Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - Notes
Uploaded by
Francine UriarteCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - Notes
Uploaded by
Francine UriarteCopyright:
Available Formats
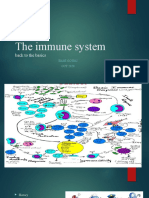
MLS 021 : Immunology & Serology – Lecture : Notes
Immunology
study of how bodily mechanisms can 1. Cellular Factors
differentiate between self and non-self 2. Humural Factors
study of the body’s defense against infection 3. Inflammation
Serology
study of serum Adaptive or Acquired Immunity
Immunity not present at birth but is developed during a
state or condition of being resistant to person’s lifetime.
infection develop later and consist of activation of
ability to ward off infections or diseases lymphocytes.
depends on the antigen that it encounters.
The immune system is composed of the lymphoid
organs: Elements of Acquired Immunity
1. primary lymphoid organs - competent in
mounting an immune response 1. Cellular: B and T lymphocytes
e.g., red bone marrow and the thymus 2. Humoral: antibodies and cytokines
Acute-Phase Reactants
2. secondary lymphoid organs and tissues -
areas where the majority of the immune protein inflammation markers that is
responses take place increased during inflammation, infection,
e.g., spleen, lymph nodes, and lymphatic injury or trauma by at least 25 percent.
nodules (follicles)
1. C-reactive protein
Peripheral Lymphoid 2. Serum amyloid A
organs are the sites of lymphocyte activation 3. Alpha1-antitrypsin
4. Fibrinogen
by antigen
5. Haptoglobin
Lymph
6. Ceruloplasmin
This fluid carries antigen taken up by
7. Complement C3
dendritic cells and macrophages to the
8. Mannose-binding protein
lymph nodes
Cellular Defense Mechanism
leukocytes are generally subdivided into
granulocytes
Composition of Immune System
Cellular Immunity
cell-mediated immunity
T cells
activation of phagocytes, release of
cytokines and chemokines
Humoral Immunity
antibody-mediated immunity
B cells
secrete antibodies against a specific antigen
Categories of Immune System
1. Natural or Innate Immunity
2. Adaptive or Acquired Immunity
Natural or Innate Immunity
provide the initial defense against infections.
present at birth and protects the body during
early stages of infection.
nonspecific, nonadaptive and prior encounter
to pathogens is not required.
Elements of Innate Immunity
External Defense System
to protect the body from infectious agents by
structural barriers, secretions and growth of
microorganisms
1. Physical or Anatomical barriers
2. Normal/Resident Flora
Internal Defense System
cells like WBCs and antibodies are the major
factors of this system
You might also like
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- NCM112 Module 2 Day 2 Immune SystemDocument12 pagesNCM112 Module 2 Day 2 Immune SystemAndrea DaracanNo ratings yet
- Altered Immune ResponseDocument20 pagesAltered Immune Responsesho bartNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Immune DisordersDocument7 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Immune DisordersIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument17 pagesInnate and Acquired ImmunityPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Third Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive ImmunityDocument7 pagesThird Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive Immunityهند نهاد سلمان حسينNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- 12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006Document99 pages12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006api-3696530No ratings yet
- The Essentials of ImmunologyDocument29 pagesThe Essentials of ImmunologyBrunoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Immune System and Its FunctionsDocument51 pagesUnderstanding the Immune System and Its FunctionsZin LimNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology ReviewerDocument71 pagesImmunology & Serology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesDefinitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- Review Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaDocument205 pagesReview Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyPRECY MAE VALETENo ratings yet
- Immunity of Parasitic InfectionsDocument4 pagesImmunity of Parasitic InfectionsCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedDocument19 pagesHUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM - Notes RepairedLoren EscotoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of a Child with Immune DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care of a Child with Immune DisordersChin T. OndongNo ratings yet
- Hematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicDocument22 pagesHematology Review Notes Dela Cruz TopicShienna Rose Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Immunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionDocument56 pagesImmunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionMiranda sekar arumNo ratings yet
- Inflammation NotesDocument45 pagesInflammation NoteskitsimonmondinNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDocument10 pagesNCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseNikitaCaitlynLeyaleyNo ratings yet
- Immune Response DRPath Part 1Document71 pagesImmune Response DRPath Part 1SITI NUR FA'IZULBA'EDAH BINTI MAT RAZINo ratings yet
- Inflammatory and Immunologic DisturbancesDocument91 pagesInflammatory and Immunologic DisturbancesRitamaria100% (6)
- LM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationDocument3 pagesLM 1 - Introduction To Concept With Immunity and InflammationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewDocument87 pagesBasic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewnovelraaaNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- The Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument47 pagesThe Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- 1.notes PowerpointDocument27 pages1.notes Powerpointt4ths999No ratings yet
- 8 10kapoyaDocument12 pages8 10kapoyaJeru Margareth TingsonNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural ImmunityDocument20 pagesDiseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural Immunitymano343No ratings yet
- Flash Cards 5Document7 pagesFlash Cards 5Brian Ernesto Leal NievesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology Lecture 3Document39 pagesClinical Immunology Lecture 3jibril channelNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument13 pagesAssessment of Immune FunctionNajmah Saaban100% (5)
- Immune System and Lymphatic SystemDocument5 pagesImmune System and Lymphatic SystemEduardson PHNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Medical Surgery CareDocument8 pagesNCM 112: Medical Surgery CareDANAH MARGARET VILLAGONZALONo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SysDocument19 pagesLymphatic SyschennielafleurNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Back To The BasicsDocument37 pagesThe Immune System: Back To The BasicsHani GowaiNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument24 pagesInfectionGarzota PrincessjhoannaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ImmunoooDocument10 pagesReviewer ImmunoooTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document12 pagesModule 5Louise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- ImmunoDocument2 pagesImmunoStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Immunology ImmunologyDocument136 pagesImmunology ImmunologyZeen_Zeen_Fern_3128No ratings yet
- Immuno - Immunology QnADocument15 pagesImmuno - Immunology QnANashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Nonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNDocument51 pagesNonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology Lecture 2Document53 pagesClinical Immunology Lecture 2jibril channelNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument29 pagesThe Immune SystemfakhirNo ratings yet
- Basic ImmunologyDocument57 pagesBasic ImmunologyRonalyn UgatNo ratings yet
- Inmunidad y SepsisDocument6 pagesInmunidad y SepsisAmmarie SanchezNo ratings yet
- Organization of Immune SystemDocument44 pagesOrganization of Immune SystemSaubie AslamiahNo ratings yet
- Physical - Hard To PenetrateDocument13 pagesPhysical - Hard To PenetrateCriselle Ruth Orendain Lardizabal0% (1)
- Underwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionDocument29 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionSANo ratings yet
- Immuno Uphsi ProtectedDocument18 pagesImmuno Uphsi ProtectedAngge Aquino OfficialNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology 2Document66 pagesBasic Immunology 2JabbarTapiheruNo ratings yet
- Nature of Antigens and MHCDocument6 pagesNature of Antigens and MHColmilloanne02No ratings yet
- Basic Concept ImmunityDocument48 pagesBasic Concept ImmunityNur Fatmah SaidNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Immune System 2020Document31 pagesOverview of The Immune System 2020mehakNo ratings yet
- A.bsfhsjsjsjgsg-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesA.bsfhsjsjsjgsg-WPS OfficeGJ MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Prakruthi ShastramDocument52 pagesPrakruthi ShastramBharatiyulam100% (3)
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Bibliography of the Indian Himalayan RegionDocument280 pagesBibliography of the Indian Himalayan RegionMadhan RajNo ratings yet
- Phillips & Van Loon (2011)Document11 pagesPhillips & Van Loon (2011)Callum BromleyNo ratings yet
- RadioimmunoassayDocument17 pagesRadioimmunoassayAyathulla Rabbani SyedNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle VocabularyDocument3 pagesCell Cycle Vocabularyapi-328162824No ratings yet
- Reproduction - Boardwork 2Document32 pagesReproduction - Boardwork 2Zidańn100% (1)
- 11 Immunology - ATFDocument35 pages11 Immunology - ATFLucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Smooth MuscleDocument33 pagesSmooth MuscleDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab Report - Activty 8Document6 pagesEnzymes Lab Report - Activty 8JengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Excretion - Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Excretion - Lecture Notesapi-372850875% (4)
- Name: - Date: - Score: - A. Label The Parts of The Digestive System. Use The Word in The Box BelowDocument1 pageName: - Date: - Score: - A. Label The Parts of The Digestive System. Use The Word in The Box BelowMary Apple Flores TagyamNo ratings yet
- Microbe MagazineDocument52 pagesMicrobe MagazinerecervictoryNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 21 Photosynthesis IntroductionDocument22 pagesLife Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 21 Photosynthesis Introductiontmalatji106No ratings yet
- Drosophila Melanogaster Models of Motor Neuron Disease 2013 (Edited by Ruben Cauchi)Document239 pagesDrosophila Melanogaster Models of Motor Neuron Disease 2013 (Edited by Ruben Cauchi)Dr.Gill_Grissom100% (1)
- Model-2 PHB Azohydromonas LataDocument11 pagesModel-2 PHB Azohydromonas LatamtlopezNo ratings yet
- Bio InvestigatoryDocument29 pagesBio InvestigatoryNysa Hajira100% (1)
- Natural Science. Level 5. Unit 5. EcosystemsDocument4 pagesNatural Science. Level 5. Unit 5. EcosystemsAna Rosa Camacho Cornejo100% (1)
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Strawberry DNA Extraction LabDocument3 pagesStrawberry DNA Extraction LabRavenica Asteroy0% (1)
- Parisites - Es.en CompressedDocument6 pagesParisites - Es.en CompressedLili KatNo ratings yet
- Automated DNA Extraction From Pollen in Honey Food Chemistry 2013Document5 pagesAutomated DNA Extraction From Pollen in Honey Food Chemistry 2013Alberto CortezNo ratings yet
- PM - NaceDocument3 pagesPM - Nacemohammad tahirNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and DDocument5 pagesName: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and Dke2No ratings yet
- 1.0 Perpetuation of LifeDocument29 pages1.0 Perpetuation of LifeSomeone SomethingNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tumbuhan InggrisDocument10 pagesAnatomi Tumbuhan InggrisKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Transformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aDocument19 pagesTransformation With Agrobacterium: PLNT2530 Plant Biotechnology 2020 Unit 8aSwati JainNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I IntroductionDocument19 pagesBiochemistry I IntroductionCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet