Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sound Checklist
Sound Checklist
Uploaded by
varshatarate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageOriginal Title
sound_checklist.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSound Checklist
Sound Checklist
Uploaded by
varshatarateCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
29Sound Checklist
Name Class
While studying this topic, tick off each item after you have covered it.
What I should know: What I should be able to do:
Sound is caused by vibrations. Understand that a sound wave transfers
A sound wave is a longitudinal wave. energy (without any matter being
In some places the molecules are closer transferred).
together (higher pressure), and in other places
they are farther apart (lower pressure).
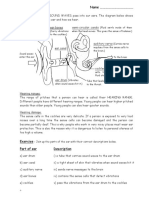
The wave travels from the source to your ear.
Like other waves: Use the formula opposite.
wave speed = frequencywavelength
(in m/s)(Hz)(m) Explain why sound cannot travel through
Sound cannot travel through a vacuum. a vacuum.
Sound can be reflected, and causes echoes.
Echo-sounding is used by fishing-boats, Use the formula:
bats, dolphins and geologists.
Sound travels faster through solids than speed distance
= travelled
through gases (or liquids). to answertime
questions
taken on sound echoes.
It travels much slower than light.
We can hear frequencies in the range
20 Hz–20 000 Hz.
Frequencies above this are called Understand why the short wavelength of
ultrasound (ultrasonic). ultrasound makes it useful.
Ultrasound has many uses, including:
detecting flaws in metal castings,
pre-natal scans of unborn babies, Compare 2 oscilloscope traces, and say
smashing kidney-stones, which is the higher frequency (higher
cleaning jewellery and machinery. pitch).
The higher the frequency, the higher the Compare 2 oscilloscope traces, and say
pitch of the sound. which has the bigger amplitude (louder
The bigger the amplitude of the vibrations, sound).
the louder the sound.
Different instruments give waveforms of
different shapes.
New Physics for You Nelson Thornes Ltd. 297 © Keith Johnson
You might also like
- Efforts For The Revival of Islam in The Sub ContinentDocument3 pagesEfforts For The Revival of Islam in The Sub ContinentS Alam100% (1)
- Necromancer Games - The Mother of All Treasure TablesDocument162 pagesNecromancer Games - The Mother of All Treasure TablesFita Avimake100% (3)
- Sound Waves and Echoes: Pages 226-227Document1 pageSound Waves and Echoes: Pages 226-227varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves and Echoes: Pages 226-227Document1 pageSound Waves and Echoes: Pages 226-227varshatarateNo ratings yet
- 29 Sound: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)Document1 page29 Sound: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Physics of WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics of WavesMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Print - Sound WavesDocument9 pagesPrint - Sound WavesantonellidejanNo ratings yet
- Echoes and UltraSoundDocument27 pagesEchoes and UltraSoundjothipriyagNo ratings yet
- Waves and SoundDocument17 pagesWaves and SoundMUHAMMAD DANIYAL KANDANo ratings yet
- Hearing.: NameDocument3 pagesHearing.: NameDuyBùiNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument25 pagesSoundsubashini silvaNo ratings yet
- Sound Space - PresentationDocument68 pagesSound Space - PresentationVic ShahNo ratings yet
- Science - Module 3 Sound DepedDocument12 pagesScience - Module 3 Sound DepedJunpel AcutNo ratings yet
- 3 - Sound Waves and The EarDocument24 pages3 - Sound Waves and The EarMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Sound - FrequencyDocument1 pageSound - Frequencyreymart.pucolangasNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Science G7 Week 4 Q3Diana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 8 1st PTDocument6 pagesReviewer in Science 8 1st PTApril AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Sound Notes With Q&A VIIIDocument12 pagesSound Notes With Q&A VIIISatwikNo ratings yet
- Hearing Sound: by Denise CarrollDocument41 pagesHearing Sound: by Denise CarrollarlikaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Notes M1Document11 pagesAcoustics Notes M1ANNA PAULA R. DULAYNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument39 pagesSound WavesNurlailie Md JamilNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument460 pagesUnit VNisarga JNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument82 pagesUnit INisarga JNo ratings yet
- Sound PDFDocument5 pagesSound PDFNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - Wave and SoundDocument32 pagesChap 6 - Wave and SoundJason Kean SengNo ratings yet
- Sound, CompressedDocument3 pagesSound, CompressedKatlo MokgethiNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Sound and LightDocument68 pagesWeek 8 - Sound and LightGenel Yutuc100% (1)
- 3.4 SoundDocument25 pages3.4 SoundMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Friday Sound MediumDocument21 pagesFriday Sound Mediumapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument36 pagesSound Wavesmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sound WavesDocument30 pagesChapter 10 Sound Wavesg-32347797No ratings yet
- 2016 SoundDocument69 pages2016 Soundryancasal959No ratings yet
- Topic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesDocument8 pagesTopic 36 Waves - Introduction To Sound WavesMarcus GohNo ratings yet
- Sound: Sounds and VibrationsDocument7 pagesSound: Sounds and Vibrationschhabra navdeepNo ratings yet
- Sound PhysicsDocument6 pagesSound Physicssreepranad DevarakondaNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument4 pagesSOUNDHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Production of Sound: - : Demo WatermarkDocument8 pagesProduction of Sound: - : Demo Watermarkkrish_cvr2937No ratings yet
- Sound Energy: Our Lady of Fatima University Basic Education DepartmentDocument28 pagesSound Energy: Our Lady of Fatima University Basic Education DepartmentMika MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physics Sound - HandwrittenDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Physics Sound - Handwrittenbr tiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter EightDocument7 pagesChapter Eightsaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1-2 TeacherDocument60 pagesUnit 2 Part 1-2 TeacherAustin KuoNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Sound NCERT Notes PDFDocument8 pagesClass 9 Science Sound NCERT Notes PDFSulveNo ratings yet
- AdvPhysics 3rdquarter Week4 EDITEDDocument16 pagesAdvPhysics 3rdquarter Week4 EDITEDAlex JustineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sound NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 10 Sound NotesAzaanNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch12 SoundDocument10 pages09 Science Notes Ch12 SoundHarshJangidNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument31 pagesSoundJoshua Verzosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- 2011-01-23 U15 SoundDocument3 pages2011-01-23 U15 SoundGanesh MuthupalaniNo ratings yet
- Good Vibrations: The Science Behind The ShowDocument2 pagesGood Vibrations: The Science Behind The ShowKristyne OliciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Propagation of Sound in SLGDocument6 pagesLesson 3 Propagation of Sound in SLGMerlpa May AlcardeNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument8 pagesSoundHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- Ound NotesDocument5 pagesOund Notesmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- Class 9th SoundDocument10 pagesClass 9th Soundakash vermaNo ratings yet
- The Michelson-Morley Experiment: Michael Fowler U. Va. Physics 9/15/08Document9 pagesThe Michelson-Morley Experiment: Michael Fowler U. Va. Physics 9/15/08محمد عثمانNo ratings yet
- Physics (Waves, Light)Document6 pagesPhysics (Waves, Light)mvfrances17No ratings yet
- Overview of Sound WavesDocument4 pagesOverview of Sound WavesEthanNo ratings yet
- Physics PPT SoundDocument20 pagesPhysics PPT SoundJoshua Chacko PonnachanNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument16 pagesSoundRSNo ratings yet
- I.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsDocument10 pagesI.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves - An EssayDocument8 pagesSound Waves - An EssayAshley RoyNo ratings yet
- Waves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Document30 pagesWaves, Sound & Music: (In One-Dimension, Mainly)Adal GanisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledCABALIDA, FELICITY H.No ratings yet
- Physics 3.5 - SoundDocument64 pagesPhysics 3.5 - Soundsnehakewlani25No ratings yet
- Adventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandAdventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes:: Physics For YouDocument10 pagesTeacher's Notes:: Physics For YouvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 1 QPDocument5 pagesElectric Circuits 1 QPvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Mind Map G10Document1 pageMind Map G10varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes:: Physics For YouDocument8 pagesTeacher's Notes:: Physics For YouvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- 29 Sound: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)Document1 page29 Sound: Use These Questions To Help You Revise (Cover The Right-Hand Side With A Sheet of Paper)varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes:: Physics For YouDocument11 pagesTeacher's Notes:: Physics For YouvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- "Twinkle Twinkle Little Star - . ." Why Do Stars Twinkle But Not Planets?Document16 pages"Twinkle Twinkle Little Star - . ." Why Do Stars Twinkle But Not Planets?varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Adaptations in Animals To ClimateDocument2 pagesAdaptations in Animals To ClimatevarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes:: Physics For YouDocument13 pagesTeacher's Notes:: Physics For YouvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- DesertresearchguidespdfDocument4 pagesDesertresearchguidespdfvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Billabong High International School, Andheri Grade IX: Speed - Time Graph: Practice Sheet 1 Name: Roll No: Date: April 2020 Subject: PhysicsDocument10 pagesBillabong High International School, Andheri Grade IX: Speed - Time Graph: Practice Sheet 1 Name: Roll No: Date: April 2020 Subject: PhysicsvarshatarateNo ratings yet
- Amount 600Document1 pageAmount 600varshatarateNo ratings yet
- Vehical ManagemsyentDocument16 pagesVehical ManagemsyentJitendraChadaramNo ratings yet
- Shape Type DESIGNATION (IMPERIAL) Weight (LBF/FT) Area (In2) Depth (In) Moment Inertia (In4) Designation (Metric)Document60 pagesShape Type DESIGNATION (IMPERIAL) Weight (LBF/FT) Area (In2) Depth (In) Moment Inertia (In4) Designation (Metric)MonicaLilianaRiveraNo ratings yet
- Breil Adélie CV enDocument1 pageBreil Adélie CV enAnonymous HIfPvVwazNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 - Imaging and Design For Online EnvironmentDocument26 pagesLESSON 4 - Imaging and Design For Online Environmentjudith c. lorica100% (1)
- Multiculturalism and Higher Education in Malaysia: Rozita Ibrahim, Nazri Muslim, Ahmad Hidayat BuangDocument7 pagesMulticulturalism and Higher Education in Malaysia: Rozita Ibrahim, Nazri Muslim, Ahmad Hidayat BuangNuraihan HashimNo ratings yet
- Leader End of Financial Catalogue Apr-Jun 2020 - LowRez - FinalDocument16 pagesLeader End of Financial Catalogue Apr-Jun 2020 - LowRez - Finaltim chambersNo ratings yet
- Why Choose AccountancyDocument13 pagesWhy Choose AccountancyRichelle Ann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- GM Repertoire 1A The Catalan PDFDocument794 pagesGM Repertoire 1A The Catalan PDFYoSoyDavidNo ratings yet
- English Worksheet 5 3Document4 pagesEnglish Worksheet 5 3Swasti MalaNo ratings yet
- Isi Sains Dan IslamDocument15 pagesIsi Sains Dan IslamSILMI QORINALLAH 2021No ratings yet
- 3 Gospel Fluency Session 1Document5 pages3 Gospel Fluency Session 1A.C. WNo ratings yet
- Bioc 311Document4 pagesBioc 311Zuksta ZukileNo ratings yet
- DSP BitsDocument5 pagesDSP BitsG Sankara raoNo ratings yet
- Buku 4 Okupasi Travel ServicesDocument119 pagesBuku 4 Okupasi Travel ServicesMGMP Pariwisata Tangerang SelatanNo ratings yet
- Barangay Livelihood CommitteeDocument3 pagesBarangay Livelihood CommitteeMary Jane Licmo-anNo ratings yet
- Johny John Medicine Bill ADocument8 pagesJohny John Medicine Bill Atgohiakri2006No ratings yet
- Ventil Preventest LTC Int v5Document3 pagesVentil Preventest LTC Int v5Teodoro Escobar Riveros100% (1)
- 14-Nm Finfet Technology For Analog and RF ApplicationsDocument7 pages14-Nm Finfet Technology For Analog and RF ApplicationsTwinkle BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 24C1 Memoria Eeprom SankeyDocument11 pages24C1 Memoria Eeprom Sankeyjavier venturaNo ratings yet
- QBK 08Document6 pagesQBK 08Jaln RodgerNo ratings yet
- Contact Lens 2 Study GuideDocument5 pagesContact Lens 2 Study GuideGenre PesselNo ratings yet
- Rizvi Java DeveloperDocument5 pagesRizvi Java DeveloperJoshElliotNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: University of Washington CSE 403 Software Engineering Spring 2011Document8 pagesMidterm Exam: University of Washington CSE 403 Software Engineering Spring 2011fikaduNo ratings yet
- InheretanceDocument8 pagesInheretancefarhan.mukhtiarNo ratings yet
- Shmoop Summary One Flew Over The Cuckoo's NestDocument61 pagesShmoop Summary One Flew Over The Cuckoo's NestDaniela Torres Noriega100% (1)
- Title T-Shirts DesigningDocument2 pagesTitle T-Shirts DesigningHumaira KhaniNo ratings yet
- Grecia AnticaDocument100 pagesGrecia AnticaIoanaCeornodoleaNo ratings yet
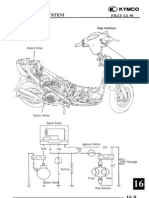
- F50LX Cap 16 (Imp Avviamento)Document6 pagesF50LX Cap 16 (Imp Avviamento)pivarszkinorbertNo ratings yet
- Hòahpch NG: - A Mare GoDocument13 pagesHòahpch NG: - A Mare Gonguyenchimaicma123No ratings yet