Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immuno
Uploaded by
Stephanie Mhae Tabasa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesIMMUNOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIMMUNOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesImmuno
Uploaded by
Stephanie Mhae TabasaIMMUNOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
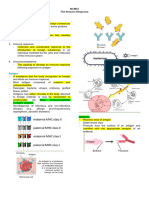
Immunology Neutro
- Study of specific immunity and how the Eiosinophil – fights parasites, phagocytic
immune system responds to specific agents
Basophil – cause inflammation in asthma,
Immune system phagocytic
-Various network of specialized cells which Monocyte – Macrphages – releases cytokinesis
participates in providing the host with specific
Phagocytosis – cell eating
immunity to infectious agents and allows us to
exist in an environment that includes hostile
microorganisms.
T cell – cell mediated immunity
Immune
- help destroy infected or cancerous cells
- Protected from a disease or the like as by
- antigen specific
inoculation
Thymus produces progenitor cells that mature
- relating to the production of antibodies or
into T cells
lymphocytes that can react with a specific
antigen.
Immunity
- state of being immune from or insusceptible
to a particular disease or the like.
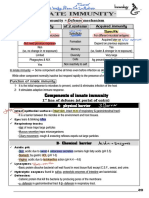
Lymphatic system – part of circulatory system
- condition that permits either natural or
acquired resistance to disease. 1. Draining excess interstitial fluid
3L remaining
- Ability of a cell to react immunologically
2. Transporting dietary lipids
Susceptibility
3. Carrying out immune responses
- state of being susceptible
primary lymphoid organ
- Capable of being affected
- Thymus
Immune system can attack, identify in just 10
- bone marrow - Produces wbc,rbc, platelets
days
and lymphocytes
Immune response
secondary
Non-specific attacks cell, invader and other
- Lymph nodes – filters interstitial fluid and
invader
activates production of phagocytes
Adaptive response can determines friendly
cells,But takes few weeks and Has immunologic
memory - spleen -
Hematopoeisis – formation of WBC &RBC -lymph nodules
Granulocytes
T cell matures in thymus –
Granulocytes – formed in bone marrow
You might also like
- Altered Immune ResponseDocument20 pagesAltered Immune Responsesho bartNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- NCM112 Module 2 Day 2 Immune SystemDocument12 pagesNCM112 Module 2 Day 2 Immune SystemAndrea DaracanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System & ImmunityDocument45 pagesLymphatic System & ImmunityRika PascualNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ImmunoooDocument10 pagesReviewer ImmunoooTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesDefinitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- MLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesDocument1 pageMLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesFrancine UriarteNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Immunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionDocument56 pagesImmunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionMiranda sekar arumNo ratings yet
- The Immune System and Immunity: By: Princess Nhoor A. AgcongDocument24 pagesThe Immune System and Immunity: By: Princess Nhoor A. AgcongCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Basic ImmunologyDocument41 pagesBasic ImmunologyFebri Yudha Adhi Kurniawan100% (1)
- Underwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionDocument29 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionSANo ratings yet
- Immunology NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology NotesDavinci LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Immune DisordersChin T. OndongNo ratings yet
- Immunity and AllergyDocument72 pagesImmunity and Allergyonlyforu_3No ratings yet
- Hematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicDocument22 pagesHematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicShienna Rose Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Sero Handout For Seminar1Document31 pagesImmuno-Sero Handout For Seminar1Jeanel Anne JovellanoNo ratings yet
- AllergenDocument2 pagesAllergenMyline TimcangNo ratings yet
- 003 Introduction To The Immune SystemDocument42 pages003 Introduction To The Immune SystemAzhar AkbarNo ratings yet
- II. Immune ResponseDocument7 pagesII. Immune ResponseMaej Marie OragaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument32 pagesImmunologympume lisahNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument13 pagesAssessment of Immune FunctionNajmah Saaban100% (5)
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Immunity: Natural Defence BarriersDocument6 pagesImmunity: Natural Defence Barriersskarun1No ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Micro NotesDocument4 pagesMicro Notesapi-680924193No ratings yet
- Physical - Hard To PenetrateDocument13 pagesPhysical - Hard To PenetrateCriselle Ruth Orendain Lardizabal0% (1)
- Path222the Immune Response-F14Document20 pagesPath222the Immune Response-F14Noah PontinoNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Veterinary Immunology: Chapter 1 - The Defense of The BodyDocument9 pagesBrief History of Veterinary Immunology: Chapter 1 - The Defense of The BodyZoe Alea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory ImmunologicDocument35 pagesInflammatory Immunologickaren dapalNo ratings yet
- BIO202!19!23 Immune SystemDocument55 pagesBIO202!19!23 Immune SystemAbhilash Kumar MuthuramanNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory and Immunologic DisturbancesDocument91 pagesInflammatory and Immunologic DisturbancesRitamaria100% (6)
- Imunologi EWSDocument83 pagesImunologi EWSEraNo ratings yet
- Third Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive ImmunityDocument7 pagesThird Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive Immunityهند نهاد سلمان حسينNo ratings yet
- Plants and Animals Have A Variety of Chemical Defenses Against Infections That Affect Dynamic HomeostasisDocument66 pagesPlants and Animals Have A Variety of Chemical Defenses Against Infections That Affect Dynamic Homeostasisapi-373344212No ratings yet
- Immunology: The Human Immune System Antigens Antibodies Cell-Mediated Immunity Immune Response To ProteinsDocument35 pagesImmunology: The Human Immune System Antigens Antibodies Cell-Mediated Immunity Immune Response To ProteinsEbook DownloadNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 3Document13 pagesالمحاضرة 3Shi no MeNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument28 pagesIMMUNITYanmolz.ghNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of He Immune SystemDocument5 pagesCells and Organs of He Immune SystemEssington BeloNo ratings yet
- Concept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDDocument163 pagesConcept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDKirk08100% (1)
- Finals (Lesson 1)Document4 pagesFinals (Lesson 1)Kevin Vincent AquinoNo ratings yet
- Types of Immune Cells: TissueDocument3 pagesTypes of Immune Cells: TissueLiz PaigeNo ratings yet
- Immune System of HumanbodyDocument49 pagesImmune System of Humanbodysayan27.sikdarNo ratings yet
- Immunologi Klinik Ama 09102019 PDFDocument101 pagesImmunologi Klinik Ama 09102019 PDFZas VutraNo ratings yet
- Harrisons: Introduction To Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesHarrisons: Introduction To Infectious Diseasesapi-3704562No ratings yet
- Basic Immunology 2Document66 pagesBasic Immunology 2JabbarTapiheruNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemsHua YueNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesDocument45 pagesThe Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesHIDE & ATTACKNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument3 pagesAssessment of Immune Functionhalloween candyNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Back To The BasicsDocument37 pagesThe Immune System: Back To The BasicsHani GowaiNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY-NOTES-by-Red ImmuneDocument4 pagesHISTOLOGY-NOTES-by-Red ImmuneEdzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document12 pagesModule 5Louise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- 1F ImmunologyDocument8 pages1F ImmunologyDANAH MARGARET VILLAGONZALONo ratings yet
- Immune DiseasesDocument101 pagesImmune DiseasesCarlo GriñoNo ratings yet
- Immuno Topics AnsweredDocument20 pagesImmuno Topics AnsweredAlesiaNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument10 pagesImmunityNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Sub058 Attachment 4Document12 pagesSub058 Attachment 4CristafeNo ratings yet
- FE Quiz 5Document3 pagesFE Quiz 5Stephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- MetaDocument74 pagesMetaStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Cervical PaDocument2 pagesCervical PaStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Need For Recognizing Atypical Manifestations of Childhood Sporadic Acute Viral Hepatitis Warranting Differences in ManagementDocument8 pagesNeed For Recognizing Atypical Manifestations of Childhood Sporadic Acute Viral Hepatitis Warranting Differences in ManagementStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- EmphysemaDocument61 pagesEmphysemaStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Conceptual NotesDocument3 pagesTheoretical Conceptual NotesStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesGuillain-Barre Syndrome Treatment & Management: Approach ConsiderationsStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System and Body Metabolism: EssentialsDocument54 pagesThe Digestive System and Body Metabolism: EssentialsSofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- NURSING DXDocument1 pageNURSING DXStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Conceptual NotesDocument3 pagesTheoretical Conceptual NotesStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- ChatDocument1 pageChatStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing ManagementStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- VARIABLESDocument4 pagesVARIABLESStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Massage Acupuncture ExerciseDocument1 pageMassage Acupuncture ExerciseStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsDocument49 pagesNCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Sample Theoretical ConceptualDocument4 pagesSample Theoretical ConceptualStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Older AdultsDocument34 pagesAssessment of Older AdultsStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 Midterms PDFDocument9 pagesCHN 2 Midterms PDFStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Arabic 4 5Document1 pageArabic 4 5Stephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Spine Knees, Ankle, HipDocument2 pagesSpine Knees, Ankle, HipStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Spread To Blood, Lymph, and Other Area MALIGNANT: Infection, Bleeding, Pain, Anorexia, SYNCOPEDocument1 pageSpread To Blood, Lymph, and Other Area MALIGNANT: Infection, Bleeding, Pain, Anorexia, SYNCOPEStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging 2020 PDFDocument13 pagesTheories of Aging 2020 PDFStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Aging 2020 PDFDocument13 pagesTheories of Aging 2020 PDFStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- First Carpometacarpal and InteDocument6 pagesFirst Carpometacarpal and InteStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Mbbs PhysioDocument27 pagesMbbs PhysioWwwanand111No ratings yet
- Friday Bulletin 712.... CompressedDocument12 pagesFriday Bulletin 712.... CompressedJamia NairobiNo ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument46 pagesBasic HematologySin RazyNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocument20 pagesBlood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewStacey CamilleNo ratings yet
- Temenoff BiomaterialsDocument0 pagesTemenoff BiomaterialsJason Chou0% (9)
- Cancer Cells Induce Metastasis-Supporting Neutrophil Extracellular DNA TrapsDocument13 pagesCancer Cells Induce Metastasis-Supporting Neutrophil Extracellular DNA TrapsJoe DaccacheNo ratings yet
- The Immune System British English StudentDocument6 pagesThe Immune System British English StudentIzabela WiśniewskaNo ratings yet
- HEMADocument6 pagesHEMAnotsoninjaninjaNo ratings yet
- Acute & Chronic Toxicity Studies of Seenthil SarkaraiDocument12 pagesAcute & Chronic Toxicity Studies of Seenthil SarkaraiManickavasagam RengarajuNo ratings yet
- MLT MCQDocument13 pagesMLT MCQRamesh Rangu88% (8)
- Case Study in Clinical MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesCase Study in Clinical Microbiologybelle navalNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument22 pagesAcute InflammationNicole Mae DavidNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Response Pathophysiology PDFDocument2 pagesInflammatory Response Pathophysiology PDFMaya Angelou Verano GarciaNo ratings yet
- Terminalia Catappa L. Extract Improves Survival, HematologicalDocument13 pagesTerminalia Catappa L. Extract Improves Survival, Hematologicalnicko.arya.dharmaNo ratings yet
- Cancer and Oncology Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz-1Document30 pagesCancer and Oncology Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz-1Susie Salmon100% (2)
- Hematology Topics 16-20Document20 pagesHematology Topics 16-20Angelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Blood WorksheetDocument2 pagesBlood WorksheetNadia ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Blood Flashcards - QuizletDocument12 pagesBlood Flashcards - QuizletJay Leheri100% (1)
- Blood Summary NotesDocument4 pagesBlood Summary NotesLaura FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Care of Clients With Inflammatory and Immunologic Response Maricris B. Florendo/Constantino Y. Mendoza/Sandra Layne G. Luczon/Rhizza AbinsayDocument23 pagesNCM 112: Care of Clients With Inflammatory and Immunologic Response Maricris B. Florendo/Constantino Y. Mendoza/Sandra Layne G. Luczon/Rhizza AbinsayRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Wrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethDocument7 pagesWrights Stain Diff Quick Manual MethJose CisnerosNo ratings yet
- De Gruchy's Clinical Haematology in Medical Practice 5th Edition PDFDocument532 pagesDe Gruchy's Clinical Haematology in Medical Practice 5th Edition PDFnarasimhahan82% (17)
- MedTech Recall NotesDocument27 pagesMedTech Recall NotesIsniharah Pangandaman100% (2)
- Netters Essential Histology With Student Consult Access 2nd Edition Ovalle Test BankDocument35 pagesNetters Essential Histology With Student Consult Access 2nd Edition Ovalle Test Bankjacobnigordon100% (14)
- Blood Components: Red CellsDocument4 pagesBlood Components: Red CellsKyle Ambis SyNo ratings yet
- Lab InvestigationsDocument25 pagesLab Investigationsbadar_aq100% (1)
- Pharmacists Clinical Round Report: Faculty of Pharmacy & Alternative Medicine The Islamia University of BahawalpurDocument9 pagesPharmacists Clinical Round Report: Faculty of Pharmacy & Alternative Medicine The Islamia University of BahawalpurNoman ZakiNo ratings yet
- Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesDocument2 pagesTumor-Infiltrating Immune Cell Marker Guide (Mouse) : LeukocytesFika Ayu SafitriNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Endterm Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Acute and ChronicDocument8 pagesNCM 112 Endterm Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Acute and ChronicApril FlorendoNo ratings yet
- IPP-LB-HEM-01-01-LH 750 Analyzer and Coulter Gen's SystemDocument13 pagesIPP-LB-HEM-01-01-LH 750 Analyzer and Coulter Gen's SystemMaria Francesca MapaNo ratings yet