Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. Overview of The: Cor Pulmonale
Uploaded by
Mhariel EdlesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I. Overview of The: Cor Pulmonale
Uploaded by
Mhariel EdlesCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
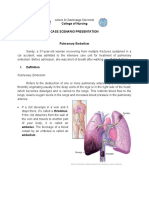
OVERVIEW OF THE COR PULMONALE
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the
arteries of the lung and right ventricle of the heart can lead to cor pulmonale. Lung conditions that cause a low blood
oxygen level in the blood over a long time can also lead to cor pulmonale.
Some of these are:
Autoimmune diseases that damage the lungs, such as scleroderma
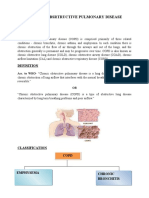
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic blood clots in the lungs
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Scarring of the lung tissue (interstitial lung disease)
Severe curving of the upper part of the spine (kyphoscoliosis)
Obstructive sleep apnea, which causes stops in breathing because of airway inflammation
Idiopathic (no specific cause) tightening (constriction) of the blood vessels of the lungs
II. SYMPTOMS OF DISORDER
Symptoms of a goiter may include:
Shortness of breath or lightheadedness during
activity is often the first symptom of cor
pulmonale. You may also have a fast heartbeat Fainting spells during activity
and feel like your heart is pounding. Chest discomfort, usually in the front of the chest
Chest pain
Over time, symptoms occur with lighter activity Swelling of the feet or ankles
or even while you are at rest. Symptoms you Symptoms of lung disorders, such as wheezing
may have are: or coughing or phlegm production
Bluish lips and fingers (cyanosis)
III. CAUSES OF THE ALTIRATION
Causes of COR pulmonale
The lungs depend on the heart to transport blood from the body to the lungs. Pulmonary hypertension is a type of
increased pressure in your lungs’ arteries and your heart’s right ventricle. It’s a result of having to overcome the high
pressure in the lungs to force blood into them. This increased pressure causes an ineffective transportation of blood to the
lungs. Untreated pulmonary hypertension is the most common cause of COR pulmonale.
Other conditions that can cause this health complication include:
blood clots in the lungs
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
lung tissue damages
sleep apnea
cystic fibrosis
IV. RISK FACTOR OF THE DISORDER
Acute cor pulmonale (most commonly caused by PE)
Chronic cor pulmonale (most commonly caused by underlying pulmonary disorder)
o Risk factors associated with pulmonary disorders
Tobacco use (COPD)
Occupational exposures (ILD)
Hypercoagulable state (chronic thromboembolic disease)
Obesity, age (chest wall/ventilatory abnormalities)
I. TREATMENT MODALITIES
Medical therapy for chronic cor pulmonale is generally focused on treatment of the underlying pulmonary disease and
improving oxygenation and right ventricular (RV) function by increasing RV contractility and decreasing pulmonary
vasoconstriction. [22] However, the approach might be different to some degree in an acute setting, with priority given to
stabilizing the patient.
Cardiopulmonary support for patients experiencing acute cor pulmonale with resultant acute RV failure includes fluid
loading and vasoconstrictor (eg, epinephrine) administration to maintain adequate blood pressure. Of course, the primary
problem should be corrected, if possible.
You might also like
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document32 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- My Cardiac and Chest SymptomsDocument58 pagesMy Cardiac and Chest SymptomsDhamirah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument11 pagesChronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary Diseasepreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- Plasma University: Guriel-Galgadud RegionDocument17 pagesPlasma University: Guriel-Galgadud RegionDr AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Samara University: Collage of Biomedical and Health Science Department of Public Health OfficerDocument32 pagesSamara University: Collage of Biomedical and Health Science Department of Public Health Officergirma melakuNo ratings yet
- Breathlessness EdittedDocument2 pagesBreathlessness EdittedSalwani MohamedNo ratings yet
- OralDocument19 pagesOralNick James CabasisNo ratings yet
- LI 8 - Differential Diagnosis of Acute Heart FailureDocument11 pagesLI 8 - Differential Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure19-034 Jefry Junaidi PurbaNo ratings yet
- MedSurg 2Document69 pagesMedSurg 2Claire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Common Diseases of the Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesThe Anatomy and Common Diseases of the Respiratory Systemshubham royalNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain and Dyspnea CausesDocument12 pagesChest Pain and Dyspnea CausesAmi DhaniaNo ratings yet
- Patokinesis EprDocument36 pagesPatokinesis EprLuis Javier Martinez EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea Is An Uncomfortable Abnormal Awareness of Breathing. A Number of DifferentDocument4 pagesDyspnea Is An Uncomfortable Abnormal Awareness of Breathing. A Number of DifferentSita SifanaNo ratings yet
- Sypmtoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesDocument22 pagesSypmtoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- An Approach To A Patient With BreathlessnessDocument35 pagesAn Approach To A Patient With Breathlessnessgl tousifNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulamonary DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulamonary Diseaseanamika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Pulmo HPNDocument36 pagesPulmo HPNAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- 5 Approach To The Patient With Disease of The Respiratory SystemDocument36 pages5 Approach To The Patient With Disease of The Respiratory SystemPhoebie Gael AsisNo ratings yet
- DyspnoeaDocument1 pageDyspnoeaShubham TarapureNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Signs of Respiratory Disease Lecture 2: DyspnoeaDocument9 pagesSymptoms and Signs of Respiratory Disease Lecture 2: DyspnoeaShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument8 pagesAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - ActivityDocument6 pagesWeek 13 - ActivityGuillana Mae CastellonNo ratings yet
- ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE GUIDEDocument10 pagesACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE GUIDEGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Ena Respiratory EmergenciesDocument30 pagesEna Respiratory Emergencieseng78ineNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale (Pneumoconiosis)Document23 pagesCor Pulmonale (Pneumoconiosis)Sai charithaNo ratings yet
- COPD Care Guide: Signs, Symptoms and Nursing InterventionsDocument32 pagesCOPD Care Guide: Signs, Symptoms and Nursing InterventionsRichard Andrew GayatinNo ratings yet
- COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDDocument37 pagesCOPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDSonny AgultoNo ratings yet
- Cor PulmonaleDocument14 pagesCor PulmonaleEvangelin MelvinNo ratings yet
- Different Respiratory System PathologiesDocument2 pagesDifferent Respiratory System PathologiesKONICNo ratings yet
- Churchill's Pocketbook of Differential Diagnosis, Fourth EditionDocument6 pagesChurchill's Pocketbook of Differential Diagnosis, Fourth EditionalexisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: by Amera GumamaDocument26 pagesRespiratory Failure: by Amera GumamaGumama AmeiyrhaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument8 pagesResearch MethodsSilver DrakeNo ratings yet
- COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument18 pagesCOPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseemilliansNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dyspnea 讲课稿 2020Document16 pages2 - Dyspnea 讲课稿 2020mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Clubbing Sign and CyanosisDocument26 pagesClubbing Sign and CyanosisKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- Cardio AssessmentDocument118 pagesCardio AssessmentNashrina NashrinaNo ratings yet
- 5 Documents HealthDocument6 pages5 Documents HealthAbdiwali AhmedNo ratings yet
- EmphysemaDocument17 pagesEmphysemaDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument32 pagesCare of Patient With Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJesselle LasernaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Dysfunction GuideDocument42 pagesRespiratory Dysfunction GuideHassan DayaxNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument23 pagesARDSDumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Cough 讲课稿 2020Document10 pages1.3 - Cough 讲课稿 2020mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Exam: Lungs, Breathing, CyanosisDocument81 pagesRespiratory Exam: Lungs, Breathing, CyanosisashuNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale GuideDocument9 pagesCor Pulmonale GuideMaríaDelPilarAguilarNo ratings yet
- Sesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Document50 pagesSesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Endik SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea: Dr. Siddharth - Med PGDocument37 pagesDyspnea: Dr. Siddharth - Med PGAlmira PutriNo ratings yet
- Structurally, The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesStructurally, The Respiratory Systemyori rafiadliNo ratings yet
- Symtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesSymtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemmohammedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Major Chronic Illnesses of Older AdultsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Major Chronic Illnesses of Older AdultsSteffiNo ratings yet
- COPD Guide: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentDocument30 pagesCOPD Guide: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsalmanhabeebekNo ratings yet
- Acute Interstitial Pulmonary Edema Power Point FixDocument29 pagesAcute Interstitial Pulmonary Edema Power Point FixnandablaguNo ratings yet
- DR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaDocument81 pagesDR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaBethelhem BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Cor PulmonaleDocument3 pagesCor PulmonaleKhalid Mahmud ArifinNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism Case PresentationDocument3 pagesPulmonary Embolism Case PresentationAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- COPD Patient With Chronic Dyspnea and CyanosisDocument2 pagesCOPD Patient With Chronic Dyspnea and CyanosisAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases AntonioDocument9 pagesCommon Diseases AntonioBARNUEVO HONEY MARIENo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisFrom EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisNo ratings yet
- Pleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Psychologis T Theory About Self Critical and Reflective ThoughtDocument3 pagesPsychologis T Theory About Self Critical and Reflective ThoughtMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication Skills for NursesDocument4 pagesEffective Communication Skills for NursesMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentDocument2 pagesPolycythemia Vera Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Overview of Leukemia Types and CausesDocument3 pagesOverview of Leukemia Types and CausesMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument2 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- 7 Protozoal Infections of Circulatory System African Trypanosomiasis (African Sleeping Sickness)Document3 pages7 Protozoal Infections of Circulatory System African Trypanosomiasis (African Sleeping Sickness)Mhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Overview of Duchenne Muscular DystrophyDocument2 pagesOverview of Duchenne Muscular DystrophyMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Hiii I Just Need To Upload A Document Here For Me To Download What I Need Hehe Anyways Stay SafeDocument1 pageHiii I Just Need To Upload A Document Here For Me To Download What I Need Hehe Anyways Stay SafeMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Hiii I Just Need To Upload A Document Here For Me To Download What I Need Hehe Anyways Stay SafeDocument1 pageHiii I Just Need To Upload A Document Here For Me To Download What I Need Hehe Anyways Stay SafeMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Microbial EcologyDocument6 pagesMicrobial EcologyMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Izza Scam I Just Need To Upload A Document HeheDocument1 pageIzza Scam I Just Need To Upload A Document HeheMhariel EdlesNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region V - BicolDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region V - BicolKevin Viernes GaraisNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Data Mining Techniques For COVID PredictionDocument6 pagesA Survey On Data Mining Techniques For COVID PredictionWARSE Journals100% (2)
- Cytomegalovirus - Causes, Signs and SymptomsDocument5 pagesCytomegalovirus - Causes, Signs and SymptomsHoorise NShineNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Digestive SYSTEM WorksheeetDocument8 pagesPaper 2 Digestive SYSTEM WorksheeetOmar AlfrouhNo ratings yet
- OB GYN Mock Board QuestionnaireDocument12 pagesOB GYN Mock Board QuestionnairejampogaottNo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument15 pagesConjunctivitisPuviyarasiNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions About The Use of Genetic Tests in PopulationsDocument4 pagesMisconceptions About The Use of Genetic Tests in PopulationsAneeshNo ratings yet
- First Aid For BurnsDocument10 pagesFirst Aid For BurnsRalc Retsel AtadNo ratings yet
- UNICEF Annual Report 2019Document68 pagesUNICEF Annual Report 2019Volodymyr DOBROVOLSKYINo ratings yet
- BAB 6. True and False StatementDocument5 pagesBAB 6. True and False StatementLentera DakwahNo ratings yet
- Arthritis OsteoarthritisDocument43 pagesArthritis OsteoarthritisMYMANo ratings yet
- Uts Advocacy PaperDocument11 pagesUts Advocacy PaperPlu AldiniNo ratings yet
- DLL ObservationDocument5 pagesDLL ObservationBelinda LapsitNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Ageing - An Introduction, 3rd EdDocument320 pagesThe Psychology of Ageing - An Introduction, 3rd Edfauziahfasya123No ratings yet
- Introduction to Radiotherapy: Blackboard AssignmentDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Radiotherapy: Blackboard AssignmentRafaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Stigma and Discrimination Towards People Living With Hiv/AidsDocument20 pagesA Study of Stigma and Discrimination Towards People Living With Hiv/Aidsmusamuwaga100% (1)
- Emergency First Initial Assesment: Monday, October 05, 2020Document50 pagesEmergency First Initial Assesment: Monday, October 05, 2020Agoes TreeyantNo ratings yet
- Rectum: Malueth AbrahamDocument19 pagesRectum: Malueth AbrahamMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Anti - HyperlipidemiaDocument18 pagesAnti - HyperlipidemiaZakarie Abdullahi Hussein100% (1)
- Clobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023Document51 pagesClobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 7Document2 pagesTransportation in Animals and Plants Worksheet 7Parul ShahNo ratings yet
- Research Article Smilacina Japonica A. Gray: Antifungal Activity of Crude Extract From The Rhizome and Root ofDocument10 pagesResearch Article Smilacina Japonica A. Gray: Antifungal Activity of Crude Extract From The Rhizome and Root ofJolianna Andrea Beatrice BallezaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Staff Accomplishment Report New LHDocument2 pagesBarangay Staff Accomplishment Report New LHUy HenryNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument11 pages1 PBNaswa Alifia PutriNo ratings yet
- Catálogo de Dispositivos PQS 2014 PDFDocument318 pagesCatálogo de Dispositivos PQS 2014 PDFGestion Biomedica Prosalco IPSNo ratings yet
- Pemphigus Foliaceus: Fig. 29.13BDocument1 pagePemphigus Foliaceus: Fig. 29.13BCristian QuitoNo ratings yet
- Nilufa Shariff - Pain Dissertation PresentationDocument31 pagesNilufa Shariff - Pain Dissertation PresentationNilufar JivrajNo ratings yet
- Bible Aromatherapy 2022Document39 pagesBible Aromatherapy 2022johanjacobvelosagomezNo ratings yet
- Specialized Group Homes For Persons With Severe or Profound Mental Retardation and Serious Problem Behaviour in EnglandDocument18 pagesSpecialized Group Homes For Persons With Severe or Profound Mental Retardation and Serious Problem Behaviour in EnglandDeborah RiskinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Health Awareness ScaleDocument17 pagesSexual Health Awareness ScaleezazpsychologistNo ratings yet