Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IFP Materials PDF
Uploaded by
Process Engineer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesOriginal Title
IFP Materials (21).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesIFP Materials PDF
Uploaded by
Process EngineerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
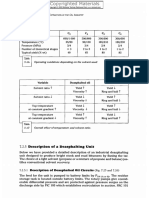
Title: Petroleum Refining, Volume 4 - Materials and Equipment
Table: Interactive Graphs
class material x-axis y-axis graph title text graph
digitizer
Distance between tube Angle factor, μ Figure 5.17. Angle factor μ for heat exchange by radiation between a plane view text
axes/tube outside diameter, and a row of tubes.
E/D
Distance between tube Exchange factor, F Figure 5.18. Overall exchange factor F for heat exchange by radiation view text
axes/tube outside diameter, between a plane and a row of tubes (the factor F applies to the area S of
E/D the plane).
Gas temperature (°C) Steam emmisivity, εw Figure 5.19. Emissivity of steam for a partial pressure pw # 0 and a total view text
pressure of the gas mass pT = 1 atm. See pdf for additional text.
gas carbon Gas temperature (°C) Carbon dioxide Figure 5.20. Emissivity of carbon dioxide for a total pressure of the gas view text
dioxide emmisivity, εc mass pT # 1 atm. See pdf for additional text.
Ratio of refractory wall Angle factor, μR1 Figure 5.24. Angle factor μR1 between the refractory wall surface AR, and view text
surface and receiving surface, the receiving surface FA.
AR/FA
Distance between tube Overall exchange Figure 5.25. Overall exchange factor F and angle factor μ for heat view text
axes/tube outside diameter, factor, F, angle factor, exchange by radiation between a radiating plane and one or two rows of
E/D μ tubes (black surface) placed in front of a refractory wall.
Tube melt temperature (°C) Heat flux density, φ Figure 5.27. Heat flux density φ on the surface of tubes in the radiation view text
(kW/m2) section of furnaces with vertical tubes heated on only one side, with 20%
excess air. See pdf for additional text.
Tube melt temperature (°C) Heat flux density, φ Figure 5.28. Heat flux density φ on the surface of tubes in the radiation view text
(kW/m2) section in furnaces with horizontal tubes heated on only one side, with 20%
excess air. See pdf for additional text.
Heat flux density (kW/m2) Height (m) Figure 5.29. Vertical distribution of incident heat flux density by radiation view text
in a vertical cylindrical furnace.
Heat flux density (kW/m2) Height (m) Figure 5.30. Vertical distribution of incident heat flux density by radiation view text
in a furnace with horizontal tubes.
hydrocarbon normal Temperature potential (°C) Flux (kW/m2) Figure 6.17. Vaporization of normal pentane. view text
pentane
Gas Velocity (cm/s) Solid fraction Figure 7.47. Diagram illustrating the different fluidization regimes found in view text
a catalytic cracking unit. See pdf for additional text.
Flow rate (m3/h) Pressure (bar) Figure 8.1. Approximate range of operation for the three main types of view text
pump.
Flow rate (m3/h) Head (m) Figure 8.10. Influence of impeller diameter on the characteristic curve. view text
liquid water Temperature (°C) Vapor pressure, Tv Figure 8.11. Water vapor pressure (expressed in meters of water column) view text
versus the temperature.
Inlet volume flow rate (m3/h) Pressure ratio Figure 8.38A. Characteristic curves of a centrifugal compressor. Pressure view text
ratio versus inlet flow rate.
Petroleum Refining, Volume 4 - Materials and Equipment © 2000 Editions Technip 1
Title: Petroleum Refining, Volume 4 - Materials and Equipment
Table: Interactive Graphs
Reynolds number, Re Power number, Np Figure 9.9. Examples of variation in the power factor Φ versus the Reynolds view text
number for different agitation impellers.
Reynolds number, Re Power factor, Φ Figure 9.10. Variation in the power factor versus the Reynolds number (for view text
an anchor).
Petroleum Refining, Volume 4 - Materials and Equipment © 2000 Editions Technip 2
You might also like
- 5.4.2019 - Heat TransDocument21 pages5.4.2019 - Heat TransMoutinhoRodriguesNo ratings yet
- 01 Weight Optimization of A Cooling System Gammeter 01Document13 pages01 Weight Optimization of A Cooling System Gammeter 01machadrsNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Saeed Mohebbi, Farzad VeysiDocument12 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Saeed Mohebbi, Farzad VeysizahiraNo ratings yet
- Air-Cooled Exchanger Design and SizingDocument19 pagesAir-Cooled Exchanger Design and Sizingnafees ahmadNo ratings yet
- ch4 5Document5 pagesch4 5RishokNo ratings yet
- Influence of Fan Setting Height On The Cooling Performance of A Plate-Fin-Type Heat Sink With MicroprocessorDocument9 pagesInfluence of Fan Setting Height On The Cooling Performance of A Plate-Fin-Type Heat Sink With Microprocessornadir boutalbiNo ratings yet
- An air-cooled exchanger guideDocument16 pagesAn air-cooled exchanger guideNirmalNo ratings yet
- HRV performance enhanced by film vibrationDocument5 pagesHRV performance enhanced by film vibrationHawraa ImadNo ratings yet
- 008 11265life1001 49 56Document8 pages008 11265life1001 49 56hajerNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Research of A New Type of Radiant Floor Heating SystemDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer Research of A New Type of Radiant Floor Heating SystemAnant NimjeNo ratings yet
- aipDocument19 pagesaipgaith.tw1997No ratings yet
- Strip dryer with air impinging jetsDocument108 pagesStrip dryer with air impinging jetsTECHXPERT SOLUTIONNo ratings yet
- GRE PrepDocument17 pagesGRE PrepkabbirhossainNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigation of Combustion Optimization in A Tangential Firing Boiler Considering Steam Tube OverheatingDocument15 pagesNumerical Investigation of Combustion Optimization in A Tangential Firing Boiler Considering Steam Tube OverheatingYogesh DewangNo ratings yet
- 5.0135995Document19 pages5.0135995gaith.tw1997No ratings yet
- Shape Optimization of Welded Plate Heat Exchangers Based On GreyDocument9 pagesShape Optimization of Welded Plate Heat Exchangers Based On GreySandro Chuqui PorteroNo ratings yet
- Aircooled ExchangersDocument20 pagesAircooled ExchangersTAHIR MAHMOODNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Mohd Zeeshan, Sujit Nath, Dipankar BhanjaDocument16 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Mohd Zeeshan, Sujit Nath, Dipankar BhanjaDedi AfandiNo ratings yet
- 11311-1034196 SilvaDocument11 pages11311-1034196 SilvaMainak DasNo ratings yet
- BusAmpacityIEEETransOct94 PDFDocument9 pagesBusAmpacityIEEETransOct94 PDFAnonymous qDCftTW5MNo ratings yet
- Calculation Spreadsheet For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 13Th Edition NomenclatureDocument6 pagesCalculation Spreadsheet For Gpsa Engineering Data Book, 13Th Edition NomenclatureĐậu BắpNo ratings yet
- WHRB (HRSG) Performance CalculationsDocument9 pagesWHRB (HRSG) Performance CalculationsLiam MoylanNo ratings yet
- Borefield OkuDocument8 pagesBorefield OkuJack HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document14 pagesPaper 1Saheera HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Estimating Power from Waste Heat Recovery Using Thermoelectric GeneratorsDocument11 pagesEstimating Power from Waste Heat Recovery Using Thermoelectric GeneratorsAkshay bypNo ratings yet
- Reference 10Document44 pagesReference 10Sahil AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Furnace DesignDocument11 pagesFurnace DesignSaidFerdjallahNo ratings yet
- 3f73 PDFDocument10 pages3f73 PDFRick HughesNo ratings yet
- GPSA Engineering Data Book 14th Edition: Revision Date Reason (S) For RevisionDocument7 pagesGPSA Engineering Data Book 14th Edition: Revision Date Reason (S) For RevisionBrayan Dali Nattez VargasNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Enhancement in Fin-Plate Heat Exchangers by Wing Type Vortex GeneratorsDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Enhancement in Fin-Plate Heat Exchangers by Wing Type Vortex Generatorsnadir adelNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Exchangers PDFDocument18 pagesAir Cooled Exchangers PDFRaghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2019-Mahdavi-Energy-Exergy Based-Evaluation of Heating Cooling Potential of PVT and EAHEDocument31 pages2019-Mahdavi-Energy-Exergy Based-Evaluation of Heating Cooling Potential of PVT and EAHEraviNo ratings yet
- Energy 2019Document48 pagesEnergy 2019zhor El hallaouiNo ratings yet
- PDF Offprint-2021-ICHMT-2021-07-01Document9 pagesPDF Offprint-2021-ICHMT-2021-07-01정재성No ratings yet
- A1. App ThermalDocument22 pagesA1. App ThermalMarcos DuarteNo ratings yet
- Effect of Evaporative Cooling Combined With Heat Sink On PV Module PerformanceDocument13 pagesEffect of Evaporative Cooling Combined With Heat Sink On PV Module PerformanceHmaedNo ratings yet
- 19 2021 Energy Saving 1-S2.0-S2352710220336858-Main - CompressedDocument12 pages19 2021 Energy Saving 1-S2.0-S2352710220336858-Main - CompressedAbo AmroNo ratings yet
- HMT 2017 550 Original V0-2Document31 pagesHMT 2017 550 Original V0-2Saheera HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer ThoughDocument15 pagesNumerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer ThoughКирилл МаксимовNo ratings yet
- Sizing of Plate and Fin HXDocument6 pagesSizing of Plate and Fin HXNithishNo ratings yet
- Floor Heating CalculationDocument6 pagesFloor Heating CalculationБаасанхүү ЛхагвачулуунNo ratings yet
- Air-side heat transfer and pressure drop analysis of spiral wire-on-tube condensersDocument13 pagesAir-side heat transfer and pressure drop analysis of spiral wire-on-tube condensersAndresInforBJNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0017931009001847-mainDocument8 pages1-s2.0-S0017931009001847-mainsoroushNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Thermal Performances of Plate Fin 2009 International JournalDocument8 pagesComparison of Thermal Performances of Plate Fin 2009 International Journalmjnjrgj2s7No ratings yet
- Split Heat PipeDocument12 pagesSplit Heat PiperodijammoulNo ratings yet
- N - Modeling and Simulation of Some Parts of A Fluidized Bed CombustorDocument14 pagesN - Modeling and Simulation of Some Parts of A Fluidized Bed CombustorAbba-Gana MohammedNo ratings yet
- 6 Heat TransferDocument19 pages6 Heat TransferPrecious Mae Cuerquis BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Abbreviations, Symbols, and Unit ConversionsDocument28 pagesAppendix A: Abbreviations, Symbols, and Unit ConversionsNajeeb A.MNo ratings yet
- 1999 - HACKERT Et Al. Combustion and Heat Transfer in Model Two-DimensioDocument15 pages1999 - HACKERT Et Al. Combustion and Heat Transfer in Model Two-Dimensiovivek joshiNo ratings yet
- Calculating Core Temperature (PAPER)Document6 pagesCalculating Core Temperature (PAPER)Giovanni Hernández DecaniniNo ratings yet
- 4 Estudo Do Desenpenho Do Trocador de Calor Via CFDDocument16 pages4 Estudo Do Desenpenho Do Trocador de Calor Via CFDMaribel ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Hassanshojaeefard 2016Document67 pagesHassanshojaeefard 2016Sateesh kumar SNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Friction Characteristics of Turbulent Flow Through a Tube With Vortex Generator InsertsDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer and Friction Characteristics of Turbulent Flow Through a Tube With Vortex Generator InsertsTejal BanmareNo ratings yet
- Limitations On Gas Turbine Performance Imposed by Large Turbine Cooling FlowsDocument8 pagesLimitations On Gas Turbine Performance Imposed by Large Turbine Cooling FlowsSickPinguNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science - ElsevierDocument8 pages2013 - Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science - Elsevierchauhan303No ratings yet
- Abu Madi - Performance Characteristics Correlation For Round Tube and Plate Finned Heat ExchangersDocument11 pagesAbu Madi - Performance Characteristics Correlation For Round Tube and Plate Finned Heat Exchangersmios30129800% (1)
- 67 Ijmperddec201867Document18 pages67 Ijmperddec201867TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Read - An Analytical Method For The Optimum Thermal Design of Convective Longitudinal Fin ArraysDocument33 pagesRead - An Analytical Method For The Optimum Thermal Design of Convective Longitudinal Fin ArraysfaraazNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document5 pagesAssignment 6Frans LoekitoNo ratings yet
- Speight2018 (1) PDFDocument1 pageSpeight2018 (1) PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- 40 Tcbiomass2019 Presentation David Dayton PDFDocument20 pages40 Tcbiomass2019 Presentation David Dayton PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Research Triangle Institute Summary PDFDocument1 pageResearch Triangle Institute Summary PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Speight2018 (1) PDFDocument1 pageSpeight2018 (1) PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Biomass Pyrolysis Studies at Pilot-Scale: TCS2016, November 1-4, 2016, Chapel Hill, NCDocument20 pagesCatalytic Biomass Pyrolysis Studies at Pilot-Scale: TCS2016, November 1-4, 2016, Chapel Hill, NCProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument35 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument15 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument47 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument12 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument19 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument14 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument31 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess Engineer100% (1)
- Technip Separations PDFDocument10 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument2 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument1 pageTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument22 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument61 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument49 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument20 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument49 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument48 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument2 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument9 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument60 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument2 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument39 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument67 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess Engineer100% (1)
- Technip Separations PDFDocument50 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess Engineer100% (1)
- Technip Separations PDFDocument48 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess Engineer100% (1)
- IFP Materials PDFDocument65 pagesIFP Materials PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- I3rc Insights Pvt. Ltd. India - Company Credentials PDFDocument28 pagesI3rc Insights Pvt. Ltd. India - Company Credentials PDFManoj Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Standard JKR Spec For Bridge LoadingDocument5 pagesStandard JKR Spec For Bridge LoadingHong Rui ChongNo ratings yet
- DS-RTCD905 H6W4Document2 pagesDS-RTCD905 H6W4david fonsecaNo ratings yet
- Keto Food List for BodybuildingDocument8 pagesKeto Food List for Bodybuildingharris81No ratings yet
- PW 160-Taliban Fragmentation Fact Fiction and Future-PwDocument28 pagesPW 160-Taliban Fragmentation Fact Fiction and Future-Pwrickyricardo1922No ratings yet
- R4850G2 Rectifier Data Sheet 05Document2 pagesR4850G2 Rectifier Data Sheet 05PP CharlyNo ratings yet
- A Rite of SpringDocument10 pagesA Rite of SpringLucius Gregory MeredithNo ratings yet
- Development PlanningDocument15 pagesDevelopment PlanningSamuelNo ratings yet
- Automation of Banking Service - EBL & EXIM BankDocument32 pagesAutomation of Banking Service - EBL & EXIM BankShaffyNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report of Landfill VisitDocument3 pagesNarrative Report of Landfill VisitNestor Jan Kenneth P BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Mobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL) Describes An Approach To Language LearningDocument7 pagesMobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL) Describes An Approach To Language Learninggusria ningsihNo ratings yet
- Battle Bikes 2.4 PDFDocument56 pagesBattle Bikes 2.4 PDFfranzyland100% (1)
- Julia Henzler - Resume 2 27Document1 pageJulia Henzler - Resume 2 27api-491391730No ratings yet
- WMS INFINEON PROJECT TOWER (11Kv VCB INSTALLATION) - REV-1Document5 pagesWMS INFINEON PROJECT TOWER (11Kv VCB INSTALLATION) - REV-1tana100% (1)
- Self-Sustainable Village: Dharm Raj Jangid 16031AA015Document2 pagesSelf-Sustainable Village: Dharm Raj Jangid 16031AA015Dharm JangidNo ratings yet
- Agile Spotify - Team - HomeworkDocument8 pagesAgile Spotify - Team - Homeworksp76rjm7dhNo ratings yet
- Javelin Mobility Ability 2.0 GuideDocument36 pagesJavelin Mobility Ability 2.0 Guideroham25156No ratings yet
- The Separation of Coherent and Incoherent Compton X-Ray ScatteringDocument8 pagesThe Separation of Coherent and Incoherent Compton X-Ray ScatteringFaisal AmirNo ratings yet
- What is phonicsDocument244 pagesWhat is phonicsNelly FernandezNo ratings yet
- Java syntax and data types tutorialDocument3 pagesJava syntax and data types tutorialpeter chan100% (1)
- RLT-Guideline Certification: Herstellerverband Raumlufttechnische Geräte E. V. AHU Manufacturer AssociationDocument22 pagesRLT-Guideline Certification: Herstellerverband Raumlufttechnische Geräte E. V. AHU Manufacturer AssociationJorge RoblesNo ratings yet
- Thermo Safety Cabinets MSC-Advantage - User ManualDocument53 pagesThermo Safety Cabinets MSC-Advantage - User ManualAhmed SalamaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Order and Rate Law Expression Worksheet KeyDocument5 pagesReaction Order and Rate Law Expression Worksheet KeyLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- S1.4.5.) Datasheet PRESSURE GAUGEDocument3 pagesS1.4.5.) Datasheet PRESSURE GAUGEEkoNo ratings yet
- ORPHEUS by GRS Mead - Electronic Text EditionDocument199 pagesORPHEUS by GRS Mead - Electronic Text EditionMartin EuserNo ratings yet
- Samruddhi ComplexDocument7 pagesSamruddhi ComplexNews Side Effects.No ratings yet
- The Historical Foundations of Law. Harold BermanDocument13 pagesThe Historical Foundations of Law. Harold BermanespinasdorsalesNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone R Salmonella Typhi 02Document8 pagesCeftriaxone R Salmonella Typhi 02docsumitraiNo ratings yet
- F2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)Document10 pagesF2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)羅天佑No ratings yet
- Accounting Project Topics and Materials in NigeriaDocument97 pagesAccounting Project Topics and Materials in NigeriaProject Championz100% (2)