Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction to Histology
Uploaded by
May Ann EnoserioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Histology
Uploaded by
May Ann EnoserioCopyright:
Available Formats
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
Histology The smallest or the basic structural
and functional unit of the human
the study of study of tissues, their body is the cell.
functions and their arrangement to If the cell be group to the other
constitute an organ cells, as long as their functions
Branch of anatomy = also known as are interrelated, they can form a
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY tissue. If the tissues are group
together and their functions are
WHAT IS A TISSUE? also interrelated, they can make up
Group of cells w/ interrelated an organ and an organ will always
functions belong to a certain human body
More to a tissue than just being a system.
group of cells
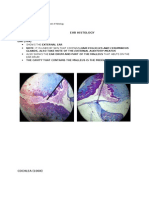
URINARY BLADDER
i.e., a neuron from the brain, a
hepatocyte from the liver, One of the organs in the body, it
keratinocyte from skin STILL CANNOT belongs to the urinary system. Organs
BE CALLED A TISSUE (NEED TO HAVE are made up of tissue.
INTERRELATED FUCNTION) X sign in the image (one of the
The cells in the tissue need not to tissues that you can find in the
be in the same type of cell urinary bladder, composed of group
of cells because tissues are
The important is their function must
actually group of cells.
be interrelated w/ each other.
Tissues are made up of group of
They don’t have to be in the same
cells w/ interrelated functions, if
size, same shape, same morphology as
tissues are grouped together, they
long as their functions are
can form an organ.
interrelated, then they can make up
a tissue. Four Basic Types of Tissue
Fibers – hairlike structures All these types of tissues have group of
Empty spaces that composed of cells, and if you’re going to combine
chemicals, empty spaces are called these four basic types of cells can form
GROUND SUBSTANCE an organ
Group of cells specialized to carry EPITHELIAL TISSUE (epithelium)
on a interrelated functions and Nearest to the lumen (a luminous
their associated extracellular term referring to the channel
matrix within a tube such as a blood
Cell + extracellular matrix vessel or to the cavity within a
(composed of fibers and ground hollow organ such as the
substance) intestine) of the stomach
The ground substance and fiber are Lining epithelium functions to
found outside the cell, they are provide covering, and functions
referred to as extracellular matrix. for absorption and secretion.
(i.e., lining epithelia of the
WHY STUDY CELLS IN A SUBJECT THAT IS large and small intestine.)
SUPPOSED TO STUDY TISSUES? It is the epithelium that can
Because tissues are made up of cell, provide protection against
you can never understand the stomach acid
characteristics off a tissue without The cells that make up the
understanding the characteristics of epithelium tissue are tightly
its individual components of the packed (they do not tolerate
cell. spaces between
The lining epithelium doesn’t
Organization in Human Body have their own blood supply
(AVASCULAR)
First Semester | Prelims
1
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
If these cells have a Predominating cells are
blood vessel, then these fibroblast
cells are no longer the bigger fiber is collagen
tightly packed, and they
fiber
cannot function for
the thinner fibers are elastic
protection
fibers
If the cells of the epithelium
are not getting enough oxygen, HOW CAN YOU FIT A LARGE HUMAN
then most likely the cells would ORGAN INTO A GLASS SLIDE?
die in histopathology laboratory or
histopathology laboratory, we
HOW DO YOU THINK THE ORGANS IN THE BODY prepare the organ and make a
MAINTAIN THE CELLS OF THE LINING
thin cut section of the organ.
EPITHELIUM?
the main purpose of preparing a
The lining epithelium doesn’t have
thin section is that when
their own blood supply, but it is
placing this thin section on the
situated there because it’s the
epithelium that can provide protection top of the slide, the light
against HCl in the stomach coming from the light source of
Connective tissue is highly the microscope can actually
vascularized meaning the connective traverse through the slide and
tissue has its own blood supply the specimen so that the light
The epithelium is there to protect the can reach the eye of the
connective from the HCl observer.
What will keep the cells of the
epithelium because they are getting Preparation of Tissues for Study
blood supply from the connective tissue To study tissues, one must prepare
thin and translucent histological
CONNECTIVE TISSUE sections or tissue slices that can
- Below the epithelium be studied with the aid of a
- Presence of the red-colored microscope.
capillary fixation -> dehydration -> clearing
- Provides blood supply to the -> infiltration -> embedding
epithelium
Fixation
- What link to the epithelium to
the muscle? – it is because of Since cellular decomposition begins
the connective tissue, it tends immediately after the death of a
to connect the epithelium to the human/patient, tissues must be fixed to
other tissue in the organ. prevent alterations in their structure
MUSCLE TISSUE through decomposition. (TO PRESERVE AND
- Below the connective tissue PREVENT CHANGES IN THE ORGAN)
- Incorporated to the organ to If you have removed an organ from
provide movement. the body because you want to process
NERVOUS TISSUE it, you have actually cut it from
- Somehow distributed between the its own blood supply, if no blood
connective tissue and muscle supply then most likely the cells of
tissue is the nervous tissue that organ will not receive oxygen
- something to feel/sensation, and the cells will start dying and
control, and information the organ will begin decomposing or
processing. decaying.
The appendix should be immersed in
Yellow cell – adipose cell or fat formalin and the main purpose of
cell which is not to allow the organ to
Mast cell - appears to have a undergo decomposition or decay.
lot of dark granules
First Semester | Prelims
2
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
Neutrophils are antibacterial, the there will use up the glucose, the
white blood cells that fight off remaining glucose in the appendix
bacteria. and then instead of producing
If you have abundance of these energy, they are building up lactic
neutrophils in your appendix it acid. The lactic acid will start
would suggest that the appendix is destroying the appendix the reason
having a current infection. And why we must terminate cell
confirm diagnoses of having acute metabolism. We should not allow the
appendicitis. glycolysis to happen or else the
cells will start producing lactic
The problem is; If the MedTech
acid and the lactic acid will
forgot to fix the organ or if the
destroy the appendix
surgeon after removing the appendix
from the body of the patient forgot
- When the muscles contract they will
to immerse the organ in the formalin
impinge on their blood vessels. The
or in the fixative agent, then most
muscles are contracting, the blood
likely you will no longer appreciate
vessels are impinged. Then most
the presence of these neutrophils
likely the muscles are not getting
because the appendix will undergo
enough oxygen or blood supply, there
the decomposition and decay.
would be build up lactic acid in the
muscle. And the build-up of the
PURPOSE OF THE FIXATION:
lactic acid now will now be felt as
1. Avoid tissue destruction by digestive
the PAMAOL.
enzymes (autolysis) or through
- If you’re going to cut a soft organ
bacterial degradation
in the body and it’s as soft as the
- (i.e., organ is small intestine,
gelatin most likely the organ will
where the enzymes from the pancreas
move while doing the cutting and
are drained onto, if the intestine
cannot make a perfect thin section.
is removed and the enzyme is still
- One of the purposes of fixation is
there, and the organ is not fixed
to harden, somehow harden the organ
then these enzymes are not
so that it can facilitate now easy
inactivated. The enzymes will start
cutting or easy sectioning of the
digesting the intestine and you will
organ
no longer be able to appreciate the
3. Harden the tissue by cross-linking or
structure of the antecedent so
denaturing proteins.
that’s what we mean by number one.
- So, the MedTech can do the tissue
2. Terminate cell metabolism – glycolysis
sectioning later
without oxygen = lactic acid.
4. Kill pathogenic microorganisms such as
- The fixed the fixation step will
bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
terminate cell metabolism
- Some of the specimens remove
- Glycolysis is the conversion of
surgically from the body are
glucose to energy, if glycolysis
infected and to protect the people
will happen without oxygen because
who are working in the laboratory
the organ was already cut off from
especially in histopath laboratory
its blood supply, then the product
the fixation must kill the
will be a lactic acid.
pathogenic microorganisms
- When you have oxygen glucose will be
- The most common used fixative in the
most likely converted to pyruvate,
laboratory is formalin.
and pyruvate will enter the
mitochondria to complete the Krebs Decalcification
cycle and the electron transport
chain and there would be generation only done in specimens such as bone,
of atp molecules. teeth, and calcified tissues
- In the absence of oxygen, the Nitric acid
glucose will be converted to lactic For soft tissue we have harden them
acid or lactate. If the appendix a little so that we can make the
remove from the body and the cell cutting. In cases of calcified
First Semester | Prelims
3
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
tissues such as bones and teeth we dehydration we removed water in the
need to decalcified them to somehow tissue and the water will be
soften them so that we can easily replaced by alcohol. The tissue now
cut them. will contain alcohol.
The most common reagent for the Clearing
decalcification is nitric acid.
Everything should start in fixation Removal of the dehydrating agent by
and the second step will be immersing the specimen in the
decalcification, but if the specimen solvent that the alcohol and
is a softest or soft tissue/organs embedding medium is miscible
such as the lungs, the heart, we Clearing agent are highly volatile
first fixation but there’s no need (becomes vapor once exposed to heat)
for decalcification. Xylene and toluene
Decalcification is not only limited Next to clearing is embedding and
to bones and teeth, it can also be embedding makes use of melted
done to arteries especially arteries paraffin that’s why this procedure
with atherosclerotic plaque is usually done inside an oven set
formation (caused by the deposition at 52-60 degree Celsius, the melting
of the cholesterol on the walls or point of the paraffin.
the lumen of the artery. The The clear fluid is the melted
presence of the cholesterol will paraffin. Once the tissue is dipped
actually trigger inflammation and into the paraffin the xylene or the
accompanying tissue destruction and toluene will immediately become
if the tissue destruction then there vapors. Allowing now the melted
would be deposition of the calcium. paraffin to infiltrate the tissue.
And the area will somehow harden)
In embedding we remove the clearing,
Dehydration and we replace it with paraffin (the
essence of doing embedding)
done by successively bathing the
The paraffin now will be allowed to
specimen in mixture of ethanol and
cool down so that you will have the
water from 70% to 100% percent%.
formation of a black with the tissue
From a lower concentration of
placed in the center
alcohol to a higher concentration of
The problem with using paraffin is
alcohol until such time you’re
that a lot of medtechs are prone to
already dipping or immersing the
having BURN INJURIES
specimen in 100 percent or absolute
alcohol. In the lab, paraffin is replaced
with plastic resins (fluid at room
Alcohol (ethanol and water – because
temp) once tried to place something
dehydration starts with using lower
it will solidify immediately
concentration of alcohol, so we can
- So there’s no need to do a
50/70% diluted form of alcohol and
procedure where there’s an oven
there’s a water in it) removes water
(no chance of having burn
out of the tissue.
injuries)
Removal of water in the tissue
- The problem with plastic resin
From 70 we will transfer the tissue is that it is too expensive
to a higher concentration of alcohol (increased charges in biopsies)
that could be 80 and 90, immersed in
a pure or 100 absolute alcohol. Cutting and Sectioning
Why do we have to immerse the Cutting
specimen from a lower concentration After the specimen is hardened, it
of alcohol to a higher concentration is trimmed into appropriately sized
of alcohol? – it actually takes blocks
time, to preserve the morphology and
Cutting involves the use of a knife
the appearance of the organ as it
to remove excess paraffin
was removed from the human body. In
First Semester | Prelims
4
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
We need to remove excess paraffin so iv. Absolute ethanol – 3 mins
that the block will fit into the v. 95% ethanol – 3 mins
block holder of the microtome - Immersed in 95% alcohol
Sectioning - To remove the tissue xylene,
The block is then mounted in immerse the tissue in
microtome and cut with a steel knife decreasing concentration of
- As you rotate the drive wheel, alcohol
the block holder vi. 95% ethanol – 3 mins
- The tissue block will go up and vii. Distilled water – 30 secs. to
down and will come in contact 1 min
with the steel knife - To remove alcohol, immerse the
- And you will now have the tissue in distilled water
production of thin sections of - We will allow water to go back
the organ you want to study to the tissue
- Most of the stains that we are
The main reason why you need to
utilizing in histopath lab or
place the tissue in the melted
histology lab are water soluble
paraffin is for us to have something
- So for the stains to impart
to hold the organ during the
color to the tissue, the tissue
sectioning
must contain
Allow the thin sections to float on
the water, then scoop them out using Staining
the slide. The sections that we
Since paraffin is colorless,
created using the microtome are
staining is a must
still transparent so even if you
have already placed them on top of Application of color too the tissue
the slide and view them under the to highlight structures
microscope you won't be able to Most commonly used stain:
appreciate the structures, the - Hemotoxylin – a basic dye thus,
composition, the cells w/in the it will stain acidic portions
tissue because the tissues are still of the cell.
transparent. - Stains blue=> PURPLE
After sectioning, after placing the - Nucleus is acidic
section on the slide it is very - Stains nucleus and RNA –
important that we should perform the containing portion of
next tissue processing steep. Which cytoplasm
is STAINING - Eosin – acidic dye, thus is
- We need to impart color onto will stains the basic portions
the tissue so that you can see of the cell.
the structures under the - Stains pink =>RED
microscope - Cytoplasm is basic
- Cytoplasmic components and
Deparaffination and Rehydration collagen
- Remove the paraffin from the thin These dyes are water-
sections soluble
i. Xylene – 5 mins.
- Remove paraffin using xylene Tissues with negative charges/acid
- Thin section is now are readily stained with basic dyes
infiltrated w/ xylene – BASOPHILLIC
ii. Xylene – 5 minss. - NUCLEIC ACIDS = NUCLEUS
iii. Absolute ethanol – 3 mins Tissues with positive charges are
- Remove xylene by using stained with acidic dyes –
absolute alcohol ACIDOPHILIC
- The tissue section at this - MITOCHONDRIA, COLLAGEN,
point will now infiltrated w/ CYTOPLASM
absolute alcohol
SPECIAL STAINS
First Semester | Prelims
5
2025 INTRODUCTION TO HISTOLOGY
BSMLS - 1M Francis Ian Salaver, RMT, MD
Feulgen reaction – DNA Astrocytes a star shape, limits the entry
Periodic acid Schiff – carbohydrates of substance from the capillary or blood
to the nervous system.
Sudan black – lipids
Silver stain – reticular fibers
how long would it take for the
tissue to be fixed – dehydrated –
cleared – embedded – sectioned –
mounted – stained – read by the
pathologist.
Philippine laboratory set-up the
tissue would require at least 48-72
hrs. tissue processing time. (2-4
days)
MOUNTING
- To preserve and support a
stained section for light,
microscopy, it is mounted on a
clear glass slide, and covered
w/ a thin glass coverslip
- Placing cut sections on a
slide w/ mounting media such
as glycerin or resins. (to
make the coverslip stick to
the specimen and glass slide)
FROZEN SECTIONS
- Rapid method
- Routinely done in hospital to
study specimen during surgery
- Lipids and enzymes are best
preserved in this method
Fixation is done freezing compressed
carbon dioxide
Sectioning is done thru cryostat, a
refrigerated compartment containing
microtome.
Dehydration remove of water replace
alcohol
Clearing remove alcohol replace w/
xylene. Clearing agents are highly
volatile.
In nervous tissue the cells are
categorized into neurons (create nerve
impulse) and neuroglia (microglia one of
the neuroglia in the nervous tissue, a
phagocytic cell eat up bacteria that kills
neurons, it support and protect the neuron
to keep it alive.
First Semester | Prelims
6
You might also like
- Structure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectFrom EverandStructure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectNo ratings yet
- Accurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andDocument4 pagesAccurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andManulat VicaiiNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Document6 pagesTranses Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Reign Saplaco100% (1)
- EDs Basic Histology PDFDocument208 pagesEDs Basic Histology PDFTemesgen Endalew0% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument40 pagesEpithelial TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Histology Module 1 LectureDocument17 pagesHistology Module 1 LectureRoselie Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Tissues: 27 January 2016 Abby R. Whittington, PHD Awhit@Mse - Vt.EduDocument23 pagesStructure and Function of Tissues: 27 January 2016 Abby R. Whittington, PHD Awhit@Mse - Vt.EduSrilekhya Meda100% (1)
- Blood Smears and The Use of Wrights StainDocument5 pagesBlood Smears and The Use of Wrights Stainkaleb16_2No ratings yet
- Microscopy TransDocument2 pagesMicroscopy TransMarco TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Cell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Document6 pagesCell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Mark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Human Histology 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesHuman Histology 1 IntroductionBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Teaching DemoDocument40 pagesEpithelial Tissue Teaching DemoFrancis Salcedo100% (1)
- Histopathology Lecture Covers Cell Structure, TissuesDocument44 pagesHistopathology Lecture Covers Cell Structure, TissuesFatimaMendozaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of MedicineDocument6 pagesVirtual Microscopy Histology Manual: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicinelucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Act.1 RQ 2 Pipettes and Others 1-3Document3 pagesAct.1 RQ 2 Pipettes and Others 1-3Francis Valdez100% (1)
- Understanding key parasitology termsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding key parasitology termsArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Document5 pagesLab Exercise 2 Microscope Anph111Jhon Leonard FatalloNo ratings yet
- Blood Histology: A. Prof Dr. Ruzanna DM, PHD, MSC, MDDocument23 pagesBlood Histology: A. Prof Dr. Ruzanna DM, PHD, MSC, MDHassoun hassoun100% (2)
- Histology of The Special SenseDocument84 pagesHistology of The Special SenseRushda100% (1)
- Tissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPDocument41 pagesTissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPLleana Tan100% (1)
- Topic 1 Learning TheoriesDocument12 pagesTopic 1 Learning Theoriesasdffasdffas asdffasdffNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination: Mark Lester B. Cauan, RMTDocument22 pagesFresh Tissue Examination: Mark Lester B. Cauan, RMTMarissa CordovaNo ratings yet
- Psthe 1Document111 pagesPsthe 1Angelica RicoNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument68 pagesTissues, Glands and MembranesMerrylFrancisco100% (1)
- Introduction To Diagnostic Parasitology: (Specimen Collection and Handling)Document26 pagesIntroduction To Diagnostic Parasitology: (Specimen Collection and Handling)RIC JOSEPH PONCIANONo ratings yet
- Histology study guide outlines tissues, cells, microscopyDocument5 pagesHistology study guide outlines tissues, cells, microscopyPau Basco100% (1)
- MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY: PATHOLOGY AND THE ROLE OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGISTSDocument11 pagesMEDICAL TECHNOLOGY: PATHOLOGY AND THE ROLE OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGISTSAmethyst TheoNo ratings yet
- Defining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionDocument27 pagesDefining The Practice of Medical Technology or Clinical Laboratory Science ProfessionKianna TicsayNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Citopathology 2009Document7 pagesGuidelines Citopathology 2009Fabrício CamargoNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination - HistopathDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination - HistopathIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology Laws AND Bioethics: Imelda A. de Leon, RMT, Mpa ProfessorDocument42 pagesMedical Technology Laws AND Bioethics: Imelda A. de Leon, RMT, Mpa ProfessorMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LECDocument14 pagesHISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LECClair TugnaNo ratings yet
- Histology Tissue Preparation MicroscopyDocument4 pagesHistology Tissue Preparation MicroscopyNel TinduganiNo ratings yet
- Pmls1 Defining The Practice of MTDocument23 pagesPmls1 Defining The Practice of MTDorothy PagapularNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Pathology and Disease MechanismsDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Pathology and Disease MechanismsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Medical Terminology and AbbreviationsDocument6 pagesLesson 4: Medical Terminology and Abbreviationsdoldol ocampoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1Document10 pagesHEMATOLOGY 1 Hematopoiesis Notes 1sansastarkNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesDocument22 pagesCh. 3 Notes - Epitheal TissuesLinda Yurani Carvajal AngaritaNo ratings yet
- Module # 2 Medical Terminologies and Abbreviations and Ethics in The ProfessionDocument6 pagesModule # 2 Medical Terminologies and Abbreviations and Ethics in The ProfessionJonice NavarroNo ratings yet
- TREMATODESDocument31 pagesTREMATODESKen Mark ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Histology of Urinary SystemDocument53 pagesHistology of Urinary SystemA1205Angelica GloryNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Clinical Microbiology: Key ConceptsDocument225 pagesIntroduction to Clinical Microbiology: Key ConceptsRichell VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- General PathologyDocument32 pagesGeneral PathologyLeul DawitNo ratings yet
- MLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M1-UNIT1 (Introduction To Histology)Document16 pagesMLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M1-UNIT1 (Introduction To Histology)ataraNo ratings yet
- Paralec 1 To 12 With 5678 LabDocument99 pagesParalec 1 To 12 With 5678 Labjomel rondinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 StreptococciDocument66 pagesChapter15 StreptococciNursheda Abangon AzisNo ratings yet
- CHPTR 1 Intro To Teaching (PSTMLS)Document10 pagesCHPTR 1 Intro To Teaching (PSTMLS)Bea Reen BurgosNo ratings yet
- Practical Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesDocument48 pagesPractical Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesliliposhianNo ratings yet
- Frozen Sections Hand OutDocument18 pagesFrozen Sections Hand OutAlyssa Clarizze MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Tissues StudentDocument40 pagesModule 4 - Tissues StudentYaemi Yormi100% (1)
- Ear HistologyDocument3 pagesEar HistologyGrace Shan Bernus100% (1)
- SASDocument4 pagesSASNicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Histology 01 02Document47 pagesHistology 01 02jhcjdjksahdjkhaNo ratings yet
- HP Lec - FixationDocument4 pagesHP Lec - FixationAaron Vincent MillomedaNo ratings yet
- StainsDocument4 pagesStainsMonique ManiwanNo ratings yet
- Tissue: Physiology: Controlling & Coordinating SystemsDocument30 pagesTissue: Physiology: Controlling & Coordinating Systemsdibya patraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Charles Z. Ariola JR, MSN, LPT, Rn. Subject ProfessorDocument124 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Charles Z. Ariola JR, MSN, LPT, Rn. Subject ProfessorCharlz Zipagan100% (1)
- HUMAN ANATOMY: SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument15 pagesHUMAN ANATOMY: SKELETAL SYSTEMKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Animal TissuesDocument34 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Animal Tissuesafsas rpNo ratings yet
- The Church Biblical FoundationDocument69 pagesThe Church Biblical FoundationMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- PECSDocument2 pagesPECSRojen SabileNo ratings yet
- Warming Up For Badminton: Passive StretchesDocument4 pagesWarming Up For Badminton: Passive StretchesMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Basic Microscopy Techniques and ProceduresDocument2 pagesBasic Microscopy Techniques and ProceduresMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Prokaryotic Cell DifferencesDocument3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Organelles and Prokaryotic Cell DifferencesMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Epithelial TissueMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Water and PHDocument9 pagesWeek 2 - Water and PHMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument5 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Organ Classification Based on StructureDocument18 pagesOrgan Classification Based on StructureKEZIA CALISTA HERLIANINo ratings yet
- Cell Theory BasicsDocument16 pagesCell Theory BasicsGehan FaroukNo ratings yet
- Joints Lecture 1Document12 pagesJoints Lecture 1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Aswini - EmbryologyDocument16 pagesAswini - EmbryologyIssac Jerin MathewsNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemDocument5 pagesLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation and Segmentation ofDocument20 pagesGastrulation and Segmentation ofAina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument99 pagesUrinary SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- 3 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT - CRANIAL VAULT and BASE - Yr 3 - Sunny - MoodleDocument43 pages3 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT - CRANIAL VAULT and BASE - Yr 3 - Sunny - MoodleJu JuNo ratings yet
- Human Body System Module 2Document20 pagesHuman Body System Module 2Sheena Claire dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Hhis Obe MidtermDocument5 pagesHhis Obe MidtermHANNAH DARLED BALIADNo ratings yet
- L 3 The Urinary Bladder& UrethraDocument28 pagesL 3 The Urinary Bladder& UrethraAdnan Al-aniNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 Lymphatic and Heart SystemDocument5 pagesActivity 8 Lymphatic and Heart SystemDanielle MerlinNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument25 pagesMuscular SystemAryan DomingoNo ratings yet
- PHA611 FirstShiftingPhotos Pt1 PDFDocument2 pagesPHA611 FirstShiftingPhotos Pt1 PDFGAILE MEIZTY MOSADANo ratings yet
- 21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberDocument6 pages21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2, Amoeba Animal and Plant TissueDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT 2, Amoeba Animal and Plant TissueEdwardLeeNo ratings yet
- The Prostate Is A Common Site of Carcinoma. It: Abdomen and PelvisDocument62 pagesThe Prostate Is A Common Site of Carcinoma. It: Abdomen and PelvissrisakthiNo ratings yet
- 300 LevelDocument4 pages300 LevelAkinsola AyomidotunNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Essentials of Medical Language 4th EditionDocument61 pagesEbook PDF Essentials of Medical Language 4th Editionollie.rutland183100% (45)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Dimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Document7 pagesDimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Linda Garcia PNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7. Leaf: Distinctive CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesExercise 7. Leaf: Distinctive CharacteristicsTers MedinaNo ratings yet
- Body Tissue and IntegumentaryDocument53 pagesBody Tissue and IntegumentarySyikin KadirNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument16 pagesTransportation in PlantsJacob PiousNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument50 pagesConnective TissueHamza SultanNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Life Sciences IEB 3 in 1 Extracts PDFDocument16 pagesGR 10 Life Sciences IEB 3 in 1 Extracts PDFteeNo ratings yet
- Bzyct-133 Jun 2022Document6 pagesBzyct-133 Jun 2022Akram HusainNo ratings yet
- ANPH M3 CU10. Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesANPH M3 CU10. Digestive Systemmark tuazonNo ratings yet
- Anat 213, Placentation-EmbryologyDocument16 pagesAnat 213, Placentation-EmbryologyChidera EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Activity#1Document2 pagesActivity#1LINDA RAGUINDINNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)