Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Salts Rule C-206: ACD/Name
Uploaded by
ivanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Salts Rule C-206: ACD/Name
Uploaded by
ivanCopyright:
Available Formats
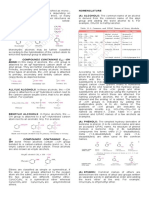
Alcohols, Phenols, and their Derivatives ACD/Name
Salts Rule C-206
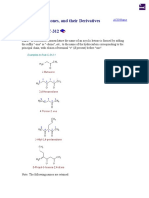
206.1 (Alternative to Rule C-206.2) - Anions derived from alcohols or phenols are named
by changing the final "-ol" of the name of the alcohol or phenol to "-olate" (compare Rule
C-84.2). This applies to substitutive, radicofunctional, and trivial names.
Examples to Rule C-206.1
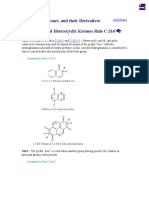
206.2 (Alternative to Rule C-206.1) - Salts composed of an anion RO and a cation
(usually a metal) are named by citing, first, the cation and then the RO anion; the latter
has the unabbreviated name used for the RO- radical but with the ending "-yloxy-"
changed to "-yl oxide" (compare Rule C-84.2).
Examples to Rule C-206.2
Exceptions: When the radical RO- has an abbreviated name listed in the exceptions to
Rule C-205.1, the ending "-oxy-" of this name is changed to "-oxide".
Examples to Rule C-206.2
Notes: (1) Radicofunctional names for salts of alcohols and phenols may, however, also
be used in some languages (not English), whereby the ending "-yl alcohol" is changed
to"-ylate", as in:
(2) For designation of as a prefix, see Rule C-86.2.
See Recommendations'93 R-5.5.3
Next:
Ethers Rule C-211, Rule C-212, Rule C-213, Rule C-214 , Rule C-215, Rule C-216
Peroxides Rule C-218
This HTML reproduction of Sections A, B and C of IUPAC "Blue Book" is as close as possible to the published version [see
Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F, and H, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979. Copyright 1979
IUPAC.] If you need to cite these rules please quote this reference as their source.
Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435
tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com
You might also like
- American National Standards Institute - STD LISTDocument15 pagesAmerican National Standards Institute - STD LISTRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- List Shell Dep Amp Mesc Spe PDFDocument9 pagesList Shell Dep Amp Mesc Spe PDFAzhar Ahmad100% (1)
- ASTM B 224 - 80 - Standard Classification of COPPERSDocument7 pagesASTM B 224 - 80 - Standard Classification of COPPERSfininho555No ratings yet
- Catalogue Cen TC 132 August 2016Document32 pagesCatalogue Cen TC 132 August 2016Mario Barbarić100% (1)
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Radicals Rule C-205Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Radicals Rule C-205ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Alcohols Rule C-201Document4 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Alcohols Rule C-201ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Phenols Rule C-202Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Phenols Rule C-202ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-215Document1 pageAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-215ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Peroxides Rule C-218Document2 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Peroxides Rule C-218ivanNo ratings yet
- r79 0243 PDFDocument1 pager79 0243 PDFivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-216Document1 pageAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-216ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Heterocyclic Compounds Rule C-204Document2 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Heterocyclic Compounds Rule C-204ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-403Document3 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-403ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-213Document2 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-213ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Trivial Names Rule C-305Document5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Trivial Names Rule C-305ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-315Document3 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-315ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyloins (-Hydroxy Ketones) Rule C-333Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyloins (-Hydroxy Ketones) Rule C-333ivanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-212Document4 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Their Derivatives Ethers Rule C-212ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-312Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-312ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-316Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-316ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-402Document2 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-402ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Cyclic Aldehydes Rule C-304Document5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Cyclic Aldehydes Rule C-304ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Hydroxy, Alkoxy and Oxo Acids Rule C-411Document1 pageCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Hydroxy, Alkoxy and Oxo Acids Rule C-411ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Aldehydes Rule C-301Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Aldehydes Rule C-301ivanNo ratings yet
- More On Nomenclature. Compounds Other Than Hydrocarbons%: IupacDocument21 pagesMore On Nomenclature. Compounds Other Than Hydrocarbons%: Iupacmail2quraishi3084No ratings yet
- Monocyclic Hydrocarbons Rule A-13. Substituted Aromatic RadicalsDocument3 pagesMonocyclic Hydrocarbons Rule A-13. Substituted Aromatic RadicalsivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acylals Rule C-332Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acylals Rule C-332ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-311Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-311ivanNo ratings yet
- Monocyclic Hydrocarbons Rule A-12. Substituted Aromatic CompoundsDocument3 pagesMonocyclic Hydrocarbons Rule A-12. Substituted Aromatic CompoundsivanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Document10 pagesActivity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Sittie Neharah S. MapandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21-25 PDFDocument134 pagesChapter 21-25 PDFHimanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Ion Charts PDFDocument5 pagesIon Charts PDFcrampingpaulNo ratings yet
- ALCOHOLSDocument12 pagesALCOHOLSAmon RicoNo ratings yet
- Iupac Nomenclature Rules 1Document1 pageIupac Nomenclature Rules 1CjES EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Notes C16 121Document13 pagesNotes C16 121Amir HussainNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives C-4.0. Simple Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives C-4.0. Simple Carboxylic AcidsivanNo ratings yet
- Recommendations 1979Document2 pagesRecommendations 1979ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and KetonesViaBNo ratings yet
- 02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Document12 pages02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument107 pagesChapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionHani ShamsedeenNo ratings yet
- WWW - Srma.co - in - Bispdf - Chemical Composition - Is 2062 - Anx - BDocument2 pagesWWW - Srma.co - in - Bispdf - Chemical Composition - Is 2062 - Anx - Bmukeshsingh6No ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document24 pagesLecture 15Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisDocument5 pages2-Phosphono-Butane-1,2,3,4-Tetracarboxylic Acids SynthesisVenu KavetiNo ratings yet
- Lubricantes Aprobados Por CopelandDocument1 pageLubricantes Aprobados Por Copelandfreeddy navarroNo ratings yet
- 20.3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersDocument5 pages20.3 Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and EstersAcieNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Document106 pagesClass 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Ridhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic Acidelizabeth merzyNo ratings yet
- FireDocument4 pagesFireRanjithrishika100% (1)
- CHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11Document8 pagesCHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11sjjsjsNo ratings yet
- Sesión 13 - Ácidos Carboxílicos - DerivadosDocument56 pagesSesión 13 - Ácidos Carboxílicos - DerivadosStephany Mariela Espinoza SachaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Unit Unit Unit Unit UnitDocument32 pagesObjectives: Unit Unit Unit Unit UnitMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketones Class XII NotesDocument60 pagesAldehyde and Ketones Class XII NotesAditya BhattNo ratings yet
- CHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11Document8 pagesCHEM1a EXPLORE NOTES WEEK 10-11sjjsjsNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Aldehydes & KetonesDocument8 pagesNomenclature of Aldehydes & KetonesChristian Dave Abelardo BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Recommendations 1979: A. HydrocarbonsDocument1 pageRecommendations 1979: A. HydrocarbonsivanNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesNomenclature of Organic CompoundsEmhNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument40 pagesAldehydes & KetonesMGoyalNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisL. G. WadeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis-1973From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis-1973R. Bryan MillerNo ratings yet
- Compare Rule .: ACD/Name C-416.3Document1 pageCompare Rule .: ACD/Name C-416.3ivanNo ratings yet
- Amines Secondary and Tertiary Amines Rule C-814: ACD/NameDocument5 pagesAmines Secondary and Tertiary Amines Rule C-814: ACD/NameivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-403Document3 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-403ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-402Document2 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Simple Carboxylic Acids Rule C-402ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Hydroxy, Alkoxy and Oxo Acids Rule C-411Document1 pageCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Hydroxy, Alkoxy and Oxo Acids Rule C-411ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyloins (-Hydroxy Ketones) Rule C-333Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyloins (-Hydroxy Ketones) Rule C-333ivanNo ratings yet
- r79 0281Document1 pager79 0281ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acylals Rule C-332Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acylals Rule C-332ivanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives C-4.0. Simple Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives C-4.0. Simple Carboxylic AcidsivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-318Document3 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-318ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-317Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-317ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyclic Aldehydes Rule C-303Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Acyclic Aldehydes Rule C-303ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-312Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-312ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic KetonesDocument1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic KetonesivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-316Document2 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-316ivanNo ratings yet
- ACD/NameDocument1 pageACD/NameivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-311Document1 pageAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-311ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Trivial Names Rule C-305Document5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Trivial Names Rule C-305ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-315Document3 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Ketones Rule C-315ivanNo ratings yet
- r79 0243 PDFDocument1 pager79 0243 PDFivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-313Document6 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Ketones Rule C-313ivanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Cyclic Aldehydes Rule C-304Document5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Their Derivatives Cyclic Aldehydes Rule C-304ivanNo ratings yet