Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2
Uploaded by
api-5308145830 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesThis document discusses fluid balance and electrolyte imbalances in the body. It covers the different fluid compartments, conditions that can cause fluid shifts like third spacing, edema, and factors that influence fluid intake and output. Signs of fluid volume deficit and excess are provided. Common electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and hypernatremia are described along with their contributing factors and clinical manifestations. Balance of important electrolytes such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium are also reviewed.
Original Description:
Original Title
week 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses fluid balance and electrolyte imbalances in the body. It covers the different fluid compartments, conditions that can cause fluid shifts like third spacing, edema, and factors that influence fluid intake and output. Signs of fluid volume deficit and excess are provided. Common electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and hypernatremia are described along with their contributing factors and clinical manifestations. Balance of important electrolytes such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium are also reviewed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesWeek 2
Uploaded by
api-530814583This document discusses fluid balance and electrolyte imbalances in the body. It covers the different fluid compartments, conditions that can cause fluid shifts like third spacing, edema, and factors that influence fluid intake and output. Signs of fluid volume deficit and excess are provided. Common electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and hypernatremia are described along with their contributing factors and clinical manifestations. Balance of important electrolytes such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium are also reviewed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Week 2: fluid & electrolytes
● Body fluid compartments
○ Intravascular: fluid inside a blood vessel
○ intracellular : fluid inside cells
○ Extracellular: fluid outside of the cells
● Third space
○ Accumulation of and sequestration of trapped extracellular fluid in an actual or
potential body space as a result of disease or injury
○ Fluid may be trapped in body spaces such as the pericardial, pleural, peritoneal, or
joint cavities, the bowel, or abdomen or within soft tissues
● Edema
○ Excess of accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces
○ Localized: in one local area of the body as a result of traumatic injury from
accident or surgery
○ Generalized: excessive accumulation of fluid throughout the body
● Body fluid
○ Infants and older adults are at a higher risk for fluid-related problems
● Intake and Output
○ Insensible water loss: immeasurable water loss through sweating or breathing
○ Average adult intake and output is around 2500-3000mL
○ Minimum output for adults should be around 30mL/hour
● Balance
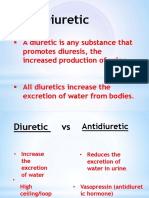
○ Kidneys work to balance fluid levels
○ Antidiuretic hormone - produced by pituitary gland to prevent more fluid loss;
holds onto fluids instead of voiding
● Fluid Volume Deficit Signs
○ Thready, tachy pulse, decreased BP, dysrhythmias,
○ Increased respiration rate and depth of breaths, dyspnea
○ Decreased CNS activity, feverm skeletal muscle weakness
○ Decreased urinary output
○ Dry skin, dry mouth, poor turgor
○ Decreased motility and diminished bowel sounds, constipation, thirst, decreased
body weight
○ Increased serum osmolality, hematocrit, BUN, serum sodium, urinary specific
gravity
● Fluid Volume Excess Signs
○ Bounding, increased pulse rate, elevated BP, distended neck & hand veins,
elevated CVP, dysrhythmias
○ Increased respiratory rate (shallow), dyspnea, crackles
○ Altered LOC, headache, visual disturbances, skeletal muscle weakness,
paresthesia
○ Increase urinary output
○ Pitting edema, pale, cool skin
○ Increased gastric motility, diarrhea, increased body weight, liver enlargement,
ascites
○ Decreased serum osmolality, hematocrit, BUN, serum sodium, urinary specific
gravity
Imbalance Level Contributing Factors Clinical Manifestations
Hypokalemia Potassium Inadequate potassium Fatigue, muscle
<3.5 mEq/L intake, diarrhea, weakness, Vfibb,
vomiting, chronic renal paresthesia, leg cramps,
disease, gastric suction, constipation, decreased
polyuria, corticosteroid, BP
digoxin
Hyperkalemia Potassium Excessive potassium Vague muscle weakness,
>5 mEq/L intake, renal failure, nausea, initial tachycardia
Addison’s disease, burns, followed by bradycardia,
use of dysrhythmia, flaccid
potassium-conserving paralysis, paresthesia,
diuretics, ACE inhibitors, irritability, anxiety
NSAIDS, chronic heparin
therapy
Hyponatremia Sodium SIADH, Diuretic therapy, Lethargy, nausea, apathy,
<135 mEq/L renal disease, excessive muscle cramps, muscular
sweating, hyperglycemia, twitching confusion
NPO, congestive heart
failure
Hypernatremia Sodium Water deficit, diabetes Elevated temp, lethargy
>145 mEq/L insipidus, diarrhea, or restlessness, thirst, dry,
hyperventilation, flushed skin, weakness,
excessive administration irritability, hyperreflexia,
of corticosteroids, ataxia, remors,
sodium bicarbonate, or tachycardia. Hyper or
sodium chloride hypotension, oliguria,
pulmonary edema
Hypocalcemia Calcium Inadequate intake or Confusion, paresthesia,
<8.5 mg/dl absorption, bone or muscle spasm,
soft-tissue deposition, hyperreflexia
blood transfusions,
decreased PTH &
vitamin D
Hypercalcemia Calcium Hyperparathyroidism, Fatigue, weakness,
>12 mg/dl bone metastasis, lethargy. Anorexia,
sarcoidosis. Excess nausea, constipation
vitamin D
Hypophosphatemia Phosphate Intestinal malabsorption, Thrombocytopenia,
<2 mg/dl increased renal excretion muscle weakness,
irritability, confusion,
numbness
Hyperphosphatemia Phosphate Chemotherapy, laxatives, Confusion, paresthesia,
>4.5 mg/dl hypoparathyroidism muscle spasm,
hyperreflexia
Hypomagnesemia Magnesium Malnutrition, intestinal Depression, confusion,
<1.5 mEq/L malabsorption, irritability, hyperreflexia,
alcoholism, renal muscle weakness, ataxia,
dysfunction, use of loop nystagmus, tetanus,
and thiazide diuretic convulsions
agents
Hypermagnesemia Magnesium Renal failure, excessive Nausea, vomiting, muscle
>2.5 mEq/L antacid intake weakness
You might also like
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document46 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Gabrielle Frances FernandezNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes 5Document14 pagesFluids & Electrolytes 5Justin Angelo SildoraNo ratings yet
- Major Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument5 pagesMajor Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancestheglobalnursingNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument3 pagesElectrolytesgheannieveleen26No ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab FindingsDocument4 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab Findingsworleyb83No ratings yet
- Basic Nursing NotesDocument4 pagesBasic Nursing Notesbonggoi100% (1)
- Electrolyte SummaryDocument3 pagesElectrolyte SummaryDeanne Morris-DeveauxNo ratings yet
- SodiumDocument3 pagesSodiumEmily FernandezNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument69 pagesFluid & ElectrolytePaul Ebenezer100% (1)
- P ImbalancesDocument15 pagesP ImbalancesglamyposhNo ratings yet
- Hipo Parati Roid Is MoDocument7 pagesHipo Parati Roid Is MoLizbeth CunalataNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure and Renal Disorders - 123159Document25 pagesChronic Renal Failure and Renal Disorders - 123159Syed Yusuf SyedNo ratings yet
- Blok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitDocument15 pagesBlok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitGogmaFirmansyahSiraitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CKDDocument53 pagesLecture 3 CKDPharmswipe KenyaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy Minilecture - Kelompok Mugi N.H PDFDocument35 pagesFluid Therapy Minilecture - Kelompok Mugi N.H PDFMugi NurhudaNo ratings yet
- C5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)Document44 pagesC5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)coco brillqnteNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Parathyroid GlandsDocument52 pagesDisorders of Parathyroid GlandsDr. Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Glands: Presented By: Dr. Mohammed Alshehri Pgy2Document28 pagesParathyroid Glands: Presented By: Dr. Mohammed Alshehri Pgy2Omar Alruwaili100% (1)
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- 2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical PatientDocument18 pages2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical Patientjqmrtc8cfgNo ratings yet
- Renal DisordersSDocument29 pagesRenal DisordersSpastrokateNo ratings yet
- Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageFurosemide (Lasix)E100% (3)
- Fluid Imbalance 2Document10 pagesFluid Imbalance 2saranya amuNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismDocument26 pagesHypercalcemia Secondary To Primary HyperparathyroidismClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte ChartDocument1 pageFluid and Electrolyte ChartJenny Varghese100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarDocument24 pagesFluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarNupurshinjiniNo ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia Handouts Group 9Document3 pagesHypermagnesemia Handouts Group 9Risha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes TableDocument4 pagesElectrolytes TableMeg NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolyteDocument16 pagesFluids and ElectrolytechijklNo ratings yet
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 pagesNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- Fluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetDocument8 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Cram SheetChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte JournalDocument10 pagesFluid and Electrolyte JournalAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Hyperparathyroidism and HypoparathyroidismDocument44 pagesHyperparathyroidism and Hypoparathyroidismshweta singhNo ratings yet
- 60 Side Effects Every Pharmacist Should KnowDocument10 pages60 Side Effects Every Pharmacist Should KnowMuhammad Noman bin FiazNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDocument157 pagesFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- Diana's Renal DiseasesDocument9 pagesDiana's Renal DiseasesdhyltonNo ratings yet
- Electrolye CheatDocument6 pagesElectrolye CheatKatie RoyNo ratings yet
- Diuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatDocument17 pagesDiuretic: A Diuretic Is Any Substance ThatAnalizaNo ratings yet
- Gangguan ElektrolitDocument27 pagesGangguan ElektrolitNatalia Lee100% (1)
- 2.3 HYPOCALCEMIA and HYPERCALCEMIADocument7 pages2.3 HYPOCALCEMIA and HYPERCALCEMIABooz Waief CaluzaNo ratings yet
- RenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Document7 pagesRenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Saheed jaladeNo ratings yet
- Etiology: I. Predisposing FactorDocument12 pagesEtiology: I. Predisposing FactorIbcp SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocument98 pagesDrugs Acting On Renal SystemIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism: DR GwerDocument14 pagesHypoparathyroidism: DR GwerMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Wk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument65 pagesWk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Major Hormone Secreting Glands: 1. HypothalamusDocument5 pagesEndocrine System: Major Hormone Secreting Glands: 1. HypothalamusSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument43 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceJoshua JoNo ratings yet
- Normal Labs ValueDocument14 pagesNormal Labs ValueMarkhistun NadhirohNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Uremia SyndromeMartien Silviandy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes Slide 21Document111 pagesElectrolytes Slide 21Elaisha Mae C. CarsulaNo ratings yet
- NM 22 Urate 2007Document35 pagesNM 22 Urate 2007api-26938624No ratings yet
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument118 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceRenuga SureshNo ratings yet
- Clinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsFrom EverandClinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hyperparathyroidism, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hyperparathyroidism, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Week 10Document3 pagesWeek 10api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 9Document3 pagesWeek 9api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 8Document3 pagesWeek 8api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 7Document3 pagesWeek 7api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 4Document3 pagesWeek 4api-530814583No ratings yet
- Extra WeekDocument3 pagesExtra Weekapi-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 1Document1 pageWeek 1api-530814583No ratings yet
- Week 3Document2 pagesWeek 3api-530814583No ratings yet
- Remediation 480Document2 pagesRemediation 480api-530814583No ratings yet
- CARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedDocument117 pagesCARDIOPULMONARY BYPASS - CompressedBayan TahaNo ratings yet
- Costing of Sea Water RO Plant KPT Manora Design at 100,000 IGPD at 35,000 PPMDocument3 pagesCosting of Sea Water RO Plant KPT Manora Design at 100,000 IGPD at 35,000 PPMMohtashim KazmiNo ratings yet
- ENGR 260 - Circuits and Devices: COURSE SYLLABUS - Spring 2015Document4 pagesENGR 260 - Circuits and Devices: COURSE SYLLABUS - Spring 2015saintNo ratings yet
- Harga Satuan Precast 2017Document2 pagesHarga Satuan Precast 2017GenTigaBrotherhood BantenNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your Own Voodoo DollsDocument4 pagesHow To Make Your Own Voodoo DollsJohn Willey100% (2)
- Gec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationDocument4 pagesGec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationClarynce MojadoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture 3 - NotesDocument14 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture 3 - NotesCraftychemistNo ratings yet
- Manual of Microbiological Culture Media - 9Document1 pageManual of Microbiological Culture Media - 9Amin TaleghaniNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument23 pagesThermal Engineeringakeey4uNo ratings yet
- Monobond Etch&PrimeDocument23 pagesMonobond Etch&Primehot_teethNo ratings yet
- List of Sports Goods of ExportersDocument389 pagesList of Sports Goods of ExportersM.Arsalan Hassan100% (1)
- Project Work On Chemistry: Change of PH During Formation of Curd From MilkDocument16 pagesProject Work On Chemistry: Change of PH During Formation of Curd From MilkYoezer Pelden100% (1)
- Proposed 2-Storey Residence: 710 Burgos St. Paliwas, Obando Bulacan Owner: Mr. & Mrs. Pascualito SantiagoDocument14 pagesProposed 2-Storey Residence: 710 Burgos St. Paliwas, Obando Bulacan Owner: Mr. & Mrs. Pascualito SantiagoAlfie Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- The IMA Volumes in Mathematics and Its Applications: Avner Friedman Willard Miller, JRDocument172 pagesThe IMA Volumes in Mathematics and Its Applications: Avner Friedman Willard Miller, JRPedro PereyraNo ratings yet
- Dine Catalogue Eng 20 21Document318 pagesDine Catalogue Eng 20 21l4k9xxxNo ratings yet
- Booklet Course 8 Chapter 5Document18 pagesBooklet Course 8 Chapter 5PaolaNo ratings yet
- Automated Sand Gravity Sand Filter SystemDocument58 pagesAutomated Sand Gravity Sand Filter SystemMichaelNo ratings yet
- Weather Proof LouvreDocument6 pagesWeather Proof Louvrentt_121987No ratings yet
- Digital Photography in OrthodonDocument48 pagesDigital Photography in OrthodonSrinivasan BoovaraghavanNo ratings yet
- LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM) : CalculusDocument88 pagesLSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM) : CalculusDharwyn Avy Advento CalmaNo ratings yet
- RmitDocument9 pagesRmitrajeevermaNo ratings yet
- Falkland War - A Brief Overview DraftDocument119 pagesFalkland War - A Brief Overview DraftKanthan JeyaprakashNo ratings yet
- DD1HW DM SourcebookDocument130 pagesDD1HW DM Sourcebookfuck uNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument541 pagesLinear Regressionaarthi devNo ratings yet
- Symbolism and Color in Folk ArtDocument11 pagesSymbolism and Color in Folk ArtshandryssNo ratings yet
- Growth RoataionDocument148 pagesGrowth Roataiondr_nilofervevai2360100% (2)
- Food and DrinkDocument5 pagesFood and DrinkHec Al-HusnaNo ratings yet
- Design of BeamsDocument112 pagesDesign of BeamskbkwebsNo ratings yet
- Vodka and Vanilla Blancmange With Warm RaspberriesDocument6 pagesVodka and Vanilla Blancmange With Warm RaspberriesFranca AkNo ratings yet
- TA202A - Manufacturing Processes II Machining Processes and MachinesDocument16 pagesTA202A - Manufacturing Processes II Machining Processes and Machinesprashant vermaNo ratings yet