Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1. Introduction To Muscle Physiology
Uploaded by
Yolande Clothier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
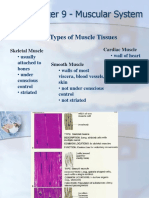
8 views5 pagesThere are three main types of muscles in the human body: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, composed of long fibers of sarcomeres that contract when stimulated by motor neurons to produce movement. Cardiac muscle is located in the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood, while smooth muscle is found in internal organs and blood vessels and contracts involuntarily without conscious control.
Original Description:
Original Title
L1+MUSCLE_Notes.Introduction+StructureFunction_2013.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are three main types of muscles in the human body: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, composed of long fibers of sarcomeres that contract when stimulated by motor neurons to produce movement. Cardiac muscle is located in the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood, while smooth muscle is found in internal organs and blood vessels and contracts involuntarily without conscious control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesL1. Introduction To Muscle Physiology
Uploaded by
Yolande ClothierThere are three main types of muscles in the human body: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, composed of long fibers of sarcomeres that contract when stimulated by motor neurons to produce movement. Cardiac muscle is located in the heart and contracts involuntarily to pump blood, while smooth muscle is found in internal organs and blood vessels and contracts involuntarily without conscious control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
L1.
Introduction to Muscle Physiology
MUSCLE TYPES
Different types of muscles in your body:
• smooth muscle
• cardiac muscle
• skeletal muscle
- all made of same ‘elastic’ material
- many fibres make up muscle
1.Smooth muscle
• involuntary - you can't control this muscle
• usually in sheets / layers
• located in:
• Stomach
• Intestine (peristalsis)
• Uterus
• Skin (ctrls body hair)
• Blood vessels
2. Cardiac muscle
• cardiac muscle involuntary (like smooth muscle)
• myocardium
• thick muscles (contract to pump blood out)
(relax to let blood back in)
• faintly striated with intercalated discs
• branched syncitium – functional unit
3. Skeletal muscles
• striated muscle | voluntary
• long fibres, many different sizes and shapes
• multinucleate
• each fibre stimulated by branch from motor neuron
• skeletal muscles work w bones - give body power & strength
Skeletal Muscle: structure
Ultrastructure: the basic functional unit – Sarcomere
striated muscle made of sarcomeres in highly regular arrangements
SARCOMERE
- two prominent Z-discs
- thick filament of myosin + two sets of thin filaments (actin mostly)
Functional physiology of skeletal muscles
• movement of actin upon myosin to produce contraction
• muscle contraction stimulated by motor neurons
• acetylcholine - neurotransmitter (NMJ)
muscle activity accounts for most of body's energy consumption
Requires a ready source of ATP
Skeletal Muscle – composition
You might also like
- Muscles: Dr. Maung MyintDocument54 pagesMuscles: Dr. Maung MyintIntan AinNo ratings yet
- Muscular System (Wk7) HandoutDocument23 pagesMuscular System (Wk7) HandoutPhoebeNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 pagesEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 1 13Document13 pagesIlovepdf Merged 1 13Abdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument26 pagesMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Anatomy of The MusclesDocument41 pagesAnatomy of The Musclestayabaiqbal66No ratings yet
- Physiology Lecture 10Document21 pagesPhysiology Lecture 10Muhammad Khubaib AzeemNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue VnaDocument55 pagesMuscle Tissue Vnavaryvira6677No ratings yet
- Bs Pharma Muscular SystemDocument36 pagesBs Pharma Muscular SystemLawrenceNo ratings yet
- 3c. Muscle 22893Document15 pages3c. Muscle 22893Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesClinical Case: Anatomy and PhysiologyGeorge KoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument13 pagesMusculoskeletal Systemmelbert nacuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesWEEK 6 Muscular SystemMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Its ClassificationDocument25 pagesMuscles and Its ClassificationJunaid ShahNo ratings yet
- Physiology05 Muscle CellDocument37 pagesPhysiology05 Muscle CellsmpoojasubashNo ratings yet
- Презентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Document28 pagesПрезентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Гулбахор ИсаковаNo ratings yet
- Histology2 Week 2Document23 pagesHistology2 Week 2Tabou GastoneNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Biology IiDocument33 pagesThe Muscular System: Biology IiBibiNo ratings yet
- 9 Muscular System Handouts FINALDocument2 pages9 Muscular System Handouts FINALRojan NavarraNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesMuscular SystemAksidaksiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Muscles (Salman)Document38 pagesAnatomy of The Muscles (Salman)Radu StoenescuNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument19 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemDani Anyika100% (1)
- 10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryDocument62 pages10 Q2 NervousMuscular-Skeletal-IntegumentaryHasmine Lara RiveroNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesMuscle Tissue: Lecturer Reham M.M. Almosawi Medical Microbiologymustafa7calligrapherNo ratings yet
- 4-Lecture Skeletal Muscles StructureDocument20 pages4-Lecture Skeletal Muscles StructureSaira SolNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 9Document41 pagesPDF Document 9Eliese Marie Antonnie TiuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledOtencianoNo ratings yet
- 2-Muscle StructureDocument33 pages2-Muscle Structureasaad AseeeNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscle TissueDocument24 pagesHistology of Muscle Tissuephillipjaurel8No ratings yet
- Kharkov National Medical University: Muscle TissueDocument42 pagesKharkov National Medical University: Muscle TissueSyed Irfan ArifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The Muscular Systemأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument16 pagesMuscle PhysiologyFranci Kay SichuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System PowerPointDocument11 pagesMuscular System PowerPointEmerald CorrineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesChapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemFatiha AmiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomi & Fisiologi IDocument25 pagesAnatomi & Fisiologi ISyasya NanaNo ratings yet
- Bab 12 - Muscular SystemDocument73 pagesBab 12 - Muscular SystemDaeng FarahnazNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- A & P Lecrure Notes For TestDocument1 pageA & P Lecrure Notes For Testdesrivera30No ratings yet
- العضلاتDocument8 pagesالعضلاتNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- NefDn Muscular System SummDocument2 pagesNefDn Muscular System SummNefertitie DanaoNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemadequateNo ratings yet
- Goal: To Describe The Structure and Function of The Muscular SystemDocument24 pagesGoal: To Describe The Structure and Function of The Muscular SystemLayne Fuentes Padillo-Mapiguid100% (1)
- Muskuloskeletal DisordersDocument15 pagesMuskuloskeletal DisordersLienyPerasNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentDocument16 pagesModule 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentLaw HacksNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Muscle: Dr. Dini Sri Damayanti, MkesDocument63 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Muscle: Dr. Dini Sri Damayanti, MkesTeguh SantosoNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle TissueFady FadyNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Muscular SystemDocument19 pagesWeek 6 - Muscular SystemKatrina Reyes100% (1)
- TheCompleteMuscular SystemDocument57 pagesTheCompleteMuscular SystemAyyappan Jayavel100% (1)
- YU - General - Muscles 1Document57 pagesYU - General - Muscles 1Mohammad BarakatNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems: Nervous /Muscles/Skeleton SystemsDocument32 pagesHuman Body Systems: Nervous /Muscles/Skeleton SystemsWilver James Satinitigan NeriNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument12 pagesMuscle and Nervous TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document22 pagesLab 3202310446No ratings yet
- Structure of Human BodyDocument19 pagesStructure of Human BodyWimrod CanenciaNo ratings yet