Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Á701Ñ Disintegration: 584 Á699ñ Density of Solids / Physical Tests USP 40
Uploaded by
Long ManOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Á701Ñ Disintegration: 584 Á699ñ Density of Solids / Physical Tests USP 40
Uploaded by
Long ManCopyright:
Available Formats
Accessed from 10.6.1.
1 by brunswick20 on Tue Feb 21 01:24:15 EST 2017
584 á699ñ Density of Solids / Physical Tests USP 40
Method
Ensure that the reference volume and the calibration volume have been determined for the gas pycnometer by an appropri-
ate calibration procedure. The test gas is helium, unless another gas is specified in the individual monograph. The temperature
of the gas pycnometer should be between 15° and 30° and should not vary by more than 2° during the course of the meas-
urement. Load the test cell with the substance under examination that has been prepared according to the individual mono-
graph. Where á699Dñ is indicated, dry the substance under examination as directed for Loss on drying in the monograph unless
other drying conditions are specified in the monograph Density of solids test. Where á699Uñ is indicated, the substance under
examination is used without drying. Use a quantity of powder recommended in the operating manual for the pycnometer.
Seal the test cell in the pycnometer, and purge the pycnometer system with the test gas according to the procedure given in
the manufacturer's operating instructions. If the sample must be degassed under vacuum, follow the recommendations in the
individual monographs and the instructions in the operating manual for the pycnometer.
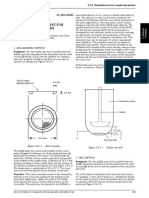
The measurement sequence above describes the procedure for the gas pycnometer shown in Figure 1. If the pycnometer
differs in operation or in construction from the one shown in Figure 1, follow the operating procedure given in the manual for
the pycnometer.
Repeat the measurement sequence for the same powder sample until consecutive measurements of the sample volume, Vs,
agree to within 0.2%. Unload the test cell and measure the final powder weight, w. Calculate the pycnometric density, r, of
the sample according to Equation 2.
General Chapters
á701ñ DISINTEGRATION
This general chapter is harmonized with the corresponding texts of the European Pharmacopoeia and/or the Japanese Phar-
macopoeia. The texts of these pharmacopeias are therefore interchangeable, and the methods of the European Pharmacopoeia
and/or the Japanese Pharmacopoeia may be used for demonstration of compliance instead of the present general chapter.
These pharmacopeias have undertaken not to make any unilateral change to this harmonized chapter.
Portions of the present general chapter text that are national USP text, and therefore not part of the harmonized text, are
marked with symbols (♦♦) to specify this fact.
This test is provided to determine whether tablets or capsules disintegrate within the prescribed time when placed in a liquid
medium at the experimental conditions presented below. ♦Compliance with the limits on Disintegration stated in the individual
monographs is required except where the label states that the tablets or capsules are intended for use as troches, or are to be
chewed, or are designed as extended-release dosage forms or delayed-release dosage forms. Determine the type of units un-
der test from the labeling and from observation, and apply the appropriate procedure to 6 or more dosage units.♦
For the purposes of this test, disintegration does not imply complete solution of the unit or even of its active constituent.
Complete disintegration is defined as that state in which any residue of the unit, except fragments of insoluble coating or cap-
sule shell, remaining on the screen of the test apparatus or adhering to the lower surface of the disk, if used, is a soft mass
having no palpably firm core.
APPARATUS
The apparatus consists of a basket-rack assembly, a 1000-mL, low-form beaker, 138 to 160 mm in height and having an
inside diameter of 97 to 115 mm for the immersion fluid, a thermostatic arrangement for heating the fluid between 35° and
39°, and a device for raising and lowering the basket in the immersion fluid at a constant frequency rate between 29 and 32
cycles per minute through a distance of not less than 53 mm and not more than 57 mm. The volume of the fluid in the vessel
is such that at the highest point of the upward stroke the wire mesh remains at least 15 mm below the surface of the fluid and
descends to not less than 25 mm from the bottom of the vessel on the downward stroke. At no time should the top of the
basket-rack assembly become submerged. The time required for the upward stroke is equal to the time required for the down-
ward stroke, and the change in stroke direction is a smooth transition, rather than an abrupt reversal of motion. The basket-
rack assembly moves vertically along its axis. There is no appreciable horizontal motion or movement of the axis from the ver-
tical.
Basket-Rack Assembly
The basket-rack assembly consists of six open-ended transparent tubes, each 77.5 ± 2.5 mm long and having an inside di-
ameter of 20.7 to 23 mm and a wall 1.0 to 2.8 mm thick; the tubes are held in a vertical position by two plates, each 88 to 92
mm in diameter and 5 to 8.5 mm in thickness, with six holes, each 22 to 26 mm in diameter, equidistant from the center of
the plate and equally spaced from one another. Attached to the under surface of the lower plate is a woven stainless steel wire
cloth, which has a plain square weave with 1.8- to 2.2-mm apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.57 to 0.66 mm. The parts
Official from null
Copyright (c) 2017 The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. All rights reserved.
Accessed from 10.6.1.1 by brunswick20 on Tue Feb 21 01:24:15 EST 2017
USP 40 Physical Tests / á701ñ Disintegration 585
of the apparatus are assembled and rigidly held by means of three bolts passing through the two plates. A suitable means is
provided to suspend the basket-rack assembly from the raising and lowering device using a point on its axis.
The design of the basket-rack assembly may be varied somewhat, provided the specifications for the glass tubes and the
screen mesh size are maintained. The basket-rack assembly conforms to the dimensions found in Figure 1.
Disks
The use of disks is permitted only where specified or allowed ♦in the monograph. If specified in the individual monograph,♦
each tube is provided with a cylindrical disk 9.5 ± 0.15 mm thick and 20.7 ± 0.15 mm in diameter. The disk is made of a
suitable transparent plastic material having a specific gravity of between 1.18 and 1.20. Five parallel 2 ± 0.1-mm holes extend
between the ends of the cylinder. One of the holes is centered on the cylindrical axis. The other holes are centered 6 ± 0.2 mm
from the axis on imaginary lines perpendicular to the axis and parallel to each other. Four identical trapezoidal-shaped planes
are cut into the wall of the cylinder, nearly perpendicular to the ends of the cylinder. The trapezoidal shape is symmetrical; its
parallel sides coincide with the ends of the cylinder and are parallel to an imaginary line connecting the centers of two adja-
cent holes 6 mm from the cylindrical axis. The parallel side of the trapezoid on the bottom of the cylinder has a length of 1.6 ±
0.1 mm, and its bottom edges lie at a depth of 1.5 to 1.8 mm from the cylinder's circumference. The parallel side of the trape-
zoid on the top of the cylinder has a length of 9.4 ± 0.2 mm, and its center lies at a depth of 2.6 ± 0.1 mm from the cylinder's
circumference. All surfaces of the disk are smooth. If the use of disks is specified ♦in the individual monograph♦, add a disk to
each tube, and operate the apparatus as directed under Procedure. The disks conform to dimensions found in Figure 11.
General Chapters
Figure 1. Disintegration apparatus. (All dimensions are expressed in mm.)
1 The use of automatic detection employing modified disks is permitted where the use of disks is specified or allowed. Such disks must comply with the require-
ments for density and dimension given in this chapter.
Official from null
Copyright (c) 2017 The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. All rights reserved.
Accessed from 10.6.1.1 by brunswick20 on Tue Feb 21 01:24:15 EST 2017
586 á701ñ Disintegration / Physical Tests USP 40
PROCEDURE
♦Uncoated Tablets
♦ Place 1 dosage unit in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if prescribed, add a disk. Operate the apparatus, using ♦water
or♦ the specified medium as the immersion fluid, maintained at 37 ± 2°. At the end of the time limit specified ♦in the mono-
graph,♦ lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets have disintegrated completely. If 1 or 2 tablets
fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets. The requirement is met if not fewer than 16 of the total
of 18 tablets tested are disintegrated.
♦Plain-Coated Tablets
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets, operating the apparatus for the time specified in the individual monograph.
Delayed-Release (Enteric-Coated) Tablets
Place 1 tablet in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if the tablet has a soluble external sugar coating, immerse the bas-
ket in water at room temperature for 5 minutes. Then operate the apparatus using simulated gastric fluid TS maintained at
37 ± 2° as the immersion fluid. After 1 hour of operation in simulated gastric fluid TS, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe
the tablets: the tablets show no evidence of disintegration, cracking, or softening. Operate the apparatus, using simulated in-
General Chapters
testinal fluid TS maintained at 37 ± 2° as the immersion fluid, for the time specified in the monograph. Lift the basket from the
fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets disintegrate completely. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat
the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Buccal Tablets
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. After 4 hours, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets
have disintegrated. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16
of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Sublingual Tablets
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. At the end of the time limit specified in the individual monograph: all of the tablets have
disintegrated. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16 of the
total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Hard Gelatin Capsules
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. Attach a removable wire cloth, which has a plain square weave with 1.8- to 2.2-mm
mesh apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.60 to 0.655 mm, as described under Basket-Rack Assembly, to the surface of the
upper plate of the basket-rack assembly. Observe the capsules within the time limit specified in the individual monograph: all
of the capsules have disintegrated except for fragments from the capsule shell. If 1 or 2 capsules fail to disintegrate completely,
repeat the test on 12 additional capsules: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 capsules tested disintegrate completely.
Soft Gelatin Capsules
Proceed as directed under Hard Gelatin Capsules.♦
á705ñ QUALITY ATTRIBUTES OF TABLETS LABELED AS HAVING A
FUNCTIONAL SCORE
PURPOSE
This chapter provides quality attributes for products with approved labeling indicating that the tablets can be split to pro-
duce multiple portions that have an accurate fractional dose (labeled as functionally scored). The label claim of the split por-
tions should be a simple fractional part of the claim for the intact tablet based on the number of scores and the size of the split
Official from null
Copyright (c) 2017 The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- 701 DisintegrationDocument4 pages701 DisintegrationbachvietdnNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Disintegration Test For Tablets and Capsules: Final Text For Revision ofDocument4 pages5.3 Disintegration Test For Tablets and Capsules: Final Text For Revision ofM. S. ChikkamaniNo ratings yet
- 711 DISSOLUTION TESTDocument15 pages711 DISSOLUTION TESTRajesh AkkiNo ratings yet
- Usp 28 DistgrDocument6 pagesUsp 28 DistgrxaverNo ratings yet
- Tablet Disintegration Test and Basket Rack AssemblyDocument2 pagesTablet Disintegration Test and Basket Rack AssemblyPhoenix100% (1)
- General Chapters 711 DISSOLUTION UspDocument17 pagesGeneral Chapters 711 DISSOLUTION UspAndrew TurnerNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Test For Solid Oral Dosage FormsDocument8 pagesDissolution Test For Solid Oral Dosage FormsPedro Marcelo Alva PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- USP40 711 DissolutionDocument13 pagesUSP40 711 Dissolutionsean_goh_8No ratings yet
- Disintegration Test for Tablets and CapsulesDocument4 pagesDisintegration Test for Tablets and CapsulesRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Test-2554700864Document12 pagesDissolution Test-2554700864Aanchal DeviNo ratings yet
- 0295-0301 (711) DissolutionDocument7 pages0295-0301 (711) DissolutionsudermanfitoNo ratings yet
- 711 USP Dissolution PDFDocument11 pages711 USP Dissolution PDFAnnisaIndahPNo ratings yet
- Disintegration test ensures tablets and capsules break down properlyDocument3 pagesDisintegration test ensures tablets and capsules break down properlyasrielisabetNo ratings yet
- 2.9.4. Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patches PDFDocument3 pages2.9.4. Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patches PDFRani RubiyantiNo ratings yet
- Change To ReadDocument15 pagesChange To ReadMin Thura OoNo ratings yet
- USP 2040 Disol y Desint SotaxDocument4 pagesUSP 2040 Disol y Desint Sotaxpatricia MedinaNo ratings yet
- 2.9.1. Disintegration of Tablets and CapsulesDocument3 pages2.9.1. Disintegration of Tablets and CapsulesPikiy PutriNo ratings yet
- Disintegration Test and Apparatus - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesDisintegration Test and Apparatus - Pharmaceutical Guidelinesmannuu00No ratings yet
- European Pharmacopoeia Disintegration Test ProceduresDocument3 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia Disintegration Test ProceduresCarlos Gómez100% (1)
- 711 Dissolution 1Document8 pages711 Dissolution 1sohrabNo ratings yet
- Change To ReadDocument15 pagesChange To Readandev RnDNo ratings yet
- General Chapters - 711 - DISSOLUTIONDocument11 pagesGeneral Chapters - 711 - DISSOLUTIONFitri WahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- About ApparaatusDocument18 pagesAbout Apparaatusachi_cantikNo ratings yet
- Appendix XII B. DissolutionDocument17 pagesAppendix XII B. Dissolutionqd2bnjdthsNo ratings yet
- 2040 Disintegration and DissolutionDocument6 pages2040 Disintegration and DissolutionWillian SilvaNo ratings yet
- 2 9 4 Dissolution Test For Transdermal PatchesDocument3 pages2 9 4 Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patchesapi-261124906No ratings yet
- SOP: USP Dissolution Instrument Calibration or PQ: Table 1: Factors Affecting The PQ ResultsDocument14 pagesSOP: USP Dissolution Instrument Calibration or PQ: Table 1: Factors Affecting The PQ ResultsMadhureddy PendleNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 1155 - 89 (Reapproved 1994) Roundness of Glass SpheresDocument3 pagesASTM D 1155 - 89 (Reapproved 1994) Roundness of Glass Spheresalin2005No ratings yet
- Mud Lab Manual - NewDocument32 pagesMud Lab Manual - Newfisco4ril67% (6)
- Norma Tension Superficial D1331Document4 pagesNorma Tension Superficial D1331cristiangggNo ratings yet
- Usp 2040 Disintegration and Dissolution of Dietary SupplementsDocument4 pagesUsp 2040 Disintegration and Dissolution of Dietary SupplementsKenneth Vergil de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- GUID - 3 en-USDocument18 pagesGUID - 3 en-USunicahayNo ratings yet
- Multispeed Universal Electromechanical Test Device CU-CD IMDocument31 pagesMultispeed Universal Electromechanical Test Device CU-CD IMkutalmış doğanNo ratings yet
- 〈711〉 DissolutionDocument17 pages〈711〉 DissolutionViridiana VázquezNo ratings yet
- Disintegration Test ApparatusDocument5 pagesDisintegration Test ApparatusabinashkumarthakurNo ratings yet
- Method of Test For Determining The Liquid Limit of Soil: (Figure 4)Document14 pagesMethod of Test For Determining The Liquid Limit of Soil: (Figure 4)Wissem TaktakNo ratings yet
- Change To Read:: USP Reference Standards 11Document14 pagesChange To Read:: USP Reference Standards 11riniNo ratings yet
- F2079Document3 pagesF2079Gustavo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Model 21150 Differential Sticking TesterDocument31 pagesModel 21150 Differential Sticking Testerwaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- USP Chapter 711 DissolutionDocument17 pagesUSP Chapter 711 DissolutionQC MahakamNo ratings yet
- Disintegration TestDocument13 pagesDisintegration TestVesh Chaurasiya100% (1)
- 183-711 - DissolutionDocument11 pages183-711 - DissolutionLong ManNo ratings yet
- Liquid Strike-Through Time 150.4-99Document5 pagesLiquid Strike-Through Time 150.4-99S6001964No ratings yet
- Uniform mass test for single-dose preparationsDocument3 pagesUniform mass test for single-dose preparationsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 814 - 95 (Reapproved 2000) Rubber Property-Vapor Transmission of Volatile LiquidsDocument2 pagesASTM D 814 - 95 (Reapproved 2000) Rubber Property-Vapor Transmission of Volatile Liquidsalin2005No ratings yet
- 〈711〉 DISSOLUTION - 221117 - 130956Document15 pages〈711〉 DISSOLUTION - 221117 - 130956Maheen TariqNo ratings yet
- Fedtmstd 191 ADocument1,110 pagesFedtmstd 191 AidflNo ratings yet
- D3148Document6 pagesD3148Jan0% (1)
- C 1182 - 91 R95 - QzexoditotfsotuDocument3 pagesC 1182 - 91 R95 - QzexoditotfsotuangeljosechuquiureNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Test: Consolidated UndrainedDocument9 pagesTriaxial Test: Consolidated UndrainedNguyễn Hòa100% (1)
- 56119096ACDocument12 pages56119096ACGustavo Godoy100% (1)
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument13 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationVenugopalan ManaladikalamNo ratings yet
- D 1823 - 95 - Rde4mjmtotuDocument3 pagesD 1823 - 95 - Rde4mjmtotujamaljamal20No ratings yet
- Astm C167 98Document2 pagesAstm C167 98tugasakhirwidiaNo ratings yet
- Particle Size AnalysisDocument31 pagesParticle Size Analysisحبيبه بيبيNo ratings yet
- Angularity Number SOPDocument5 pagesAngularity Number SOPSolankiNo ratings yet
- Official Paper Chromatography ProcedureDocument13 pagesOfficial Paper Chromatography ProcedureCarla Luna MinucheNo ratings yet
- t227 D 2 SargDocument18 pagest227 D 2 SargAngel Azathoth GoetzNo ratings yet
- Flow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsFrom EverandFlow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsNo ratings yet
- Vision Life TechnologiesDocument28 pagesVision Life TechnologiesLong ManNo ratings yet
- BNB G19Document4 pagesBNB G19Long ManNo ratings yet
- 07 Solutions For Taste-Masking and PalatabilityDocument49 pages07 Solutions For Taste-Masking and PalatabilityLong ManNo ratings yet
- Dầu cám gạo lot 2319SVA2021Document1 pageDầu cám gạo lot 2319SVA2021Long ManNo ratings yet
- Celluloses: 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All Rights ReservedDocument47 pagesCelluloses: 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All Rights ReservedLong ManNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structures Acid Function Rec. Input Processing NotesDocument5 pagesMolecular Structures Acid Function Rec. Input Processing NotesLong ManNo ratings yet
- Bio-Oil Product InformationDocument9 pagesBio-Oil Product InformationLong ManNo ratings yet
- Tác D NG C A P-Coumaric AcidDocument8 pagesTác D NG C A P-Coumaric AcidLong ManNo ratings yet
- Thakor 2016Document12 pagesThakor 2016Long ManNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Rosmarinic Acid in Rats: Frutescens Britton Var. Acuta Kudo (Labiatae), Has BeenDocument4 pagesMetabolism of Rosmarinic Acid in Rats: Frutescens Britton Var. Acuta Kudo (Labiatae), Has BeenLong ManNo ratings yet
- phát hiện vết trong Cối xay PDFDocument12 pagesphát hiện vết trong Cối xay PDFLong ManNo ratings yet
- 9P CX4 Dept PDFDocument2 pages9P CX4 Dept PDFLong ManNo ratings yet
- BioGenic Sallic 210Document2 pagesBioGenic Sallic 210Long Man100% (1)
- P CoumaricDocument15 pagesP CoumaricLong ManNo ratings yet
- Ali 2009Document5 pagesAli 2009Long ManNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis of Leaves Extract of Abutilon Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)Document10 pagesPhytochemical Analysis of Leaves Extract of Abutilon Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)Long ManNo ratings yet
- O CoumaricDocument24 pagesO CoumaricLong ManNo ratings yet
- Chemical Constituents from Abutilon indicumDocument6 pagesChemical Constituents from Abutilon indicumLong ManNo ratings yet
- HPTLC Asia 2018 - Abstract Book - FinalDocument102 pagesHPTLC Asia 2018 - Abstract Book - FinalLong ManNo ratings yet
- 10 5530pj 2015 6 2Document3 pages10 5530pj 2015 6 2BharathiNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Atibala: An OverviewDocument9 pagesReview Article: Atibala: An OverviewLong ManNo ratings yet
- Columnas CromatograficasDocument2 pagesColumnas CromatograficasDANIBATANo ratings yet
- Application Note: Ultrapure Water For HPLC AnalysisDocument5 pagesApplication Note: Ultrapure Water For HPLC AnalysisLong ManNo ratings yet
- Sampling For Chemical Analysis (Analytical Chemistry)Document9 pagesSampling For Chemical Analysis (Analytical Chemistry)Long ManNo ratings yet
- Powders and Bulk Solids Behavior Characterization PDFDocument517 pagesPowders and Bulk Solids Behavior Characterization PDFLong Man100% (1)
- 79 How To Buy HPLC Technology 2020Document18 pages79 How To Buy HPLC Technology 2020Long ManNo ratings yet
- HPLC Columns 186-234Document49 pagesHPLC Columns 186-234Long ManNo ratings yet
- Methods of Sampling & Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesMethods of Sampling & Analysis PDFAnonymous BcT42WLnNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Moisture & Water Guide: Proven Methods & ProceduresDocument12 pagesThe Ultimate Moisture & Water Guide: Proven Methods & ProceduresLong ManNo ratings yet
- Pipetting Handbook enDocument40 pagesPipetting Handbook enbluedolphin7No ratings yet
- Mec281 NotesDocument498 pagesMec281 NotesRasyidi AhmadNo ratings yet
- Conner 2013 (Enargite Treatments and Pressure Oxidation of Concentrates)Document9 pagesConner 2013 (Enargite Treatments and Pressure Oxidation of Concentrates)lakefieldNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Mechanical SealDocument20 pagesDifferent Types of Mechanical SealGlobe Star Engineers Pvt Ltd63% (8)
- Forensic Science International: Marianne Hädener, Sina Vieten, Wolfgang Weinmann, Hellmut MahlerDocument6 pagesForensic Science International: Marianne Hädener, Sina Vieten, Wolfgang Weinmann, Hellmut MahlerlunahermannNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Kvogell - L940Document5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Kvogell - L940ravikunwar14No ratings yet
- Photochemical Screening, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant PropertiesDocument23 pagesPhotochemical Screening, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant PropertiesBismark AffulNo ratings yet
- Electroorganic Chemistry: Brandon Rosen 8 November 2014Document6 pagesElectroorganic Chemistry: Brandon Rosen 8 November 2014Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations: Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesBalancing Equations: Practice ProblemsAdeenaNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheets FOR 3P-9171A D/S FOUNDATION Pump: TASNEE Petrochemicals Ethylene Project Al-Jubail, Saudi ArabiaDocument22 pagesCalculation Sheets FOR 3P-9171A D/S FOUNDATION Pump: TASNEE Petrochemicals Ethylene Project Al-Jubail, Saudi ArabiaCarlo BarceloNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae, Equations, Calculations MSDocument9 pagesChemical Formulae, Equations, Calculations MSNewton JohnNo ratings yet
- Catalogo New Foam - NewDocument20 pagesCatalogo New Foam - NewGledson TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Beckosol 12-035 Short Oil Non-Drying Alkyd: Product Code: 12035-00Document2 pagesBeckosol 12-035 Short Oil Non-Drying Alkyd: Product Code: 12035-00Manoj Lalita GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Silikoftal® HTL 1: Description SolubilityDocument1 pageSilikoftal® HTL 1: Description SolubilityWangYunNo ratings yet
- Active Knowledge Extraction From Cyclic VoltammetryDocument19 pagesActive Knowledge Extraction From Cyclic VoltammetryikoutsNo ratings yet
- Specification For Filler Metals For Brazing and Braze WeldingDocument42 pagesSpecification For Filler Metals For Brazing and Braze WeldingJoão BatistaNo ratings yet
- ONMEDDocument3 pagesONMEDTyas DesmaniasNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Synthesis, Third Edition (2012) PDFDocument2,008 pagesEnzyme Catalysis in Organic Synthesis, Third Edition (2012) PDFbluedolphin7No ratings yet
- Quarter-3-Module-3-in-Gen-Chem-2.2nd Edition 2021 - RemovedDocument16 pagesQuarter-3-Module-3-in-Gen-Chem-2.2nd Edition 2021 - RemovedEfren James ParasNo ratings yet
- SP Sendo KF 122Document5 pagesSP Sendo KF 122nurhadri azmiNo ratings yet
- Turbine Gland Seal Steam SystemDocument15 pagesTurbine Gland Seal Steam SystemFahad Khalil75% (8)
- Assignment-1: Physical Chemistry: Na (Sodium Sir)Document2 pagesAssignment-1: Physical Chemistry: Na (Sodium Sir)Aaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Photoinitiator 2Document6 pagesPhotoinitiator 2Ashwary Sheel Wali Research Scholar, Dept of Mech Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Thermochemistry ProblemsDocument1 pageThermochemistry ProblemsAmudala HemashviniNo ratings yet
- Api 570 Final Practice ExamDocument23 pagesApi 570 Final Practice ExamCong BuiNo ratings yet
- Kimia Modul Peace Cemerlang 2018Document23 pagesKimia Modul Peace Cemerlang 2018AjlaaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer Module 1 2Document9 pagesBiochem Reviewer Module 1 2cam broquelNo ratings yet
- Liu - Hydrogenation of Acrylonitrile-Butadiene Copolymer Latex Using Water-Soluble Rhodium Catalysts, 2013 +Document10 pagesLiu - Hydrogenation of Acrylonitrile-Butadiene Copolymer Latex Using Water-Soluble Rhodium Catalysts, 2013 +oreamigNo ratings yet
- Topalian Game Engine 019 by Christopher TopalianDocument352 pagesTopalian Game Engine 019 by Christopher TopalianCollegeOfScriptingNo ratings yet
- IR SPECTROSCOPY GUIDEDocument44 pagesIR SPECTROSCOPY GUIDEJHidgiwiwNo ratings yet