Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture - Conditional Probability
Uploaded by
Reygie FabrigaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture - Conditional Probability
Uploaded by
Reygie FabrigaCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditional Probability
The usual notation for “event A occurs given that event B has occurred” is A⃒B (A given B). The
symbol ⃒is a vertical line does not imply division. P(A⃒B) denotes the probability that event A will occur
given that event B has occurred already. We define conditional probability as follows:
For any two events A and B with P(B) > 0, the conditional probability of A given that B has occurred
is defined by
P ( A ∩B)
P ( A⃒B ) =
P(B)
Illustrative Examples:
1. A mathematics teacher gave her class two tests. Twenty-five percent of the class passed both tests and
42% of the class passed the first test. What percent of those who passed the first test also passed the
second test?
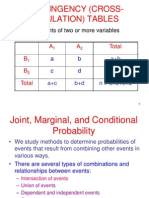
2. Consider the table below showing A as the age group under 30 years old who purchase 2 different
brands of shoes.
Age Group Brand X Brand Y Total
A (under 30 years old) 6% 34% 40%
A’ (30 years and older) 9% 51% 60%
Total 15% 85% 100%
a. What is the probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X?
b. What is the probability that a person chosen at random is under 30 years old?
c. What is probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X and is under 30 years old?
d. What is the probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X and he or she is under 30
years old?
Conditional Probability
The usual notation for “event A occurs given that event B has occurred” is A⃒B (A given B). The
symbol ⃒is a vertical line does not imply division. P(A⃒B) denotes the probability that event A will occur
given that event B has occurred already. We define conditional probability as follows:
For any two events A and B with P(B) > 0, the conditional probability of A given that B has occurred
is defined by
P ( A ∩B)
P ( A⃒B ) =
P(B)
Illustrative Examples:
1. A mathematics teacher gave her class two tests. Twenty-five percent of the class passed both tests and
42% of the class passed the first test. What percent of those who passed the first test also passed the
second test?
2. Consider the table below showing A as the age group under 30 years old who purchase 2 different
brands of shoes.
Age Group Brand X Brand Y Total
A (under 30 years old) 6% 34% 40%
A’ (30 years and older) 9% 51% 60%
Total 15% 85% 100%
a. What is the probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X?
b. What is the probability that a person chosen at random is under 30 years old?
c. What is probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X and is under 30 years old?
d. What is the probability that a person chosen at random purchases Brand X and he or she is under 30
years old?
You might also like
- Blaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsFrom EverandBlaze Through the GRE 120 Quantitative Exercises and ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Conditional Probability and Bayes TheoremDocument68 pagesConditional Probability and Bayes TheoremLipi Ghosh100% (1)
- QUANTITATIVE METHODS - Common Probability Distribution Test QuestionsDocument28 pagesQUANTITATIVE METHODS - Common Probability Distribution Test QuestionsEdlyn KooNo ratings yet
- Factor AnalysisDocument56 pagesFactor Analysissanzit0% (1)
- District Achievement Test of Math 10 WITH Answer KeyDocument4 pagesDistrict Achievement Test of Math 10 WITH Answer KeyReygie Fabriga100% (1)
- Quiz RegressionDocument27 pagesQuiz Regressionnancy 1996100% (2)
- Midtermtest 158-1Document5 pagesMidtermtest 158-1minhchauNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantum MechanicsDocument33 pagesPhysical Quantum MechanicsJerome ColicoNo ratings yet
- En1992 ManualDocument80 pagesEn1992 ManualLuana PamelaNo ratings yet
- Sports Club ProposalDocument2 pagesSports Club ProposalReygie Fabriga100% (2)
- Annual School Disaster Risk Reduction Management Committee Action PlanDocument6 pagesAnnual School Disaster Risk Reduction Management Committee Action PlanReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Long QuizDocument2 pagesContemporary World - Long QuizReygie Fabriga0% (1)
- Solutions HatcherDocument33 pagesSolutions HatcherAnonymous AtcM8k5J100% (1)
- Math 10 Module - Q2, WK 3 - 4Document7 pagesMath 10 Module - Q2, WK 3 - 4Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Stat 101 Final Exam ReviewerDocument6 pagesStat 101 Final Exam RevieweralephNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q3, WK 1Document10 pagesMath 10 Module - Q3, WK 1Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- q4 Statistics and Probability Summative FinalDocument4 pagesq4 Statistics and Probability Summative FinalMaire Narag83% (6)
- Sta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDocument54 pagesSta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidMahr Arslan SunyNo ratings yet
- Stat & Prob 11 Exam 4th FINALDocument6 pagesStat & Prob 11 Exam 4th FINALBill Villon100% (2)
- Biostat FinalDocument11 pagesBiostat FinalIashdip iashdipNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz 4th QuarterDocument2 pagesLong Quiz 4th QuarterRhen Degracia Panaligan100% (1)
- Math 10 Module - Q3, WK 2Document10 pagesMath 10 Module - Q3, WK 2Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- NSE BA Sample Paper With SolutionDocument18 pagesNSE BA Sample Paper With SolutionSanjay Singh100% (1)
- Math 10 Module - Q2, WK 5 - 6Document3 pagesMath 10 Module - Q2, WK 5 - 6Reygie Fabriga100% (2)
- Math 10 Module - Q3, WK 4Document10 pagesMath 10 Module - Q3, WK 4Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Statistic and ProbabilityDocument21 pagesStatistic and ProbabilityChris Paris100% (4)
- Module 2 Revision W AnswerDocument8 pagesModule 2 Revision W AnswerJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- R9 Common Probability DistributionsDocument33 pagesR9 Common Probability Distributionsszssg888No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 K53Document4 pagesQuiz 1 K53HàMềmNo ratings yet
- Question Paper FinalDocument10 pagesQuestion Paper FinalasdNo ratings yet
- Bharat Ratna Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Delhi School of Liberal Studies Entrance Test 2015-16 MA EconomicsDocument18 pagesBharat Ratna Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Delhi School of Liberal Studies Entrance Test 2015-16 MA EconomicsBidishaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalProbabilityProblems PDFDocument5 pagesConditionalProbabilityProblems PDFManabendra DasNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Management Bangalore Postgraduate Programme in Management Decision Sciences I Problem SetDocument14 pagesIndian Institute of Management Bangalore Postgraduate Programme in Management Decision Sciences I Problem Setmanisha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Activities 1,2,3Document3 pagesActivities 1,2,3Manuel BelangoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document19 pagesLesson 7History RoseNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Nur Arisya AinaaNo ratings yet
- Appilication of Statistics in PsychologyDocument16 pagesAppilication of Statistics in PsychologyMehak BatoolNo ratings yet
- Tut 05Document4 pagesTut 05Anh TúNo ratings yet
- ECON 6001 Assignment1 2023Document9 pagesECON 6001 Assignment1 2023雷佳璇No ratings yet
- Stats Q3 Summative TestDocument3 pagesStats Q3 Summative TestBrent John TelmoroNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Assignment Ch4 PDFDocument6 pagesWeek 6 Assignment Ch4 PDFprabu2125No ratings yet
- Quiz Statekbis 2 2020Document31 pagesQuiz Statekbis 2 2020Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- MCQs 2Document5 pagesMCQs 2anyzenNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper - StatsDocument5 pagesPractice Paper - StatsglacsecgroupNo ratings yet
- HW - Session 4Document2 pagesHW - Session 4koitosakimi2209No ratings yet
- Probability QuestionDocument6 pagesProbability QuestionAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 5Document18 pagesExercises Chapter 5ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- ECON1203 HW Solution Week06Document5 pagesECON1203 HW Solution Week06Bad BoyNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Two Sample TestsDocument17 pagesCh10 Two Sample TestssameerNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Neural and Cognitive Sciences - 2019Document25 pagesM.SC - Neural and Cognitive Sciences - 2019Akanksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 2021 ModifiedDocument9 pagesPractice Problems 2021 ModifiedmbamjoshiNo ratings yet
- ECON2123B Midterm1 SolutionDocument11 pagesECON2123B Midterm1 SolutionWen LiangNo ratings yet
- Sta2020 Tutorial Sheet 2Document2 pagesSta2020 Tutorial Sheet 2gavinhost2No ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheDocument13 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers TheaaxdhpNo ratings yet
- Probability in Business: Dr. Sujay K Mukhoti Associate Professor of StatisticsDocument16 pagesProbability in Business: Dr. Sujay K Mukhoti Associate Professor of StatisticsJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Basic Probability Concepts: Number of Waysthat A Can Occur Totalnumber of Possible OutcomesDocument5 pagesLecture 4: Basic Probability Concepts: Number of Waysthat A Can Occur Totalnumber of Possible OutcomesKhadim HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MCQSDocument7 pagesUnit 1 MCQSHargun Singh KheraNo ratings yet
- Sta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDocument55 pagesSta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by Junaidmalik rehmanNo ratings yet
- Stab22h3 A16Document46 pagesStab22h3 A16fiona.li388No ratings yet
- Rec 6B - Probability Rules - Part 2 - NDocument7 pagesRec 6B - Probability Rules - Part 2 - NSkylar HsuNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsAnish JohnNo ratings yet
- Some Super DocumentDocument36 pagesSome Super DocumentMijn NaamNo ratings yet
- Chi 2Document4 pagesChi 2CamilaNo ratings yet
- P&S QBDocument4 pagesP&S QBTrigun TejaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 9Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument63 pagesEbook Elementary Statistics A Step by Step Approach 9Th Edition Bluman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFTraciLewispwng100% (10)
- TQ StatDocument5 pagesTQ Statgabezarate071No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Statistics Learning From Data 2nd Edition Roxy Peck Tom ShortDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Statistics Learning From Data 2nd Edition Roxy Peck Tom Shortjessemcdonaldoagdwepsxq100% (15)
- Sports Club Registration Form (Final, Revised)Document3 pagesSports Club Registration Form (Final, Revised)Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Sports Club Registration FormDocument4 pagesSports Club Registration FormReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Class Programme For 2022-2023Document12 pagesClass Programme For 2022-2023Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- GEC 104 - Compound InterestDocument6 pagesGEC 104 - Compound InterestReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Expanded F2F Schedule 2nd Semester 2021 2022 RevisedDocument6 pagesExpanded F2F Schedule 2nd Semester 2021 2022 RevisedReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- School Form 7 (SF7) School Personnel Assignment List and Basic ProfileDocument31 pagesSchool Form 7 (SF7) School Personnel Assignment List and Basic ProfileReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Class Programme For Expanded F2F 2021-2022 - Core Subjects OnlyDocument12 pagesClass Programme For Expanded F2F 2021-2022 - Core Subjects OnlyReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- GEC 104 Week 13 - Promissory NoteDocument3 pagesGEC 104 Week 13 - Promissory NoteReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Formative Assessment Rubric SDocument33 pagesGuide To Formative Assessment Rubric SReygie Fabriga100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: To The Personnel Division/Section/UnitDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: To The Personnel Division/Section/UnitReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- IT 104 - Introduction To Number TheoryDocument6 pagesIT 104 - Introduction To Number TheoryReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- IT 104 Week 1 - PropositionsDocument7 pagesIT 104 Week 1 - PropositionsReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q1, WK 3Document6 pagesMath 10 Module - Q1, WK 3Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q3, WK 6Document9 pagesMath 10 Module - Q3, WK 6Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q1, WK 5Document5 pagesMath 10 Module - Q1, WK 5Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Work From Home Work From Home / Lac Session/Genera L Cleaning/ Meeting/ ConferenceDocument3 pagesWork From Home Work From Home / Lac Session/Genera L Cleaning/ Meeting/ ConferenceReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- CorrectionDocument24 pagesCorrectionDeepa RameshNo ratings yet
- Mixed Table 1Document3 pagesMixed Table 1MIANo ratings yet
- Composite Functions PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Functions PDFShane Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityMohsin AnsariNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument101 pagesGeneral ChemistryNohelia Fer GavNo ratings yet
- OOP Java ArraysDocument60 pagesOOP Java ArraysIm Just A SimplexDNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech II Semester II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations August - 2014 Control Systems 2014Document8 pagesII B. Tech II Semester II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations August - 2014 Control Systems 2014Sandeep YandamuriNo ratings yet
- New Lec 14 ReviewDocument58 pagesNew Lec 14 ReviewMonir HossainNo ratings yet
- School Supplies Ways To Get To School School Map/ Model, Rooms Social Study: How To Make Friends Rules in Class School SubjectsDocument85 pagesSchool Supplies Ways To Get To School School Map/ Model, Rooms Social Study: How To Make Friends Rules in Class School SubjectsNgọc Viễn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsDocument20 pagesThe Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Epoch Forumotions in t67 General Sas Macro Interview QuestioDocument8 pagesEpoch Forumotions in t67 General Sas Macro Interview QuestioNagesh KhandareNo ratings yet
- TN TRB Aeeo SyllabusDocument3 pagesTN TRB Aeeo SyllabusvijayenglishliteratureNo ratings yet
- Fixed Length and Horizontal Compositing Options in MinesightDocument7 pagesFixed Length and Horizontal Compositing Options in MinesightJosé R. CastroNo ratings yet
- SNA Lecture2CGrowthModelsDocument36 pagesSNA Lecture2CGrowthModelsJuan VegaNo ratings yet
- An Automatic Speaker Recognition SystemDocument11 pagesAn Automatic Speaker Recognition Systemapi-20008301No ratings yet
- Handyscan3d ScannersDocument16 pagesHandyscan3d ScannersdiearmanNo ratings yet
- To Finance: by George BlazenkoDocument45 pagesTo Finance: by George BlazenkoMoktar Tall ManNo ratings yet
- Compsa - ReviewerDocument5 pagesCompsa - ReviewerCARMONA, Monique Angel DapitanNo ratings yet
- The Importance and Potential of Golden Ratio in Architecture DesignDocument26 pagesThe Importance and Potential of Golden Ratio in Architecture DesignPham Chi ThanhNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter 1st Summative Test Practical Resaerch IIDocument2 pages1st Quarter 1st Summative Test Practical Resaerch IILea PasquinNo ratings yet
- Ta Hautou PrátteinDocument19 pagesTa Hautou PrátteinmpdallesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Lab ReportRowlandNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Effectiveness of Different Var Compensation Devices in Large-Scale Power NetworksDocument9 pagesComparative Study of Effectiveness of Different Var Compensation Devices in Large-Scale Power NetworksRamkumarNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Multiqudit States: Stars, Entanglement, RotosensorsDocument35 pagesSymmetric Multiqudit States: Stars, Entanglement, RotosensorsDonGerardNo ratings yet
- Sakshi Education Class 10Document4 pagesSakshi Education Class 10Khaja NusrathNo ratings yet
- Act 3 New MMWDocument2 pagesAct 3 New MMWMatthew PaghubasanNo ratings yet