models. In the system model, the
organisation looks at the overall structure and team environment, and considers that individuals have different goals, talents and potential. Work that is
ethical, respectful, integrated with trust and integrity and gives space to develop a community feeling.
The intent of the system model is to try and balance the goals of the individual with the goals of the organisation. Individuals obviously want good
remuneration, job security, but also want to work in a positive work environment where the organisation adds value to the community and/or its customers.
The system of model should be an overall partnership of managers and employees with a common goal, and where everybody feels that they have a stake in
the organisation.
Example: A corporate firm
You might also like
- Autocratic ModelDocument5 pagesAutocratic ModelVenkatesh KesavanNo ratings yet
- Goals of Organizational BehaviorDocument5 pagesGoals of Organizational BehaviorAnmol Saxena83% (6)
- Importance of Organisational BehaviourDocument4 pagesImportance of Organisational BehaviourMayank Jha100% (4)
- Lesson Plan 4thDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 4thShielo Marie CardinesNo ratings yet
- Class 101: Remarkable Mind On-Demand Event: Session 1 (1:51:29)Document6 pagesClass 101: Remarkable Mind On-Demand Event: Session 1 (1:51:29)bull rootNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Model NotesDocument12 pagesOrganizational Behavior Model NotesSanjeevani PandeyNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Models - Autocratic to CollegialDocument3 pagesOrganizational Behavior Models - Autocratic to CollegialJaya AravindNo ratings yet
- Models of Organisation BehaviourDocument3 pagesModels of Organisation BehaviourManish SinghNo ratings yet
- OB Assignment-1Document6 pagesOB Assignment-1MUHAMMED FARSIN ENo ratings yet
- Autocratic ModelDocument6 pagesAutocratic Modeltopoonamjadhav3680No ratings yet
- Five Organizational Behavior ModelsDocument3 pagesFive Organizational Behavior ModelsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational Behaviour: S-O-B-C Model of Human BehaviourDocument8 pagesModels of Organizational Behaviour: S-O-B-C Model of Human BehaviourPAULOMI DASNo ratings yet
- OB Models104Document7 pagesOB Models104Rakesh Mohan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- A Project On Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument21 pagesA Project On Models of Organizational BehaviorRohit Deb GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Choose Healthy Foods For You and Your FamilyDocument4 pagesChoose Healthy Foods For You and Your FamilyNormawati RazakNo ratings yet
- Autocratic ModelDocument2 pagesAutocratic ModelTsegay TeklayNo ratings yet
- OB ReportDocument7 pagesOB ReportRajarshi RoychoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Ob Models: Seema WadhawanDocument10 pagesOb Models: Seema WadhawanpranavNo ratings yet
- 5 MODELS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOURDocument21 pages5 MODELS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOURsubhash221103No ratings yet
- OB Lec 3Document13 pagesOB Lec 3arnobkhan821No ratings yet
- Models of OBDocument15 pagesModels of OBrkpreethiNo ratings yet
- Green Minimalist Professional Business Proposal PresentationDocument16 pagesGreen Minimalist Professional Business Proposal Presentationrainna merquitaNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational Behavior-BriefDocument15 pagesModels of Organizational Behavior-BriefVikram ShahNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2 Course: Management Strategies in Educational Institutions (8615) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: B.Ed. (1.5 YearsDocument20 pagesAssignment No.2 Course: Management Strategies in Educational Institutions (8615) Semester: Spring, 2022 Level: B.Ed. (1.5 Yearsmunn chNo ratings yet
- Understanding Organizational Behavior ModelsDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Organizational Behavior ModelsJay Mark EscondeNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument11 pagesModels of Organizational Behaviorulanrain311No ratings yet
- The Four Models of Organizing BehaviorDocument10 pagesThe Four Models of Organizing BehaviorDanish RazaNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument13 pagesModels of Organizational BehavioruddindjmNo ratings yet
- OB ModelsDocument11 pagesOB ModelsShashank BundelNo ratings yet
- Five Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument6 pagesFive Models of Organizational BehaviorSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Models of Organisational Behaviour PDFDocument8 pagesModels of Organisational Behaviour PDFOTP On the pointNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviourDocument5 pagesModels of Organizational BehaviourKHUSHI ALTHAFNo ratings yet
- Analyzing leadership vs management roles and applying theoriesDocument7 pagesAnalyzing leadership vs management roles and applying theoriesmahaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Five Models of Organisational Behavior: Executed For A Group AssignmentDocument9 pagesA Study On Five Models of Organisational Behavior: Executed For A Group AssignmentSilky GaurNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1Mohammed HilalNo ratings yet
- Models of Organisational BehaviourDocument13 pagesModels of Organisational BehaviourMudassir IslamNo ratings yet
- HUMABEH1Document2 pagesHUMABEH1Romarie AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument20 pagesModels of Organizational Behaviorlibroaklat100% (3)
- BBA III Sem Organizational Behaviour ModelsDocument34 pagesBBA III Sem Organizational Behaviour ModelsVikas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Management Strategies in Educational InstitutionsDocument16 pagesManagement Strategies in Educational InstitutionsGhulam ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Performance" Which Results in The Participation and Task Involvement of Employees. The FourthDocument2 pagesPerformance" Which Results in The Participation and Task Involvement of Employees. The FourthRomarie AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 HBODocument4 pagesModule 2 HBOMarjan ValmonteNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational CultureDocument19 pagesWhat Is Organizational CultureTaddyBestNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviourlogoDocument27 pagesModels of Organizational Behaviourlogoitee0510No ratings yet
- STUDYGUIDE5Document3 pagesSTUDYGUIDE5Lyneah MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Case 4Document4 pagesCase 4cuong462003No ratings yet
- Challenges and Ooportunities of Organiztion Behaviour PDFDocument7 pagesChallenges and Ooportunities of Organiztion Behaviour PDFBabul YumkhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document26 pagesChapter - 2Md. Tanvir HasanNo ratings yet
- Models of OBDocument12 pagesModels of OBhasnut_zamilNo ratings yet
- 4 Key Forces Affecting Organizational BehaviorDocument4 pages4 Key Forces Affecting Organizational BehaviorShashank BundelNo ratings yet
- Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument7 pagesModels of Organizational BehaviorHospitality BridgeNo ratings yet
- A Contingency Theory Is An Organizational Theory That Claims Behavior of Leader Depend On A Certain Condition or Situation That Influence A BehaviorDocument4 pagesA Contingency Theory Is An Organizational Theory That Claims Behavior of Leader Depend On A Certain Condition or Situation That Influence A BehaviorAlex MaugoNo ratings yet
- Collegial and System Model: Reporter: Danilo P. AbrajanoDocument4 pagesCollegial and System Model: Reporter: Danilo P. AbrajanoJENEVIE B. ODONNo ratings yet
- Models of OBDocument8 pagesModels of OBMohammed Abu ShaibuNo ratings yet
- MGT101 1&2Document5 pagesMGT101 1&2Shariar HossainNo ratings yet
- Module III-1Document14 pagesModule III-1Harish InglikarNo ratings yet
- Importance of Organisational Behaviour PDFDocument4 pagesImportance of Organisational Behaviour PDFmail2joe7No ratings yet
- Leadership and Organizational BehaviorDocument2 pagesLeadership and Organizational BehaviorRipin Vashist100% (1)
- Different Models of Organisational BehaviourDocument20 pagesDifferent Models of Organisational BehaviourAyaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Complex ManDocument6 pagesComplex ManMadhuri MathaNo ratings yet
- BEE COUNTY - Beeville Isd - 2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseDocument249 pagesBEE COUNTY - Beeville Isd - 2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol Use2009 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseNo ratings yet
- Professional Learning RecordDocument2 pagesProfessional Learning Recordapi-240202637No ratings yet
- The 8 Stages of Writing DevelopmentDocument2 pagesThe 8 Stages of Writing DevelopmentEva Wong AlindayuNo ratings yet
- CD Rom 7 Slides Westgard Multirule SystemDocument11 pagesCD Rom 7 Slides Westgard Multirule SystemJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Confident Guy - Ciaran MartinDocument148 pagesConfident Guy - Ciaran Martinsamui11No ratings yet
- Programmed LearningDocument18 pagesProgrammed LearningRukhsana KhanNo ratings yet
- Panduan Verifikasi InacbgDocument8 pagesPanduan Verifikasi InacbgDhoni SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Langton Ignorance of Things in ThemselvesDocument16 pagesLangton Ignorance of Things in ThemselvesMilica ZmigiNo ratings yet
- Alex Collier - On ReptiliansDocument13 pagesAlex Collier - On Reptiliansproj3ct2018No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 HRDocument47 pagesChapter 3 HRAnonymous s98FwgOYCNo ratings yet
- Effects of Internet AddictionDocument14 pagesEffects of Internet AddictionHeraHeccateNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Self EvaluationDocument3 pagesReflection and Self Evaluationapi-246570385No ratings yet
- Bonding and NurturingDocument14 pagesBonding and Nurturingapi-325621104No ratings yet
- Administrative and Labour Law Syllabus: Industrial Organization Engineering Degree Academic Year 2012-2013Document8 pagesAdministrative and Labour Law Syllabus: Industrial Organization Engineering Degree Academic Year 2012-2013Antonio Ignacio Jimenez LopezNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2 Graph of Rational FunctionDocument9 pagesWORKSHEET 2 Graph of Rational Functiongina coNo ratings yet
- Johnstone Et Al 1976 LancetDocument3 pagesJohnstone Et Al 1976 LancetvaughanbellNo ratings yet
- Automated MPS and Item Analysis Workbook InstructionsDocument68 pagesAutomated MPS and Item Analysis Workbook Instructionscharlene albateraNo ratings yet
- Historic TraumaDocument121 pagesHistoric Traumasprite_bere4830100% (5)
- Maintenance Stationary EngineerDocument3 pagesMaintenance Stationary EngineerShams TabrezNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ba4305.5u2.10u Taught by Jing Quan (jxq072000)Document11 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Ba4305.5u2.10u Taught by Jing Quan (jxq072000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- District Reading Action PlanDocument4 pagesDistrict Reading Action PlanAnthony ChanNo ratings yet
- Sensorial SkillsDocument4 pagesSensorial SkillsTejaswiNo ratings yet
- TIMADO RESEARCH Edited Again and AgainDocument62 pagesTIMADO RESEARCH Edited Again and AgainLeighNo ratings yet
- k-2 EngineeringDocument1 pagek-2 Engineeringapi-235408695No ratings yet
- Research Essay - Annalise BoothDocument12 pagesResearch Essay - Annalise Boothapi-608960274No ratings yet
- Andrew J. Mitchell and Peter Trawny (Eds.) - Heidegger's Black Notebooks - Responses To Anti-Semitism-Columbia University Press (2017) PDFDocument275 pagesAndrew J. Mitchell and Peter Trawny (Eds.) - Heidegger's Black Notebooks - Responses To Anti-Semitism-Columbia University Press (2017) PDFfernapoNo ratings yet
- Booklet - Romeo and JulietDocument25 pagesBooklet - Romeo and Julietapi-298366936No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Assignment: Stimulus GeneralizationDocument3 pagesConsumer Behavior Assignment: Stimulus GeneralizationSaurabh SumanNo ratings yet