Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ah - Painters - Cavin Hamilton
Uploaded by
Željko ĐurićOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ah - Painters - Cavin Hamilton
Uploaded by
Željko ĐurićCopyright:
Available Formats
AH - PAINTERS - CAVIN HAMILTON
Gavin Hamilton (1723, Lanarkshire – 4 January 1798, Rome) was a Scots neoclassical history painter, who is more widely remembered for his hunts
for antiquities in the neighbourhood of Rome. These roles in combination made him an arbiter of neoclassical taste. Gavin Hamilton was born in Lanark
in 1723, into the prominent family for whom the town of Hamilton, South Lanarkshire was named, the Hamiltons of Murdiston, linked to the Dukes of
Hamilton.
By 1744 he was in Italy, and probably studied in Rome in the studio of Agostino Masucci. From 1748 to 1750 he shared an apartment with James Stuart,
Matthew Brettingham and Nicholas Revett, and with them visited Naples and Venice. On returning to Britain, he spent several years portrait-painting in
London (1751–1756). At the end of that period, he returned to Rome. He lived there for more than the next four decades, until his death in 1798.
Aside from a few portraits of friends, the Hamilton family, and British people on the Grand Tour, most of his paintings, many of which are very large,
were of classical Greek and Roman subjects. His most famous is a cycle of six paintings from Homer's Iliad. As engraved by Domenico Cunego and
reproduced, these were widely disseminated widely and were enormously influential. Also influential was Hamilton's Death of Lucretia (1760s), also
known as the Oath of Brutus. This inspired a series of "oath paintings" by European painters, which included Jacques-Louis David's noted Oath of the
Horatii (1784). Like most later paintings of the scene, it placed it over Lucretia's dead body. In Livy it is made later, after the overthrow of the Roman
monarchy.
As a painter of classical subjects, Hamilton was highly regarded by Johann Joachim Winckelmann, writer Goethe, young sculptor Antonio Canova and
others in Rome, but was less appreciated in Britain. He did receive a commission to paint the altar piece of Sant'Andrea degli Scozzesi, the Scottish
national church in Rome, for which he portrayed the Martyrdom of St Andrew.
As an art dealer and archaeologist, Hamilton undertook excavations at Hadrian's Villa in Tivoli in 1769–1771, at first to acquire marble for his sculptor to
restore sculptures. His excavators reopened the outlet of a low-lying swampy area and "after some weeks' work underground by lamp-light and up to the
knees in muddy water" retrieved sculptures from the muck, where they had been thrown centuries before with timber when Christians levelled the sacred
grove.(Smith 1901:308). From 1771 Hamilton excavated other sites in the environs of Rome: Cardinal Flavio Chigi's Tor Colombaro, 1771–72, Albano,
1772, Monte Cagnolo 1772–73, Ostia 1774–75, the Villa Fonseca on the Caelian Hill in Rome, Roma Vecchia (the Villa dei Quintili), ca 1775 Castel di
Guido and Gabii.
In an age when restorations to Roman sculptures were broadly conceived and the refinishing of whole surfaces was still common practice, Hamilton
maintained a reputation as an honest man who did not tamper unduly with the sculptures that passed through his hands. Hamilton sold many of the
works of art he recovered to his British clients, most notably to Charles Townley, to whom the painter wrote: "the most valuable acquisition a man of
refined taste can make, is a piece of fine Greek Sculpture"; and to William Petty, 2nd Earl of Shelburne at Shelburne, later Lansdowne House, London.
In 1771 Hamilton discovered the Warwick Vase at Hadrian's Villa. He sold it to Sir William Hamilton, a connoisseur and the British envoy at Naples.
Gavin Hamilton worked closely with Giovanni Battista Piranesi. He was an early advisor of Antonio Canova, a young sculptor whom he met at a dinner
party in December 1779 on Canova's first visit to Rome. The painter advised the younger man to put aside his early, Rococo manner and concentrate on
conflating the study of nature with the best of antiquities and a narrow range of classic modern sculptors.
In 1785 Hamilton bought Leonardo da Vinci's Virgin of the Rocks and sent it to London for sale. His purchase was the version now held by the National
Gallery, London.
Such hunting and sale of antiquities was considered a marginally shady undertaking. Hamilton was successful in making generous offerings to the
Vatican's Museo Pio-Clementino, as the Pope claimed one-third of all excavated works and had the right to forbid export of outstanding treasures. In
addition, Hamilton paid landowners for excavating rights, so kept his peace with them.
He died in Rome on 4 January 1798.
For more information follow: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gavin_Hamilton_(artist)
https://www.nationalgalleries.org/art-and-artists/artists/gavin-hamilton
https://www.britannica.com/biography/Gavin-Hamilton
https://artuk.org/discover/artists/hamilton-gavin-17231798
https://electricscotland.com/history/other/hamilton_gavin.htm
http://www.artcyclopedia.com/artists/hamilton_gavin.html
https://www.tate.org.uk/art/artists/gavin-hamilton-234
https://oxfordindex.oup.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803095918103
https://www.invaluable.com/artist/hamilton-gavin-pcu5trxdgn/sold-at-auction-prices/
https://www.mutualart.com/Artist/Gavin-Hamilton/1606376A9D98ACBC
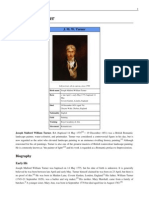
Gavin Hamilton
by Ozias Humphry,
1778, pencil, NGS
Source: Wikipedia
You might also like
- Vân_HỘI HOẠ ANH MỸDocument7 pagesVân_HỘI HOẠ ANH MỸDũng Tiến PhanNo ratings yet
- From Frith's Derby To The Cult of Beauty Christie's Victorian & British Impressionist Art SaleDocument3 pagesFrom Frith's Derby To The Cult of Beauty Christie's Victorian & British Impressionist Art SaleGavelNo ratings yet
- Art GalleriesDocument4 pagesArt GalleriesLucian GiscaNo ratings yet
- Romantic EraDocument37 pagesRomantic EraRhian Geena VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Neo ClassicismDocument37 pagesNeo ClassicismManoj RajahulliNo ratings yet
- James McNeill WhistlerDocument9 pagesJames McNeill WhistlerDavid BriceñoNo ratings yet
- NeoClassicism ArtDocument37 pagesNeoClassicism Artyokotanavasx.cvc.z422.6No ratings yet
- Oxartj 8.1.69Document3 pagesOxartj 8.1.69Juan ManuelNo ratings yet
- Rooms Richard Hamilton and PostmodernismDocument31 pagesRooms Richard Hamilton and PostmodernismMehmet SakallıNo ratings yet
- British Highlights - MergedDocument11 pagesBritish Highlights - MergedGavelNo ratings yet
- Dutch and Flemish Paintings From The HermitageDocument158 pagesDutch and Flemish Paintings From The HermitageJaneth Rodríguez Nóbrega100% (12)
- Lines Illustrations CatalogueDocument36 pagesLines Illustrations CataloguesanbornfairNo ratings yet
- The Art BookDocument518 pagesThe Art BookDuxlux Sanduzi88% (8)
- Neoclassical Literature Was Written Between 1660 and 1798. ..Document5 pagesNeoclassical Literature Was Written Between 1660 and 1798. ..Evangeline Cruz OrtizNo ratings yet
- J M W TurnerDocument12 pagesJ M W Turnerapi-193496952No ratings yet
- By: Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NYDocument37 pagesBy: Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NYGi ChoiNo ratings yet
- Neo ClassicismDocument37 pagesNeo ClassicismSuperKing CowBabyNo ratings yet
- July 2011 - CowdrayDocument5 pagesJuly 2011 - CowdrayGavelNo ratings yet
- FrenchDocument33 pagesFrenchPragati BansalNo ratings yet
- Landmark Rediscoveries & Works of Exceptional Quality Lead Old Master & British Paintings at Christie'S London in JulyDocument4 pagesLandmark Rediscoveries & Works of Exceptional Quality Lead Old Master & British Paintings at Christie'S London in JulyGavelNo ratings yet
- Background Story Classic BeautiesDocument8 pagesBackground Story Classic BeautiesAROOJ ANJUMNo ratings yet
- Aristocratic Collecting PresentationDocument8 pagesAristocratic Collecting PresentationDylan Vieites GlennonNo ratings yet
- Neoclassicism - WikipediaDocument271 pagesNeoclassicism - Wikipediaarieljay naunganNo ratings yet
- Illusion in Painting 1964Document33 pagesIllusion in Painting 1964Ljubica Velkova100% (3)
- William Blake: Seen in My Visions: A Descriptive Catalogue of PicturesFrom EverandWilliam Blake: Seen in My Visions: A Descriptive Catalogue of PicturesNo ratings yet
- An Outline of English PaintingDocument2 pagesAn Outline of English PaintingMariNo ratings yet
- The Lequesne Coffee-PotDocument11 pagesThe Lequesne Coffee-Pothbraga_sruivalNo ratings yet
- The Collection of The Late Earl of Jersey To Be Offered at Sotheby'S London in February 2013Document4 pagesThe Collection of The Late Earl of Jersey To Be Offered at Sotheby'S London in February 2013GavelNo ratings yet
- Neoclassicism's Rise and Influence in European ArtDocument6 pagesNeoclassicism's Rise and Influence in European ArtSchokobananen PaulaNo ratings yet
- William BeckfordDocument8 pagesWilliam BeckforddantevantesNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical Art: Neoclassical Art, Also Called Neoclassicism and Classicism, ADocument27 pagesNeoclassical Art: Neoclassical Art, Also Called Neoclassicism and Classicism, AKavya BansalNo ratings yet
- Ermitage - Peintures de L'ouest Européen - Livre D'art (En Anglais) (PDF)Document194 pagesErmitage - Peintures de L'ouest Européen - Livre D'art (En Anglais) (PDF)Rod100% (1)
- Christie's London Evening Auction of Post-War & Contemporary Art Totals 80.6 Million / $126.5 Million / 96.1 MillionDocument3 pagesChristie's London Evening Auction of Post-War & Contemporary Art Totals 80.6 Million / $126.5 Million / 96.1 MillionGavelNo ratings yet
- Dec 12 - Modern British Art, 12 December 2012 - ProcessedDocument4 pagesDec 12 - Modern British Art, 12 December 2012 - ProcessedGavelNo ratings yet
- CanalettoDocument2 pagesCanalettoanroseyNo ratings yet
- Old Master DrawingsDocument27 pagesOld Master Drawingsflorinj72100% (1)
- Art Movement Rococo PeriodDocument19 pagesArt Movement Rococo PeriodSarah Socorro PadillaNo ratings yet
- Ann Bermingham - The Consumption of Culture. IntroductionDocument11 pagesAnn Bermingham - The Consumption of Culture. IntroductionElizabethNo ratings yet
- Western Art Timeline (Jeremiah Pornillosa)Document25 pagesWestern Art Timeline (Jeremiah Pornillosa)Jeremiah PornillosaNo ratings yet
- Gustav Klimt: (1862-1918) Early Life and EducationDocument4 pagesGustav Klimt: (1862-1918) Early Life and EducationRachael D'costa100% (1)
- Young British Artists or Ybas: (1) London GoldsmithsDocument8 pagesYoung British Artists or Ybas: (1) London GoldsmithssubirNo ratings yet
- RomanticismDocument6 pagesRomanticism陆宇熙No ratings yet
- Revelation 1:8Document12 pagesRevelation 1:8Željko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- U-Pjt Washer-Md Simpleux SG Dc68-04204h-04 en Ro BG Cs SK LT LV Et SQ HR MK SR SLDocument364 pagesU-Pjt Washer-Md Simpleux SG Dc68-04204h-04 en Ro BG Cs SK LT LV Et SQ HR MK SR SLŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- SM Ww6000t Serbian End User 201207Document43 pagesSM Ww6000t Serbian End User 201207Željko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- sr-SP-Latn - SM 1Document32 pagessr-SP-Latn - SM 1Željko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Genesis 3:15: Verse ConceptsDocument13 pagesGenesis 3:15: Verse ConceptsŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- SM WW6000T CROATIAN End User 201207Document43 pagesSM WW6000T CROATIAN End User 201207Željko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- More Notes of A Dirty Old Man (Converted FromDocument499 pagesMore Notes of A Dirty Old Man (Converted FromŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Absurdity, Angst, and The Meaning of LifeDocument14 pagesAbsurdity, Angst, and The Meaning of LifeŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Psalm 2:7Document14 pagesPsalm 2:7Željko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Dokument 1 EesfsfDocument3 pagesDokument 1 EesfsfŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Stretched Forth Over Their Heads AboveDocument1 pageStretched Forth Over Their Heads AboveŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Isaiah's prophecy of the Messiah fulfilled in JesusDocument2 pagesIsaiah's prophecy of the Messiah fulfilled in JesusŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Peter Handke - 20 novels, plays, poetry and essaysDocument2 pagesPeter Handke - 20 novels, plays, poetry and essaysŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- MILLERDocument2 pagesMILLERŽeljko Đurić100% (1)
- Pharma KateDocument1 pagePharma KateŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Algoritmi JavaDocument5 pagesAlgoritmi JavaMuamer BesicNo ratings yet
- WHO 2019 Ncov IPC - Masks 2020.4 Eng PDFDocument16 pagesWHO 2019 Ncov IPC - Masks 2020.4 Eng PDFSyed DanishNo ratings yet
- Free Audiobook VersionDocument1 pageFree Audiobook Versioncigevoyani0% (1)
- Algoritmi JavaDocument5 pagesAlgoritmi JavaMuamer BesicNo ratings yet
- Audio Books RecommendationsDocument6 pagesAudio Books RecommendationsJacques Djurich100% (1)
- DFGDFGDFGDFHDFHDFDocument4 pagesDFGDFGDFGDFHDFHDFŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- Cyber Threat SummaryDocument9 pagesCyber Threat SummaryJacques DjurichNo ratings yet
- ZantraDocument1 pageZantraJacques DjurichNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical DevicesDocument3 pagesRhetorical DevicesPhil PhamNo ratings yet
- Distilling Systems TrifoldDocument4 pagesDistilling Systems TrifoldŽeljko ĐurićNo ratings yet
- 03-1-The Influence of Surface Treatment On Heating Effectiveness of Ceramic VesselsDocument9 pages03-1-The Influence of Surface Treatment On Heating Effectiveness of Ceramic VesselsDante .jpgNo ratings yet
- The Lippens Collection of Ancient Chinese BronzesDocument79 pagesThe Lippens Collection of Ancient Chinese BronzeslucijaNo ratings yet
- Survey and Excavations Reveal Diverse Ceramics at Cerro Narrio SiteDocument238 pagesSurvey and Excavations Reveal Diverse Ceramics at Cerro Narrio SiteBheronykaNo ratings yet
- General History of Africa Vol 2: Ancient Civilizations of AfricaDocument825 pagesGeneral History of Africa Vol 2: Ancient Civilizations of Africaalagemo100% (7)
- Egypt - The Gift of NileDocument12 pagesEgypt - The Gift of NileIoana SaracuNo ratings yet
- IskiripDocument2 pagesIskiripRomeoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Historic SheltersDocument39 pagesPre-Historic SheltersKristian IlaganNo ratings yet
- Presentation On The Egyptian CivilisationDocument9 pagesPresentation On The Egyptian CivilisationDivine MuwanguziNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamia NotesDocument4 pagesMesopotamia NotesRyan McLay100% (1)
- 2023 Rácz - Pánya Ampulla - AngolDocument8 pages2023 Rácz - Pánya Ampulla - AngolpanyaistvanNo ratings yet
- Anth 340 PPT Lecture 11 Middle Bronze 2BDocument177 pagesAnth 340 PPT Lecture 11 Middle Bronze 2Bhelios1949No ratings yet
- Prajnaparamita 8000 19Document53 pagesPrajnaparamita 8000 19အသွ်င္ ေကသရNo ratings yet
- Cauvin ReviewDocument18 pagesCauvin ReviewЛазар Лаки МарковићNo ratings yet
- (PDF) The Controversial Lintels From Great Zimbabwe PDFDocument1 page(PDF) The Controversial Lintels From Great Zimbabwe PDFEmelda MimieNo ratings yet
- LKS2 Tutankhamun Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument11 pagesLKS2 Tutankhamun Differentiated Reading Comprehension ActivityAlvaro Anton PerezNo ratings yet
- Stein 1987 (Deposits For Archaeology)Document60 pagesStein 1987 (Deposits For Archaeology)Robert Ponce VargasNo ratings yet
- Meta F. Janowitz, Diane Dallal - Tales of Gotham, Historical Archaeology, Ethnohistory and Microhistory of New York City (2013, Springer)Document375 pagesMeta F. Janowitz, Diane Dallal - Tales of Gotham, Historical Archaeology, Ethnohistory and Microhistory of New York City (2013, Springer)henriquemelatiNo ratings yet
- F. ENGEL. A Preceramic Settlement On The Central Coast of Peru Asia, Unit 1Document140 pagesF. ENGEL. A Preceramic Settlement On The Central Coast of Peru Asia, Unit 1katherine zuzuNo ratings yet
- The Deaf Centre, Love Lane, Salisbury, WiltshireDocument7 pagesThe Deaf Centre, Love Lane, Salisbury, WiltshireWessex ArchaeologyNo ratings yet
- H-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationDocument79 pagesH-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationVinayak RuhelaNo ratings yet
- 603 MesopotamiaDocument2 pages603 MesopotamiaabilodeauNo ratings yet
- Lost-Wax Casting - Wikipedia PDFDocument13 pagesLost-Wax Casting - Wikipedia PDFKyaw Bhone WinNo ratings yet
- Kutha: Kutha, Cuthah, Cuth or Cutha (Arabic: Gudua), Modern Tell Ibrahim (ArabicDocument4 pagesKutha: Kutha, Cuthah, Cuth or Cutha (Arabic: Gudua), Modern Tell Ibrahim (ArabicErdincNo ratings yet
- Nubia and Ancient EgyptDocument6 pagesNubia and Ancient EgyptDena ThomasNo ratings yet
- PP 5th Stone Age EnochDocument16 pagesPP 5th Stone Age Enochjenoch4575No ratings yet
- Beyond the Medieval Village: Landscape Diversification in Southern BritainDocument336 pagesBeyond the Medieval Village: Landscape Diversification in Southern BritainCulic DanNo ratings yet
- UCSP - Q1 - Wk4 - Social Backgorund by DaketanDocument23 pagesUCSP - Q1 - Wk4 - Social Backgorund by DaketanZeporah OrdonNo ratings yet
- GT Reading Test 5Document15 pagesGT Reading Test 5Satnam SinGhNo ratings yet
- Decipherment of Indus Script From Rosettas and Chimeras, Part 1Document46 pagesDecipherment of Indus Script From Rosettas and Chimeras, Part 1Senthil asNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Floor MosaicsDocument13 pagesConservation of Floor MosaicspostiraNo ratings yet