Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Embryo Lab Reviewer
Uploaded by
Arianna Francesca VillarazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Embryo Lab Reviewer
Uploaded by
Arianna Francesca VillarazaCopyright:
Available Formats
Embryo Lab
Oogenesis
– process of producing egg cells
– oogonium grows —> primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I —> polar body + secondary oocyte (both
haploid) undergoes meiosis II —> polar body + ovum undergoes growth —> mature egg cell
– Secondary oocyte is bigger than polar body because it has a greater cytoplasm because of asymmetrical
cytokinesis where cytosol and other organelles go to the oocyte
– polar body receives other half of chromosome but eventually disintegrates; does not serve any function
for reproduction
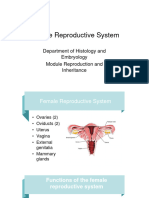
Frog ovary
– Theca externa - outermost connective tissue; individual sacs are suspended here
– Theca interna - envelopes entire ovary and each egg
– Oogonia - in periphery; smaller; each cluster represents future ovarian unit; enter quiescent phase after
meiosis (period of growth) if they do not grow, they become follicle cells
– Oocytes - potential egg cells
– their oogenic cells are large sacs of yolk
– Follicle cells - small cells bounding each oocyte; derived from oogonia
– more oogonia turns into follicle cells than ovum
– Center:
– Germinal vesicle with nucleoli - immature nucleus
– not possible to distinguish primary from secondary oocytes (answer oocyte only do not specify)
– Vitelline membrane - non-cellular transparent membrane between follicle cells and oocyte
– derived from ovum and follicle cells
– develops during maturation
– not observable during early stages
– necessary for retaining shape of egg
– aids in cleavage and gastrulation
– Yolk granules - food of embryo; heavily stained
– Yolk inclusions - effect of preparation of slide; fats from yolk dissolve and appear on oocyte as air
bubbles
– Nucleoli- small dots in periphery of germinal vesicle
– produce ribosomes for protein synthesis
– controls rate of transcription
– young cells have more nucleoli
Cat ovary
– Mesovarium - towards left end; sheet of tissue which is attached at one end of ovary
– attaches ovary to body wall
– Central medulla - consists largely of connective tissue and blood vessels
– continuous with mesovarium
– Peripheral cortex - where the action is
– Germinal epithelium - thin single-layer of simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
– on outermost surface of ovary
– Tunica albuginea - connective tissue beneath germinal epithelium; thicker than germinal epithelium
– no oogenic cells
– Stroma - beneath tunica albuginea
– cells are unspecialized
– penetrate ovary
– where all oogenic cells are embedded
– oogonia/ oogonium - potential ova = small
– each oogonium is surrounded by SINGLE layer of follicle cells (primary follicle stage/maturation stage)
– Single follicle cell layer - primary follicle stage
– during late primary follicle stage, oogonium and follicle cells are pushed inside
– primary oocyte is bigger than oogonium
– follicle cells separate from oocyte to form second layer
– follicle cells separate from oocyte to form second layer
– if only one layer of follicle cell - primary follicle stage
– oogonia without follicle cells are earlier in stage of development (oogonium - developmental stage of cell)
– Zona pellucida - secreted by germ cells and follicle cells; thick membrane bounding the oocyte
– follicle cells at this point will proliferate mitotically to form another layer
– SECOND layer has been FULLY formed = growing follicle stage
– Primary oocytes have zona pellucida
– Antrum is deforming when the
– indicator: follicle cell layer separates from oocyte
– spaces bc follicular fluid
– tunica albuginea
– stroma
– Mature graafian follicle - maturation stage of follicle
– present in primary oocyte
– if near membrane —> secondary oocyte
– has antrum
– surrounded by zone pellucida ang oocyte
– theca follicle - divided in to theca externa and theca interna (covers only graafian follicle)
– T. interna - nearer to stratum granulosum
– highly vascularised and rich in secretory cells mainly oestrogen producing
– T. externa - outer layer;
– composed of connective tissue having arosed from stroma
– remains in ovary
– stratum granulosum - granular cells; started as follicle cells
– termed based on position
– bounds antrum
– Cumulus oopherus - eccentric bound surrounding
– Corona radiata - part of c. oopherus
– layer nearest oocyte
– attached to oocyte by microvilli
– goes with oocyte
– Graafian follicle - when antrum is far from follicle cells
– tissues of ovary and follicle rupture to release egg cell during ovulation
– Corpus luteum haemorrhagicum - will persist; pregnancy
– responsible for production of progesterone
– Corpus albicans - no pregnancy
– storm forms capsule around regressing corpus luteum and invades ______
– hyalinized scar is left remaining
– identified by pale stain
– Degenerative process when
– Atretic follicle - follicle cells have lost connection with one another
– Advanced atresia: zona pellucida collapses
Human ovary
– less visible bc cat’s have multiple reproduction
– one egg cell at a time
– Corpus luteum
– Corpus albicans
– many blood vessels
– differentiate artery from vein
–
You might also like
- Reproductive System (Female)Document64 pagesReproductive System (Female)Marin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- Animal Bio PresentationDocument14 pagesAnimal Bio Presentationapi-266034924No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System HistologyDocument23 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histologyjmizai100% (1)
- 1 - Gametogenesis & Early Development of The Fertilized Ovum v2Document1,803 pages1 - Gametogenesis & Early Development of The Fertilized Ovum v2moamen.nlNo ratings yet
- Female Anatomy 07Document41 pagesFemale Anatomy 07Rudolph Antony ThomasNo ratings yet
- Female Repro List of TermsDocument8 pagesFemale Repro List of TermsMARKUS GERARD REYESNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture Morphological Changes During Maturation o Te GameteaDocument25 pages3rd Lecture Morphological Changes During Maturation o Te GameteaHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Oogenesis Serap Arbak SONDocument43 pagesOogenesis Serap Arbak SONozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Caring For The Family During Pregnancy: Ischemic PhaseDocument11 pagesCaring For The Family During Pregnancy: Ischemic PhaseDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Oogonium) - Oogonia Are Diploid (2n) Stem Cells That Divide Mitotically To Produce Millions ofDocument2 pagesOogonium) - Oogonia Are Diploid (2n) Stem Cells That Divide Mitotically To Produce Millions ofstriata100% (1)
- Embryology IDocument94 pagesEmbryology Imasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Histology IDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histology ISolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 OogenesisDocument7 pagesActivity 2 OogenesisHILARY PARAGAS. CORUÑANo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive OrganDocument42 pagesFemale Reproductive OrganGenerato, Todd MatthewNo ratings yet
- General Embryology: Gametogenesis: Formation of Male & Female GametesDocument19 pagesGeneral Embryology: Gametogenesis: Formation of Male & Female Gametes이희승No ratings yet
- 14 - Fertilization To Implantation-MbbsDocument52 pages14 - Fertilization To Implantation-MbbsRaoulSusanto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive SystemNo StradamusNo ratings yet
- History of EmbryologyDocument35 pagesHistory of EmbryologyAdrienne Chelsea GabayNo ratings yet
- Femalereprod (Author T.globa)Document56 pagesFemalereprod (Author T.globa)Angelina BulaiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument12 pagesReproduction in AnimalsYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemFitriyatun Nisa ZulisaNo ratings yet
- Histo Female ReproductiveDocument3 pagesHisto Female ReproductiveAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- ReproDocument6 pagesReprorianaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Module Viva PoolDocument52 pagesFoundation Module Viva PoolKumail LakraNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesOverview of The Female Reproductive SystemMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- 4 FertilizationDocument389 pages4 FertilizationAngel Gabriel Fornillos100% (1)
- Seminar 3Document6 pagesSeminar 3gatorssoccer1313No ratings yet
- Maturation of Oocytes Begins at Birth: OogenesisDocument2 pagesMaturation of Oocytes Begins at Birth: OogenesisJoseph MuimiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: TestesDocument30 pagesQuiz 1: TestesEmpress SaltNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Growing FetusDocument4 pagesChapter 9 The Growing FetusCarrie ANo ratings yet
- 1 - Midterms MCHNDocument16 pages1 - Midterms MCHNIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Embryology Ovary and OogenesisDocument3 pagesVeterinary Embryology Ovary and OogenesisbingchillingNo ratings yet
- 12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionDocument16 pages12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionNishant ShahNo ratings yet
- Fertilization 1 1Document219 pagesFertilization 1 1Edwin TiuNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument21 pagesFertilizationRashmi GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Lab-2021Document37 pagesFemale Reproductive System Lab-2021Oo OoNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument30 pagesEMBRYOLOGYMSc. PreviousNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of HenDocument20 pagesReproductive System of HenThanh Nguyen Van100% (1)
- 5.1 Female 2023 - JPDocument89 pages5.1 Female 2023 - JPtexasrepublican1976No ratings yet
- Exercise5 Mature OvumDocument7 pagesExercise5 Mature OvumleyNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument5 pagesSummaryDuhreen Kate CastroNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology (Post Embryonic Devlopment in Birds)Document11 pagesDevelopmental Biology (Post Embryonic Devlopment in Birds)hafsa yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Reproductive System 2020Document45 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive System 2020Devina Kriskineya100% (2)
- Female ReproductiveDocument34 pagesFemale ReproductiveAbdallah A. Abu Mattar100% (2)
- Organa Genitalia Feminina: Oleh Dr. Hendra SutardhioDocument90 pagesOrgana Genitalia Feminina: Oleh Dr. Hendra SutardhioMirah WilayadiNo ratings yet
- 01 OogenesisDocument21 pages01 OogenesisMu LokNo ratings yet
- 3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessDocument83 pages3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Vertebrates Exhibit SexualDocument41 pagesReproductive System: Vertebrates Exhibit SexualSalsabila LuqyanaNo ratings yet
- Oo GenesisDocument39 pagesOo Genesismayssenbenmaad1970No ratings yet
- Veterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 5Document4 pagesVeterinary Embryology Lab Exercise 5john benedickNo ratings yet
- Fertilization NCM107Document9 pagesFertilization NCM107Jasmin NatocNo ratings yet
- 0ogenesis OutlineDocument5 pages0ogenesis OutlineJustine Ian Sean CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemراوند اعبيدNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2Document7 pagesSeminar 2gatorssoccer1313No ratings yet
- Human Development Days 1-4Document43 pagesHuman Development Days 1-4Kriztine Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Embryology 2020Document8 pagesEmbryology 2020A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document11 pagesChapter 25Kathy Wollschleger100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Female Repruductive SystemDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Female Repruductive SystemPEÑAFLOR, Shealtiel Joy G.No ratings yet
- VILLARAZA, Arianna J. 4bio-1: 1. Is There A Need For A Country To Participate in International Trade? Why?Document1 pageVILLARAZA, Arianna J. 4bio-1: 1. Is There A Need For A Country To Participate in International Trade? Why?Arianna Francesca VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Notebook For Eco LabDocument7 pagesNotebook For Eco LabArianna Francesca VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Notebook For Eco LabDocument7 pagesNotebook For Eco LabArianna Francesca VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lec - Mitosis ReviewerDocument5 pagesGenetics Lec - Mitosis ReviewerArianna Francesca VillarazaNo ratings yet
- A Living Unit, Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsDocument55 pagesA Living Unit, Greater Than The Sum of Its PartsowjnfNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Who Peforms The Autopsy?: Aut-+ Opsis Sight, Appearance - More at OpticDocument5 pagesAutopsy Who Peforms The Autopsy?: Aut-+ Opsis Sight, Appearance - More at Opticmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8th Edition Bontrager Test BankDocument35 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 8th Edition Bontrager Test Bankcostardrivel.4vwhu100% (30)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDanelleNo ratings yet
- 4Document5 pages4Anonymous czrvb3h100% (3)
- SP 21Document1 pageSP 21ray72roNo ratings yet
- Transfusion MedicineDocument396 pagesTransfusion Medicinemjtjdomingo85% (26)
- Diagnostic Imaging - 11 - Regional Pathologies and Evaluation - Shoulder - Elbow - Wrist - Hand - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERDocument34 pagesDiagnostic Imaging - 11 - Regional Pathologies and Evaluation - Shoulder - Elbow - Wrist - Hand - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERAly MssreNo ratings yet
- World of PlantsDocument3 pagesWorld of PlantsWinter Summer SmithNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemMir Rehan Mushtaq100% (1)
- Lab Report 24 HormonesDocument3 pagesLab Report 24 HormonesLyka ElenaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 10140 Practical 2 2022 - Body Plans of The BilateriaDocument18 pagesBIOL 10140 Practical 2 2022 - Body Plans of The BilateriaJjRach HiNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TestDocument6 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TestDevilsnareNo ratings yet
- Project in BiologyDocument5 pagesProject in BiologyViah TronzalNo ratings yet
- Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Prannoy George, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaDocument41 pagesTransfusion in Emergency Room by DR Prannoy George, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Body RegionsDocument3 pagesHandout 1 - Body RegionsminionofcthulhuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition MahonDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 6th Edition MahonNorma Elliot97% (29)
- Legal MedicLegal MediciineDocument1 pageLegal MedicLegal MediciineJuan S. EnricoNo ratings yet
- 2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsDocument23 pages2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsNurul Izzatul AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Circulatory SystemAlessandro Arellano HmuaNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Vertebral Lesion Mimicking An Atypical Hemangioma WithDocument8 pagesMetastatic Vertebral Lesion Mimicking An Atypical Hemangioma Withsica_17_steaua6519No ratings yet
- Hemolytic Transfusion ReactionDocument3 pagesHemolytic Transfusion ReactionAinin SofiyaNo ratings yet
- HistopathDocument37 pagesHistopathFait HeeNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology (2015) PDFDocument199 pagesMCQs For Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology (2015) PDFLokesh Bakshi100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument62 pagesConnective Tissuehnm mnhNo ratings yet
- Sample Pre-Test Histopathology Part 1Document21 pagesSample Pre-Test Histopathology Part 1Katrina JornadalNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PDFDocument27 pagesUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD: Study of Tissues, Their Functions and Their ArrangementDocument6 pagesFrancis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD: Study of Tissues, Their Functions and Their ArrangementMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Wound Healing: Ziv Peled, M.DDocument8 pagesWound Healing: Ziv Peled, M.Dapi-26007957No ratings yet