Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aspirin
Aspirin
Uploaded by
Shermayne Mallapre Hernandez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageOriginal Title
Aspirin.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageAspirin
Aspirin
Uploaded by
Shermayne Mallapre HernandezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
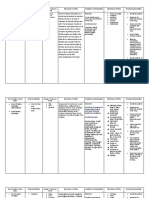
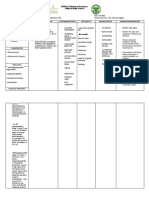
DRUG STUDY
NAME____________________________________________________________ AGE____________
DIAGNOSIS_________________________________________________
DRUGS ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING CONSIDERATION
Generic Name: Analgesic and Mild to moderate People with allergy to Acute aspirin toxicity: Assess skin color and presence of lesions as this
Aspirin antirheumatic effects pain salicylates or NSAIDs. This is respiratory alkalosis, may indicate hepatotoxicity, allergy, bleeding,
are attributable to Fever more common to people with hemorrhage, tachypnea, and other complications.
Brand name: aspirin’s ability to Inflammatory nasal polyps, asthma, and confusion, asterixis, pulmonary Give drug with food or after meal if GI upset
Aspergum inhibit the synthesis of conditions chronic urticaria. edema, seizures, tetany, occurs.
prostaglandins, such as People with haemophilia, metabolic acidosis, renal and To reduce the risk of the tablet lodging in the
Classification: important mediators rheumatic allergy to tartrazine (cross- respiratory failure esophagus, give drug with full glass of water.
Analgesic of inflammation. fever, sensitivity is common), Aspirin intolerance: Ensure that patient does not crush and chew
Anti- Antipyretic effects are arthritis, and bleeding ulcers, blood exacerbation of bronchospasm, tablets as well as sustained release preparations
inflammatory not fully understood, coagulation defects, and with rhinitis to prevent losing drug’s effectivity.
spondyloarthr
Antiplatelet but aspirin probably Vitamin K deficiency Gastrointestinal: nausea, In case of overdose, institute emergency
opaties
Antipyretic acts in the (increased risk of bleeding) dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric procedures and prepare equipments for gastric
Reduction of risk
Antirheumatic thermoregulatory Caution with people who have discomfort, anorexia, lavage, induction of emesis, and activated
of recurrent
NSAID center of the impaired renal function, hepatotoxicity charcoal.
transient ischemic
Salicylate hypothalamus to block children and teenagers (risk Hematologic: occult blood loss, •Observe patient for signs and symptoms of
effects of endogenous attack (precursor for developing Reye’s hemostatic defects bleeding such as easy bruising, bleeding in the
pyrogen by inhibiting to stroke) or Syndrom), patients who will Hypersensitivity: anaphylactoid gums, and nosebleeds.
Dosage:
synthesis of the cardiovascular have surgery within 1 week, reactions to anaphylactic shock Monitor vital signs.
51-325mg/day
prostaglandin accident (stroke) in and pregnant women (it Salicylism: dizziness, tinnitus, Raise side rails up to ensure patient’s safety.
intermediary. patients with readily crosses placenta and is difficulty hearing, nausea, Monitor for signs and symptoms of drug allergy
history of TIA due a possible teratogen) as well vomiting, diarrhea, mental such as difficulty of breathing, pruritus, and
to fibrin platelet as lactating mothers. confusion rashes.
emboli or ischemic
stroke
Prepared by:
March 2, 2019 Prof. Marcial Mesias De V MAN
Steven Matthew L. Dasig
Student Nurse and Signature DATE Clinical Instructor
You might also like
- Тести, розділені за темамиDocument361 pagesТести, розділені за темамиАнна Олексіївна ГайченкоNo ratings yet
- Steven Buser Leonard Cruz Luke Sloan DSM 5 Insanely Simplified UnlockingDocument142 pagesSteven Buser Leonard Cruz Luke Sloan DSM 5 Insanely Simplified Unlockingechevskaya3415100% (4)
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Study - AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AspirinStefano James Pajarillo0% (1)
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- GENTIMICINDocument1 pageGENTIMICINVinzNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY Butorphanol LRDR AngelicaRonquilloDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY Butorphanol LRDR AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Document7 pagesDRUG STUDY (Clopidogrel)Fatima MohammedNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- DRug Study PhenytoinDocument1 pageDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study...Document5 pagesDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY NaproxenDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY NaproxenMargarette Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OralDocument1 pageDrug Study OralBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneMaja DeraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaDocument1 pageAripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaRHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- RifampicinDocument2 pagesRifampicinChaeL90No ratings yet
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug Studysandal_meenuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of PatientDocument1 pageDrug Study: Name of PatientKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HeparinDocument2 pagesDrug Study HeparinArianne NicoleNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- AMIKACINDocument2 pagesAMIKACINJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline Drugstudy 1Document3 pagesTerbutaline Drugstudy 1Prince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtropineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AtropineAerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Document5 pagesLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Ceftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeDocument3 pagesCeftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMarychen Cabunas100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyJeoffrey MatiasNo ratings yet
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- QuinineDocument3 pagesQuinineDoubleHeartedNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeDave Michael GeliNo ratings yet
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- CefadroxilDocument2 pagesCefadroxilArvie AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin)Mae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- A Drug Study ofDocument17 pagesA Drug Study ofJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezDocument15 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- History: Allergy To CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageHistory: Allergy To CiprofloxacinShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Steven Matthew L. Dasig March 1, 2019 Prof. Marcial Mesias de V ManDocument1 pageSteven Matthew L. Dasig March 1, 2019 Prof. Marcial Mesias de V ManShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Care For The Clients With Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesCare For The Clients With Diabetes MellitusShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Checklist On Incentive Siprometry Procedure 1 2 3 4 5 Remarks Preparatory PhaseDocument1 pageChecklist On Incentive Siprometry Procedure 1 2 3 4 5 Remarks Preparatory PhaseShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- HypermagnesimiaDocument2 pagesHypermagnesimiaShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Real Cures - Parkinsons Lead - Parris LampropoulousDocument29 pagesReal Cures - Parkinsons Lead - Parris LampropoulousONONo ratings yet
- 99 TMCPractice QuestionsDocument31 pages99 TMCPractice QuestionsGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- CPH-LEC Chaper 12Document25 pagesCPH-LEC Chaper 12John Vincent TacalNo ratings yet
- 5) +nematodes Fall2020 PDFDocument118 pages5) +nematodes Fall2020 PDFJessica KadykNo ratings yet
- Infantile Seizure Presentation SlidesDocument7 pagesInfantile Seizure Presentation Slidesjuliana marquezNo ratings yet
- Maxiliary SinusDocument6 pagesMaxiliary SinusNourhan ElgnainyNo ratings yet
- Probiotics Can Cause D-Lactic Acidosis and Brain FDocument2 pagesProbiotics Can Cause D-Lactic Acidosis and Brain FRiccardo MartaNo ratings yet
- 10.1136@archdischild 2020 318841Document8 pages10.1136@archdischild 2020 318841Feer VillarrealNo ratings yet
- EsplenomegaliaDocument24 pagesEsplenomegaliaJhonatan Efraín López CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psych BookletDocument36 pagesClinical Psych BookletNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Emetine - Dehydroemetine - Chloroquine (Liver Only)Document2 pagesEmetine - Dehydroemetine - Chloroquine (Liver Only)rajeshmangalNo ratings yet
- Past Papers MergedDocument29 pagesPast Papers MergedDr IqraNo ratings yet
- PDF Pathophysiology Jacquelyn L Banasik Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Pathophysiology Jacquelyn L Banasik Ebook Full Chaptermary.moffatt586100% (1)
- Assignment: Course Packet 04a: Expanded Program On ImmunizationDocument2 pagesAssignment: Course Packet 04a: Expanded Program On ImmunizationShaira GumaruNo ratings yet
- Homelessness - Class Presentation 10/01/23Document38 pagesHomelessness - Class Presentation 10/01/23Juan joseNo ratings yet
- Assignment On TreacheostomyDocument7 pagesAssignment On Treacheostomysantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Icd 09 Codes PDFDocument156 pagesIcd 09 Codes PDFRetta Gabriella PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Removing Gallstones From Your Body: Recommended PracticeDocument1 pageRemoving Gallstones From Your Body: Recommended PracticeRyok DaysNo ratings yet
- EBRSR Handbook Chapter 2 - Brain Reorganization, Recovery and Organized Care - 2020Document64 pagesEBRSR Handbook Chapter 2 - Brain Reorganization, Recovery and Organized Care - 2020anjelikaNo ratings yet
- 9, Concept of Isolation Unit-VDocument9 pages9, Concept of Isolation Unit-VUrdu Kahani100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Scuba DivingDocument7 pagesLesson 4 Scuba DivingErron Francisco NicolNo ratings yet
- Reading 1 - Exercises of Multiple Choice Questions (M1)Document5 pagesReading 1 - Exercises of Multiple Choice Questions (M1)Chris Chris KurtsNo ratings yet
- Dengue Combi Pack InsertDocument2 pagesDengue Combi Pack InsertYvette TiongsonNo ratings yet
- GIT Individual Case StudyDocument13 pagesGIT Individual Case StudyKirito Dokkie100% (1)
- Dr. Shubhajit Roy Chowdhury: Biomedical SystemsDocument53 pagesDr. Shubhajit Roy Chowdhury: Biomedical SystemsRohit BhamuNo ratings yet
- MIS-C 20220805講義Document12 pagesMIS-C 20220805講義Sid HNo ratings yet
- Review Jurnal Varicella - Dewi Manik Aulia Fadli - 16700096Document26 pagesReview Jurnal Varicella - Dewi Manik Aulia Fadli - 16700096Lia FadliNo ratings yet
- Philhealth CPGsDocument16 pagesPhilhealth CPGsLeen Dvg-Alban100% (2)