Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Go To Page
Uploaded by
api-530124992Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Go To Page
Uploaded by
api-530124992Copyright:
Available Formats
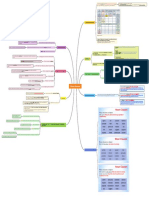
GO TOs
Core Values (TIU3)
Love Knowledge
Knowledge
Learning Styles (TIU4) Learning styles with 2 examples – place a star by your preferred styles
Style: Visual Learner* Style: Kinesthetic Learner Style: Auditory Learner*
ex. Screen Projection in class ex. Small group role play ex.
Lecture in class
through Pics
ex. ex. Allowing student to get up ex. Participation in class
Link to read on web and move to study discussion
Activate the Brain – The R’s (TIU7)
1. Relationships 4. Retrieval 7. Re-Exposure
2. 5. 8.
Rigor Routing Rehearsing
3. 6. 9.
Relevance Retaining Recognizing
Teach the Vocabulary (SS1)
1. 3. Word walls – designate in good location in classroom
Frayer model – Uses a 4 square graphic organizer 5-10 or 15 depends on age words that help students
to define, give examples, characteristics, pictures, who are learning to read and write. Repetition Tchart
connections or an illustration of the main word. or tree map.
2. 4.
Students can learn vocabulary by writing Word games – Such as wheel of fortune and password
text and oral speech.
Strategies for Differentiation (SS2)
Respectful Tasks – Ones that recognize and honor
Individualized Instruction – Instruction should be individual students learning differences. Teachers should
tailored to meet the specific needs of individual pay attention to the readiness level of each student and
1. students. Student readiness, student interest and 3. offer all students opportunities to learn according to their
student learning preferences. own readiness levels. Equally interesting, important, and
engaging.
Tiered Instruction – Teachers evaluate their students and
2. Flexible grouping – Allows students to be 4. then use the data they collect to provide a different tier of
instruction for each student. 3 levels - Students who do
Strategies for Success
appropriately (SS2-7)
challenged and helpProvide
you avoid2 labeling
examplesa of each
not know the concept or who do not have the skill,
students readiness or skill level. Work as members of students who have some understanding of the concept or
many different groups depending on the task and skill and students who have mastered and understand the
content. concept or skill.
Strategies for Success (SS2-7) – Provide 2 examples of each
Rally-Robin – Teacher poses the question. Think time.
Think-pair-share – Students work together to solve a problem or
Partners take turns verbally listing responses.
answer a question about an assigned reading. Think individually about
a topic or answer to a question share ideas with classmates
Mind Map – central theme placed in center. Associations
Venn Diagram – uses circles to show the relationships among things from central theme, curved lines keywords summarize
or finite groups of things. They help to visually represent the information proximity color and images
similarities and differences between two concepts.
Advanced Org. an ex is an Analogy which Advanced Org. an ex is an Expository in
means a comparison between 2 things typically Writing. Expository means intended to
for the purpose of explanation or clarification. explain or describe something.
Analogies – Can help explain new or confusing concepts by aligning or comparing it to something Classifying – Group items after we see how they are similar or
familiar providing students with examples of the relationships can help them recognize the implication different. Specify elements to items to arrange them in groups
of “A is to B as C is to D.”
Notetaking aka Cornell Notes – Is the process of writing down
Summarizing – Is the process that helps students determine essential ideals and synthesize key elements in their own words. 3 primary parts are notes,
important details that support them.. EXAMPLES 3-2-1 Summary comments/questions and summarization. EXAMPLE The 5
FINGER SIMPLE SUMMARY
Continued for cues/questions - Routinely pose questions to the
Cues & Questions – Will guide students to analyze and apply information while evoking critical students, give students ample time to process question than call on
thinking skills them after student respond follow up with more probing questions
Blooms Verbs (SS8 and SS9)
Create Develop, setup, arrange, summarize, write
Skype
APPS: Spark Video
Describe, explain, interpret, compare, support
Evaluate Twitter
Weebly
APPS:
Apply, show, write, use, change
Analyze Google Sheets
We Video
APPS:
Illustrate, solve, write, relate, apply
Apply
Zoom
Sway
APPS:
Explain, summarize, discuss, give, example, identify
Comprehension Befunky
Spark Post
APPS:
Define, describe, label, match, list
Remember
One Note
Popplet
APPS:
Four Questions to redirect behavior (CBM5)
1. Rule- Follow directions immediately. 1. Rationale-Following directions can help with safety and make sure you are
1. doing your work correctly. 1. Consequence - Verbal warning 1. Reward -All homework in on time –10 free points
2. Rule -Be on time with your materials ready. Rationale-We have a lot of information to learn so we need to make
2.
good use of all the time we have. 2. Consequence - Name on board –as a warning (-) 2. Reward-Special privileges
3. 3. Classroom rules -Keep hands, feet, and objects to yourself. Rationale -If you bother others, someone might get hurt
or get their things damaged. Consequence In-class time-out- Reward -Name on the board – as a rock star (+)
4. Actively participate in class activities. Rationale -You learn by doing. It’s ok not to know everything. We will all
4.
make mistakes. By practicing and making those mistakes, our brains grow. Consequence-Referral to office. Reward-
Cell phone use.
Modifications and Accommodations (E6)
Quantity Definition Time Definition Level of Support Definition
Adapt the number of items that Adapt the time allotted and allowed Increase the amount of personal assistance to keep
the learner is expected to learn or for learning, task completion, or the student on task or to reinforce or prompt the
the number of activities student testing. use of specific skills. Enhance adult-student
will complete prior to assessment relationship; use physical space and environmental
for mastery. Example Example
structure.
Example Individualize a timeline for completing
Assign peer buddies, teaching
a task; pace learning differently
Reduce the number of Health terms a assistants, peer tutors, or cross-age
(increase or decrease) for some
learner must learn at any one time. tutors. Specify how to interact with the
learners.
Add more practice activities or student or how to structure the
worksheets. environment.
Input Difficulty Output
Definition Definition Definition
Adapt the way instruction is Adapt the skill level, problem type, or Adapt how the student can respond to
delivered to the learner. the rules on how the learner may instruction.
approach the work.
Example Example Example
Use different visual aids, enlarge text, Instead of answering questions in
Allow the use of material given by the
plan more concrete examples, provide writing, allow a verbal response. Use a
teacher to figure out, simplify task
hands-on activities, place students in communication book for some students,
directions, or change rules to
cooperative groups, pre-teach key or allow students to show knowledge
accommodate learner needs.
concepts or terms before the lesson. with hands-on materials.
Participation Notes:
Definition
Adapt the extent to which a
learner is actively involved in the
task.
Example
Have a student do one part of the
assignment, while others do
different parts to assist in
breaking the assignment down.
Ask the student to lead a group.
Have the student partner with
another student.
Suggestions for working with Students in Poverty (E12)
Provide access to computers, magazines, newspapers, and
books so low-income students can see and work with printed Be careful about the school supplies you expect
materials. School may be the only place where they are students to purchase. Keep your requirements as
exposed to print media. simple as you can for all students.
Keep your expectations for poor students high. Poverty Arrange a bank of shared supplies for your students
does not mean ignorance. to borrow when they are temporarily out of materials
for class.
Don’t make comments about your students’ clothes or
Do not require costly activities. For example, if you
belongings unless they are in violation of the dress code.
require students to pay for a field trip, some of them
will not be able to go.
Reading Strategies to Strengthen Literacy Skills (R8)
Exit slips are written student responses to
questions teachers pose at the end of a
When to use- After reading. How to class or lesson. These quick, informal
EXIT SLIP use-Individually, small groups, assessments enable teachers to quickly
whole class settings. At the end of assess students' understanding of the
your lesson ask students to respond material.
to a question or prompt.
Shared Reading is an interactive reading
experience that occurs when students join
in or share the reading of a book or other
text while guided and supported by a
SHARED READING When to use-Before during and after teacher. The teacher explicitly models the
reading. How to use-Individually, skills of proficient readers, including
small groups, whole class. reading with fluency and expression. The
shared reading model often uses
oversized books (referred to as big
books) with enlarged print and
illustrations.
WORD WALL When to use-before, during and after A word wall is a collection of words
reading How to use-Individually, which are displayed in large visible letters
small groups, and whole settings. on a wall, bulletin board, or other display
surface in a classroom. The word wall is
designed to be an interactive tool for
students and contains an array of words
that can be used during writing and
reading.
Making content comprehensible for ELL students (R9)
Write at least 3 strategies / techniques that you could easily implement in your classroom for your content
1. Prepare the lesson
1. Highlighted text 2. Outlines T-Charts 3. Jigsaw text reading
2. Build background
1. Contextualizing key vocabulary 2. Content word wall specific to content area 3. Visual Vocabulary (pictures)
3. Make verbal communication understandable
1. Scaffolding techniques 2. Model techniques 3. Use gestures when presenting lessons
4. Learning strategies (this one should be easy!)
1. Mnemonics 2. Scaffolding Tech – graphic organizer 3. Questioning Tech – Higher order thinking
5. Opportunities for interaction
1. Elaborate responses. 2. Homogeneous or heterogeneous grouping 3. Clarify key concepts in native language
6. Practice and application
1. Hands on practice 2. Social interaction. 3. Practice in anyone area – listening, speaking, reading, writing
7. Lesson delivery
1. Content objective. 2. Language objective. 3. Students engaged.
8. Review and assess
1. Review of key vocabulary. 2. Providing feedback. 3. Assessment
You might also like
- Common Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreFrom EverandCommon Core Snapshot: Administrator's Guide to the Common CoreNo ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-469053152No ratings yet
- Go To Page Joanna CruzDocument4 pagesGo To Page Joanna Cruzapi-523399530No ratings yet
- Go To Ka 3 3 - 1 2 2 1 2Document4 pagesGo To Ka 3 3 - 1 2 2 1 2api-462453006No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-340637026No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable CompletedDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable Completedapi-520622423No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-570575701No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-583972926No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-474654385No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-469013911No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-515609227No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-510325289No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-506774410No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-511731781No ratings yet
- Go ToDocument4 pagesGo Toapi-519213101No ratings yet
- GTP ExportDocument4 pagesGTP Exportapi-480969929No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-522702297No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-588120954No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-514491655No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-616973358No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-558436275No ratings yet
- RacitiDocument12 pagesRacitiapi-710906492No ratings yet
- Lsanchez - Go To PageDocument4 pagesLsanchez - Go To Pageapi-509515347No ratings yet
- Go To Page 1 1 1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page 1 1 1 1 1api-514926981No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-653779848No ratings yet
- Go ToDocument4 pagesGo Toapi-513371370No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-660941021No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-519782199No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-517815541No ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Grade 2 Topics and Texts With Peers and AdultsDocument4 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: Grade 2 Topics and Texts With Peers and Adultsapi-534288634No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument5 pagesGo To Pageapi-618128891No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-595404596No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-519065425No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-620568882No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-512760489No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-531857613No ratings yet
- CPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleDocument8 pagesCPE 104 Lesson 1 - ModuleHuda MadiNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-647617886No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-554381190No ratings yet
- UWP Lesson Plan TemplateDocument20 pagesUWP Lesson Plan Templateapi-583559840No ratings yet
- Core ValuesDocument4 pagesCore Valuesapi-508554958No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-624104394No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-559213951No ratings yet
- Myp Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionDocument5 pagesMyp Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit Questionkhush1802No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-517773047No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-607084998No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-524545342No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 2 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 2 1 1api-622986234No ratings yet
- Ilp - Kristen WebsterDocument6 pagesIlp - Kristen Websterapi-622508187No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-515469030No ratings yet
- Go-To Page FinalDocument4 pagesGo-To Page Finalapi-542633696No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word FillableDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillableapi-524477527No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-470471721100% (1)
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-513026137No ratings yet
- Go-To PageDocument4 pagesGo-To Pageapi-538158244No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-518630332No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word For TimDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word For Timapi-519778159No ratings yet
- Fraction Vocab LessonDocument12 pagesFraction Vocab Lessonapi-666837211No ratings yet
- Phonics Word Recognition (2) Common Core Standards and Best PracticesDocument11 pagesPhonics Word Recognition (2) Common Core Standards and Best PracticesmakaylaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Digital PortfolioDocument13 pagesComprehension Digital Portfolioapi-584337135No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide LPG Word-JcDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Guide LPG Word-Jcapi-530124992No ratings yet
- Jeanettes ResumeDocument2 pagesJeanettes Resumeapi-530124992No ratings yet
- Qualities of Effective TeachersDocument2 pagesQualities of Effective Teachersapi-530124992No ratings yet
- Classroom Behavior Managment Plan HealthDocument1 pageClassroom Behavior Managment Plan Healthapi-530124992No ratings yet
- Intro Letter 3rd GradeDocument5 pagesIntro Letter 3rd Gradeapi-530124992No ratings yet
- 2020-10-20 Basic Gatekeeper TrainingDocument1 page2020-10-20 Basic Gatekeeper Trainingapi-530124992No ratings yet
- Noun ClausesDocument1 pageNoun ClausesPhương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Understanding cultural differences is key for international businessDocument5 pagesUnderstanding cultural differences is key for international businessCông NguyênNo ratings yet
- Preposition: Place. Thus, Contrary To Other "Small Words", They Are Not An Element of Style, But AbsolutelyDocument9 pagesPreposition: Place. Thus, Contrary To Other "Small Words", They Are Not An Element of Style, But AbsolutelyAsya FahiraNo ratings yet
- Read The Text and Answer The Questions 1, 2 and 3.: Model Test Subject: English Marks: 50 Time: 1 Hour Class: 4Document7 pagesRead The Text and Answer The Questions 1, 2 and 3.: Model Test Subject: English Marks: 50 Time: 1 Hour Class: 4Zahid Hasan Suvo50% (2)
- A Case Study of Reading Instruction in A Philippine PDFDocument13 pagesA Case Study of Reading Instruction in A Philippine PDFAvegail Tolentino100% (1)
- C1 - Listening Unit 18 - JobsDocument7 pagesC1 - Listening Unit 18 - JobsSantos0% (1)
- Druggist ManualDocument136 pagesDruggist ManualTony DunsworthNo ratings yet
- Innovative Methods in Teaching EspDocument2 pagesInnovative Methods in Teaching Espmekahli mehdiNo ratings yet
- UnravelDocument2 pagesUnravelHannah San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cacophony: Ho How T Wtopr O Pronounc Onounce Cac E Cacophony OphonyDocument3 pagesCacophony: Ho How T Wtopr O Pronounc Onounce Cac E Cacophony Ophonykamran khanNo ratings yet
- Mark Mcwatt The Language of El Dorado 3Document15 pagesMark Mcwatt The Language of El Dorado 3Adrian100% (1)
- GEC 003 Module 3.3Document17 pagesGEC 003 Module 3.3Daphne ApiadoNo ratings yet
- There is/there are document with simple past tense verbsDocument10 pagesThere is/there are document with simple past tense verbsCarlos Delgado0% (1)
- Focus1 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupADocument1 pageFocus1 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupALol OloNo ratings yet
- Tep Lesson Plan Template and Description - TechnologyDocument2 pagesTep Lesson Plan Template and Description - Technologyapi-565363108No ratings yet
- Mandarin/ Fukien LanguageDocument1 pageMandarin/ Fukien LanguageFirst Alliance Business and Management ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs Infinitive Form Meaning Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument6 pagesIrregular Verbs Infinitive Form Meaning Past Tense Past ParticipleAndrea JaniecNo ratings yet
- P61963 International GCSE Bangla 4BA0 01 Jun 2021 TestDocument20 pagesP61963 International GCSE Bangla 4BA0 01 Jun 2021 TestMd Abu Zaher73% (11)
- Beta Week 4 Unit 12BDocument2 pagesBeta Week 4 Unit 12BEmirhan YılmazNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2a-BDocument2 pagesGrammar 2a-BJosé Alberto PradoNo ratings yet
- Session 12 - Module 3: The World Around Us: IELTS 4.0 - 5.0Document10 pagesSession 12 - Module 3: The World Around Us: IELTS 4.0 - 5.0Lucy BlueNo ratings yet
- Effective Listening SkillsDocument3 pagesEffective Listening SkillsAmber EbayaNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Argumentative Text: Modal Verbs and Modal AdverbsDocument32 pagesEnglish: Quarter 2 - Module 4 Argumentative Text: Modal Verbs and Modal AdverbsJohanisa Dandamun100% (1)
- Actividad 6 SantiagoDocument7 pagesActividad 6 SantiagoSantiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Eng 120 1 PDFDocument9 pagesEng 120 1 PDFJc James TorinoNo ratings yet
- 6 DarsDocument12 pages6 DarsNafisa SamandarovaNo ratings yet
- Essential Teacher Knowledge ANSWERSDocument149 pagesEssential Teacher Knowledge ANSWERSMaratNo ratings yet
- Nlp1a Intro 11 Aug 21Document15 pagesNlp1a Intro 11 Aug 21Arundhuti NaskarNo ratings yet
- Prelim 1Document35 pagesPrelim 1Leymelynn LanuzaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Adverbes de FréquenceDocument2 pages5 - Adverbes de FréquencevictorNo ratings yet