Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Molecules To Metabolism October 25
Uploaded by
Earl Cris RiggsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Molecules To Metabolism October 25
Uploaded by
Earl Cris RiggsCopyright:
Available Formats
WESTERN MINDANAO STATE UNIVERSITY
EXTERNAL STUDIES UNIT- PAGADIAN CITY
Name: ______________________________________________________ Score: ___________
Year & Section: ____________________________ Date: ____________
Biochemistry: Molecules to Metabolism
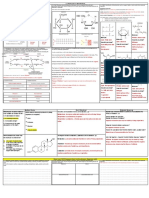
2.1.1 Biochemostry explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved. 2.1.4 Skill: Drawing molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a generalized 2.1.5 Skill: Identification of biochemicals such as sugars, lipids or amino acids from molecular
2.1.2 Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to amino acid. (only the ring forms of D-ribose, alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose are expected in diagrams.
exist. drawings).
2.1.3 Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic Identifying molecules:
acids. *Draw each of the molecules in the table: Sugars: glucose is a 6-carbon ring, ribose & deoxyribose are 5-carbon rings
Organic compounds are the basis of life on Earth. Which compound is β-glucose Ribose Lipids: triglycerides (three fatty acid tails), phospholipids (phosphate & two fatty acid tails), steroids
(multiple ring-link structures), fatty acids (hydrocarbon chain – CH2)
life based on? ………………………………….
List the four types of biological molecules: Amino acids & Dipeptides: Look for nitrogen (N), amine group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH).
1. ………………………………….
In the table below, in each row there is one sugar, one lipid and on amino acid:
2. …………………………………. Identify each molecule (specific names not required)
3. …………………………………. Highlight/ annotate what allowed you to identify the molecule.
4. …………………………………. (we will cover this in the DNA topic)
Saturated Fatty Acid Generalized Amino Acid
Molecule: Molecule: Molecule:
……………………….. ……………………….. ………………………..
How did you know? How did you know? How did you know?
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
2.1.6 Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism. 2.1.9 Application: Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can
2.1.7 Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the also be artificially synthesized. ………………………… ………………………… …………………………
formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions.
2.1.8 Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the
Use the words below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs below.
hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers.
kidneys protein organic vitalism
metabolic urea organic liver
Urea is produced by the ……………………….. breakdown of excess
……………………….. in the body. This occurs in the ……………………….. and the Molecule: Molecule: Molecule:
urea is filtered out of the blood by the ……………………….. ……………………….. ……………………….. ………………………..
How did you know? How did you know? How did you know?
Friedrich Wohler synthesized urea artificially. This was the first time that an ………………………… ………………………… …………………………
……………………….. compound had been synthesized artificially ………………………… …………………………
…………………………
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
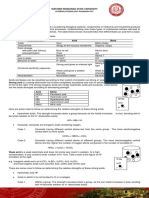
In the diagram above, what does each “E” represent? …………………………………. The theory of ……………………….. is based on the idea that living organisms which
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism produce and are composed of ……………………….. macromolecules, that can only
be synthesized within the living organisms themselves due to some ‘vital force’.
Anabolic Reaction Catabolic Reactions
Wohlers synthesis of ……………………….. falsified this idea, as he made urea (an
Break down complex molecules
organic compound produced in the body) synthetically in the lab.
Molecule: Molecule:
Condensation reactions (removal of water) Explain it yourself:
……………………….. Molecule:
………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………..
E.g. Respiration
How did you know? ………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………….. How did you know?
………………………… How did you know?
………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………
Monomers Macromolecules
………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………… ………………………… …………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………… ………………………… …………………………
Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………… ………………………… …………………………
Proteins
…………………………
Lipids
Multiple Choice Short Structured Extended Response
What feature of carbon makes it Which carbon compound produced by living Describe cell respiration in terms of metabolism. (2) Explain how Friedrich Wohler’s synthesis of urea falsified the
most suitable as a basis for life? organisms is inorganic? theory of “vitalism”. (4)
…………………………………………………………………………………………
A. Its abundance in nature ………………………………………………………………………………………… How to answer the question:
A. DNA
B. Its bonding properties Explain the theory of “vitalism”:
B. Cellulose …………………………………………………………………………………………
C. Its reactivity to light ……………………………………………………………………………...
C. Glucose …………………………………………………………………………………………
D. Its presence in the early ……………………………………………………………………………...
D. Carbon dioxide
atmosphere of the Earth ……………………………………………………………………………...
……………………………………………………………………………...
What characteristic shows that Distinguish between anabolism, catabolism and metabolism. (3)
What did Friedrich Wohler synthesise?
this molecule is cholesterol?
Metabolism:………………………………………………………………………..… ……………………………………………………………………………...
A. It is made of carbon rings.
……………………………………………………………………………………...… How is the substance that Friedrich Wohler made, usually made?
B. It has a very low proportion ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………...
of oxygen to carbon.
Anabolism:………………………….…………………………………………..……. ……………………………………………………………………………...
C. It contains OH groups as do
fatty acids. ………………………………………………………………………………………… Link it all together – how did Friedrich Wohler disprove “vitalism”?
D. It is made only of nitrogen, ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………...
oxygen and hydrogen. Catabolism…………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………...
………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………...
………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………...
Make your OWN Summary (key words, phrases, diagrams only)
2.1.1 Biochemistry explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved. 2.1.4 Skill: Drawing molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a generalized 2.1.5 Skill: Identification of biochemicals such as sugars, lipids or amino acids from molecular
2.1.2 Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to amino acid. (only the ring forms of D-ribose, alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose are expected in diagrams.
exist. drawings). Make statement on how to identify each of the biochemicals mentioned in the objective.
2.1.3 Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic β-glucose Ribose
acids …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
Saturated Fatty Acid Generalized Amino Acid
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
2.1.6 Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism. 2.1.9 Application: Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can …………………………………………………………………………………………
2.1.7 Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the
also be artificially synthesized.
formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. …………………………………………………………………………………………
2.1.8 Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the …………………………………………………………………………………………
hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
You might also like
- Chromatography of Lipids in Biomedical Research and Clinical DiagnosisFrom EverandChromatography of Lipids in Biomedical Research and Clinical DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Test 2018Document10 pagesTopic 2 Test 2018Hadi BeydounNo ratings yet
- Plants Worksheet 2Document1 pagePlants Worksheet 2Avinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Biology Module Chemical Composition in The Cell: WaterDocument16 pagesBiology Module Chemical Composition in The Cell: Waternorrmus71No ratings yet
- AS - Alkenes-OR2Document12 pagesAS - Alkenes-OR2vintu pvNo ratings yet
- Y7 2023 TextbookDocument42 pagesY7 2023 TextbookAdina GuttentagNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Metaheuristics by Sean LukeDocument237 pagesEssentials of Metaheuristics by Sean Lukerafi_buetNo ratings yet
- Biochem HandoutDocument695 pagesBiochem HandoutJoey WallachNo ratings yet
- Lipids 2 QPDocument10 pagesLipids 2 QPreyNo ratings yet
- 1) Eukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division QP PDFDocument10 pages1) Eukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division QP PDFAbigail DNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Holiday HomeworkDocument15 pagesGrade 4 Holiday HomeworkMariappan SNo ratings yet
- 1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisDocument44 pages1.4 DNA and Protein SynthesisericychenNo ratings yet
- Anatrace Detergents Booklet FINALDocument12 pagesAnatrace Detergents Booklet FINALjfeiwgNo ratings yet
- Biology-Foodchain Worksheet Gradde 6Document8 pagesBiology-Foodchain Worksheet Gradde 6aim instituteNo ratings yet
- A2 Chirality ORDocument6 pagesA2 Chirality ORvintu pvNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument1 pageVocabularyKhalil MesrarNo ratings yet
- Statin As Primary Prevention in CVDDocument60 pagesStatin As Primary Prevention in CVDErvan ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Essentials of HeuristicsDocument233 pagesEssentials of HeuristicsAbidin Zein100% (1)
- Development of Biolubricants From Vegetable Oils Via Chemical ModificationDocument12 pagesDevelopment of Biolubricants From Vegetable Oils Via Chemical ModificationAlex SustaitaNo ratings yet
- Proteins Question Booklet: Name . .Document11 pagesProteins Question Booklet: Name . .James ChongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3Document8 pagesChemistry 3Ronald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Abbass Et Al Cochrane 2014Document87 pagesAbbass Et Al Cochrane 2014Mario ColliNo ratings yet
- Beginner Bass OverthrowDocument97 pagesBeginner Bass OverthrowChrysNo ratings yet
- Essay Concerning Color ConstancyDocument24 pagesEssay Concerning Color ConstancydavidrojasvNo ratings yet
- A Review of The CucurbitaceaeDocument15 pagesA Review of The CucurbitaceaeGuillermo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Singh 2011Document84 pagesSingh 2011Iuliana NitaNo ratings yet
- NLC TeamDocument15 pagesNLC TeamRizqi ChairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Chem. Grade 8Document152 pagesChem. Grade 8Hirko BelayNo ratings yet
- Mi Mundo en Otra LenguaDocument293 pagesMi Mundo en Otra LenguaYareli HernándezNo ratings yet
- Bio Sec1 Ter1Document38 pagesBio Sec1 Ter1RebelMLMlNo ratings yet
- Philip Shaddock - [TOC only] The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations of Guppy Color Biology and Genetics (aka The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations in Guppy Color Biology and Genetics)-Guppy Designer (JunDocument8 pagesPhilip Shaddock - [TOC only] The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations of Guppy Color Biology and Genetics (aka The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations in Guppy Color Biology and Genetics)-Guppy Designer (JunAditya Choudhury0% (1)
- BTEC L3 Sport & Exercise Science 31813H Unit 1 Jan 2020 p3 PDFDocument20 pagesBTEC L3 Sport & Exercise Science 31813H Unit 1 Jan 2020 p3 PDFEddie FraserNo ratings yet
- Intro BotanyDocument192 pagesIntro BotanyAhmedNo ratings yet
- Hartshorne Solution PDFDocument119 pagesHartshorne Solution PDFManuel Cebollo0% (1)
- Topic 2.1 Worksheet (Answers) PDFDocument2 pagesTopic 2.1 Worksheet (Answers) PDFFaridaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2 Human Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.2 Human Organ SystemsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal LipidDocument14 pagesJurnal Lipidnikhayatul qibtiyahNo ratings yet
- Artichoke Leaf Extract For Treating Hypercholesterolaemia (Review)Document23 pagesArtichoke Leaf Extract For Treating Hypercholesterolaemia (Review)Fajar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Complete Paragraph Booklet 3Document39 pagesComplete Paragraph Booklet 3georgie14No ratings yet
- 17 Ortega PBBDocument14 pages17 Ortega PBBMaría Paula TorresNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Kumar Hemnani - UNIT TEST 2 - MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS - BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESDocument7 pagesGaurav Kumar Hemnani - UNIT TEST 2 - MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS - BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESSlavic GauravNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Interventions For Cannabis Abuse And/or Dependence in Outpatient Settings (Review)Document25 pagesPsychotherapeutic Interventions For Cannabis Abuse And/or Dependence in Outpatient Settings (Review)LuisNo ratings yet
- Student Notes Structure of DNADocument15 pagesStudent Notes Structure of DNAAli DokmakNo ratings yet
- 36carey BioDocument3 pages36carey BioSU CHENG LAM, CAREY F4S (36)No ratings yet
- World Religions Paper 1 SLDocument16 pagesWorld Religions Paper 1 SLJohnny SinsNo ratings yet
- Meditation Therapy For Anxiety DisordersDocument23 pagesMeditation Therapy For Anxiety DisordersJosé AntônioNo ratings yet
- Nervous Transmission 4 QPDocument13 pagesNervous Transmission 4 QPmoumita.hazra2008No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument38 pagesLipidsDaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- GR 8 CH 4 WS 22 23Document4 pagesGR 8 CH 4 WS 22 23Aayan AjayNo ratings yet
- IGCSE-Revision-Booklet-Part-1-2018-2019 - (New-Spec)Document69 pagesIGCSE-Revision-Booklet-Part-1-2018-2019 - (New-Spec)MaryamNo ratings yet
- Joel M. Skousen - Strategic Relocation - North American Guide To Safe Places (2011) PDFDocument359 pagesJoel M. Skousen - Strategic Relocation - North American Guide To Safe Places (2011) PDFRb50% (14)
- 1.3 ProteinsDocument38 pages1.3 ProteinsericychenNo ratings yet
- Choco SolverDocument47 pagesChoco SolverHenne PopenneNo ratings yet
- Osmotic Micropumps For Drug Delivery at ADDRDocument12 pagesOsmotic Micropumps For Drug Delivery at ADDRKumar GalipellyNo ratings yet
- WS-3 IX Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesWS-3 IX Biological MoleculesM. ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Amprente in Blood - 0Document11 pagesAmprente in Blood - 0Diyana ChirilaNo ratings yet
- 8th Online Variation and InheritanceDocument4 pages8th Online Variation and Inheritance20I1190 G-7CNo ratings yet
- CowDocument1 pageCowEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- CS Form No 4 Rev2018-Cert of Assumption To DutyDocument1 pageCS Form No 4 Rev2018-Cert of Assumption To DutyNiña PacoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Region IX, Zamboanga Peninsula San Jose Heights, Pagadian CityDocument1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Region IX, Zamboanga Peninsula San Jose Heights, Pagadian CityEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Comments Feedback Template FinalDocument1 pageComments Feedback Template FinalEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Test II. Write The Letters of Your Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberDocument5 pagesTest II. Write The Letters of Your Answer On The Space Provided Before The NumberEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- GooseDocument2 pagesGooseEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- CarabaoDocument1 pageCarabaoEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Metabolic Protein Liver KidneysDocument5 pages2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Metabolic Protein Liver KidneysEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- WHLP GenMath - Week 1 v1Document3 pagesWHLP GenMath - Week 1 v1Earl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification in Physical Science Diagnostic ExaminationDocument4 pagesTable of Specification in Physical Science Diagnostic ExaminationEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- OFFICIAL Lipid Metabolism CrosswordsDocument2 pagesOFFICIAL Lipid Metabolism CrosswordsEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Official Gen Chem MidTerm Exam Set ADocument4 pagesOfficial Gen Chem MidTerm Exam Set AEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 6Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 6Earl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 in Gen ChemDocument8 pagesModule 4 in Gen ChemEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao State University: External Studies Unit-Pagadian CityDocument4 pagesWestern Mindanao State University: External Studies Unit-Pagadian CityEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Official BiochemistryGraphicOrganizer-1Document2 pagesOfficial BiochemistryGraphicOrganizer-1Earl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment and Observation ReportDocument5 pagesPre Assessment and Observation ReportEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Writing Part I AnswersDocument1 pageWriting Part I AnswersEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Science of DeathDocument1 pageAssessment of Science of DeathEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment and Observation ReportDocument5 pagesPre Assessment and Observation ReportEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- OFFICIAL Lipid Metabolism CrosswordsDocument2 pagesOFFICIAL Lipid Metabolism CrosswordsEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- "Spoken Word Poetry" (Filipino) : Global Technical School of Zamboanga, Inc. Pagadian CampusDocument6 pages"Spoken Word Poetry" (Filipino) : Global Technical School of Zamboanga, Inc. Pagadian CampusEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Convert CK Easy1Document2 pagesConvert CK Easy1Frederick AgliamNo ratings yet
- Multimedia ContentDocument3 pagesMultimedia ContentEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Tvl-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Survey For Electric Bills of Home, Business Establishments, and The LikeDocument2 pagesTvl-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Survey For Electric Bills of Home, Business Establishments, and The LikeEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Writing Part I AnswersDocument1 pageWriting Part I AnswersEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- DANCE CONTEST Criteria RubricsDocument2 pagesDANCE CONTEST Criteria RubricsEarl Cris Riggs100% (5)
- CybercrimeDocument1 pageCybercrimeEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- DR Ip (Perbedaan Profil Perdarahan Pemberian Antiplatelet Pada Pasien Stroke Iskemik - Mukernas Perdossi Yogyakarta 27-30 Juli 2017Document15 pagesDR Ip (Perbedaan Profil Perdarahan Pemberian Antiplatelet Pada Pasien Stroke Iskemik - Mukernas Perdossi Yogyakarta 27-30 Juli 2017fajarrudy qimindraNo ratings yet
- UG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintDocument42 pagesUG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintHosni ShowikeNo ratings yet
- History of Plant EcologyDocument44 pagesHistory of Plant EcologyRizka Eka ApcNo ratings yet
- Clinical - Bilirubin TestDocument9 pagesClinical - Bilirubin Testbarbie.monster89100% (3)
- Hsslive-Xi-Zoology-Rev-Test-4-Qn-By-Zta-Malappuram (1) - 230212 - 105754Document5 pagesHsslive-Xi-Zoology-Rev-Test-4-Qn-By-Zta-Malappuram (1) - 230212 - 105754എസ്സാർപി ഊരുചുറ്റൽ തുടരുന്നുNo ratings yet
- Fluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryDocument1 pageFluids Foods Did You Urinate?: Bladder DiaryAnika TasnimNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries and Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesDental Caries and Diabetes MellitusAgung HartadwitamaNo ratings yet
- Postreading Self-Assessment and CME Test-Preferred ResponsesDocument10 pagesPostreading Self-Assessment and CME Test-Preferred Responsesdr.cidgutNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationNoN -Na100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Design of Manual Handling and BiomechanicsDocument50 pagesLecture 3 Design of Manual Handling and BiomechanicsIki KagawaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Smell and Taste-MyDocument46 pagesPhysiology of Smell and Taste-MyHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Serology NewDocument116 pagesSerology NewFarlogyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Name: - Class: - DateDocument20 pagesNervous System: Name: - Class: - DateKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- A. K. Tripathi and Mukesh Gautam PDFDocument6 pagesA. K. Tripathi and Mukesh Gautam PDFLingga NimpunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 - HypertensionDocument70 pagesChapter 30 - HypertensionSakaC.TanayaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAdrenal PathophysiologyditabokNo ratings yet
- Major Case 3Document3 pagesMajor Case 3Christine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plansapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Risk Factors: Stroke PreventionDocument2 pagesRisk Factors: Stroke PreventionPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Guide To Clerking 2014Document24 pagesGuide To Clerking 2014Ridhwan Amid100% (1)
- Infant Feeding Tube: Paediatric Department Nepalese Army Institute of Health SciencesDocument32 pagesInfant Feeding Tube: Paediatric Department Nepalese Army Institute of Health Sciencesmac.rupakhetiNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik (PPOK) : Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sultan Khairun (Unkhair)Document53 pagesPenyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik (PPOK) : Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sultan Khairun (Unkhair)WahyunitadotokaNo ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFDocument2 pagesNucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFsathya50% (2)
- Abraham Hernandez - Copy of PT 8Document5 pagesAbraham Hernandez - Copy of PT 8api-653578039No ratings yet
- STEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022Document1 pageSTEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022M. Baidar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna Structureapi-315792432No ratings yet
- Seminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of PeriodontiaDocument57 pagesSeminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of Periodontiashreya dasNo ratings yet
- The Forced-Choice Paradigm and The Perception of Facial Expressions of EmotionDocument11 pagesThe Forced-Choice Paradigm and The Perception of Facial Expressions of EmotionjnkjnNo ratings yet
- Kidney Dissection Practical SheetDocument3 pagesKidney Dissection Practical SheetIvona Matković100% (1)
- Edexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFDocument18 pagesEdexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFtas xo100% (1)































![Philip Shaddock - [TOC only] The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations of Guppy Color Biology and Genetics (aka The Guppy Color Manual_ Explorations in Guppy Color Biology and Genetics)-Guppy Designer (Jun](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/444898930/149x198/daebe2b33a/1710563758?v=1)