Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 4
Uploaded by
api-5308145830 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThis document discusses renal diseases and renal failure. It outlines risk factors for renal disorders like diabetes, hypertension, and family history. It defines normal renal function values and stages of acute kidney injury caused by prerenal, intrarenal, or postrenal factors. Chronic kidney disease is identified by a GFR below 60mL/min for over 3 months. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are renal replacement therapies for kidney failure, with hemodialysis using an arteriovenous fistula to cleanse the blood and peritoneal dialysis exchanging fluid through the peritoneum.
Original Description:
Original Title
week 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses renal diseases and renal failure. It outlines risk factors for renal disorders like diabetes, hypertension, and family history. It defines normal renal function values and stages of acute kidney injury caused by prerenal, intrarenal, or postrenal factors. Chronic kidney disease is identified by a GFR below 60mL/min for over 3 months. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are renal replacement therapies for kidney failure, with hemodialysis using an arteriovenous fistula to cleanse the blood and peritoneal dialysis exchanging fluid through the peritoneum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesWeek 4
Uploaded by
api-530814583This document discusses renal diseases and renal failure. It outlines risk factors for renal disorders like diabetes, hypertension, and family history. It defines normal renal function values and stages of acute kidney injury caused by prerenal, intrarenal, or postrenal factors. Chronic kidney disease is identified by a GFR below 60mL/min for over 3 months. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are renal replacement therapies for kidney failure, with hemodialysis using an arteriovenous fistula to cleanse the blood and peritoneal dialysis exchanging fluid through the peritoneum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
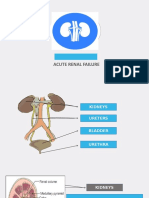
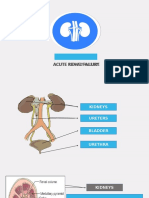
Week 4: renal diseases & renal failure
● Risk factors associated with renal disorders
○ Chemical or environmental toxin exposure, contact sports, diabetes mellitus,
family history of renal disease, frequent UTIs, heart failure, high-sodium diet,
hypertension, medications, polycystic kidney disease, trauma, urolithiasis or
nephrolithiasis
● Normal renal function values
○ BUN - 10-20 mg/dL
○ Serum creatinine level 0.5-1.1 mg/dL (female); 0.6-1.2 mg/dL (male)
○ BUN/creatinine ratio 6-25
● Acute Kidney Injury
○ Rapid loss of kidney function from renal cell damage
○ Occurs abruptly and can be reversible
○ Causes
■ Prerenal: outside the kidney, caused by intravascular volume depletion
such as blood loss, decreased cardiac output, dehydration, decreased
peripheral vascular resistance, decreased renovascular blood flow
■ Intrarenal: within the parenchyma of the kidney; caused by tubular
necrosis, prolonged prerenal ischemia, intrarenal infection or obstruction,
and nephrotoxicity
■ Postrenal: between the kidney and urethral meatus, such as bladder neck
obstruction, bladder cancer, calculi and postrenal infection
○ Phases of AKI
■ Oliguric
● Sudden decrease in urine output; less than 400mL/day
● Signs of excess fluid volume, uremia, metabolic acidosis,
neurological changes, pericarditis
● Interventions
○ Restrict fluid intake to 400-1000mL, administer meds such
as diuretics to increase blood flow and diuresis of retained
fluid and electrolytes
■ Diuretic
● Urine output rises slowly, followed by diuresis (4-5L/day)
● Dehydration, hypovolemia, hypotension, and tachycardia can
occur
● Interventions
○ Administer IV fluids as prescribed to replace losses
■ Recovery
● Complete recovery may take up to 1-2 years
● Urine volume returns to normal, memory improves, strength
increases
■ Interventions
● Monitor vital signs, urine, intake and output, daily weight, monitor
kidney labs, urinalysis, LOC, infection
● Administer prescribed diet (low - moderate protein and high
carbohydrate)
● Restrict potassium and sodium intake
● Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
○ Slow, progressive, irreversible loss of kidney function GFR less than or equal to
60mL/min for 3 months or longer, occurs in stages
○ Special problems in kidney failure
■ Activity intolerance & insomnia, anemia, GI bleeding, hyperkalemia,
hypermagnesemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypertension, hypervolemia,
hypocalcemia, hypovolemia, infection, metabolic acidosis, muscle cramps,
neurological changes, ocular irritation, potential for injury, pruritus,
psychosocial problems
○ Primary causes
■ May follow AKI, DM & other metabolic disorders, hypertension, chronic
urinary obstruction, recurrent infections, renal artery occlusion,
autoimmune disorders
○ Interventions
■ Same as AKI
■ Provide oral care, provide skin care, teach client about fluid & dietary
restrictions and daily weights
● Hemodialysis
○ Intermittent renal replacement therapy involving the process of cleansing the
client’s blood
○ Cleanses the blood of accumulated waste products
○ Removes byproducts of protein metabolism such as urea, creatinine, & uric acid
○ Maintains or restores buffer system of the body
○ Corrects electrolyte levels
○ Uses an arteriovenous fistula
■ Permanent access of choice for dialysis
■ Surgically created by anastomosis of a large artery and vein in the arm
● Peritoneal dialysis
○ Type of dialysis where the peritoneum in a person's abdomen is used as the
membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the
blood
○ Solution for this is STERILE!!
○ Increase in proteins for patients on peritoneal dialysis
You might also like
- Acute Kidney Injury: Sarah Abigail C. Ong Siu Second Year ResidentDocument41 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Sarah Abigail C. Ong Siu Second Year ResidentSarah Ong SiuNo ratings yet
- MSN PresentationDocument36 pagesMSN Presentationsanangamba akhamNo ratings yet
- Definition-Acute Kidney InjuryDocument6 pagesDefinition-Acute Kidney Injuryashi leginNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure March 2020Document46 pagesRenal Failure March 2020dicksonsamboNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) :: FeaturesDocument3 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) :: FeaturesDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure PDFDocument6 pagesAcute Renal Failure PDFChris PaguioNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes: Balance and DisturbanceDocument47 pagesFluid and Electrolytes: Balance and DisturbanceSavanna ChambersNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Dr. Jayachandran N Assistant Professor Dept. of MedicineDocument22 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Dr. Jayachandran N Assistant Professor Dept. of MedicineAnandhapadmanabhan KSNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument50 pagesAcute Renal FailureMUNA NNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument30 pagesAcute Renal FailureJerinNo ratings yet
- Renal EmergenciesDocument63 pagesRenal EmergenciesSandeepa WeerawarnaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument6 pagesHeart FailureErrol JasonNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis: Lamya Alnaim, PharmdDocument86 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Lamya Alnaim, PharmdNzau MuangeNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument35 pagesAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- Renal FailureDocument29 pagesRenal FailureMohammad Doctor CabdiraxmanNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument45 pagesAcute Renal FailureRubinNo ratings yet
- Renal NotesDocument11 pagesRenal NotesPatty Pasarilla Passehl100% (2)
- Presentation مسنين عمليDocument19 pagesPresentation مسنين عمليzoubia209No ratings yet
- DD of Acute Kidney Injury: Mobashirul Islam - Roll No. 91 Moksha Manglani - Roll No. 92Document17 pagesDD of Acute Kidney Injury: Mobashirul Islam - Roll No. 91 Moksha Manglani - Roll No. 92122ritik goyalNo ratings yet
- Renal DisordersSDocument29 pagesRenal DisordersSpastrokateNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation (ARF & CRF), Nephrology, 2017Document60 pagesClinical Presentation (ARF & CRF), Nephrology, 2017mohameeedar1No ratings yet
- AKIDocument22 pagesAKISatyabrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Renal: Anatomy + PhysiologyDocument29 pagesRenal: Anatomy + PhysiologyAdriana ChasiguanoNo ratings yet
- Renal IiDocument24 pagesRenal Iijacobcw2003No ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument48 pagesRenal FailureCindy MamalangkasNo ratings yet
- Acute Chronic Kidney InjuryDocument29 pagesAcute Chronic Kidney InjuryPriya GKNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Renal Failure and Renal Transplantation: Rama Shehatha 317i4Document27 pagesAcute and Chronic Renal Failure and Renal Transplantation: Rama Shehatha 317i4Mohammad ShehathaNo ratings yet
- CirrhosisDocument10 pagesCirrhosisJames FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases " Review "Document22 pagesRenal Diseases " Review "api-3827876No ratings yet
- Renal Faliure 1Document50 pagesRenal Faliure 1180045No ratings yet
- Renal Failure PresentationDocument110 pagesRenal Failure PresentationMusa yohana100% (1)
- Care of The Patient With Renal and Urinary Disorders - HandoutDocument52 pagesCare of The Patient With Renal and Urinary Disorders - HandoutAaron Ramirez LuNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument38 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryLyssaMarieKathryneEgeNo ratings yet
- Acuterenalfailure2filesmerged 190509071023Document85 pagesAcuterenalfailure2filesmerged 190509071023ellise abundoNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Prepared By, Gayathri R 2 Yr MSC (N) UconDocument41 pagesPrepared By, Gayathri R 2 Yr MSC (N) UconGayathri RNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome + ArfDocument64 pagesNephrotic Syndrome + ArfkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Management of Renal Failure and Replacement Therapy For Stage V Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument30 pagesPathogenesis and Management of Renal Failure and Replacement Therapy For Stage V Chronic Renal DiseaseByzantine Wulandari ParubakNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure: DR Uzma BanoDocument29 pagesRenal Failure: DR Uzma BanoUzma BanoNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury - TransesDocument3 pagesAcute Kidney Injury - Transesmelba040510No ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Chronic Renal FailureDocument48 pagesAcute Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failurekimchi girlNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Presented by RLE 5Document24 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis: Presented by RLE 5April Mae Magos LabradorNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument18 pagesChronic Renal FailureJoan Carla BocoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 AntihypertensiveDocument18 pagesLECTURE 8 AntihypertensiveanaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument90 pagesEndocrine DisordersdaisyNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Kidney DiseasesDocument34 pagesDrug Induced Kidney DiseasesManhal A AbdulkaderNo ratings yet
- Seminar On NEPHRITISDocument33 pagesSeminar On NEPHRITISyeon kookminNo ratings yet
- EndokrinologiDocument28 pagesEndokrinologiChris LaurenNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument35 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseNur'ain Nabila100% (2)
- What Is: Acute Renal FailureDocument31 pagesWhat Is: Acute Renal FailureDanielle KayeNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseasesDocument26 pagesRenal Diseasesjpatel24No ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument35 pagesRenal FailureJawad SaleemNo ratings yet
- NEPHROSISDocument31 pagesNEPHROSISvinnu kalyanNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi 1 11. Obat Diuretika: Apt. NUR ATIKAH, M.Sc. 2021Document20 pagesFarmakologi 1 11. Obat Diuretika: Apt. NUR ATIKAH, M.Sc. 2021Zona DiskusiNo ratings yet
- World Kidney DayDocument61 pagesWorld Kidney DayfatimaNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disease by Rehana Mam.Document22 pagesKidney Disease by Rehana Mam.raisameh23No ratings yet
- What Is: Acute Renal Failure Acute Kidney InjuryDocument32 pagesWhat Is: Acute Renal Failure Acute Kidney InjuryCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument54 pagesChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Week 9Document3 pagesWeek 9api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 10Document3 pagesWeek 10api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 8Document3 pagesWeek 8api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 7Document3 pagesWeek 7api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2api-530814583No ratings yet
- Extra WeekDocument3 pagesExtra Weekapi-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 3Document2 pagesWeek 3api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 1Document1 pageWeek 1api-530814583No ratings yet
- Remediation 480Document2 pagesRemediation 480api-530814583No ratings yet
- Mga SALITANG TAGALOG Set 1 (English-Tagalog Words)Document8 pagesMga SALITANG TAGALOG Set 1 (English-Tagalog Words)MsDs ReadinglabNo ratings yet
- BL Bosch Esp 5.3Document55 pagesBL Bosch Esp 5.3Abi ArbianaNo ratings yet
- Sea Lions in Danger of Extinction in Chimbote: National University of Santa Language Center CeidunsDocument12 pagesSea Lions in Danger of Extinction in Chimbote: National University of Santa Language Center CeidunsLuis Giancarlo Saénz GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Weekly Training Schedule - Samples: Warmup SMR (Foam Roll, LAX Ball,) 5-10 Rolls or 30sec EachDocument6 pagesWeekly Training Schedule - Samples: Warmup SMR (Foam Roll, LAX Ball,) 5-10 Rolls or 30sec Eachogalloza100% (2)
- Research Paper Electric Car 1Document13 pagesResearch Paper Electric Car 1api-519881982No ratings yet
- JD 90 - 40 Rows 3 - 6 On 8 RowDocument7 pagesJD 90 - 40 Rows 3 - 6 On 8 Rowalaynnastaabx786No ratings yet
- GIS IN URBAN PLANNING - ASSIGNMENT 1 - ATHIRA & CHIPPY - Planning Techniques PDFDocument10 pagesGIS IN URBAN PLANNING - ASSIGNMENT 1 - ATHIRA & CHIPPY - Planning Techniques PDFathirarejizachariahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Formulas and Problems Engineering Mechanics 2 by - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inDocument219 pagesMechanics of Materials Formulas and Problems Engineering Mechanics 2 by - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inHữu Danh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Frame 8124B Winding 6S: Arep/PmgDocument3 pagesFrame 8124B Winding 6S: Arep/PmgscribdledeeNo ratings yet
- List Perushaan Cargil Global MillDocument42 pagesList Perushaan Cargil Global MilljefriNo ratings yet
- Site of The First MassDocument39 pagesSite of The First MassCherry Mae PalilioNo ratings yet
- Effect of Kitten Vocalizations On Maternal Behavior: Ron H AskinsDocument9 pagesEffect of Kitten Vocalizations On Maternal Behavior: Ron H AskinsAne MagiNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid BacteriaDocument628 pagesLactic Acid BacteriaPat Chuthamas100% (3)
- Ags PrimusDocument1 pageAgs PrimusGireesh HegdeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Hospitality IndustryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To The Hospitality IndustryHarmohinder BhinderNo ratings yet
- Elaboration of Actual FreedomDocument197 pagesElaboration of Actual FreedomJustine50% (2)
- Tuntungin-Putho Integrated National High SchoolDocument6 pagesTuntungin-Putho Integrated National High SchoolMARIA PAMELA SURBANNo ratings yet
- BK 700 707 Dyna-Jet Tube Tester Repair and CalibrationDocument14 pagesBK 700 707 Dyna-Jet Tube Tester Repair and CalibrationKaj LydestadNo ratings yet
- DEP Spec IndexDocument33 pagesDEP Spec IndexAzhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kunci Bahasa Inggris 6 K13 32B - HeriDocument13 pagesKunci Bahasa Inggris 6 K13 32B - HeriVani AnggaNo ratings yet
- JTlecture 01 PrintDocument17 pagesJTlecture 01 PrintJae-Soo ChangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Copper Coordination CompoundDocument4 pagesAnalysis of A Copper Coordination Compoundapi-340385716No ratings yet
- SATIP-P-104-10 Rev 7 FinalDocument2 pagesSATIP-P-104-10 Rev 7 FinalHatemS.MashaGbeh0% (1)
- STUDIOBRICKS QUOTE ONE ONE PLUS Automized Quote10Document38 pagesSTUDIOBRICKS QUOTE ONE ONE PLUS Automized Quote10Brady WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Steel and Fury (DCC)Document57 pagesSteel and Fury (DCC)Fiddles McHorsedung100% (3)
- A Healthy Man Is A Happy ManDocument2 pagesA Healthy Man Is A Happy ManYan KyawNo ratings yet
- Second Quantization Representation For Classical Many-Particle System PDFDocument14 pagesSecond Quantization Representation For Classical Many-Particle System PDFAzhar MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A Study of Permeability and Tortuosity of Concrete: August 2005Document10 pagesA Study of Permeability and Tortuosity of Concrete: August 2005khawar aliNo ratings yet
- Aclf: Pengelolaan Terkini Dan Hentikan Nekroinflamasi Pada Pasien HepatitisDocument17 pagesAclf: Pengelolaan Terkini Dan Hentikan Nekroinflamasi Pada Pasien Hepatitistitis dwi tantiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat SG ReportDocument544 pagesGujarat SG ReporthareshNo ratings yet