Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermofluids Quiz 1 Problems
Uploaded by
Yaird MalakaraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermofluids Quiz 1 Problems
Uploaded by
Yaird MalakaraCopyright:
Available Formats
THERMOFLUIDS QUIZ 1
FIRST EVALUATION
NAME ___________________________________________________ Register number __________________
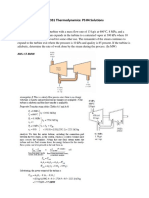
1) PROBLEM (2 points) A piston-cylinder device contains 80 kg of water at 160 kPa and 20°C. The cross-
sectional area of the piston is 0.12 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and
expand. When the volume reaches 0.3 m 3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 120
kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. Determine:
a) the final pressure in KPa and temperature in °C
b) the work done during this process in KJ
2) PROBLEM (2 points) A Carnot heat engine receives heat from a reservoir at 1000°C at a rate of 850 KJ/min
and rejects the waste heat to the ambient air at 30°C. The entire work output of the heat engine is used to
drive a refrigerator that removes heat from the refrigerated space at -4°C and transfers it to the same ambient
air at 30°C. Determine:
a) the maximum rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space in KJ/min
b) the total rate of heat rejection to the ambient air in KJ/min
3) PROBLEM (2 points) Consider two Carnot heat engines operating in series. The first engine receives heat
from the reservoir at 3000 k and rejects the waste heat to another reservoir at temperature “T”. The second
engine receives this energy rejected by the first one, converts some of it to work, and rejects the rest to a
reservoir at 350 K. if thermal efficiencies of both engines are the same, determine the temperature “T”.
4) PROBLEM (2 points) A heat pump with COP of 3 is used to heat an airtight house. When running, the heat
pump consumes 8 KW of power. If the temperature in the house is 5°C when the heat pump is turned on, how
long in min will it take for the heat pump to raise the temperature of the house to 22°C. Assume the entire
mass within the house (air, furniture, etc.) is equivalent to 1800 kg of air.
5) PROBLEM (2 points) Combustion gases enter an adiabatic gas turbine at 1600°F and 130 psia and leave at
50 psia with a low velocity. Treating the combustion gases as air and assuming an isentropic efficiency of 89%,
determine the work output of the turbine in BTU/lbm
You might also like
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3happy20212025No ratings yet
- Problem Sets For Solutions AnalysisDocument2 pagesProblem Sets For Solutions AnalysisKamil Guillergan100% (1)
- MEE 302 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesMEE 302 - Tutorial 1acemumbiNo ratings yet
- Test 1 With AnsDocument4 pagesTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS #4 Solutions: Numeric 1Document15 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS #4 Solutions: Numeric 1Crimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- Me8391 - EtdDocument3 pagesMe8391 - Etdsyed1188No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocument4 pagesThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiNo ratings yet
- TER201E 2011-12 F Midterm2 SoltnDocument4 pagesTER201E 2011-12 F Midterm2 SoltnWassen HejjawiNo ratings yet
- First Law Applied To Flow Process and Second Law of Thermodynamics Assignment - 2Document3 pagesFirst Law Applied To Flow Process and Second Law of Thermodynamics Assignment - 2Supriyo sahuNo ratings yet
- Course 228 FileDocument7 pagesCourse 228 FilegrfNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems in Industrial Plant Design Pumps and CompressorsDocument26 pagesSample Problems in Industrial Plant Design Pumps and CompressorsSdhfdh Hdfhd100% (1)
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 PDFRima ChinnasamyNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me8391 Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesMe8391 Important QuestionsMohsin EngrNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer AssignmentDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer AssignmentHreaan SighaniaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3B V V HANUMA GAYATHRINo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3api-3802845No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Tutorial 2Document2 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorial 2vicopipNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207Document3 pagesAssignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207nageshNo ratings yet
- Thermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With AnswersDocument21 pagesThermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With Answersmarc rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Me2202 - EtDocument7 pagesMe2202 - EtAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Aero Engineering Thermodynamics PDFDocument22 pagesAero Engineering Thermodynamics PDFSridharanNo ratings yet
- Answer Problem Sheet-05 Me201 2nd LawDocument9 pagesAnswer Problem Sheet-05 Me201 2nd LawshantanuNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Document4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Wilbard IitulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document2 pagesAssignment#3Ashish ManwarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics seatwork problemsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics seatwork problemsMarie Angeline BautistaNo ratings yet
- 082 CH 20Document3 pages082 CH 20Jagdip ShethNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 EOT 1032Document5 pagesAssignment 2 EOT 1032Rajbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Design and Refrigeration Cycle CalculationsgodadNo ratings yet
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- Department of Aeronautical / Aerospace Engineering U20AE301 - Aero Engineering Thermodynamics 50 Big QuestionsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Aeronautical / Aerospace Engineering U20AE301 - Aero Engineering Thermodynamics 50 Big QuestionsGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- BT Quiz - 2Document8 pagesBT Quiz - 2Navdha KapoorNo ratings yet
- AE8301 Aero Engineering Thermodynamics, QP, Model (2020 - 2021) - SDocument2 pagesAE8301 Aero Engineering Thermodynamics, QP, Model (2020 - 2021) - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Heatex 02 AwDocument3 pagesHeatex 02 AwyvethendoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument64 pagesUntitledAgilan ChellaramNo ratings yet
- A1 4Document6 pagesA1 4Mohit PassiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Quiz KeyDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Quiz KeysonuNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur KANPUR-208016 (INDIA) CAD of Thermal Systems (ME 648) Home Assignment - 11Document2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur KANPUR-208016 (INDIA) CAD of Thermal Systems (ME 648) Home Assignment - 11AsheeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Aryan NayanNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 2Document4 pagesDigital Assignment 2KhojaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 finalDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 finalhamimmuhammedadem0579No ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics Problem SetDocument4 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics Problem SetGy Ra0% (1)
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocument2 pages16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- FinalExam Fall2010Document10 pagesFinalExam Fall2010asselNo ratings yet
- Tut 6,7,8 - 2013Document3 pagesTut 6,7,8 - 2013SourabhNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Practice Problem 1Document2 pagesBasic Engineering Practice Problem 1neva000No ratings yet
- Your AnswerDocument6 pagesYour AnswerJASHANPREET SinghNo ratings yet
- Test #2Document3 pagesTest #2Dar QuetzalNo ratings yet
- Problems Part2Document21 pagesProblems Part2Sharif Mohd Zaki100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2KARTHICK MNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics Practice Questions - Without AnsDocument4 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics Practice Questions - Without AnsKirti KumarNo ratings yet
- ME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 2021 FinalDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 2021 FinalRichard GrahamNo ratings yet
- Old-Exam-Questions-Ch.#20-082 (Dr. Naqvi-Phys102.04-06Document3 pagesOld-Exam-Questions-Ch.#20-082 (Dr. Naqvi-Phys102.04-06czds6594No ratings yet