0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views11 pagesFirst Order System Dynamics
The document discusses different types of forcing functions used to model dynamic systems, including:
1) Impulse forcing functions and how to sketch the response of a first order system with a time constant of 6 sec to an impulse of magnitude 5.
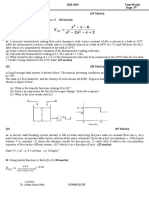
2) Ramp forcing functions and how to determine the dynamic error and time lag for a thermometer with an 8 sec time constant placed in a bath that increases linearly at 3°C/min.
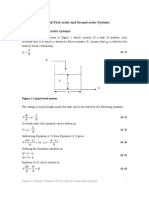
3) Sinusoidal forcing functions and transfer functions used to model mixing processes where the flow in equals the flow out of a fixed volume tank.
Uploaded by
Siddhant SinhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views11 pagesFirst Order System Dynamics
The document discusses different types of forcing functions used to model dynamic systems, including:
1) Impulse forcing functions and how to sketch the response of a first order system with a time constant of 6 sec to an impulse of magnitude 5.
2) Ramp forcing functions and how to determine the dynamic error and time lag for a thermometer with an 8 sec time constant placed in a bath that increases linearly at 3°C/min.
3) Sinusoidal forcing functions and transfer functions used to model mixing processes where the flow in equals the flow out of a fixed volume tank.
Uploaded by
Siddhant SinhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd