Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internal Control - Self Assessment Checklist
Uploaded by
吳思穎Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal Control - Self Assessment Checklist
Uploaded by
吳思穎Copyright:
Available Formats
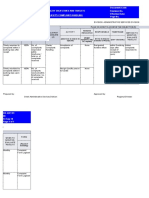
Internal Control – Self Assessment Checklist
Control
Environment
Risk
Monitoring
Assessment
Information
Control
&
Activities
Communication
1. Control Environment 3. Control Activities
1. Demonstrate Commitment to Integrity 10. Design Control Activities
and Ethical Values 11. Design Activities for the Information
2. Exercise Oversight Responsibility System
3. Establish Structure, Responsibility, and 12. Implement Control Activities
Authority
4. Demonstrate Commitment to 4. Information and Communication
Competence 13. Use Quality Information
5. Enforce Accountability 14. Communicate Internally
15. Communicate Externally
2. Risk Assessment
6. Define Objectives and Risk Tolerances 5. Monitoring
7. Identify, Analyze, and Respond to Risks 16. Perform Monitoring Activities
8. Assess Fraud Risk 17. Evaluate Issues and Remediate
9. Identify, Analyze, and Respond to Deficiencies
Change
Evaluation the factors below using the 5 to 1 scale, where 5 means Completely Agree and 1 means Completely Disagree
Section 1 – Control Environment
1 - Demonstrate Commitment to Integrity and Ethical Values
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management demonstrates the importance of integrity and ethical values through their directives,
a) Tone at the top.
attitudes, and behavior.
Management establishes standards of conduct to communicate expectations concerning integrity
b) Standards of conduct.
and ethical values.
Management establishes processes to evaluate performance against the entity’s expected
c) Adherence to standards of conduct.
standards of conduct and evaluates adherence to the standards of conduct.
2 – Exercise Oversight Responsibility
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
There is an oversight body that oversees operations, provides constructive feedback to
a) Oversight structure. management, and informs decision-making to ensure that objectives are met and in alignment
with the entity’s integrity and ethical values.
The oversight body oversees management’s design, implementation, and operation of the internal
b) Oversight for the internal control system. control system, including the control environment, risk assessment, control activities,
information and communication, and monitoring.
The oversight body provides input to management’s plans for remediation of deficiencies in the
c) Input for remediation and deficiencies.
internal controls and is responsible for overseeing the remediation of deficiencies.
3 – Establish Structure, Responsibility, and Authority
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management establishes an organizational structure that is appropriate to plan, execute, control,
a) Organizational structure. and assess its ability to achieve its objectives. Lines of reporting are clear and defined at all
levels so that communication can flow down, across, up, and around.
b) Assignment of responsibility and delegation Management assigns responsibilities and delegates authority to key roles throughout the
of authority. office/unit.
c) Documentation of the internal control Management develops and maintains documents of its internal control system so that the
system. components of internal control can be designed, implemented, and operate effectively.
4 – Demonstrate Commitment to Competence
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management establishes responsibilities and expectations that are clearly defined in writing and
a) Expectations of competence.
communicated as appropriate.
b) Recruitment, development, and retention of
Management recruits, develops, and retains competent personnel to achieve desired objectives.
individuals.
Management defines succession plans to address the need to replace competent personnel over
c) Succession and contingency plans and
the long term, as well as contingency plans to address the need to respond to sudden personnel
preparation.
changes that could compromise the internal control system.
5 – Enforce Accountability
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management holds personnel accountable for performing internal control responsibilities through
a) Enforcement of accountability.
mechanisms such as performance appraisals and disciplinary actions.
Management evaluates pressure on personnel and reduces or rebalances workloads when
b) Consideration of excessive pressures.
necessary.
Section 2 – Risk Assessment
6 – Define Objectives and Risk Tolerances
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management defines objectives in specific and measurable terms to enable the design of internal
a) Definition of objectives.
control for related risks.
Management defines the acceptable level of variation in performance relative to the achievement
b) Definitions of risk tolerances.
of objectives.
7 – Identify, Analyze, and Respond to Risks
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management has a process for analyzing risks, including both inherent and residual risk, and
a) Identification of risks.
considers internal and external risk factors.
Management has a process to estimate the significance of the identified risks and their effect on
b) Analysis of risks.
achieving the defined objectives.
c) Response to risks. Management has specific actions to respond to the analyzed risk.
8 – Assess Fraud Risk
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management considers the types of fraud that can occur (e.g., fraudulent financial reporting,
a) Types of fraud. misappropriation of assets, corruption), as well as other forms of misconduct (such as waste and
abuse).
Management considers fraud risk factors (incentive/pressure, opportunity, and
b) Fraud risk factors.
attitude/rationalization) and uses this information to identify fraud risk.
Management performs a risk analysis to identify fraud risk and responds to fraud risk so they are
c) Response to fraud risks. effectively mitigated.
9 – Identify, Analyze, and Respond to Change
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management identifies significant changes to internal and external conditions that have already
a) Identification of change. occurred, or are expected to occur, and that could significantly impact the internal control
system.
Management analyzes and responds to identified changes and related risks in order to maintain
b) Analysis of and response to change.
an effective internal control system.
Section 3 – Control Activities
10 – Design Control Activities
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management designs policies, procedures, techniques, and mechanisms in response to the
a) Response to objectives and risk.
program office’s objectives and risks to achieve an effective internal control system.
Management designs appropriate types of control activities (i.e., management of human capital,
b) Design of appropriate types of control
physical control over vulnerable assets, access restrictions to records, etc.) for its internal control
activities.
system.
c) Design of control activities at various
Management designs control activities for appropriate coverage of objectives and risks.
levels.
Management considers segregation of duties in designing control activity responsibilities to help
d) Segregation of duties.
prevent fraud, waste, and abuse in the internal control system.
11 – Design Activities for the Information System
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management designs the office’s information system and the use of information technology to
a) Design of the entity’s information system.
respond to the office’s objectives and risk.
Management designs appropriate types of general control activities (e.g., security management,
b) Design of appropriate types of control
physical access, contingency planning, etc.) and application control activities (controls over
activities.
processing, input, output, etc.) in the information system.
c) Design of information technology Management designs control activities over the information technology infrastructure to support
infrastructure. the completeness, accuracy, and validity of information processing by information technology.
Management designs control activities (e.g., access rights to data) for security management of
d) Design of security management.
the office’s information system for appropriate access by internal and external sources.
Management designs control activities over the acquisition, development, and maintenance of
e) Design of information technology information technology.
acquisition, development, and maintenance.
12 – Implement Control Activities
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
a) Documentation of responsibilities through
Policies exist that document the control activities utilized by the office.
policies.
Management periodically reviews the control activities for effectiveness.
b) Periodic review of control activities.
Section 4 – Information and Communication
13 – Use Quality Information
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
a) Identification of information requirements. Management identifies the information required to support the internal control system.
Management obtains the relevant data from reliable internal and external sources in a timely
b) Relevant data from reliable sources.
manner.
c) Data processed into quality information. Management processes the obtained data and uses it to inform the internal control system.
14 – Communicate Internally
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management communicates information throughout the entity using established reporting lines,
a) Communication throughout the entity. ensuring that communication flows to all levels of the organization (down, across, up, and
around).
Management selects the appropriate method for communicating internally after considering the
b) Appropriate methods of communication.
relevant factors (i.e., audience, nature of the information, etc.).
15 – Communicate Externally
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management communicates with, and obtains quality information from, external parties (i.e.,
a) Communication with external parties.
contractors, grantees, general public, etc.) using established reporting lines.
Appropriate methods of communication. Management selects the appropriate method for communicating externally after considering the
relevant factors (i.e., audience, nature of the information, cost, etc.)
Section 5 – Monitoring
16 – Perform Monitoring Activities
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management assesses the current state of the internal control system, compared against the
a) Establishment of a baseline.
intended design of the internal control system.
Management monitors the internal control system through on-going monitoring and periodic
b) Internal control system monitoring.
separate evaluations (e.g., self-assessments, audits).
Management evaluates and documents the results of on-going monitoring and separate
c) Evaluation of results.
evaluations to identify internal control issues.
17 – Evaluate Issues and Remediate Deficiencies
Assessment Factor Indication of Controls 1 2 3 4 5
Management and personnel identify internal control issues and report the issues through
a) Reporting of issues.
established reporting lines on a timely basis.
Management evaluates and documents internal control issues and determines appropriate
b) Evaluation of issues.
corrective actions for deficiencies.
Management completes and documents corrective actions to remediate internal control
c) Corrective actions.
deficiencies on a timely basis.
You might also like
- Conduct of PNP Office Inspections and AuditsDocument37 pagesConduct of PNP Office Inspections and AuditsRhenfacel ManlegroNo ratings yet
- The MenuDocument25 pagesThe MenuShiella Mae Duque100% (1)
- Internal Control Assessment PDFDocument9 pagesInternal Control Assessment PDFRomlan D.No ratings yet
- Director IV - Internal AuditDocument4 pagesDirector IV - Internal AuditedpaalaNo ratings yet
- Total Audit Team Hours 6,780: Budgeted Number of Hours Remaining Number of Hours For Other ActivitiesDocument6 pagesTotal Audit Team Hours 6,780: Budgeted Number of Hours Remaining Number of Hours For Other ActivitiesLester SardidoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Culture Enablers and ReviewDocument35 pagesKnowledge Culture Enablers and ReviewrnaganirmitaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Process VIZAG STEELDocument106 pagesRecruitment and Selection Process VIZAG STEELManish Sood100% (1)
- Compliance Test Program: State Accounting OfficeDocument10 pagesCompliance Test Program: State Accounting OfficeChristen CastilloNo ratings yet
- GoalsDocument8 pagesGoalsapi-437604571No ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal System: Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesPerformance Appraisal System: Human Resource Managementdivya_manchandaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument11 pagesRisk Management Planmpriceatccusa100% (1)
- SOP 11-Conflict of Interest Rev 1Document3 pagesSOP 11-Conflict of Interest Rev 1Bang CacihNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Charter ChecklistEACF436E4153Document2 pagesInternal Audit Charter ChecklistEACF436E4153Phạm Duy ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Management AuditDocument4 pagesManagement AuditSATHURI VANSHIKA 1923271No ratings yet
- Presented by Miss - Rupa.j.bhatt 30120315 Batch-32Document27 pagesPresented by Miss - Rupa.j.bhatt 30120315 Batch-32tinmaungtheinNo ratings yet
- Key Internal ControlDocument5 pagesKey Internal ControlBarkah Wahyu PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource and Payroll Substantive Procedures: Account BalanceDocument3 pagesHuman Resource and Payroll Substantive Procedures: Account BalancealtheguruNo ratings yet
- Iqa Audit Checklist Form 4 EempsdDocument22 pagesIqa Audit Checklist Form 4 EempsdRonald PreNo ratings yet
- Methods, Process and Practices of Management AuditDocument48 pagesMethods, Process and Practices of Management AuditSana RubabNo ratings yet
- Manual de Generadores de Gas SolarDocument49 pagesManual de Generadores de Gas SolarJuvenal Segundo Chavez Acosta100% (7)
- BaselineDocument84 pagesBaselineMARISSANUNEZNo ratings yet
- BAICS CommunicationsDocument4 pagesBAICS CommunicationsDenmark CostanillaNo ratings yet
- Personal ChangeDocument46 pagesPersonal ChangePurushottam KumarNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesstmentDocument12 pagesRisk AssesstmentJulian RapushiNo ratings yet
- HR Audit Plan 7.17.20Document9 pagesHR Audit Plan 7.17.20Malaybalaycity TiktokchallengeNo ratings yet
- OPM 360 Degree AssessmentDocument12 pagesOPM 360 Degree AssessmentPei Kuang ChenNo ratings yet
- E - Test of Controls Work PaperDocument1 pageE - Test of Controls Work Papershane natividadNo ratings yet
- OCA Tool For USAID-Funded Organizations Facilitators PDFDocument68 pagesOCA Tool For USAID-Funded Organizations Facilitators PDFEko JasintusNo ratings yet
- TQS TRAINING STANDARDS LIBRARYDocument9 pagesTQS TRAINING STANDARDS LIBRARYealbu7330No ratings yet
- HL300SDocument128 pagesHL300SElizabeth Octagon100% (1)
- Procurement QuestionnaireDocument1 pageProcurement QuestionnaireDenmark CostanillaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Communication Skills: Submitted By: Rishabh NandaDocument17 pagesPresentation On: Communication Skills: Submitted By: Rishabh NandaRishab NandaNo ratings yet
- C2 - IAD-GP-1901 Rev.01 Nonconformance Management - 1585473787Document7 pagesC2 - IAD-GP-1901 Rev.01 Nonconformance Management - 1585473787jherson gravidesNo ratings yet
- 03 - FoAM Form-02 - Fraud Risk Assessment TemplateDocument3 pages03 - FoAM Form-02 - Fraud Risk Assessment Templatenonavi lazoNo ratings yet
- Workplace Violence ChecklistDocument2 pagesWorkplace Violence ChecklistPatricia GeraldesNo ratings yet
- 2022 Global Hallyu Trends Report Analyzes Issues and Regional ConsumptionDocument80 pages2022 Global Hallyu Trends Report Analyzes Issues and Regional ConsumptionDodo100% (1)
- BSI ISOIEC27001 Assessment Checklist UK enDocument3 pagesBSI ISOIEC27001 Assessment Checklist UK enDanushkaPereraNo ratings yet
- BAICS AppendixesDocument7 pagesBAICS AppendixesDenmark CostanillaNo ratings yet
- Employee Development Plan TemplateDocument1 pageEmployee Development Plan TemplateMona Abouzied IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit PerformanceDocument9 pagesInternal Audit Performanceshreya sheteNo ratings yet
- Home Appliances Controlling Using Bluetooth On Android Mobile AbstractDocument2 pagesHome Appliances Controlling Using Bluetooth On Android Mobile AbstractramyaNo ratings yet
- Consolidated ReportDocument111 pagesConsolidated ReportMa. Alene MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Ford & Nichols - Human GoalsDocument1 pageFord & Nichols - Human GoalsIs LoNo ratings yet
- Milky Mist Dairy Food Private Limited: Report On Review ofDocument29 pagesMilky Mist Dairy Food Private Limited: Report On Review ofAswath SNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Focus Group DiscussionsDocument3 pagesChecklist For Focus Group DiscussionsAbebaw100% (1)
- Counterproductive Behaviour TestDocument8 pagesCounterproductive Behaviour TestRobinson JaqueNo ratings yet
- Detroit Inspector General Report On Board of Police CommissionersDocument389 pagesDetroit Inspector General Report On Board of Police CommissionersWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Definition of Internal AuditingDocument10 pagesDefinition of Internal AuditinghossainmzNo ratings yet
- Brief HR Audit ChecklistDocument6 pagesBrief HR Audit ChecklistAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Audit Manual for Auditing MMDAsDocument135 pagesAudit Manual for Auditing MMDAsBristo Chiluba MelmanNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit PositionDocument2 pagesInternal Audit Positiondoha suprovatNo ratings yet
- Take Stand Against Domestic Violence BrochureDocument2 pagesTake Stand Against Domestic Violence BrochureLAPDSouthBureauNo ratings yet
- TheproactiveCopingInventoryFORADOLESCENTS EnglishversionDocument2 pagesTheproactiveCopingInventoryFORADOLESCENTS EnglishversionYanie RaisNo ratings yet
- Quirino Province Internal Audit of Engineering Office Controls 2018Document2 pagesQuirino Province Internal Audit of Engineering Office Controls 2018Queenie QuisidoNo ratings yet
- Entity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesEntity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireKirby C. LoberizaNo ratings yet
- Family Impact Analysis ChecklistDocument4 pagesFamily Impact Analysis Checklistapi-283593680No ratings yet
- Self-assessment of drama performanceDocument3 pagesSelf-assessment of drama performancekosovare3No ratings yet
- Preparing witness and suspect listsDocument32 pagesPreparing witness and suspect listsAbdelAziz AkashiwoueNo ratings yet
- Audit ProjectDocument14 pagesAudit ProjectDhara MehtaNo ratings yet
- Regular Board Meeting Agenda Package - June 18, 2019 - 1Document42 pagesRegular Board Meeting Agenda Package - June 18, 2019 - 1Jess PetersNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication Skills - ICSDocument41 pagesInterpersonal Communication Skills - ICSArGee AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Assigmnet IMR454Document13 pagesAssigmnet IMR4542011273434No ratings yet
- BISU Organizational StructureDocument3 pagesBISU Organizational StructureJude Vincent MacalosNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Control EnvironmentDocument6 pagesSelf Assessment Control EnvironmentSidinNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Assessment of Romlan’s FurnitureDocument8 pagesInternal Control Assessment of Romlan’s FurnitureRomlan D.No ratings yet
- CHP 5Document14 pagesCHP 5ali iqbalNo ratings yet
- RBS LogDocument1,351 pagesRBS Logsalman7467No ratings yet
- Company Profile: Our BeginningDocument1 pageCompany Profile: Our BeginningSantoshPaul CleanlandNo ratings yet
- Philippine Income Tax Exemptions and Personal DeductionsDocument5 pagesPhilippine Income Tax Exemptions and Personal DeductionsQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- Sirius-4 4 29-Manual PDFDocument49 pagesSirius-4 4 29-Manual PDFJovanderson JacksonNo ratings yet
- Checklist Whitepaper EDocument3 pagesChecklist Whitepaper EMaria FachiridouNo ratings yet
- GoogleDocument88 pagesGoogleAshrin KumarNo ratings yet
- ICE Export Catalog 2011Document72 pagesICE Export Catalog 2011Thien BinhNo ratings yet
- Breast Problems After DeviveryDocument19 pagesBreast Problems After DeviverySanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Refregeration & Airconditioning 2011-2012Document29 pagesRefregeration & Airconditioning 2011-2012erastus shipaNo ratings yet
- BCA IV Sem Open Source TechnologyDocument4 pagesBCA IV Sem Open Source TechnologyKavya NayakNo ratings yet
- The Need For International Accounting StandardsDocument1 pageThe Need For International Accounting StandardsYuvaraj RajNo ratings yet
- 3hac13347 1Document18 pages3hac13347 1CJ MallickNo ratings yet
- Premobilisation Grader InspectionDocument1 pagePremobilisation Grader InspectionArjun SatheesanNo ratings yet
- 5197-Car Hire 04 Dates-Ltr 157 DT 23.04.19Document1 page5197-Car Hire 04 Dates-Ltr 157 DT 23.04.19arpannathNo ratings yet
- Codeigniter Library: 77 Free Scripts, Addons, Tutorials and VideosDocument6 pagesCodeigniter Library: 77 Free Scripts, Addons, Tutorials and VideosmbahsomoNo ratings yet
- Ap04-01 Audit of SheDocument7 pagesAp04-01 Audit of Shenicole bancoroNo ratings yet
- Labour Welfare Management at Piaggio vehicles Pvt. LtdDocument62 pagesLabour Welfare Management at Piaggio vehicles Pvt. Ltdnikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- Safe Operating Area Testing Without A Heat SinkDocument4 pagesSafe Operating Area Testing Without A Heat SinkCarlos MeloNo ratings yet
- Article 20 Salary Scales 10-Month Teachers 2019-2020 (Effective July 1, 2019)Document10 pagesArticle 20 Salary Scales 10-Month Teachers 2019-2020 (Effective July 1, 2019)Robert MaglocciNo ratings yet
- Railway Products CatelogueDocument12 pagesRailway Products CatelogueRie RNo ratings yet
- FINAL REPORT (L ND M)Document84 pagesFINAL REPORT (L ND M)MuzamilNo ratings yet
- MemTest86 User Guide UEFIDocument101 pagesMemTest86 User Guide UEFIDani CentNo ratings yet
- RESIDENT NMC - Declaration - Form - Revised - 2020-2021Document6 pagesRESIDENT NMC - Declaration - Form - Revised - 2020-2021Riya TapadiaNo ratings yet
- D-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) Fuel Filter and LinesDocument3 pagesD-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) Fuel Filter and LinesMANUALES100% (1)