Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maturation of Oocytes Begins at Birth: Oogenesis
Uploaded by
Joseph MuimiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maturation of Oocytes Begins at Birth: Oogenesis
Uploaded by
Joseph MuimiCopyright:
Available Formats
OOGENESIS
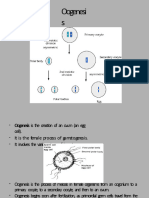
Process in which oogonia differentiate into mature oocytes
Maturation of oocytes begins at birth
Once the primordial germ cells reach the ovary,they differentiate into oogonia
They undergo mitosis and by the end of the third month,they are arranged in clusters
surrounded by flat epithelial cells(Follicular cells)
Some oogonia are arrested in prophase 1 (Primary oocytes)
By the fifth month,the cells have multiplied in their number to reach maximum number then cell
death begins and many degenerate and become atretic and by the seventh month,most of them
have degenerated except for a few on the surface
Surviving cells enter the prophase of meiosis 1 and are surrounded by a layer of follicular
epithelial cells
Primordial follicle---It is a primary oocyte surrounded by flat follicular epithelial cells
Maturation of oocytes continues at puberty
Near the time of birth, all primary oocytes have entered the prophase of meiosis 1 but instead of
proceeding to metaphase,they are arrested and enter the diplotene stage and finish the first
meiotic division only when puberty is reached
The arrested state is produced by OMI(Oocyte Maturation Inhibitor),a peptide secreted by the
follicular cells
Primordial follicles continue to grow and the surrounding follicular cells change from flat to
cuboidal and proliferate to produce a stratified layer of granulosa cells(Primary follicle)
Granulosa cells rests on the basement separating them from the surrounding ovarian connective
tissues that form the Theca Folliculi,which organise themselves into Theca Interna and Theca
Externa
Granulosa cells and the oocyte secrete the Zona Pellucida
Also,small finger-like processes of follicular cells extend across the Zone Pellucida and
interdigitate with the microvilli of plasma membrane of the oocyte.These processes are
important for the transfer of materials from follicular cells to the oocyte
Fluid-filled spaces appear between granulosa cells.Coalescion of these spaces forms the
antrum,and the follicle is termed as a vesicular or an antral follicle
Initially the antrum is crescent shaped but enlarges
Granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte are intact and referred to as Cumulus Oophorus
During each ovarian cycle ,only one oocyte develops to maturity,the others degenerate and
become atretic,then a surge in luteinizing hormone induces preovulatory growth
Meiosis 1 is then completed and the cell divides into two unequal cells each with 23 double
structured chromosomes
One cell,the secondary oocyte receives most of the cytoplasm,whereas the other,the polar
body ,receives practically none and lies in the perivitelline space
The cell then begins meiosis 2 and arrests at metaphase 3 hours before ovulation.This phase is
completed only when the oocyte is fertilised.
You might also like
- Histology of Female Reproductive System 2020Document45 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive System 2020Devina Kriskineya100% (2)
- Menstrual CycleDocument22 pagesMenstrual CycleDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYDocument72 pagesOogenesis and Ovarian Cycle, Uterus, Menstrual Cycle ABORTION TERATOLOGYElizabeth OmobolanleNo ratings yet
- OogenesisDocument10 pagesOogenesisOm Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument17 pages1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture Morphological Changes During Maturation o Te GameteaDocument25 pages3rd Lecture Morphological Changes During Maturation o Te GameteaHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- ALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSDocument35 pagesALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSDOUGLAS KIPRUTONo ratings yet
- 01 OogenesisDocument21 pages01 OogenesisMu LokNo ratings yet
- Compre - NP 2 Ans. KeyDocument12 pagesCompre - NP 2 Ans. KeyJune Dumdumaya100% (1)
- Gametogenesis: The Formation of Eggs and SpermDocument52 pagesGametogenesis: The Formation of Eggs and SpermMUDIN ABDELLANo ratings yet
- DIESTRO - EINC Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesDIESTRO - EINC Reaction PaperAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- The Following Presentation Contains Slides Not Suitable For Very Young Audiences. Parental Guidance Is Recommended.Document102 pagesThe Following Presentation Contains Slides Not Suitable For Very Young Audiences. Parental Guidance Is Recommended.Princess Aira Bucag CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Proplased Umbilical CordDocument2 pagesProplased Umbilical Cordkurlstein94% (17)
- Female Reproductive System Histology IDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histology ISolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Precipitated Labour 1Document8 pagesPrecipitated Labour 1priyankaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Leaflet Dosage High-Resolution-1Document4 pages2014 Leaflet Dosage High-Resolution-1Zarbakht AliNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and SpermatogenesisDocument46 pagesGametogenesis and SpermatogenesisDenis KaguiNo ratings yet
- Oo GenesisDocument39 pagesOo Genesismayssenbenmaad1970No ratings yet
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheDocument7 pagesOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- DR Anangwe-GametogenesisDocument23 pagesDR Anangwe-GametogenesisStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument101 pagesEmbryologytawandarukwavamadisonNo ratings yet
- Embryology - The Ovarian CycleDocument9 pagesEmbryology - The Ovarian CycleViswa GiriNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis: The formation of eggs in the ovariesDocument2 pagesOogenesis: The formation of eggs in the ovariesstriata100% (1)
- DR Mohtaseb Slide 8 Embryology 3Document17 pagesDR Mohtaseb Slide 8 Embryology 3api-249972919No ratings yet
- 1 - Gametogenesis & Early Development of The Fertilized Ovum v2Document1,803 pages1 - Gametogenesis & Early Development of The Fertilized Ovum v2moamen.nlNo ratings yet
- Folluculogenesis and OogenesisDocument12 pagesFolluculogenesis and Oogenesisಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Oogenesis: Queenie VargasDocument11 pagesOogenesis: Queenie VargasMariella MoniqueNo ratings yet
- Game To GenesisDocument3 pagesGame To GenesisSerge JacobeNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument5 pagesBiology Projectayushaaryan209No ratings yet
- Oo GenesisDocument7 pagesOo GenesisRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- OogenesisDocument7 pagesOogenesisRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Histo Female ReproductiveDocument3 pagesHisto Female ReproductiveAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis 0Document3 pagesOogenesis 0naji 12No ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Elishae SamonteNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 01Document12 pagesAssignment No 01zuha khanNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Female 2023 - JPDocument89 pages5.1 Female 2023 - JPtexasrepublican1976No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - 30.12.2022Document17 pagesLecture 8 - 30.12.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- Embryology IDocument94 pagesEmbryology Imasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- Applications of Biology 9700 - Nos - As - 5Document9 pagesApplications of Biology 9700 - Nos - As - 5Nana_Banana_94No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Repruductive SystemDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Female Repruductive SystemPEÑAFLOR, Shealtiel Joy G.No ratings yet
- Khalisha Azis 121 444 1 009 Icp A: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesKhalisha Azis 121 444 1 009 Icp A: Mitosis and MeiosisKhalishaAzisNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument9 pagesEmbryologyRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System OverviewDocument56 pagesFemale Reproductive System OverviewAngelina BulaiNo ratings yet
- Fertilisation in HumansDocument47 pagesFertilisation in HumansVVS .b.s2126No ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysiologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To PhysiologyTimothy usmanNo ratings yet
- Mikes First Semester Embryology-1Document8 pagesMikes First Semester Embryology-1obianujuonyeka6No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - Jan. 22, 24, 2013 - Dr. C. AyochokDocument10 pagesFemale Reproductive System - Jan. 22, 24, 2013 - Dr. C. AyochokmbdelenaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics: The Normal Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesObstetrics: The Normal Menstrual Cycleapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Oogenesis serap arbak SON (1)Document43 pagesOogenesis serap arbak SON (1)ozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Fertilisation Ad ImplantationDocument3 pagesFertilisation Ad ImplantationAine GrahamNo ratings yet
- EMBRIOLOGYDocument36 pagesEMBRIOLOGYHelena Pascual PérezNo ratings yet
- Gamete Production: Spermatogenesis vs OogenesisDocument4 pagesGamete Production: Spermatogenesis vs OogenesisMichael Angelo DejandoNo ratings yet
- First Week of Human DevelopmentDocument81 pagesFirst Week of Human DevelopmentAsfoor gake10% (1)
- 3 Oogenesis DR - GosaiDocument29 pages3 Oogenesis DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology ProjectsivaNo ratings yet
- Human Embryonic DevelopmentDocument16 pagesHuman Embryonic DevelopmentsivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 22 The Female Reproductive SystemEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- Abnormal ImplantationDocument3 pagesAbnormal ImplantationMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyguide.pk: Aspects of Human Reproduction Key ObjectivesDocument9 pagesWWW - Studyguide.pk: Aspects of Human Reproduction Key ObjectivesP.P.KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument12 pagesReproduction in AnimalsYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesOverview of The Female Reproductive SystemMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- 7 GametogenesisDocument35 pages7 GametogenesisBlè SsìngsNo ratings yet
- Fertilization - ImplantationDocument4 pagesFertilization - ImplantationEzeoke ChristabelNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument22 pagesEmbryologyamitNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGY 1 Intro-1-1Document64 pagesEMBRYOLOGY 1 Intro-1-1Joseph MuimiNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis Summary NotesDocument1 pageSpermatogenesis Summary NotesJoseph MuimiNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle Short NotesDocument1 pageMenstrual Cycle Short NotesJoseph MuimiNo ratings yet
- Please Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDocument1 pagePlease Circle Tests Needed and Provide Relevant ICD10 CodesDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Vaginal PH An Important Indicator of Urogenital Health and Role of Vagin...Document34 pagesVaginal PH An Important Indicator of Urogenital Health and Role of Vagin...Nita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Childhood Psychiatric DisordersDocument85 pagesChildhood Psychiatric DisordersVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- 105 - Day Expanded Maternity Leave LawDocument14 pages105 - Day Expanded Maternity Leave LawDenise MarambaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Understanding the Principles that Guide Child DevelopmentDocument14 pagesGrowth and Development: Understanding the Principles that Guide Child DevelopmentAbdirahman AbdisalanNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Analysis of Infant Mortality in Oyo State, NigeriaDocument6 pagesBayesian Analysis of Infant Mortality in Oyo State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- GE1 Module 7 Sexual SelfDocument20 pagesGE1 Module 7 Sexual SelfBrenda CaballaNo ratings yet
- UPHC Guideliens - UpdatedDocument34 pagesUPHC Guideliens - Updatedradhe sharmaNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis in Capsicum SPP.: March 2016Document154 pagesPhytochemical Analysis in Capsicum SPP.: March 2016AbdurrohimnNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Reproductive For Nursing To Be PresentDocument96 pagesPhysiology of The Reproductive For Nursing To Be PresentraphatoelNo ratings yet
- Newborn Movement Assessment 1687969489Document68 pagesNewborn Movement Assessment 1687969489Selva Srinivasan mNo ratings yet
- Medcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Document3 pagesMedcard Warfarin (Coumadin)Tricia SicbaldiNo ratings yet
- Men CycDocument90 pagesMen CycBrendon MuriraNo ratings yet
- Medical Management Include Drug Therapy: Hydatidiform MoleDocument2 pagesMedical Management Include Drug Therapy: Hydatidiform MoleMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- International Ayurvedic Medical Journal: Arif Khan Goran, Pramod Kumar Mishra, Mahesh Kumar, Neha BhanotDocument7 pagesInternational Ayurvedic Medical Journal: Arif Khan Goran, Pramod Kumar Mishra, Mahesh Kumar, Neha BhanotRitu ShewaniNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Gynecology, 7e 7th Edition Comprehensive Gynecology, 7e 7th EditionDocument1 pageComprehensive Gynecology, 7e 7th Edition Comprehensive Gynecology, 7e 7th Editionjohn puruntongNo ratings yet
- Symposium Simulation ScriptDocument9 pagesSymposium Simulation ScriptJakob A GimenaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in PregnancyDocument29 pagesHypertension in PregnancyArchana KumariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory AnimalDocument8 pagesLaboratory AnimalCherrie AnneNo ratings yet
- Pain Management During Labor Part 1: Pathophysiology of Labor PainDocument8 pagesPain Management During Labor Part 1: Pathophysiology of Labor PainAmanda SaphiraNo ratings yet
- Breeding Management of Sheep and GoatDocument7 pagesBreeding Management of Sheep and GoatblackvenumNo ratings yet
- cOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSDocument11 pagescOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSChari RivoNo ratings yet
- DIC in PregnancyDocument24 pagesDIC in PregnancySergio Alberto Sulub NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Transition Slides For CME FINALDocument8 pagesTransition Slides For CME FINALMark A. CasintahanNo ratings yet