Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N-Butyl Alcohol (1 Sec-Butyl Alcohol (2 Tert-Butyl Alcohol (3
Uploaded by
Alyssa CubillaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N-Butyl Alcohol (1 Sec-Butyl Alcohol (2 Tert-Butyl Alcohol (3
Uploaded by
Alyssa CubillaCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT 9 – CLASSIFICATION TESTS FOR (1) order of reaction AND the (2) color of the
–OH AND C=O CONTAINING COMPOUNDS crystals
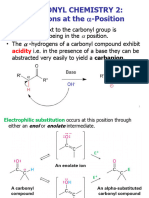
§ (1) For aldehydes, the carbonyl
A. SOLUBILITY OF R-OH IN H2O functional group is found at carbon
• Alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary and #1. For ketones, the carbonyl is
tertiary found at carbon #2.
• SAMPLES § (2) If aldehyde/ketone is
o Benzyl alcohol (1°) conjugated, the color is more
o n-butyl alcohol (1°) distinct or darker. We obtain orange
o sec-butyl alcohol (2°) crystals instead of yellow crystals.
o tert-butyl alcohol (3°)
o Ethanol (1°) D. JONES OXIDATION TEST
• FACTORS TO CONSIDER ABOUT SOLUBILITY • REAGENT: K2Cr2O7, conc. H2SO4
o POLARITY à Presence of polar functional o Can also use H2CrO4 or KMnO4
groups o These are strong oxidizing agents
§ All are polar because of the • POSITIVE RESULT: Blue-green solution
hydroxyl
o Presence of Cr2(SO4)3 (visible result)
o HYDROPHOBICITY à R groups present in
o Reduction product because the compounds
the structure of the alcohol that go under oxidation is alcohols (primary
o BRANCHING and secondary)
• All have hydroxyl so it’s not a factor we consider • REACTION: Redox
anymore
• OBJECTIVE: Check for the oxidizable and reducing
• We look at the number of R groups and the branching properties of the samples
• RESULTS (Decreasing solubility in H2O)
• RESULTS:
o Ethanol (few C atoms) o 1° ROH is oxidized to Aldehyde then to a
o tert-butyl alcohol (branching)
Carboxylic Acid (final oxidation product)
o sec-butyl alcohol (branching)
o 2° ROH is oxidized to Ketone (final oxidation
o n-butyl alcohol (branching)
product)
§ Borderline is four C atoms for
• OTHER NOTES
solubility in water
o Use PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) to
o Benzyl alcohol (presence of benzene ring)
form Aldehyde
o Formation of Cr2(SO4)3 confirms that the
B. LUCAS TEST sample is oxidizable or has reducing
• REAGENT: Conc. HCl, ZnCl2 properties
• POSITIVE RESULT: Formation of a cloudy
suspension or of two layers E. TOLLENS’ TEST
• REACTION: Nucleophilic Substitution (SN1) • REAGENTS: AgNO3, NaOH, NH4OH
o REACTIVITY: 3° > 2° > 1° o Mix AgNO3 and NaOH first and this will
• OBJECTIVE: Differentiate the types of alcohols produce a ppt
• RESULTS: o NH4OH is added to dissolve the ppt. This
o First = 3° R-OH forms the Tollens’ Reagent.
o Second = 2° R-OH o Tollens’ Reagent is the Silver Ammonia
o Third = 1° R-OH (No cloudy suspension) Complex/Ag(NH3)
2+
0
• POSITIVE RESULT: Formation of Ag
C. 2,4 – DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZONE TEST • REACTION: Redox
• REAGENT: 2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine • OBJECTIVE: Only for aldehydes
• POSITIVE RESULT: Formation of yellow/orange • POSITIVE RESULT:
crystals (ozazone crystals) o Positive for Aldehydes
o Check which ppt is darker • OTHER NOTES
o The color depends on the structure o Makes use of a weaker oxidizing agent that’s
• REACTION: Nucleophilic Addition followed by why it cannot oxidize alcohol and is used
Elimination (ANE) only for aldehydes
• OBJECTIVE: Test for the presence of carbonyl group o All aldehydes will form a silver mirror
(aldehydes and ketones)
• RESULTS: F. FEHLING’S TEST
o Positive for all aldehydes and ketones and • REAGENTS: CuSO4 pentahydrate (Fehling’s A) &
negative for alcohol Rochelle salt (sodium potassium tartrate) and NaOH
o n-butyraldehyde (Fehling’s B)
o Benzaldehyde o Purpose of adding Fehling’s B (?) is to
o Acetone prevent the precipitation of copper as cupric
o Acetophenone oxide which is color black
o Acetaldehyde o The positive result of brick red is cuprous
• OTHERS NOTES oxide
o Hydrazine reagent will add to the carbonyl • POSITIVE RESULT: Brick-red ppt
o Both aldehydes and ketones will show a o Cu2O (reduction product)
positive result but they will differ in the • REACTION: Redox
• OBJECTIVE: Determine of aldehyde or ketone
• POSITIVE RESULT:
o Positive for Aldehydes
• OTHER NOTES
o Makes use of a weaker oxidizing agent than
Tollens’
o Since it is a weaker oxidizing agent, we can
use it to differentiate Conjugated Aldehydes
from Unconjugated Aldehydes
§ Conjugated will have a (-) result
§ It has a hard time oxidizing
conjugated samples
§ Unconjugated aldehydes will still
form a brick red ppt but it takes a
longer time
o Aldehydes will be oxidized to carboxylic
acids
G. IODOFORM TEST
• REAGENT: KI, NaOCl
o NaOCl à sodium hypochlorite
o Bleach
• POSITIVE RESULT: Formation of yellow crystalline
ppt
o CHI3 (iodoform/triiodomethane)
• REACTION: Oxidation
• OBJECTIVE: Test for presence of methyl carbonyl
group in the structure
• RESULTS:
o Positive for those with methyl carbonyl after
oxidation
• OTHERS NOTES
o Isopropyl alcohol formed a yellow crystalline
ppt because it can be oxidized to a ketone
o If it’s a ketone already, it has methyl carbonyl
na.
o But not all secondary alcohols can make a
positive result. Basta if the ketone has a
methyl carbonyl after the secondary alcohol
is oxidized, dun siya magiging positive.
You might also like
- CHEMISTRY LAB REPORT ON ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY LAB REPORT ON ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLYe Woon LimNo ratings yet
- Samples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesSamples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsAlyssa CubillaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry 22Document21 pagesStereochemistry 22Ahmed SideegNo ratings yet
- Propertise of Natural FibreDocument14 pagesPropertise of Natural FibreBoier Sesh Pata100% (21)
- Chemical-Profiles by ICISDocument143 pagesChemical-Profiles by ICISk_paresh100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Alkyl Halides (CHM258 Notes)Document40 pagesChapter 6 - Alkyl Halides (CHM258 Notes)Izz002No ratings yet
- Spreading Fabric for CuttingDocument4 pagesSpreading Fabric for CuttingarunkadveNo ratings yet
- POCtheoryDocument7 pagesPOCtheoryPreetesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Idk PDFDocument25 pagesIdk PDFNael NomanNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl & C10 Carboxylic AcidsDocument46 pagesCarbonyl & C10 Carboxylic AcidsSivaneasan NadarajahNo ratings yet
- Chem 121 Carbonyl CompsDocument36 pagesChem 121 Carbonyl CompsAbubakarNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument12 pagesAldehydes and KetonesSalwa KaramanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument8 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethersmv7602456No ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 10Document29 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 10Anonymous WAnr0jvNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument19 pagesAldehydes and KetonesVaibhav TarkasbandNo ratings yet
- Chemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Organic CompoundDocument11 pagesChemical Test To Distinguish Between Pair of Organic CompoundHishq Dhiman100% (1)
- Lesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument18 pagesLesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- Organic functional group testsDocument19 pagesOrganic functional group testsThị Thu Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument95 pagesChapter 16 Aldehydes and KetonesXue XuNo ratings yet
- Chem 12 Organic DistinguishDocument5 pagesChem 12 Organic DistinguishNabaratna Biswal0% (1)
- L2 - Halogen Family - 11 MarDocument29 pagesL2 - Halogen Family - 11 MarVivek PathakNo ratings yet
- Organic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesOrganic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesNitty MeYa50% (2)
- CarbonylsDocument7 pagesCarbonylsThanadet PhongchompornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Alcohol Phenol 2022Document55 pagesChapter 8 - Alcohol Phenol 2022Hoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholsSAKET TYAGINo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document42 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Gloria NumpaqueNo ratings yet
- Things To Remember Only Alc Phe 2022-23Document17 pagesThings To Remember Only Alc Phe 2022-23poornaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-Ans SchemeDocument23 pagesLab Report-Ans SchemeAiman Syafiq100% (1)
- Chemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Document4 pagesChemical Test Orgnic Chemistry 2020Mukesh GanjawalaNo ratings yet
- Xii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSDocument10 pagesXii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSTanmay RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument102 pagesChapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsCute ni LeynesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlidesDocument63 pagesChapter 8 SlidespoojaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument52 pagesTestShivam Mittal100% (1)
- Reactions of Aldehydes & Ketones: Oxidation & ReductionDocument4 pagesReactions of Aldehydes & Ketones: Oxidation & ReductionjnfjngsdjNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CorrectDocument44 pagesCarbonyl CorrectMuhammad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument36 pagesChapter 9 Aldehydes and KetonesRoshan GillNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde & Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde & Ketone ReactionsAinsssNo ratings yet
- Chap 16 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument88 pagesChap 16 Aldehydes and KetonesAna Liza DolomandingNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones LectureDocument21 pagesAldehydes and Ketones LectureEvelyn MushangweNo ratings yet
- (Topic 2) Carbonyl Chemistry 2 2022Document31 pages(Topic 2) Carbonyl Chemistry 2 2022VirginiaNo ratings yet
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic CompoundsDocument20 pagesPurification and Characterisation of Organic CompoundspsshivaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols ChemistryDocument24 pagesAlcohols ChemistryBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument7 pagesChemistry of Aldehydes and KetonesGaelle TomkoNo ratings yet
- Ncea L3 Organic Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesNcea L3 Organic Chemistry NoteszepphiagonzalesNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A-level Chemistry Practical 8 TestsDocument6 pagesEdexcel A-level Chemistry Practical 8 TestsPOPNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Anorganik Nitrogen Dan AmmoniaDocument24 pagesPraktikum Anorganik Nitrogen Dan Ammoniaqurrota ainynNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Aldehyde and KetonesDocument12 pagesAlcohol, Aldehyde and KetonesFranky TeeNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: T C F PDocument11 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: T C F PAKSHAY JNo ratings yet
- Ch7Summary AlcoholDocument6 pagesCh7Summary AlcoholdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Single Organic Test PDFDocument15 pagesSingle Organic Test PDFgreatNo ratings yet
- Reagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-LDocument10 pagesReagent Function Notes: Any/all 2° R-Lbluebeary22No ratings yet
- Reatividade Carbonilas Chap19Document41 pagesReatividade Carbonilas Chap19darthcaedusNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of NaCl Exp.3Document9 pagesElectrolysis of NaCl Exp.3mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Woah! So Practicool!Document6 pagesWoah! So Practicool!fuzzy pillowNo ratings yet
- Formation of C-C-bonds by Base Catalysed Condensation 2022Document39 pagesFormation of C-C-bonds by Base Catalysed Condensation 2022Thabiso GwijiNo ratings yet
- Produce N2 Gas from NH4Cl & NaNO2Document30 pagesProduce N2 Gas from NH4Cl & NaNO2qurrota ainynNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 AlcoholDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 2 AlcoholChristine MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- Distinction Test Org - Chem.Document3 pagesDistinction Test Org - Chem.ht.9.hitakshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRDocument19 pagesUnit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRThilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- AldolDocument7 pagesAldolrecordNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974From EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Virtual Lab ActivityDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Virtual Lab ActivityAlyssa CubillaNo ratings yet
- Copy EXPTS 11 TO 13Document3 pagesCopy EXPTS 11 TO 13Alyssa CubillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Reactions For UnknownDocument1 pageExperiment 7 Reactions For UnknownAlyssa CubillaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Class - 12: UT 1st (2021 - 2022)Document2 pagesSubject: Chemistry Class - 12: UT 1st (2021 - 2022)Tarun Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- IAPD Plastics Intro1Document4 pagesIAPD Plastics Intro1eduardo_umNo ratings yet
- 316H Direct Roving Technical Data SheetDocument3 pages316H Direct Roving Technical Data SheetHuber Abad Alvarado CoronelNo ratings yet
- Phychem Expt #2Document7 pagesPhychem Expt #2Candace AguilarNo ratings yet
- Common Names: ApplicationsDocument3 pagesCommon Names: ApplicationsLeo CerenoNo ratings yet
- HF-4760 (BL) : Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesHF-4760 (BL) : Product Data SheetCarito LopezNo ratings yet
- De Metal de Transición de Acoplamiento Cruzado Catalizada de Arilo Reactivos de Grignard Con Fluoruros de AriloDocument7 pagesDe Metal de Transición de Acoplamiento Cruzado Catalizada de Arilo Reactivos de Grignard Con Fluoruros de AriloWillmann Jimenez MoralesNo ratings yet
- NucleotideDocument56 pagesNucleotideDhara NPNo ratings yet
- Bentone 38 - TDS - eDocument2 pagesBentone 38 - TDS - eYến HoàngNo ratings yet
- Yellow BookDocument16 pagesYellow BooksylvestreNo ratings yet
- Seat Material Guide 2" 345 Butterfly ValveDocument1 pageSeat Material Guide 2" 345 Butterfly ValveAndrey IVanNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 - Carboxylic Acids, Acid Halides, Ethers, EstersDocument4 pagesActivity 7 - Carboxylic Acids, Acid Halides, Ethers, EstersNowair TuanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Polymers CseDocument56 pagesUnit 3 Polymers CseAdam MichelleNo ratings yet
- US20150344725A1Document9 pagesUS20150344725A1Thuận LêNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing Quiz - 4Document3 pagesTextile Testing Quiz - 4ashish sharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Fillers and ReinforcementsDocument8 pages4 - Fillers and ReinforcementsGloria GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Sterlitamak Product Catalog enDocument48 pagesSterlitamak Product Catalog enMartin BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 NotesDocument4 pagesSci 10 NotesBerza Mikaela ArianneNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Constant Viscosity Natural Rubber from ClonesDocument6 pagesManufacturing Constant Viscosity Natural Rubber from ClonesEren ZorgNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CBSE Practical ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry CBSE Practical ProjectRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- Gehring Product Sheet - Vasiform - Woven GLS - V01.1Document1 pageGehring Product Sheet - Vasiform - Woven GLS - V01.1Patrick MackNo ratings yet
- Textile Internship Alok IndustriesDocument31 pagesTextile Internship Alok IndustriesAditya DevNo ratings yet
- WPT 2Document141 pagesWPT 2SalimNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Pretreatment of Textile Wet ProcessingDocument3 pagesCourse Outline Pretreatment of Textile Wet ProcessingrehanabbaciNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Polymer TestingDocument74 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Polymer Testingsergio martinezNo ratings yet
- Galvastop - TDSDocument3 pagesGalvastop - TDSThanh Hoàng GiaNo ratings yet