Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foodborne Diseases: Clostridium Botulinum
Uploaded by
Christopher CastorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foodborne Diseases: Clostridium Botulinum
Uploaded by
Christopher CastorCopyright:
Available Formats
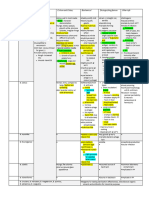
FOODBORNE DISEASES
Name Characteristics Pathogenesis Source Symptoms Other
Botulinum toxin (heat- - Tx: Botulinum-specific
labile neurotoxin). antitoxin (hyperimmune
Inhibits release of ACh at 5 D’s: Dysarthria, globulin)
Clostridium NMJ, flaccid paralysis Improperly canned - Can affect infants:
Dysphagia,
foods, food not “floppy baby” (raw honey)
botulinum Dysphonia, Diplopia,
sufficiently heated
Descending paralysis
Heat-labile pore-forming
enterotoxin, damages
Gram (+) bacilli brush border in SI, alters
Catalase (-) cell membrane
Clostridium Endospores permeability, loss of fluid Reheated meats,
Watery diarrhea
perfringens Anaerobic gravy dishes
-hemolytic
Motile
Toxin A: enterotoxin. MCC of nosocomial
Toxin B: cytotoxin. diarrhea
Hypervirulent strains - Dx: EIA for glutamate
dehydrogenase (GDH) or
Clostridium Recent antibiotic Watery diarrhea EIA for toxins- specific
difficile exposure severe: bloody diarrhea
- Tx: discontinue antibiotics
Enterotoxin (SEA),
superantigen (stimulates
Gram (+) rod
vomiting)
Catalase (+)
Staphylococcus Salty, high fat foods Watery diarrhea,
Facultative an.
(mayo, ham), hard nausea, vomiting, abd
aureus Coagulase (+)
boiled eggs pain
Yellow colonies
(mannitol salt agar)
Emetic Form:
Cerulide (enterotoxin),
binds serotonin receptors of
CN X Vomiting Short incubation
Catalase (+)
-hemolytic Fried rice dishes,
Bacillus cereus Endospores Diarrheal Form: starchy foods, meats
Aerobic vegetative cells,
cAMP, fluid secretion
Profuse watery
into SI (pores) Long incubation
diarrhea
TCP (pilus): adherence to - Cholera cots
mucosal lining. Lysogenic - “rice water” stools.
Bacteriophage (CTX): - TCBS agar
carries toxin. Profuse watery - Tx: fluid replacement,
Cholera Toxin: enterotoxin, Fecally- diarrhea and antibiotics
Vibrio cholerae activates adenylate cyclase contaminated water vomiting,
hypovolemic shock
Gram (-) bacilli
Curved rod
Oxidase (+) Direct invasion Dx: TCBS agar (blue-green
Vibrio Alkalophile Explosive watery colonies), requires salt for
Raw seafood
parahaemolyticu O-antigen diarrhea, mild fever, growth
(oysters)
abd pain, vomiting
s
Capsule: bloodstream TCBS agar
survival. Diarrhea, septicemia, (blue-green)
RtxA toxin: pore-forming, Raw seafood, wound
Vibrio vulnificus induces ROS infections
cellulitis, bullous,
necrotic skin lesions
ETEC: Antibiotics can worsen
CFA (pili): adhesion.
Stable Toxin (STa): converts
GTP to cGMP, Travelers, fecally-
hypersecretions. Watery diarrhea, mild
contaminated
Labile Toxin (LT) fever, no RBC/WBC
water/food
EPEC:
Bundle-Forming Pilus (BFP):
binds receptors,
aggregation. Watery diarrhea,
A/E lesions, Tir receptor Children, neonatal
hypovolemia,
binds intimin, actin nursey outbreaks, Persistent
malnutrition, death,
rearrangement direct contact
no RBC/WBC
Gram (-) bacilli
Facultative an.
Escherichia coli Oxidase (-)
Lactose ferm. EAEC:
Adherence fimbriae (AAFs),
cytotoxins causes rounding
Children, adult HIV
of villi, biofilms Watery diarrhea Persistent
patients
EHEC, STEC: - O157:H7 -Hemolytic
Shiga Toxin 1/2: inhibits Uremic Syndrome (HUS):
protein synthesis, A/E hemolytic anemia,
lesions. No BFP schistocytes,
Watery diarrhea, abd thrombocytopenia,
Children, meat, leukocytosis.
cramping, bloody
vegetables - SMAC agar
diarrhea
EIEC:
Similar to Shigella, direct Watery diarrhea,
tissue invasion dysentery
Gram (-) bacilli Urease: protects against False appendicitis
Facultative an. stomach acids. Watery diarrhea, low-
Yersinia Oxidase (-) Enterotoxin.
Milk, dairy
grade fever,
enterocolitica Non-lactose f. To mesenteric nodes leukocytosis,
H2S (-) pharyngitis
Bipolar staining
Non-Typhoidal: invades M Salmonellosis
cells in Peyer Patches, (gastroenteritis)
replicates in endocytic
Watery diarrhea,
vacuoles Eggs, poultry, dairy
cramps, fever
Gram (-) bacilli
Facultative an.
Salmonella Oxidase (-)
enterica Non-lactose f. Salmonella Typhi: Type III - “Typhoid Mary”
H2S secretion, infects bone - low infectious dose
Motile marrow, liver, spleen,
Diarrhea, constipation
gallbladder
high fever
S. sonnei: attach to M cells “Shigella does nothing but
in Peyer Patches, actin tails shit”
Day care centers,
Gram (-) bacilli Mild diarrhea
developed countries
Facultative an.
Oxidase (-)
Shigella spp. Non-lactose f. S. dysenteriae: shiga toxin HUS
H2S (-) (Stx) Shigellosis: bloody
Non-motile Developing
diarrhea, tenesmus,
countries
inflammation
- Guillain-Barre syndrome,
Gram (-) bacilli - skirrow medium
Curved rod
Campylobacter Aerobic Raw poultry Bloody diarrhea
jejuni Oxidase (+)
Grows at 42C
Facultative intercellular - Cold temps
parasite, enters via - Fetal loss (placental
Gram (+) bacilli
Listeria internalins transfer)
Non-spore Soft cheeses, deli Diarrhea, muscle
monocytogenes Aerobic meats aches, arthralgia
Catalase (+)
Acute Viral Gastroenteritis
Name Characteristics Source Symptoms Other
Caliciviridae Institutional settings
Sudden onset vomiting and Acute infectious diarrhea,
Norovirus Fecal-oral (schools, hospitals, hotels,
watery diarrhea, no fever self-limiting, short duration
Cooler months cruise ships, camps)
Cooler months Sudden onset vomiting, Childhood diarrhea
Rotavirus Affects very young and Institutional settings watery diarrhea, epidemics, self-limiting, long
elderly dehydration, low-grade fever duration
Enteric
Asymptomatic, watery
(serotypes 40, 41)
Adenovirus Affects very young
Institutional settings diarrhea, mucus in stool, Self-limiting
vomiting
No seasonality
Cooler months
Rainy seasons Self-limiting, less severe than
Astrovirus Infants, children, elderly,
Institutional settings Watery diarrhea
Rotavirus
immuno.
You might also like
- Neurotoxin (A & B: StructureDocument5 pagesNeurotoxin (A & B: StructureRiyam WannasNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus AureusDocument11 pagesStaphylococcus Aureusdorsolya92No ratings yet
- Disease Patho Manifestations Assessment Labs Other Notes DKA Used To Suppress Ketogenesis, Gluconeogenesis NOT Just To Lower BGDocument1 pageDisease Patho Manifestations Assessment Labs Other Notes DKA Used To Suppress Ketogenesis, Gluconeogenesis NOT Just To Lower BGSara SabraNo ratings yet
- Bacteria ChartsDocument11 pagesBacteria ChartsFlowerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument13 pagesMicrobiology NotesMalekNo ratings yet
- Endocrine/ Metabolic Infectious/Inflammatory Neurological GastroentericDocument1 pageEndocrine/ Metabolic Infectious/Inflammatory Neurological Gastroentericjjj hhhNo ratings yet
- AEROBIC, GRAM POS BACILLI NON-SPORE FORMER (Nahaeminrmt)Document7 pagesAEROBIC, GRAM POS BACILLI NON-SPORE FORMER (Nahaeminrmt)Rach ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Amebiasis: Vaginalis), GiardiasisDocument6 pagesDrugs For Amebiasis: Vaginalis), GiardiasisCarla C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chart - Gram Positive BacteriaDocument2 pagesChart - Gram Positive BacteriaRedNo ratings yet
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocument14 pagesS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiNo ratings yet
- ????? ?????????Document2 pages????? ?????????KIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Med Micro BugsDocument16 pagesMed Micro BugsKaitlyn CabreraNo ratings yet
- S. Pyogenes: 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F Conjugated With Nontoxic Diphtheria-ToxinDocument1 pageS. Pyogenes: 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F Conjugated With Nontoxic Diphtheria-ToxinRica MarquezNo ratings yet
- Causitive Agent TableDocument10 pagesCausitive Agent TableStephanie EncinaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Animal Compilation Mid TermDocument6 pagesLaboratory Animal Compilation Mid TermWenn Marc Catuiran DuceNo ratings yet
- Other Bacteria: Gram-NegativeDocument18 pagesOther Bacteria: Gram-NegativeZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocument17 pagesGastrointestinal SystemAlexis NicoleNo ratings yet
- Salmonella Enterica - Escherichia Coli - Listeria MonocytogenesDocument4 pagesSalmonella Enterica - Escherichia Coli - Listeria MonocytogenesKaitlyn KaoNo ratings yet
- Parasite Habitat Diagnostic Features IS MOT Disease Diagnosic Procedure Prevention/ ControlDocument1 pageParasite Habitat Diagnostic Features IS MOT Disease Diagnosic Procedure Prevention/ Controljust100% (1)
- Protozoa-Gastrointestinal Infections: Giardia Lamblia GiardiasisDocument7 pagesProtozoa-Gastrointestinal Infections: Giardia Lamblia GiardiasisHanunNo ratings yet
- Corynebacterium Diphtheriae Listeria Monocytogenes Erysipelothrix Rhusopathiae Lactobacillus Spp. Streptomycetes Spp. Nocardia SPPDocument1 pageCorynebacterium Diphtheriae Listeria Monocytogenes Erysipelothrix Rhusopathiae Lactobacillus Spp. Streptomycetes Spp. Nocardia SPPAbcd ReyesNo ratings yet
- Veronika Vita Kurniawati - Ringkasan MikroDocument7 pagesVeronika Vita Kurniawati - Ringkasan MikroVeronika Vita KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Vid Lec 1-3 Sir GerryDocument10 pagesWeek 13 - Vid Lec 1-3 Sir Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- BACTERIADocument14 pagesBACTERIARochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cholera PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Cholera PDFRameshKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cholera PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Cholera PDFRameshKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Table of TapewormsDocument5 pagesTable of TapewormsErrol ChioNo ratings yet
- Etiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDocument2 pagesEtiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table ProtozoaDocument10 pagesParasitology Table ProtozoaMae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Flash Notes SyndromesDocument8 pagesFlash Notes SyndromesschxzerrydawnNo ratings yet
- Micro paraDocument2 pagesMicro parafeminaNo ratings yet
- Tropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiDocument1 pageTropical Fevers Table Case 2 by Rahaf AlzoubiR. nounNo ratings yet
- Every Drug EverDocument72 pagesEvery Drug EverMalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Document1 pagePathophysiology Chart Anaphy 1Carl John ManaloNo ratings yet
- Endoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsDocument5 pagesEndoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsimarzenNo ratings yet
- Week-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-GerryDocument10 pagesWeek-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- Bacte Chapter 10Document2 pagesBacte Chapter 10barbiegahibNo ratings yet
- BACTERIADocument1 pageBACTERIAKumkum MahajanNo ratings yet
- Virus - SystemsDocument9 pagesVirus - SystemsHanunNo ratings yet
- Micro by DR - Hesham (GIT)Document65 pagesMicro by DR - Hesham (GIT)abcde990075No ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cleocin Generic Name: Clindamycin Drug Classification: Antiinfective AntibioticDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cleocin Generic Name: Clindamycin Drug Classification: Antiinfective AntibioticYura KimNo ratings yet
- Draft Micro NotesDocument2 pagesDraft Micro NotesIAN GABRIELLE MERCADO CUYNONo ratings yet
- Infectious-Disease Tables PDFDocument81 pagesInfectious-Disease Tables PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- StaphDocument6 pagesStaphpekibelssNo ratings yet
- Materia Medica Summary SheetDocument6 pagesMateria Medica Summary Sheetglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Culture Media NoteDocument5 pagesCulture Media Notestudymedic100% (1)
- Gram Positive Bacteria TableDocument6 pagesGram Positive Bacteria Tables2128226No ratings yet
- 2.01 - Vibrio, Campylobacter, HelicobacterDocument2 pages2.01 - Vibrio, Campylobacter, HelicobacterPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Le 2 - Microbio SupertableDocument9 pagesLe 2 - Microbio Supertabletocinolover0102No ratings yet
- P2 REVIEWER (Part 2)Document6 pagesP2 REVIEWER (Part 2)ArllrNo ratings yet
- Schem DiagramDocument9 pagesSchem DiagramDATO-ON JOANA PAULANo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea in MedicineDocument10 pagesDiarrhoea in MedicineMohd NadeemNo ratings yet
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of CholelithiasisNicol John CeballosNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table: ProtozoaDocument10 pagesParasitology Table: ProtozoaKate Alyssa CatonNo ratings yet
- Waterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenDocument6 pagesWaterborne Diseases: DR Hafez Q Shaheen DR Hafez Q Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. Shaheen Dr. Hafez Q. ShaheenMichael SamwelNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Acute, Sub Acute, & Chronic: - ! DefinitionDocument7 pagesDiarrhea: Acute, Sub Acute, & Chronic: - ! DefinitionWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram - BacilliDocument4 pagesAerobic Gram - BacilliJewel BenaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Circulation DrillingDocument6 pagesReverse Circulation DrillingHabib Ur Rahman100% (1)
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- A Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDocument7 pagesA Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDennis Daniel Condori EspilcoNo ratings yet
- Aviation Fuel Quality Control Manual - Rev.2015Document56 pagesAviation Fuel Quality Control Manual - Rev.2015Aswin Lorenzo Gultom100% (1)
- Penetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Document13 pagesPenetapan Kadar Sakarin, Asam Benzoat, Asam Sorbat, Kofeina, Dan Aspartam Di Dalam Beberapa Minuman Ringan Bersoda Secara Kro...Wisnu WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Mic Fright and Camera PanicDocument5 pagesMic Fright and Camera PanicNica Arizapa100% (1)
- How IoT Changed Our LifeDocument5 pagesHow IoT Changed Our LifeJawwad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Consumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalDocument20 pagesConsumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalCerboh MazibukoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Import Coordinates From Excel To AutoPIPEDocument23 pagesTutorial - Import Coordinates From Excel To AutoPIPEFabio MiguelNo ratings yet
- Forklift Bucket 1400B - ManualDocument4 pagesForklift Bucket 1400B - ManualVie LiesnaNo ratings yet
- Detection of Food AdulterationDocument10 pagesDetection of Food AdulterationDavara Paresh R.No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Exam 3 - This SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Exam 3 - This Semesterapi-3723612100% (1)
- Zeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsDocument24 pagesZeroing Neural Networks, An Introduction To, A Survey Of, and Predictive Computations For Time-Varying Matrix ProblemsgoatcockNo ratings yet
- 42mehd 24 11Document1 page42mehd 24 11Evin VargheseNo ratings yet
- C190Document64 pagesC190thelmagrNo ratings yet
- Orallichenplanus 170929075918Document40 pagesOrallichenplanus 170929075918Aymen MouradNo ratings yet
- 7 AcousticsDocument23 pages7 AcousticsSummer Yeoreumie100% (1)
- Vo 1263 AaDocument8 pagesVo 1263 Aa801400No ratings yet
- Ant WorldDocument17 pagesAnt WorldGerardo TorresNo ratings yet
- PHontDawg Vol.2 2007Document8 pagesPHontDawg Vol.2 2007Tanczos AndrasNo ratings yet
- Assignment CHAP NO 1.... Computer Fundamentals by PK SinhaDocument7 pagesAssignment CHAP NO 1.... Computer Fundamentals by PK SinhaThreating King100% (2)
- Reviewer 3RD Exam FinalDocument14 pagesReviewer 3RD Exam FinalReane Romblon GerozagaNo ratings yet
- Title: "The Effect of Flooding in The Tourism Industry in Dagupan City" Rationale and Background of The StudyDocument4 pagesTitle: "The Effect of Flooding in The Tourism Industry in Dagupan City" Rationale and Background of The StudyTaehyung KimNo ratings yet
- Can Bus ScaniaDocument21 pagesCan Bus Scaniajose breno vieira silva96% (25)
- TNSTCDocument1 pageTNSTCMohamed MNo ratings yet
- EMI Unit 1Document98 pagesEMI Unit 1Anirudhh RaviNo ratings yet
- 80 MT Crawler CraneDocument40 pages80 MT Crawler CraneramyaNo ratings yet
- 06 Story StiffnessDocument2 pages06 Story StiffnessDigvijay GiraseNo ratings yet
- Adverb of TimeDocument5 pagesAdverb of TimeIsha kaleNo ratings yet
- Egg, Boiled: Nutrition FactsDocument5 pagesEgg, Boiled: Nutrition FactsbolajiNo ratings yet