Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assingnment E Commerce
Assingnment E Commerce
Uploaded by
ROHIT JAISWALOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assingnment E Commerce
Assingnment E Commerce
Uploaded by
ROHIT JAISWALCopyright:
Available Formats
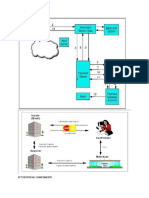
Packet Switching
Packet Switching sends information across computerized systems by separating it into
squares or packets for more productive exchange utilizing different system gadgets. Each
time one gadget sends a document to another, it separates the record into packets with the
goal that it can decide the most proficient course for sending the information over the system
around then. The system gadgets would then be able to course the packets to the goal where
the accepting gadget reassembles them for use.
What is Packet Switching?
Packet switching is the exchange of little bits of information across different systems. These
information pieces or "packets" take into consideration quicker, more effective information
move. Regularly, when a client sends a record over a system, it gets moved in littler
information packets, not in one piece. For instance, a 3MB record will be separated into
packets, each with a packet header that incorporates the starting point IP address, the goal IP
address, the quantity of packets in the whole information document, and the succession
number.
Kinds of Packet Switching
There are two significant kinds of packet switching:
Connectionless Packet Switching: This great kind of packet switching incorporates different
packets, each independently steered. This implies every packet contains total directing data—
however it likewise implies various ways of transmission and faulty conveyance are
conceivable, contingent upon the fluctuating burdens on the system's hubs (connectors,
switches and switches) right now. This sort of packet switching is once in a while called
datagram switching.
Every packet in connectionless packet switching remembers the accompanying data for its
header area:
Source address
Goal address
All out number of packets
Succession number for reassembly
When the packets arrive at their goal by means of different courses, the getting gadgets adjust
them to frame the first message. Association Oriented Packet Switching. In association
arranged packet switching, likewise called virtual circuit switching or circuit switching,
information packets are first collected and afterward numbered. They at that point traverse a
predefined course, consecutively. Address data isn't required in circuit switching, since all
packets are sent in grouping.
E-COMMERCE SECURITY PROTOCOLS
Security and encryption in e-commerce is a growing need among companies and
marketplaces. A Check Point report assured that cybercrime will remain constant in 2019, but
that its attacks will be more sophisticated and intelligent.
Encryption is one of the most effective methods of improving cybersecurity. With the first
option, sensitive customer information (user names, passwords, bank details, etc.) can be
protected through encryption. This process is not easy to explain but can be summed up in the
use of a unique code, which allows the recipient and recipient to decrypt the data needed in
the transaction. In this way, the theft of such data makes no sense to cybercriminals, who will
not be able to decipher them.
Another excellent resource for optimizing security in e-commerce are security certificates.
We are talking about digital identification, capable of verifying the identity of users, as well
as their « humanity » (most cyber-attacks are perpetrated by bots). SSL and SET certificates
are the most widely used and are worth studying in depth.
SSL: INFALLIBLE PROTECTION IN ONLINE DATA TRANSFER
Also known as Secure Sockets Layer, this security certificate has become one of the must of
the internet. It is used by both large companies and minority bloggers. Its purpose is to
protect your data transactions between a website (provider) and its visitors (recipients).
Identifying sites with SSL certificates is easy: a green padlock appears in the browser,
indicating to users that all their data is secure. However, creating a secure SSL connection
requires the hosting server to have a pre-installed SSL certificate. Fortunately for those
interested, these certificates have a very low cost. Some hosting providers even offer the free
installation of Let’s Encrypt and other SSL software.
SET: SECURITY PLUS FOR YOUR MONETARY TRANSACTIONS
And if you’re wondering what secure e-commerce payment protocol you should implement,
SET is an excellent answer. The initials of this protocol correspond to Secure Electronic
Transaction. As its name indicates, it is a system to guarantee the security of monetary
transactions in digital environments.
The operation of SET is simple. Generally speaking, this protocol provides a series of
certificates and digital signatures between the consumer, the company and the banking entity,
which regulate the monetary transaction from its beginning to its end. Considering that it was
created by Visa and MasterCard in collaboration with giants such as Microsoft, IBM or
Netscape, the effectiveness of the SET protocol should not surprise us.
TLS: THE BIG BROTHER OF THE SSL CERTIFICATE
The TLS or Transport Layer Security certificate is an evolution of the aforementioned SSL.
Its objective is to provide secure connections by encrypting data sent between two parties.
This certificate is mainly used in e-mail environments and is not incompatible with its
predecessor (in fact, they can be reconciled).
Netscape created the SSL protocol, and later the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
developed the TLS. As you may have noticed, both certificates work in a similar way, but
they are not the same: the algorithms of the TSL certificate are more solid and versatile than
those of its predecessor.
HTTPS: ADDING A SECURITY LAYER TO THE CLASSIC HTTP
When we talk about HTTPS, we mean Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. This protocol is
an evolution of the HTTP, which incorporates an extra layer of security to the data that are
sent in SSL or TLS connections. Today most digital enterprises are carried out with HTTPS
protocols, instead of HTTP, created by Eric Rescorla and Allan M. Schiffman in 1999, which
are on the way to disappear.
Due to the growing number of cyber-attacks, the use of the HTTPS protocol has become
widespread since 2018. This is due to the fact that the previous HTTP had greater weaknesses
and was not as secure. Specialists recommend the use of HTTPS, but in some cases the S-
HTTP protocol may be needed. Any of these e-commerce security protocols is a safe bet to
shield your business from phishing, malware, online fraud and other cyber-attacks. Its
objective is not to avoid monetary losses derived from an attack: it is to avoid the loss of
customer confidence.
Web 2.0
Web 2.0 generally refers to the world wide site that highlights the user-generated content,
interoperability, and usability for the end-users. Web 2.0 is called a participative social web.
Web browser technologies can be used in Web 2.0 development as well as includes
JavaScript and AJAX frameworks. Currently, JavaScript and AJAX frameworks have also
become the most popular ways to create web 2.0 websites.
Major features of the Web 2.0 –
Dynamic content is responsive to user input.
Free sorting of the information, allows users to retrieve as well as classify information
collectively.
Developed APIs that will allow the self-usage, by the software application.
Web access can lead to a concern different, from a traditional Internet base to a wider
range of users.
Information flows between the website owner and users by evaluation and online
commenting.
Web 3.0 –
Semantic Web or 3.0 assures to establish “world’s information” in a reasonable way
compared to Google that will ever attain with the current engine schema. It is mainly true
from the perspective of the machine conception when opposed to human understanding.
Semantic Web necessitates the use of the declarative ontological language such as OWL to
make domain-specific ontologies, which machines will use to reason on information as well
as make some new conclusions, not just match the keywords.
Main features that will help us to define Web 3.0 with Web 2.0:
Artificial Intelligence
Combining such capability with natural language processing, Web 3.0, computers will
distinguish the information just like humans to provide faster and relevant results.
Semantic Web
Succeeding the evolution of the Web involves Semantic Web. This semantic web
improves web technologies to create, connect and share content through the search
and the analysis based on the capability of comprehending the meaning of the words,
instead of on the keywords and numbers.
Connectivity
With Web 3.0, the information will be connected due to semantic metadata. Thus,
user experience evolves at another connectivity level that leverages available
information.
Ubiquity
Content is available by the multiple applications, each device will be connected to the
web, and services will be used all over.
3D Graphics
Three-dimensional design can be used widely in the websites and services at Web 3.0. The
museum guides, e-commerce, computer games, geospatial contexts are some of the examples
that make use of 3D graphics.
You might also like
- JAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 12Document55 pagesJAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 12Joe VaTa100% (2)
- Card Payment Security Using RSADocument23 pagesCard Payment Security Using RSAKaataRanjithkumar100% (2)
- BRIDGE SOLUTIONS PVT LTD 12Document9 pagesBRIDGE SOLUTIONS PVT LTD 12ROHIT JAISWAL100% (1)
- BCP WorksheetDocument15 pagesBCP WorksheetSushma KishoreNo ratings yet
- theTinHat - Complete I2P Tutorial and Information GuideDocument52 pagestheTinHat - Complete I2P Tutorial and Information GuideTruco El Martinez100% (1)
- Webp - Case Study - 601Document15 pagesWebp - Case Study - 601Prateek KumarNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester IV MI0026 Computer Networks - 2 Credits (Book ID: B1041) Assignment Set-1 (30 Marks)Document5 pagesMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester IV MI0026 Computer Networks - 2 Credits (Book ID: B1041) Assignment Set-1 (30 Marks)Tenzin KunchokNo ratings yet
- E CommerceDocument15 pagesE Commercersoni soniNo ratings yet
- Instant and Secure Messaging Platform Based On BlockchainDocument6 pagesInstant and Secure Messaging Platform Based On BlockchainIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: Network SecurityDocument16 pagesApplication Layer: Network SecuritySunanda BansalNo ratings yet
- Security in e - CommerceDocument4 pagesSecurity in e - CommerceAlex T BinoyNo ratings yet
- Btech It Ecommerce ReportDocument11 pagesBtech It Ecommerce Reportdishant_kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics On Computer NetworkingDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Topics On Computer Networkinggz91rnat100% (1)
- Ece4013 A2Document10 pagesEce4013 A2Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- NSC Unit - 3 - 221210 - 134942Document29 pagesNSC Unit - 3 - 221210 - 134942SurenderNo ratings yet
- Ecure Client Server Message Integrity Verification Using Robust Encrypted TechniqueDocument5 pagesEcure Client Server Message Integrity Verification Using Robust Encrypted Techniquesurendiran123No ratings yet
- Document 4Document2 pagesDocument 4Last SummerNo ratings yet
- Cloud Cryptography and Data Security IJERTV10IS110100Document2 pagesCloud Cryptography and Data Security IJERTV10IS110100techieNo ratings yet
- Implication Blockain BusinessDocument2 pagesImplication Blockain BusinessMahama Ibrahim OuattaraNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Reading5 - InternetSecurityDocument7 pagesModule 6 - Reading5 - InternetSecurityChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- 5 WpiDocument15 pages5 WpiDIAN SURGAWIWAHANo ratings yet
- Blockchain Developed On A Proxy Re EncryptionDocument48 pagesBlockchain Developed On A Proxy Re EncryptionNexgen TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Proxy Re-EncryptionDocument8 pagesBlockchain Based Proxy Re-EncryptionBhanu RoyalNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT TASK 3.editedDocument7 pagesASSESSMENT TASK 3.editedAritra ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Internal Assessment 3Document5 pagesInternal Assessment 3Sheanopa MunatsiNo ratings yet
- Authentication and Key Agreement Based On Anonymous Identity For Peer-to-Peer CloudDocument8 pagesAuthentication and Key Agreement Based On Anonymous Identity For Peer-to-Peer CloudcalciummNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis On TwitterDocument7 pagesSentiment Analysis On TwitterRohan ChavanNo ratings yet
- Uport Whitepaper DRAFT20170221Document16 pagesUport Whitepaper DRAFT20170221matkoshyNo ratings yet
- Man-In-The-Middle-Attack Prevention Using HTTPS and SSL: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingDocument11 pagesMan-In-The-Middle-Attack Prevention Using HTTPS and SSL: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingzeeshanNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Notes: Transport Level Security: Web Security Considerations, Secure Sockets Layer, TransportDocument45 pagesModule - 1 Notes: Transport Level Security: Web Security Considerations, Secure Sockets Layer, Transportrushil prasadNo ratings yet
- OTP GenerationDocument18 pagesOTP GenerationSOUMYA S. TAWARAKHED100% (1)
- Ali Raad AbdulrazzaqDocument7 pagesAli Raad AbdulrazzaqOmar AbooshNo ratings yet
- Editing - Untitled - NoteDocument7 pagesEditing - Untitled - NoteAxjxlaNo ratings yet
- Module 15Document38 pagesModule 15Fazlee KanNo ratings yet
- Sockets Layer (SSL) and The Follow-On (Subsequent) Internet Standard ofDocument8 pagesSockets Layer (SSL) and The Follow-On (Subsequent) Internet Standard ofFazeelur RahmanNo ratings yet
- End-To-End Web Security-Protocols OverviewDocument7 pagesEnd-To-End Web Security-Protocols OverviewvivekNo ratings yet
- 2017-07-25 Streamr Datacoin Whitepaper v1Document28 pages2017-07-25 Streamr Datacoin Whitepaper v1Long TranNo ratings yet
- Iaetsd Carrying Out Safe Exploration Short of The Actual Data of Codes and TrapdoorsDocument5 pagesIaetsd Carrying Out Safe Exploration Short of The Actual Data of Codes and TrapdoorsiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Sheanopa MunatsiNo ratings yet
- Web Security Unit 6 Notes PDFDocument24 pagesWeb Security Unit 6 Notes PDFMohd FareeduddinNo ratings yet
- SSL TlsDocument22 pagesSSL Tlsvice pyNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 Background of StudyDocument24 pagesChapter One 1.1 Background of StudyPeter OsasNo ratings yet
- Secure Socket Layer: M S.Bhiogade Patni Computer Services, Mumbai, IndiaDocument6 pagesSecure Socket Layer: M S.Bhiogade Patni Computer Services, Mumbai, Indiadidiey87No ratings yet
- PLUTO: Cloud Assist Parallel Encryption For Data in Mobile Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesPLUTO: Cloud Assist Parallel Encryption For Data in Mobile Cloud ComputingasfNo ratings yet
- E Commm PDFDocument5 pagesE Commm PDFChamoadh DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Security Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesE Commerce Security Literature Reviewea219sww100% (2)
- Title of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inDocument19 pagesTitle of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inErwinFunaNo ratings yet
- A Lightweight Data Sharing SchemeDocument15 pagesA Lightweight Data Sharing SchemeAbhishek Basnyat100% (1)
- Chapter 17Document32 pagesChapter 17pravin_renold7435No ratings yet
- Card Payment Security Using RSADocument23 pagesCard Payment Security Using RSAKaataRanjithkumar100% (1)
- Risks of The Passport Single Signon Protocol: David P. Kormann, Aviel D. RubinDocument8 pagesRisks of The Passport Single Signon Protocol: David P. Kormann, Aviel D. RubinNurse MyIctNo ratings yet
- File and Text Encryption and Decryption Using Web Services (Synopsis)Document12 pagesFile and Text Encryption and Decryption Using Web Services (Synopsis)sanjaykumarguptaa100% (2)
- VTU Network and Cyber Security Module-1 (15ec835, 17ec835)Document51 pagesVTU Network and Cyber Security Module-1 (15ec835, 17ec835)jayanthdwijesh h p100% (2)
- Cost-Effective Authentic and Anonymous Data Sharing With Forward SecurityDocument6 pagesCost-Effective Authentic and Anonymous Data Sharing With Forward SecuritySagi samyukthaNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Threats On The Internet, Which Can Create DamageDocument11 pagesThe Different Types of Threats On The Internet, Which Can Create DamageHariharKaliaNo ratings yet
- Lets EncryptDocument2 pagesLets EncryptXian Manny MaraonNo ratings yet
- Secure and Decentralized Sharing of Iot DataDocument8 pagesSecure and Decentralized Sharing of Iot DataI AmNo ratings yet
- Security Mechanisms For Cloud StorageDocument6 pagesSecurity Mechanisms For Cloud StorageMoktar AmmarNo ratings yet
- Proneo Large File Transfer Using Webworkers and Cloud ServicesDocument5 pagesProneo Large File Transfer Using Webworkers and Cloud ServicesEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- MetaDisk: A Blockchain-Based Decentralized File Storage ApplicationDocument11 pagesMetaDisk: A Blockchain-Based Decentralized File Storage ApplicationPenNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Reading9 - InternetSecurityDocument11 pagesModule 4 - Reading9 - InternetSecurityChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- BC Unit I, Ii, IiiDocument22 pagesBC Unit I, Ii, Iiiss9933575No ratings yet
- REMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicFrom EverandREMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) ActDocument20 pagesThe Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) ActROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Centre For Railway Information Systems: Case StudyDocument12 pagesCentre For Railway Information Systems: Case StudyROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Pride of India: Pros: Statue of Unity: Key FactsDocument2 pagesPride of India: Pros: Statue of Unity: Key FactsROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Position Objective: Job Description JOB TITLE: Assistant Manager - Strategic Management Department/Directorate: HRDocument1 pagePosition Objective: Job Description JOB TITLE: Assistant Manager - Strategic Management Department/Directorate: HRROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Centre For Railway Information Systems Case Study: Chapter-7 E-Customer Relationship ManagementDocument13 pagesCentre For Railway Information Systems Case Study: Chapter-7 E-Customer Relationship ManagementROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Why Product Sold in E-Commerce Is Much Cheaper Than in Retail Shops?Document1 pageWhy Product Sold in E-Commerce Is Much Cheaper Than in Retail Shops?ROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Attempt All QuestionsDocument2 pagesSolutions: Attempt All QuestionsROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- On Snap ChatDocument19 pagesOn Snap ChatROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Automation in The HRDocument1 pageAutomation in The HRROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Ayushi SrivastavaDocument7 pagesAyushi SrivastavaROHIT JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Impact2013 - TSI-3089 - DataPower Common Use Cases PDFDocument82 pagesImpact2013 - TSI-3089 - DataPower Common Use Cases PDFnakamuroshiNo ratings yet
- Amazon EC2 TutorialDocument20 pagesAmazon EC2 TutorialAnkita Vishwakarma0% (1)
- Microsoft: Product VersionDocument10 pagesMicrosoft: Product VersionBoudhiafi SawssenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 AUDocument80 pagesChapter 1 2 AUYididiya TilahunNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 SlidesDocument41 pagesUnit 3 Slidesharshsavaliya0905No ratings yet
- Load Balancer: Level 200Document32 pagesLoad Balancer: Level 200Harish NaikNo ratings yet
- Matrix Navan Cnx200 DatasheetDocument4 pagesMatrix Navan Cnx200 DatasheetrvaironNo ratings yet
- Digital Twin in GeneralDocument18 pagesDigital Twin in GeneralFabricio Rosado UrquhartNo ratings yet
- Hak Cipta Di Dunia DigitalDocument13 pagesHak Cipta Di Dunia Digitalaldo islamiNo ratings yet
- Badland Buggy - ST2-LT Plans - 1 of 2 PDFDocument1 pageBadland Buggy - ST2-LT Plans - 1 of 2 PDFCebo MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Firebox T35 & T55: Big Security For Small BusinessesDocument2 pagesFirebox T35 & T55: Big Security For Small Businessesvijay gopalNo ratings yet
- Script Blokir Virus MikrotikDocument1 pageScript Blokir Virus MikrotikTatmimul FataNo ratings yet
- How To Use Our Branded MaterialsDocument6 pagesHow To Use Our Branded MaterialsAlba Martínez GondarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction and Security ThreatsDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Introduction and Security ThreatsAmdavadi ChokaroNo ratings yet
- 8 Static - and - Dynamic - DataDocument2 pages8 Static - and - Dynamic - DataJay D.No ratings yet
- How To Access WorkdayDocument13 pagesHow To Access WorkdaySunandha SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Ultimate CCNA ChallengeDocument3 pagesUltimate CCNA ChallengegobinathNo ratings yet
- Monologue: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Document3 pagesMonologue: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Zuk V CastilloNo ratings yet
- How To Use and Register in The SSS Website (Member Account)Document62 pagesHow To Use and Register in The SSS Website (Member Account)Jin DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Spear Phishing: Diagnosing Attack Paradigm: Deepali N. Pande and Preeti S. VoditelDocument5 pagesSpear Phishing: Diagnosing Attack Paradigm: Deepali N. Pande and Preeti S. VoditelSantosh KBNo ratings yet
- EcomerceDocument4 pagesEcomerceMustafaAbdAliNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Course by Digital King Hub PDFDocument11 pagesDigital Marketing Course by Digital King Hub PDFrahul thumarNo ratings yet
- SSH Feature Overview GuideDocument20 pagesSSH Feature Overview GuideNaveen KolliNo ratings yet
- WebStrike PDF ReportDocument4 pagesWebStrike PDF ReportBiswajitNo ratings yet
- FB Marketing Tips For YouDocument13 pagesFB Marketing Tips For YouPamoris PamorisNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Web ComponentsDocument26 pagesAn Introduction To Web ComponentsAlison Lemos GarantizadoNo ratings yet
- EXCH - Technical Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesEXCH - Technical Interview QuestionsNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Ocial EngineeringDocument26 pagesOcial Engineeringafiq syahmiNo ratings yet