Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amazon's Success Through Innovation
Uploaded by
Mmc MixOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amazon's Success Through Innovation
Uploaded by
Mmc MixCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
Assessment 1 - BSBWOR 1
Diploma of leadership and management (Victoria University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
Unit code: BSBINN502
Build and sustain an innova7ve work
environment
Name: HARPINDER SINGH JASSI
Student I.D:- BIT1443
Email: - harpindersingh85497@gmail.com
Course: - Diploma of Leadership and Management
Trainer: - PIR HARMEET SIDHU
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
ASSESSMENT TASK 1
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
1.1 Research report
Introduc7on
By simply looking at the de5ni6on, Innova6on management is simply the process of coming
up with and introducing new things and developing the business, one way or the other. Any
new development in the organiza6on can be considered to be related to innova6on.
Amazon, which is the most customer centric organiza6on, started its journey in 1995.
Amazon used e-commerce business model to run its business worldwide successfully and
came to be known as the world’s largest retailer. In the beginning, Amazon started their
business in the name of Cadabra.com and today it is opera6ng the whole of its business in
the area of selling books. With 6me, Amazon expanded its business by diversifying
strategies and began selling everything as per customers’ requirements online. Currently
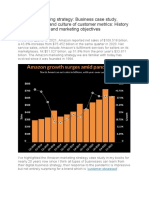
Amazon has 24,000 employees and generates $ 24 billion revenue in the year 2009. During
the whole journey of success, Amazon faced numerous logis6cs problems but at the end
due to least expensive place for shopping and due to its bePer management strategies,
Amazon achieved success which was second to none. Amazon started its journey as “Earth
biggest bookstore” where in as per customers, the requirement the e-commerce company
entered into other media, including DVD, CDs, VHS and many other varie6es of products like
electronics, toys, furniture and apparel.
The ini6al founda6on was cleverly built on the intelligent decision of selling books online as
it had a signi5cant appeal and was easy to ship. The Amazon founder and CEO, JeZ Bezos
made the right decision of star6ng his online business in books since he considered books as
easy to ship products. This developed a considerable appeal among the users and convinced
them to place. As opined by JeZ Bezo.
Another cri6cal success factor that de5nes Amazon in an eZec6ve manner is the extensive
research conducted by it’s team. The Amazon study shows how in 2015, Amazon had spent
as much as $12.5 billion to comprehend trade secrets and evaluate latest business
innova6ons. Amazon web services, Alexa, Prime Pantry, Amazon Fresh, Prime Now and
Prime music are some of the greatest innova6ons that has marked the business growth. This
organiza6on has made eZec6ve use of the relevant resources to meet up the business
needs.
Amazon’s marke6ng strategies are based on six main concepts:
– To use eco-friendly interface for bePer enhancing the services.
– The company oZers great products and services to its customers.
– The company deals with small to large scale industries in its 5eld.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
– There is an a`lia6on in its products.
– The communica6on and interac6on system is good in the company.
– The behaviour of the company in responding to the customers is good.
– Amazon focuses on its customers with the help of bePer talented people and always
applies new concepts to make them happy and sa6s5ed. The main focus of the company has
always been customers. Amazon is always 5nding new customers and has strong online
presence for its exis6ng customers
To analyze, there were diZerent reasons for Amazon’s success discussed below:-
Amazon was successful with certain key parameters such as:-
Amazon controlled the internal retail market and thus they were also able to control
the purchasing power of the online customers which was the reason of great success
for the company.
They focused on customers and tried to maintain the good rela6onship with their
customers. Thus they also added high variety of products to their online store. This
created great presence of the company, added high value, and maintained strong
reputa6on around the whole world.
Amazon focused on every aspect to deal with the solu6ons and customers
eZec6vely.
They had a strong vision and strong leaders for their company.
They provided easy accessibility and availability to their customers which proved
advantageous for the company.
Best services, strong support and network, good processes created high level of
awareness, good reputa6on among customers and also there were no complaints
because the response system of the company was very fast and the staZ members of
the company dealt with everyone posi6vely and with posi6ve behaviour.
Every daring aPempt bring certain level of risk as well as opportunity. In 2014 Amazon
made two big investments, one of which was tremendous success while the other failed
miserably and be discon6nued within a year. On June 18th 2014 Amazon unveil its 5rst ever
Smartphone (The Fire Phone). The Fire Phone was aimed at integra6ng various media
streaming op6ons but this fail to secure consumer interest leading to serious failure.
Amazon was forced to discon6nue the Fire phones produc6on ader only one year resul6ng
in a $180 million loss. In August of the same year, Amazon 5nalized the acquisi6on of Twitch
for a staggering $970 million. The social video game streaming site would be integrated to
the game produc6on division at Amazon which helped further enhance Amazon Web
Services.
Inven6on of the Amazon prime services, Amazon launch two-day delivery post program.
This proved to be game changer in s6mula6ng the Amazon success story on the most
descrip6ve way. Amazon has occupied a signi5cant posi6on among the customers owing to
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
the fact that this company possesses updated IT services, intact networking of warehouses,
mul6faceted inventory management and e`cient transporta6on services. Amazon’s clever
strategy of outsourcing the inventory management to third party service providers was
another clever move. The drone based delivery system called the Amazon Prime Air was
great innova6on Amazon.
Amazon is a vast online service provider with diverse products and services, their basic style
of business is e-commerce. This organisa6on has been an ideal portrayer of sustainability
and business credibility as they have shown enough innova6on in their business strategy
and techniques. This Amazon Case Study focuses on the impeccable performer in terms of
supply chain management. Their supply chain team undergoes con6nuous monitoring and
scru6ny to prevent any kind of customer disappointment.
Conclusion
An acknowledgement of apprecia6on must be given to Amazon for their unique eZorts of
taking the E-commerce sector to the next level. This had been possible because of their
innova6ve strategies and intelligent business decisions. The above report portrays an in
depth men6on of the cri6cal success factors behind its long drawn success journey.
Moreover, this organiza6on is a pioneer in aligning small business sellers to huge customer
base. Finally the Opera6ons Management Study of Amazon outlines the organiza6on is
planning to expand in the market to enhance their global sales.
1.2 Research and iden7fy innova7on system features under the following headings
(dimensions of innova7on):
“Managed Innova6on” thus refers to handling of all the ac6vi6es needed to “introduce
something new”, which in prac6ce means things like coming up with ideas, developing,
priori6zing and implemen6ng them (innova6on management), as well as pugng them into
prac6ce, for example by launching new products, or by introducing new internal processes.
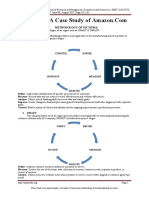
Innova7on system features:
Capabili7es
Capability is a term used to cover the diZerent abili6es and resources the organiza6on has
for crea6ng and managing innova6on. The capabili6es aspect revolves primarily around
people, as innova6on relies heavily on the abili6es of both individuals and teams
collec6vely. It refers 5rst and foremost to the abili7es, prac7cal skills of the people working
for the organiza6on. However, it also covers areas, such as the informa7on capital and tacit
knowledge of the organiza6on, as well as their other resources and available [nancial
capital, all of which might be required to create innova6on.
Structures
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
The diZerence between structures and capabili6es is that structures enable the e\ec7ve
use of the said capabili7es. In prac6ce, this means the organiza7onal structure, processes,
and infrastructure of the organiza7on. The right structure allows the organiza6on to
operate and innovate much more eZec6vely. For example, without the right communica6on
channels, the right processes for making decisions, and the right infrastructure for
implemen6ng ideas, very few of the ideas that people are coming up with will be actually
applicable.
Teams working on innova6on need to be able to move fast and adapt to their environment,
as well as make decisions independent of the tradi6onal ways of doing things in the
organiza6on.
Culture
If structures allow the eZec6ve use of capabili6es, culture is what enables the organiza7on
to acquire the capabili7es related to people. An appropriate culture encourages the right
kind of behaviour and discourages the wrong kind.
Here are some of the commonly accepted traits for an innova6ve culture:
Emphasizes always think of ways to get be_er
Values speed, learning and experiments
Considers failure as just a normal part of the process for crea6ng anything new
Provides enough freedom and responsibility and primarily with vision and culture
instead of a chain-of-command approach
Strategy
Strategy is, simply the plan the organiza6on has for achieving long-term success. But
it is crucial to understand is that strategy is ul7mately about making a deliberate choice
between a number of possible op6ons to have the best chance of “winning” and this choice
shouldn’t be separate from the execu6on. The link between innova6on and strategy is
correlated; innova6on is simply one of the means to achieving your strategic goals. If you
want to be eZec6ve at managing innova6on, it’s paramount for you to be able to
understand both the big picture, as well as the individual components that make it up.
Strategic Alignment
The process of bringing the ac6ons of an organiza6on's business divisions and staZ
members into line with the organiza6on’s planned objec6ves. The ability of most businesses
to achieve their strategic goals is being bene5ted by performing a comprehensive strategic
alignment assuring that its divisions and employees are jointly working toward the
company's stated goals.
Industry foresight
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
1. Industry Foresight as a Strategic Innova6on Understanding Emerging Trends for
Business Growth
2. The Challenge of Foresight it’s impossible to forecast the future, it is possible to
make a series of opinions about the future, and test these opinions against future
scenarios that are grounded on understanding of emerging and converging industry
trends. Without a crea6ve view of the future, companies are limited by the
strategies and opportuni6es of the past.
3. Industry Foresight represents a deep understanding of the emerging trends, drivers,
inhibitors and emerging opportuni6es within a market, industry or set of converging
markets and industries. Organiza6ons that possess Industry Foresight are bePer
posi6oned to establish a strategy that leverages future trends and even helps de5ne
them, to create a leadership posi6on in the marketplace.
4. Aspects need to be consider to compile industry foresight
Economic Condi6ons, Macro (trade, inma6on), Emerging technologies, wages,
preferences of consumers, regional varia6on, Interna6onal Rela6ons Compe66on
Aging trends, compe66on, labour force, exchange rates, Social/Lifestyle Factors
Poli6cal, Air/water/land pollu6on trends, Energy prices and availability, Surprise
forces with major impact, environmental protec6on trends, raw materials supplies,
global warming eZects, poten6al market opportuni6es.
Customer insight
A customer insight, or consumer insight, is an interpreta6on of trends in human
behaviours which aims to increase eZec6veness of a product or service for the consumer, as
well as increase sales for mutual bene5t.
Speci5cally, Consumer Insights is a 5eld that focuses on analyzing market research and
ac6ng as a bridge between Research and Marke6ng departments within a company.
Commonly referred to as CI, it is the intersec6on between the interests of the consumer and
the features of a brand. Its main purpose is to understand why the consumer cares for the
brand as well as their underlying mindsets, moods, mo6va6on, desires, aspira6ons, that
mo6vates and trigger their agtude and ac6ons.
Another de5ni6on of consumer insight is the collec6on, deployment and interpreta6on of
informa6on that allows a business to acquire, develop and retain their customers.
Core Competencies
Core competencies are the resources and/or strategic advantages of a business, including
the combina6on of pooled knowledge and technical capaci6es that allow it to be
compe66ve in the marketplace. In other words, core competencies are what the company
does best and consist of the combined ac6vi6es, opera6ons, and resources that dis6nguish
the company from compe6tors. For example, with over $495 billion in sales in 2018, Wal-
Mart exhibits the core competencies of buying power, superior logistics, and supply chain
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
management to keep prices low while maintaining a high availability of products within its
stores.
Organiza7onal readiness:
An organiza6onal readiness assessment is an o`cial measurement of the preparedness of
your company to undergo a major change or take on a signi5cant new project. You don’t
want to jump into a big change or project without knowing if your company has the
resources to accomplish it eZec6vely. Conduc6ng an organiza6onal readiness assessment
gives you the knowledge and assurance that your company’s proposed theme will be
successful if you decide to go ahead and do it. It can also save your company’s reputa6on by
allowing you to avoid a poten6ally high-pro5le failure for engaging in a project you were not
ready to complete.
A readiness assessment usually assesses the following:
Project goals and objec6ves
Expecta6ons and concerns
Leadership support of the project
Ability to adapt to change
Ways to minimize poten6al project failure
Project governance and decision making
Other cri6cal project needs
Readiness Assessments Help You Address Poten7al Project Failures
This type of assessment also gives your company the ability to address any poten6al issues
before they become big problems as you move forward on the proposed project. This is
important because it will save your company 6me and money, and even improve the
pro5tability of the change, if the change is a project you are taking on for a client.
Readiness Assessments Help You Address Changes with Employees
In addi6on, the organiza6onal readiness assessment allows you to address the details of the
change with your employees to determine if they are ready for such change and have the
ability and resources they need to do their part in it. This is another way that doing the
assessment is a smart move.
A good readiness assessment means having good organiza6onal programs and project
readiness. These are the precursors of quality improvement and are achieved when your
company feels like it is ready to make a big change, alter the current way you do things,
restructure the business, or take on a large and important new project for a client. The 5rst
sign of organiza6onal readiness is your company’s willingness to alter your current prac6ces
to be more compa6ble with the needs of the change or project you are proposing.
Your professionally prepared organiza6onal readiness assessment will pinpoint:
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
Your available company resources,
the characteris6cs of your employees,
Areas in which your company needs to improve in order to take on the change or
project and make it a success.
The results of the organiza6onal assessment will give you the addi6onal bene5t of
iden6fying the strengths of your organiza6on, most par6cularly the things that will be the
strongest assets for you in your proposed change.
Finally, your organiza6onal readiness assessment will allow you to know whether your
organiza6on meets the requirements to even consider the change or project you have in
mind. If you don’t have the requirements now, the assessment will let you know what you
need to acquire and any changes you need to make or training you need to do in order to
make the proposed project a successful one that your company actually can accomplish, and
accomplish brilliantly.
Factors That Influence Team Dynamics
A complex factor that impacts team dynamics is employee personality types. According to
Harvard Business Review, extroverted team leaders perform better when matched with
employees looking for guidance, while introverted team leaders fare better with workers who
are proactive and take initiative. This idea is known as “dominance complementarity,” which
means that groups tend to be more cohesive and effective when there is a balance of
dominant and submissive leaders.
To test this concept, researchers tracked extroverted leaders and how proactive employees
were in a U.S. pizza delivery chain. The study looked at 57 different stores and each leader’s
level of extraversion, as well as employees’ opinions of how proactive their store was as a
group.
Extroverted leadership was linked to signi5cantly higher store pro5ts when employees were
passive. Stores with extroverts leading passive employees achieved 16 percent higher pro5ts
than those led by introverts.
Extroverted leadership was linked to signi5cantly lower store pro5ts when employees were
proac6ve. Stores with extroverts leading proac6ve employees had 14 percent lower pro5ts.
Researchers pointed out that introverts’ strengths are often “locked up” by the way work is
structured. For example, meetings can turn into events where outgoing qualities are needed,
requiring introverts to adjust in negative ways.
Personality types, work structure and other factors (e.g. team size and available resources) all
impact team dynamics. Changing one factor can have implications on another, as
demonstrated in the research on dominance complementarity.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
10
Building High-Performing Teams
Eight qualities that successful teams share:
1. Manageable size
There is no perfect size, but teams can be ordered in sub-groups to take advantage of the
benefits of larger and smaller teams. Larger teams tend to have more ideas, diverse
perspectives and more human capital overall. Small teams tend to be more cohesive and are
easier to manage, when it comes to arranging meetings, distributing tasks and making
decisions.
2. Equitable work division
Participation and efficiency increase when work and responsibilities are divided
appropriately. In Ataya’s survey, more than half of teams have a sense of collective
responsibility (or accountability). Everyone receives credit when the team succeeds or takes
responsibility when the team fails.
3. Balanced leadership
Most professionals (60.7 percent) who were polled consider the team leader to be the primary
decision maker. “A team without a decisive, skilled, and hardworking leader is deficient,”
Ataya says. “A team leader gives direction and clarity to the team, coordinates between
different members, updates and corresponds to management, and generally ensures that the
team is on the desired track.” This person also influences other team dynamics in the
workplace.
The poll found that for every team, the ideal team leader is someone who is able to:
Make decisions, but also nego6ate.
Take responsibility, but also delegate.
Speak up, but also listen.
Work hard, but also help others reach their poten6al.
4. Open communication
Teams brainstorm, share ideas, provide feedback and follow up with one another to
accomplish tasks. Some of the most important communication styles include openness,
transparency and active participation.
Everyone on the team talks and listens in roughly equal measure, keeping contribu6ons
short and sweet.
Members face one another, and their conversa6ons and gestures are energe6c.
Members connect directly with one another — not just with the team leader.
Members have side conversa6ons within the team.
Members take occasional breaks to explore and bring informa6on back to the team.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
11
“The data also establish another surprising fact: Individual reasoning and talent contribute far
less to team success than one might expect,” the researcher says. “The best way to build a
great team is not to select individuals for their smarts or accomplishments but to learn how
they communicate and to shape and guide the team so that it follows successful
communication patterns.”
5. Quick conflict resolution
Disagreements and disputes will happen with any team. What is important is the team’s
ability to move past differences and resolve conflicts in a healthy and productive manner.
Conflict can help a team improve certain practices and decisions, ultimately bringing a team
together. Almost 90 percent of teams in Ataya’s poll said that their team resolves conflicts
honestly, quickly and effectively.
6. Efficient use of resources
An efficient team is able to create the highest value out of available resources. Budgets and
time can be sources of frustration, but efficient teams can overcome these types of obstacles
with creativity and by optimizing what is available to them.
7. Ability to deliver
More than 90 percent of teams in the poll meet their deadlines all or most of the time.
Delivering on required outcomes is a direct indicator of an effective team. It is also the result
of a team that communicates well, resolves conflict and other key concepts in this list.
Idea generation
Idea generation is described as the process of creating, developing and communicating
abstract, concrete or visual ideas. It’s the front end part of the idea management funnel and
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
12
focuses on coming up with possible solutions to perceived or actual problems and ortunities.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
13
1. Substitute – Substitution technique refers to replacing a part of your product, concept or
process with another to achieve even better outcome.
2. Combine – The combine technique explores the possibility to combine two ideas into a
single, more effective solution.
3. Adapt – Adaptation analyses the possibilities to make the process more flexible and
focuses on other similar incremental improvements to the idea, process, or concept.
4. Modify – Modifying the idea looks at the problem or opportunity from a bigger
perspective and aims for improving the overall results, not just the idea.
5. Put to another use – This approach focuses on finding ways to use the idea or existing
solution for another purpose and analyses the possible benefits if applied to other parts of the
business.
6. Eliminate – The elimination technique is quite straightforward: it examines the possible
outcomes if one or more parts of the concept were eliminated.
7. Reverse – This action focuses on reversing the order of interchangeable elements of an
idea.
Managing ideas
Although generating ideas is often the easy part of innovation, collecting and managing them
can be challenging without a proper tool.
Because people often come up with new ideas then and there, they should be able collect
these ideas right when they arise.
Many people use digital or physical notebooks to write down their ideas on the go. This
method works well when you just want to make notes for your own use. However, when you
want to share that information with others and ask for feedback for further improvement, this
isn’t the most effective way.
If you need to involve more people in your ideation process, you might want to consider a
dedicated idea management tool to make sure all of the potential ideas are collected in one
place.
Idea Management Tool
As idea management is such a vast topic and larger companies are always going to have
thousands of ideas, using a dedicated idea management tool often makes sense for most
companies.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
14
An idea management tool serves as the backbone of your idea management process. It's
where you’ll collect the ideas, discuss them, evaluate and prioritize them, and keep track of
their progress, as well as the strategic direction of your ideation activities.
Succeeding with Idea Generation
Before engaging more people to use these tools and techniques for generating more ideas,
there are a few more tips that can help you get more out of your ideation methods.
De[ne the problem or opportunity
Although this seems obvious, the more accurately you’re able to describe your current or
perceived problem or opportunity, the better chances you have of actually generating useful
ideas.
Before you start, try to gather as much information about the problem as possible to get to the
heart of the problem. Identify what you already know about it and what information is still
needed.
Involve the right people
For your ideation to be as productive as possible, it is important to involve the right people to
the process. Engage those people who know about the topic and are genuinely interested in
making a change in your organization.
If your plan is to engage a larger group of people to generate ideas, make sure your audience
is relevant and well informed on the subject.
Conclusion
The purpose of generating new ideas is about improving what already exists as well as
coming up with something new.
Often when trying to solve a problem or approaching a new opportunity, people use existing
solutions or mental models instead of trying to come up with new ones. The problem with
this approach is that it doesn’t allow you to explore different opportunities and it narrows
down the number of possible solutions.
Coming up with completely new ideas can help you approach your problem or opportunity
from a new perspective. It enables you to expand the range of ideas beyond your current way
of thinking which eventually leads to more ideas.
There are several different methods and techniques that can be used to challenge that
conventional mindset and to get more of those high-quality ideas. The ones introduced in this
post can be used as a reference in your brainstorming sessions or when generating ideas on
your own.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
15
The next step towards generating more ideas would be to try some of these methods in
practice. You can download our idea generation toolkit that consists of some of our favorite
tools for idea generation.
Idea evalua7on
Organizational innovation is not just about generating creative business ideas. It is also about
reviewing ideas in order to identify those which are most likely to become successful
innovations. Unfortunately, many organizations make mistakes in their idea review processes
that result in rejecting the most potentially innovative ideas in favour of less innovative ones.
Iden6fy the ideas that are most likely to succeed as innova6ons for the company.
Ensure that complex ideas are reviewed by people with the appropriate exper6se necessary
to understand what would be necessary to implement the idea – and what might go wrong.
Enable a middle manager to defend the idea to senior management, stakeholders, and
5nancial o`cers who may need to grant budgetary approval of the idea.
Make it possible to review a large number of ideas in a resource e`cient manner.
Improve the idea by iden6fying poten6al implementa6on problems and preparing suitable
ac6ons to overcome those problems. Sadly, this last aspect is oden lost in formal idea review
procedures.
Methods
There are all kinds of idea review methods. We will look at three methods that we use, pass-
fail evaluation, evaluation matrices and SWOT analysis.
Pass-fail evaluation
If there are a large number of ideas that need to be reviewed — for instance, you have run a
company-wide ideas campaign on a popular issue and have generated hundreds of ideas – a
simple pass-fail evaluation is often essential to bring the idea pool down to manageable
levels.
It is best to start with a simple criterion for determining whether an idea will go on to a more
in-depth evaluation. This criterion might be related to budget, time-frames, fit with company
culture or just practical viability. Whatever the criterion, it should be made clear. If a
colleague later asks what happened to her idea, you can explain why it did not pass this initial
stage. Knowing that her idea did not get implemented for a pragmatic reason – such as being
too expensive to implement – is more reassuring than having the idea rejected for no apparent
reason.
It is also important to be careful that you are not too quick to reject ideas which, with
modification, might meet the pass-fail criterion. For example: a very creative idea that does
not meet your budget criterion ought nevertheless to pass. You may be able to determine a
means of implementing the idea at lower cost.
If there are few ideas, the pass-fail evaluation is often not necessary. It is easier to move on to
the more sophisticated evaluation matrix.
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|6210682
16
Idea development
Once an idea passes these initial hurdles, it may be ready for implementation or it may
require more detailed testing. We call this phase of idea review: “idea development” as it is
no longer a process of evaluating an idea so much as a method to develop it for
implementation.
Idea development may include business case preparation, prototype development, project
management initiation or test marketing. There is not room enough in this issue of Report 103
to go into idea development in detail – so we’ll save it for another issue. Moreover, how a
firm develops an idea depends on the nature of the idea, the nature of the firm and existing
processes for implementing ideas.
Criticism versus improvement
Over the years, I have noticed that business analysts tend to be overly critical of new ideas.
This is understandable, they are tasked with managing and minimising risk. And creative
ideas tend to be the riskiest. As a result, many evaluators stress weaknesses and threats. On
one hand, this is understandable. Your company should not be implementing ideas that will
prove to be costly failures. But, many weaknesses can readily be improved. An idea that
would be very expensive to implement may, with minor changes, be implemented at far
lower cost. And by improving a creative idea’s weaknesses, you may be turning a costly
failure into a profitable success!
Evaluation teams
Evaluations should be performed by a team of people with relevant expertise. Ideally, that
expertise should be varied. For instance, if you are evaluating new product ideas for an
electronic gadget, your experts might include engineers, marketing people, retailers (who
would sell the product) and one or more people representative of the consumers expected to
buy the new products.
Evaluator agendas and prejudices
A particular benefit to having teams review ideas is that while individual evaluators are
prejudiced, a varied team is likely to cancel such prejudices out.
For example: an engineer trained in an older technology may well be reluctant to give a high
evaluation score to an idea that uses a new technology with which she is not familiar. The
success of such an idea might well threaten her job! A jealous manager might not like the fact
that her subordinates are more creative than her and so might give poor evaluation scores to
creative ideas. At the other end of the spectrum, creativity and innovation people like you and
I are often too enthusiastic about the most creative ideas and so give overly high scores for
creativity. Sometimes, a less creative idea might prove to be the more innovative (in terms of
being profitable)
Downloaded by Mmc Mix (mickey_mouse_iz@hotmail.com)
You might also like
- The Amazon Management System: The Ultimate Digital Business Engine That Creates Extraordinary Value for Both Customers and ShareholdersFrom EverandThe Amazon Management System: The Ultimate Digital Business Engine That Creates Extraordinary Value for Both Customers and ShareholdersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Individual Assignment OMDocument13 pagesIndividual Assignment OMThe Shelby BoyNo ratings yet
- BUS203 - Team Amazon ReportDocument26 pagesBUS203 - Team Amazon Reportbhallashray101No ratings yet
- Amazon ViewDocument20 pagesAmazon Viewhercules GiantNo ratings yet
- HRM Project On AmazonDocument17 pagesHRM Project On AmazonFalaq Khowaja100% (2)
- Group No 4 ProjectDocument30 pagesGroup No 4 Projectshubhamgupta5295No ratings yet
- Amazon Value Chain Analysi1Document19 pagesAmazon Value Chain Analysi1farhan100% (1)
- Amazon Research PapersDocument6 pagesAmazon Research Papersgw1wayrw100% (1)
- Amazon Case StudyDocument8 pagesAmazon Case StudyHuy Trần100% (1)
- MBA 5040 Company Analysis PaperDocument13 pagesMBA 5040 Company Analysis PaperpravinNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy For AmazonDocument4 pagesBusiness Strategy For AmazonEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Amazon ThesisDocument5 pagesAmazon ThesisPaperWritingHelpOnlineReno100% (2)
- Amazon StrategyDocument9 pagesAmazon StrategySaradha Devi GrandhiNo ratings yet
- Amazon Written Assignment - 2018Document2 pagesAmazon Written Assignment - 2018francess gideonNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report-2 "Metamorphosis Changes in Amazon": Master of Business Administration (MBA)Document27 pagesMini Project Report-2 "Metamorphosis Changes in Amazon": Master of Business Administration (MBA)Ritul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Amazon StartegyDocument24 pagesAmazon StartegyMIHAELACARMEN OLTIANUNo ratings yet
- Amazon Case StudyDocument3 pagesAmazon Case StudyChristian Jay PorciunculaNo ratings yet
- SixSigma Amazon CaseDocument4 pagesSixSigma Amazon CaseKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument6 pagesExecutive Summaryapi-454213734No ratings yet
- Amazon Case Study: Working Capital, Valuation, and LeadershipDocument7 pagesAmazon Case Study: Working Capital, Valuation, and LeadershipbonnieNo ratings yet
- Strategy AmazonDocument108 pagesStrategy AmazonVusumuziKuneneNo ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument36 pagesGroup Assignmenttooba siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management Approach With Reference To Amazon - Com INCDocument5 pagesTotal Quality Management Approach With Reference To Amazon - Com INCAshwini JamkhandiNo ratings yet
- Innovation Design and Business Model (Amazon - Com) Final ReportDocument8 pagesInnovation Design and Business Model (Amazon - Com) Final ReportYaqoob EsmailNo ratings yet
- A Study About Remarketing To Consumers Abandoning Carts at E-Commerce Sites With Respect To Women in Pune City Reference - Amazon (Target Group-Women's in Pune)Document7 pagesA Study About Remarketing To Consumers Abandoning Carts at E-Commerce Sites With Respect To Women in Pune City Reference - Amazon (Target Group-Women's in Pune)Virat KohliNo ratings yet
- Amazon Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesAmazon Strategic ManagementAssignment WriterNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Group Assignment 1Document14 pagesStrategic Management: Group Assignment 1vaibhav naharNo ratings yet
- Amazon Term PaperDocument8 pagesAmazon Term Paperafmzwlpopdufat100% (1)
- CASE STUDY MIS NewDocument23 pagesCASE STUDY MIS NewWayne De FranceNo ratings yet
- Ajay's Case Study On AmazonDocument7 pagesAjay's Case Study On AmazonRashika guptaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial5 Case AmazonDocument3 pagesTutorial5 Case AmazonQiu yiiNo ratings yet
- BUS-4210 Case Study 3.editedDocument7 pagesBUS-4210 Case Study 3.editedBONFACE MUTUKUNo ratings yet
- Amazon's Marketing Research SuccessDocument11 pagesAmazon's Marketing Research SuccessSugar Berry ArtsNo ratings yet
- Production 0 ManagementDocument13 pagesProduction 0 ManagementMOTIVATIONAL CLIMATENo ratings yet
- Amazon Com Case Study Analysis Marketing PDFDocument12 pagesAmazon Com Case Study Analysis Marketing PDFRasha Elbanna100% (1)
- Business Case Study: Customer ObsessedDocument5 pagesBusiness Case Study: Customer Obsessedzaidi zaynNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document1 pageCase Study 5shreya vermaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Amazon CompanyDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Amazon Companycakvaw0q100% (1)
- Amazon Retail VRIO and SWOT Analysis 1Document6 pagesAmazon Retail VRIO and SWOT Analysis 1Gladys vidzoNo ratings yet
- Management Theory and Practice Assignment: American College of Technology Master of Business AdministrationDocument10 pagesManagement Theory and Practice Assignment: American College of Technology Master of Business AdministrationKaleab AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument5 pagesAmazonAakriti BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Report On Brand: (Batch 2020-2022)Document8 pagesReport On Brand: (Batch 2020-2022)Akanksha LoveeNo ratings yet
- Role of MIS in Amazon's E-commerce SuccessDocument5 pagesRole of MIS in Amazon's E-commerce SuccessShruti DhawanNo ratings yet
- Amazon PPT NotesDocument9 pagesAmazon PPT NotesarpitNo ratings yet
- How Amazon Manages Technology InnovationDocument10 pagesHow Amazon Manages Technology InnovationAqsa IjazNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument12 pagesAmazonHarsh RajputNo ratings yet
- Amazon Research PaperDocument6 pagesAmazon Research Paperaflbtvmfp100% (1)
- Amazon Is A Multinational TechnologyDocument12 pagesAmazon Is A Multinational TechnologyJakia Sultana BrishtiNo ratings yet
- Amazon Success Factors: Innovation, Customer Service, DiversificationDocument5 pagesAmazon Success Factors: Innovation, Customer Service, Diversificationelijah mutukuNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media Marketing on Amazon's SuccessDocument12 pagesImpact of Social Media Marketing on Amazon's SuccessSameer ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Strategy ReportDocument17 pagesStrategy ReportFun Toosh345No ratings yet
- Written Assignment Unit 6Document8 pagesWritten Assignment Unit 6Aby ElenwoNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On AMAZON NEW 2020Document20 pagesA Project Report On AMAZON NEW 2020Deepak PrithianiNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument16 pagesAmazonMohit Shukla75% (4)
- Amazon 2021 - Chantelle Monica RochesterDocument7 pagesAmazon 2021 - Chantelle Monica RochesterChantelle RochesterNo ratings yet
- "Many of The Problems We Face Have No Textbook Solution, and So We-Happily-Invent New Ones." - Jeff BezosDocument15 pages"Many of The Problems We Face Have No Textbook Solution, and So We-Happily-Invent New Ones." - Jeff BezosNimish NamaNo ratings yet
- Amazon's Marketing Strategy for Entering VietnamDocument18 pagesAmazon's Marketing Strategy for Entering Vietnammegan75% (4)
- Running Head: Amazon Internal and External Environment AnalysisDocument9 pagesRunning Head: Amazon Internal and External Environment AnalysisJimmy Kapoor100% (2)
- UKS40251Document12 pagesUKS40251sanjay.warrgyizmorschNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument39 pagesAmazonMuhammad Adnan100% (1)
- Assessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsDocument54 pagesAssessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsMmc Mix0% (1)
- Special MenuDocument1 pageSpecial MenuMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Work Place Log 4Document1 pageWork Place Log 4Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Online Order SothaiDocument4 pagesOnline Order SothaiMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Work Place Log 3Document2 pagesWork Place Log 3Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Certificate II in Tourism SIT20116 Term 1 ProjectDocument3 pagesCertificate II in Tourism SIT20116 Term 1 ProjectMmc MixNo ratings yet
- BookingDocument1 pageBookingMmc MixNo ratings yet
- So Thai Kogagrah Restaurant Menu Log Nov 2022Document2 pagesSo Thai Kogagrah Restaurant Menu Log Nov 2022Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- WHS policy ensures safety firstDocument7 pagesWHS policy ensures safety firstMmc MixNo ratings yet
- CCC4 3.3 Coaching 55566778Document178 pagesCCC4 3.3 Coaching 55566778Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsDocument58 pagesAssessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsMmc Mix100% (1)
- SITHFAB005 - Prepare Serve Espresso Coffee - Learner Guide - Coffee - DrinkDocument137 pagesSITHFAB005 - Prepare Serve Espresso Coffee - Learner Guide - Coffee - DrinkMmc MixNo ratings yet
- SITTIND001 - Source and Use Information On The Tourism and Travel Industry - Sell Tourism Products and Services - Report Writing Assignment HelpDocument7 pagesSITTIND001 - Source and Use Information On The Tourism and Travel Industry - Sell Tourism Products and Services - Report Writing Assignment HelpMmc MixNo ratings yet
- SITHFAB005 - AT 6678h43Document38 pagesSITHFAB005 - AT 6678h43Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- SITHFAB005 - AT 6678h43Document38 pagesSITHFAB005 - AT 6678h43Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsDocument46 pagesAssessment Task 1 - Knowledge QuestionsMmc Mix100% (2)
- HC3 2.1 SITXFSA001 002 GDDocument65 pagesHC3 2.1 SITXFSA001 002 GDMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Sitxhrm001 Coach Others in Job Skills: Learner GuideDocument35 pagesSitxhrm001 Coach Others in Job Skills: Learner GuideMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Caf AssesDocument33 pagesCaf AssesMmc MixNo ratings yet
- (Insert Month) (Insert Date Range) : Attended: Sick Leave: Personal LeaveDocument6 pages(Insert Month) (Insert Date Range) : Attended: Sick Leave: Personal LeaveMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Assessment HACCP .Docx: HOSPITALIT SITXHRM002: Australian National University - Course HeroDocument7 pagesAssessment HACCP .Docx: HOSPITALIT SITXHRM002: Australian National University - Course HeroMmc MixNo ratings yet
- BSBWOR502 - Task 2 Part BDocument15 pagesBSBWOR502 - Task 2 Part BMmc MixNo ratings yet
- BSBADM502: M. Kalpana M. Perera Advanced Diploma in Leadership Management YORKE INSTITUTE-Melbourne 00496Document19 pagesBSBADM502: M. Kalpana M. Perera Advanced Diploma in Leadership Management YORKE INSTITUTE-Melbourne 00496Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- 4-Hour / 2-Hour RuleDocument2 pages4-Hour / 2-Hour RuleMmc MixNo ratings yet
- Sitxhrm001 Coach Others in Job SkillsDocument47 pagesSitxhrm001 Coach Others in Job SkillsMmc Mix100% (1)
- Hc3 1.2 Sitxhrm001 Sesspln V15jul17Document5 pagesHc3 1.2 Sitxhrm001 Sesspln V15jul17Mmc Mix100% (1)
- Bsbadm502 Manage Meetings Task 1 PDFDocument10 pagesBsbadm502 Manage Meetings Task 1 PDFMmc MixNo ratings yet
- HC3 1.2 Hotel Guidelines AT1Q1.5Document33 pagesHC3 1.2 Hotel Guidelines AT1Q1.5Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Governance Templates Staff Leave Policy 2018Document16 pagesGovernance Templates Staff Leave Policy 2018Mmc MixNo ratings yet
- Excellent School Status and ExistenceDocument16 pagesExcellent School Status and ExistenceShadøwWølfNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 3.6.73.78 On Wed, 21 Dec 2022 07:40:53 UTCDocument81 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 3.6.73.78 On Wed, 21 Dec 2022 07:40:53 UTCabcdNo ratings yet
- Howden PDFDocument24 pagesHowden PDFskb2550% (2)
- Brain Size Evolution: How Fish Pay For Being Smart: Dispatch R63Document3 pagesBrain Size Evolution: How Fish Pay For Being Smart: Dispatch R63Nika AbashidzeNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICSDocument1 pageHYDRAULICSOrland Son FactorNo ratings yet
- Philippine Legal CitationDocument72 pagesPhilippine Legal CitationArwella GregorioNo ratings yet
- API Documentation Alpha VantageDocument55 pagesAPI Documentation Alpha VantageFun WorldNo ratings yet
- Surveying - Mcqs On Unit I - SJMDocument6 pagesSurveying - Mcqs On Unit I - SJMKalyani ingole100% (1)
- Bi006008 00 02 - Body PDFDocument922 pagesBi006008 00 02 - Body PDFRamon HidalgoNo ratings yet
- 22-02-13 Samsung Answer To Staton Techniya Complaint & CounterclaimsDocument72 pages22-02-13 Samsung Answer To Staton Techniya Complaint & CounterclaimsFlorian MuellerNo ratings yet
- Envision Math 8.1 - Use Models To Multiply A Whole Number by A Fraction PracticeDocument2 pagesEnvision Math 8.1 - Use Models To Multiply A Whole Number by A Fraction PracticeMerlin D SilvaNo ratings yet
- Prelims Module On Forensic 1Document17 pagesPrelims Module On Forensic 1Vanessa CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Yuken Series PVL Vane Pumps Catalogue en PDFDocument69 pagesYuken Series PVL Vane Pumps Catalogue en PDFAgilRinaldiNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Separation of VariablesDocument9 pages4 1 Separation of Variablesapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Partlist Sym Vf3i 185Document83 pagesPartlist Sym Vf3i 185Jack Wilder100% (1)
- Daily DAWN News Vocabulary With Urdu Meaning (05 April 2020) PDFDocument6 pagesDaily DAWN News Vocabulary With Urdu Meaning (05 April 2020) PDFAEO Begowala100% (2)
- Accident Avoiding Bumper SystemDocument3 pagesAccident Avoiding Bumper SystemDeepak DaineNo ratings yet
- BID 2021 046 6913 VendorList3. (237110)Document1 pageBID 2021 046 6913 VendorList3. (237110)JAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Tema Line Solutions BrochureDocument8 pagesTema Line Solutions BrochureUmair Mushtaq SyedNo ratings yet
- GE Café™ "This Is Really Big" RebateDocument2 pagesGE Café™ "This Is Really Big" RebateKitchens of ColoradoNo ratings yet
- DRAFT RoA (TSBINUANG) TSB 12 PDFDocument1 pageDRAFT RoA (TSBINUANG) TSB 12 PDFAchwan FebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Redundant Arithmetic: Keshab K. ParhiDocument21 pagesChapter 14: Redundant Arithmetic: Keshab K. ParhiInJune YeoNo ratings yet
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureDocument49 pagesG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Phrase Structure AnalysisDocument2 pagesPhrase Structure Analysismerlino99No ratings yet
- Cycle1 Parta GettingtoknowyourstudentsDocument7 pagesCycle1 Parta Gettingtoknowyourstudentsapi-295073409No ratings yet
- Hydro Distillation Method Extraction of Eucalyptus Oil Lemongrass OilDocument9 pagesHydro Distillation Method Extraction of Eucalyptus Oil Lemongrass OilSIVANESAN JOTHIVELNo ratings yet
- Switches Demystified Assembly PDFDocument1 pageSwitches Demystified Assembly PDFkocekoNo ratings yet
- UCT APM M2 U1 - TP Leadership QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesUCT APM M2 U1 - TP Leadership QuestionnaireLincolyn MoyoNo ratings yet
- Welder Training in SMAW, GTAW & GMAW Welding Engineering & NDT Consultancy Welding Engineering Related TrainingDocument4 pagesWelder Training in SMAW, GTAW & GMAW Welding Engineering & NDT Consultancy Welding Engineering Related TrainingKavin PrakashNo ratings yet
- Iso 19108Document56 pagesIso 19108AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Arduino PWM To DC Voltage Op Amp Converter - Henry's BenchDocument8 pagesArduino PWM To DC Voltage Op Amp Converter - Henry's BenchAlan A. TorresNo ratings yet