Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ocumentation:Mini-Lessons Basics - BOPPPS Model For Planning Lessons
Uploaded by
Филарет ЯкуповOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ocumentation:Mini-Lessons Basics - BOPPPS Model For Planning Lessons
Uploaded by
Филарет ЯкуповCopyright:
Available Formats
ocumentation:Mini-Lessons Basics - BOPPPS
Model for Planning Lessons
Many models exist for planning lessons. The lesson basics used in Instructional Skills Workshops
are sometimes referred to by an acronym. "BOPPPS" and are focused on the following six
components[1]:
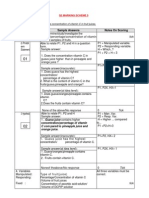
Acronym Name Description
Begins the learning cycle, gains learner
attention, builds motivation, and explains
why the lesson is important.
Sometimes known as the "motivational
statement" or "hook", the bridge-in helps
the learners focus on what is about to
happen in the lesson. Bridge-ins are
usually short. Some simple strategies
include: Providing reasons for learning this
topic; explaining why this topic is important
and how it may be useful in other
situations; describing how it is a
1. B Bridge-in transferable skill
Telling a story connected with the
lesson topic
Referring to something in the
learners' realm of experience
posing a provocative question
linked to a current topic or the
learners' personal lives
Offering a startling statement or
unusual fact
Linking current topic to material
already studied or to future learning
Clarifies and specifies the learning
intention: clarifies what the learner should
know, think, value or do by the end of the
lesson, under what conditions and how
well.
While a course may have a few broad
general goals and a limited number of
learning outcomes, individual
lessons usually focus on one or more
2. O Objective or Outcome specific learning objectives to reach those
goals or outcomes. Generally, an objective
is written as one sentence that includes:
Who (always the learner or
student)
Will do what (performance)
Under what conditions
How well (to what standard
or criteria)
3. P Pre-assessment Answers the question, "What does the
learner already know about the subject of
the lesson?"
Pre-assessment can:
Reveal learners' interests
Identify learners who can be
resources within the class
Allow learners to express their
needs for review or clarification
Focus attention and signal the
purpose of the lesson
Help the instructor adjust the
lesson for depth and pace to better fit
a particular group of learners
Enable the instructor to respond to
individual strengths and weaknesses
This is the body of the lesson, where
learners are involved as actively in the
learning process as possible. There is an
intentional sequence of activities or
learning events that will help the learner
achieve the specified objective or desired
outcome. The lesson may include the use
of media.
Some ways to encourage active
participation include:
Small group discussion around a
specific question or problem arising
from the course material
Pauses in lectures for individual
student reflection through writing or
4. P Participatory Learning discussion, question development or
short application tasks like solving an
equation or a small problem
Critical discussions of the main
point of the lesson by the learners-
perhaps through a think-pair-share
strategy
Prediction or forecasting (usually
at the beginning of a concept or unit)
Individual tasks/presentations
Students working on a problem,
then evaluating each other's work
Role plays, case studies,
scenarios, simulations
Posing a "thought" question, one
that is not answered until later in the
activity
5. P Post-assessment Formally or informally demonstrates if the
learner has indeed learned and is linked
directly with the objective or outcome.
The post-assessment answers two
questions:
What did the learners learn?
Were the desired objectives
accomplished?
Basic knowledge and thinking (knowledge
recall and comprehension) can be
assessed by:
multiple choice
true/false
matching
completion
short written answer
short verbal answer (if testing
through oral or interview
format)
Higher level thinking (application,
analysis, evaluation and creating)
can be assessed by:
problem solving tasks
essays, critiques
creating a novel theory or
interpretation
analysis of a scenario
Skill (doing) can be assessed by:
checklists
rating scales
products or examples of
production using the skill(s)
performance or demonstration
Attitudes (values) can be
assessed by:
attitude scales
performance
essays
journals and other personal
reflection pieces
artefacts
6. Summary/Closure Provides an opportunity
S for learners to reflect
briefly and integrate the
learning during the
closing of the learning
cycle.
The summary may
include:
content review (either
instructor or learners
briefly recap main
points)
group process (time
for learners to discuss
their group process)
feedback
recognition
(acknowledgment of
effort and
achievement)
application (how to
use this later; create
a personal action
plan)
individual voice (quick
round-table for each
person to have a "last
word")
You might also like
- What Is Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesWhat Is Lesson PlanCherrylen Villanueva-MendezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning: Patrobinson Moreno Salumag, PH.DDocument19 pagesLesson Planning: Patrobinson Moreno Salumag, PH.DJos Van ElzNo ratings yet
- TeachertoolkitDocument6 pagesTeachertoolkitapi-379700595No ratings yet
- Greek Word: Lectura Read: Traditional Teaching StrategiesDocument5 pagesGreek Word: Lectura Read: Traditional Teaching StrategiesJunah DayaganonNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Template: Lesson Objective: Possible Student Misconceptions: MaterialsDocument2 pages5E Lesson Template: Lesson Objective: Possible Student Misconceptions: MaterialsAngelito DailegNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan Provides You With A General OutlineDocument6 pagesA Lesson Plan Provides You With A General OutlineOtrebor OmalaNo ratings yet
- Gagne's Condition of LearningDocument2 pagesGagne's Condition of LearningMary Jane T. SalutaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Using The Table and Example As Your Guide Identify and Explain The Parts of The Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesInstructions: Using The Table and Example As Your Guide Identify and Explain The Parts of The Lesson PlanSam GanancialNo ratings yet
- Identify The Learning Objectives: Characteristic DescriptionDocument6 pagesIdentify The Learning Objectives: Characteristic DescriptionSaiqa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Notes #2Document6 pagesNotes #2sydneyNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 MarioDadisDocument9 pagesLesson2 MarioDadisRegine AdizasNo ratings yet
- Learning Tasks For DL - Madeleine PaduraDocument1 pageLearning Tasks For DL - Madeleine PaduraMADELEINE PADURANo ratings yet
- System Learning Plan Preparation: Krislizz International AcademyDocument11 pagesSystem Learning Plan Preparation: Krislizz International AcademyQhutie Little CatNo ratings yet
- (Course, Unit) Lesson PlanDocument36 pages(Course, Unit) Lesson PlansuchitraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2, Activity 2Document2 pagesLesson 2, Activity 2MARVELYN DULPINANo ratings yet
- Develop A Lesson Plan Basis On Philosophy of Realism? Regards: Shahzad Sharif MughalDocument10 pagesDevelop A Lesson Plan Basis On Philosophy of Realism? Regards: Shahzad Sharif MughalsurraiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Definition of A ModuleDocument7 pagesBasic Definition of A ModuleJess ArceoNo ratings yet
- Principles 2Document20 pagesPrinciples 2Field StudyNo ratings yet
- FS1 - EP8 DoneeDocument9 pagesFS1 - EP8 DoneeDorado Lammy S.No ratings yet
- Alexa Gandionco - Take-Away #5.0 Teaching Strategies in Elementary ScienceDocument2 pagesAlexa Gandionco - Take-Away #5.0 Teaching Strategies in Elementary ScienceAlexa GandioncoNo ratings yet
- AOL Draft (Activity 2)Document3 pagesAOL Draft (Activity 2)Alexander RamirezNo ratings yet
- Active Lecturing NotesDocument9 pagesActive Lecturing Notesapi-391350016No ratings yet
- 2022 Backward DesignDocument3 pages2022 Backward DesignSan ShweNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching For 21st CenturyDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Teaching For 21st CenturyMay ManongsongNo ratings yet
- 7es Lesson Plan ENGLISHDocument2 pages7es Lesson Plan ENGLISHsheina palmaNo ratings yet
- Vbbbob VFFDocument5 pagesVbbbob VFFnoralyn.ligananNo ratings yet
- Second ObservationDocument3 pagesSecond Observationapi-280052256No ratings yet
- CurriculumDocument19 pagesCurriculumIlene Rose BuencochilloNo ratings yet
- Nsta 5eDocument6 pagesNsta 5eXeldrakNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A LectureDocument9 pagesHow To Prepare A LectureBougara HananeNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson Planmusa.juhanyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task For DL: Caw-Oy Elementary SchoolDocument2 pagesLearning Task For DL: Caw-Oy Elementary SchoolMark Allan RojoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activities PlanningDocument1 pageLearning Activities PlanningBushra Ahmed KhurramNo ratings yet
- ParkDocument16 pagesParkapi-437885257No ratings yet
- Episode 11Document11 pagesEpisode 11Rhea Mae SicanNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Lesson 2 RioDocument7 pagesModule 3A Lesson 2 RioRioVierraMadriagaMallaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed9Document12 pagesProf Ed9shaira alliah de castro100% (1)
- 08.29-09.01DLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 1Document4 pages08.29-09.01DLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 1Verfe TuyogonNo ratings yet
- Understanding A Research ProjectDocument3 pagesUnderstanding A Research ProjectSran LouthNo ratings yet
- Grade-9-Music-Q1-Mod-3-Music-MEdieval-Renaissance-and-Baroque-Period - For MergeDocument22 pagesGrade-9-Music-Q1-Mod-3-Music-MEdieval-Renaissance-and-Baroque-Period - For MergeRegine Rellores Baliat71% (7)
- Accteach PrelimsDocument6 pagesAccteach PrelimsKDumpNo ratings yet
- A Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesA Lesson PlanJordine UmayamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Pursuing WisdomDocument65 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Pursuing WisdomFrancine Valerie AripolNo ratings yet
- Episode 8Document11 pagesEpisode 8annieguillermaNo ratings yet
- Planning Worksheet Based On Gagne's Nine Events of InstructionDocument4 pagesPlanning Worksheet Based On Gagne's Nine Events of InstructionNurdini ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Senior WRBS-Q1-M3 For PrintingDocument29 pagesSenior WRBS-Q1-M3 For PrintingRolando Corado Rama Gomez Jr.100% (2)
- Integrative ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntegrative ReviewerKEMPIS, Jane Christine PearlNo ratings yet
- Accteach Prelims Chapter 1&2Document7 pagesAccteach Prelims Chapter 1&2KDumpNo ratings yet
- Ela Ss UnitDocument49 pagesEla Ss Unitapi-506200500No ratings yet
- Exercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYDocument5 pagesExercise 6 (TTSC) - ALILIN, RENA ROSE S. BEED 3A DAYJeremy NeriNo ratings yet
- Tubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingDocument4 pagesTubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingihlaNo ratings yet
- Aspects Observations Strengths Areas For Improvement Action PointsDocument2 pagesAspects Observations Strengths Areas For Improvement Action PointsEJAY verj100% (1)
- DLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 1Document4 pagesDLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 1franchezkalidalivaNo ratings yet
- School Caloocan High School Grade Level 12 Teacher Maricar T.Artuz Learning Area Diss Date Quarter Class ScheduleDocument3 pagesSchool Caloocan High School Grade Level 12 Teacher Maricar T.Artuz Learning Area Diss Date Quarter Class Schedulearthur the great100% (1)
- 7es DiscussionDocument25 pages7es DiscussionAmando MayhayNo ratings yet
- PSTMT M2Document3 pagesPSTMT M2Aldous FajardoNo ratings yet
- Key Pedagogical TermsDocument4 pagesKey Pedagogical Termsashusol2015No ratings yet
- Motivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsFrom EverandMotivating and Rewarding University Teachers to Improve Student Learning: A Guide for Faculty and AdministratorsNo ratings yet
- Growth Opportunities For Brands During The Coronavirus CrisisDocument12 pagesGrowth Opportunities For Brands During The Coronavirus CrisisAleeza AnjumNo ratings yet
- Ans Q2 6.1 Vit CDocument3 pagesAns Q2 6.1 Vit Cnikkishya28No ratings yet
- Elucidating The Body Ma Ala: Clarifications On The Recitation Manual of The Female Practice of The Queen of Great BlissDocument9 pagesElucidating The Body Ma Ala: Clarifications On The Recitation Manual of The Female Practice of The Queen of Great BlissGloria Rinchen ChödrenNo ratings yet
- Art Gallery WorksheetsDocument14 pagesArt Gallery WorksheetsCarme Florit Ballester100% (1)
- Module 1Document11 pagesModule 1Rhembea Gardose FerasolNo ratings yet
- Andrew Steele v. United States, 362 F.2d 536, 10th Cir. (1966)Document3 pagesAndrew Steele v. United States, 362 F.2d 536, 10th Cir. (1966)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Neurolocalization in PediatricsDocument66 pagesNeurolocalization in PediatricsNigussie MershaNo ratings yet
- Webquest - Supp Material StalinDocument1 pageWebquest - Supp Material Stalinapi-254303832No ratings yet
- Notes On As Short StoriesDocument12 pagesNotes On As Short StoriesFarah NoreenNo ratings yet
- History of Philosophy of EducationDocument12 pagesHistory of Philosophy of EducationPDPPTESLJUN2021 Nurfarahin Binti ArifNo ratings yet
- Man Singh's Manakutuhala and The DhrupadDocument10 pagesMan Singh's Manakutuhala and The DhrupadAman ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Uts Finals ReviewerDocument21 pagesUts Finals Reviewercharles babasaNo ratings yet
- Carkhuff Counselling Skills Level 1Document2 pagesCarkhuff Counselling Skills Level 1Mohamad Shuhmy ShuibNo ratings yet
- How Fresh Graduates & Experienced Hires Can Start A Career in Consulting?Document9 pagesHow Fresh Graduates & Experienced Hires Can Start A Career in Consulting?ozu98989898980898No ratings yet
- Q2e LS5 U01 AnswerKeyDocument4 pagesQ2e LS5 U01 AnswerKeyTkp AndroidNo ratings yet
- Adriana Trigiani - Brava ValentineDocument182 pagesAdriana Trigiani - Brava ValentineMonica StrimbeiNo ratings yet
- BeltDocument24 pagesBeltGuru Mahesh100% (1)
- AStarDocument125 pagesAStarOsama AdeelNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary and Critical Care MnemonicsDocument10 pagesPulmonary and Critical Care MnemonicsnmahpbooksNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: DR - Prathibha.M.ChachadiDocument28 pagesCase Presentation: DR - Prathibha.M.ChachadiPrathibha M ChachadiNo ratings yet
- Control Chart For Mean and Range: Quality CharacteristicDocument7 pagesControl Chart For Mean and Range: Quality Characteristiciosin1No ratings yet
- MODULE-3 Doing PhilosophyDocument19 pagesMODULE-3 Doing PhilosophyRoyce100% (1)
- Human Right Mahatma Gandhi University BBA CBCS 5-1Document19 pagesHuman Right Mahatma Gandhi University BBA CBCS 5-1Rajesh MgNo ratings yet
- ADMU V CapulongDocument21 pagesADMU V CapulongjunjunNo ratings yet
- Note PianoDocument3 pagesNote PianoMimi MansorNo ratings yet
- "Case Study On N.R Narayana Murthy As A Strategic Leader": Subject BatchDocument38 pages"Case Study On N.R Narayana Murthy As A Strategic Leader": Subject Batchmrg8339No ratings yet
- Sped ResumeDocument2 pagesSped ResumeDavid EisenbNo ratings yet
- Soal Ramedial Bahasa Inggris Kelas XIDocument3 pagesSoal Ramedial Bahasa Inggris Kelas XIKusnadi DahariNo ratings yet
- The Cambridge Law Journal Volume 7 Issue 02Document6 pagesThe Cambridge Law Journal Volume 7 Issue 02KkkNo ratings yet